【keras】YOLO:实时目标检测
1.为什么使用Yolo进行实时目标检测任务
与其他目标检测器相比较而言,Yolov3非常快速和准确。在0.5度测得的地图上,Yolov3与RetinaNet持平,但大约快了4倍。此外,只需更改模型的大小,您就可以轻松地在速度和准确性之间进行权衡,不需要再训练!简单来说,就是Yolo比RetinaNet快很多。
2.使用预先训练的模型进行目标检测
2.1 从YOLO 网站上下载Darknet YOLO模型
A Keras implementation of YOLOv3 (Tensorflow backend) inspired by allanzelener/YAD2K.
2.2 将下载好的Darknet YOLO模型转换为Keras模型
python convert.py yolov3.cfg yolov3.weights model_data/yolo.h52.3 运行YOLO目标检测程序yolo_video.py
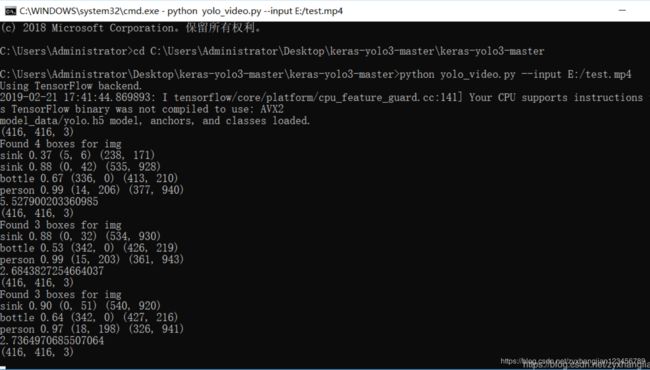
python yolo_video.py --input E:/test.mp43.利用Yolo实现实时目标检测
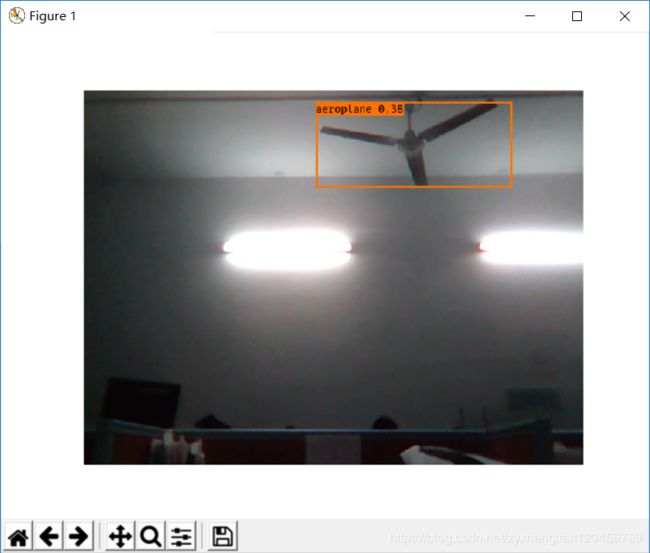
由于上面项目只能够通过命令行的方式调用,因此,笔者接下来介绍一下如何利用该项目,得到一个适合自己需求的实时目标检测系统。具体的思路较为简单:首先,从摄像头中读取一帧图像。接着,将目标检测应用到每一帧里。最后,将结果显示出来,实例效果(没有训练风扇,识别成飞机了,哈哈):
自己定义的 real_time_object_detection.py 代码:
# import miscellaneous modules
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import cv2
from PIL import Image,ImageFont,ImageDraw
from timeit import default_timer as timer
from keras.models import load_model
import os
import colorsys
from keras import backend as K
from yolo3.model import yolo_eval
configs = {
"model_path": 'model_data/yolo.h5',
"anchors_path": 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt',
"classes_path": 'model_data/coco_classes.txt',
"score" : 0.3,
"iou" : 0.45,
"model_image_size" : (416, 416),
"gpu_num" : 1,
};
# 载入网络模型
yolo_model = load_model('model_data/yolo.h5')
# 读取类名
classes_path = os.path.expanduser(configs['classes_path'])
with open(classes_path) as f:
class_names = f.readlines()
class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
# 生成颜色
hsv_tuples = [(x / len(class_names), 1., 1.)
for x in range(len(class_names))]
colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
colors = list(map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)), colors))
np.random.seed(10101) # Fixed seed for consistent colors across runs.
np.random.shuffle(colors) # Shuffle colors to decorrelate adjacent classes.
np.random.seed(None) # Reset seed to default.
# anchors
anchors_path = os.path.expanduser(configs['anchors_path'])
with open(anchors_path) as f:
anchors = f.readline()
anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]
anchors = np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)
# 生成tensorflow对象.
input_image_shape = K.placeholder(shape=(2, ))
boxes, scores, classes = yolo_eval(yolo_model.output, anchors, len(class_names), input_image_shape,
score_threshold=configs['score'], iou_threshold=configs['iou'])
# 获取摄像头对象
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# 获取tensorflow会话
sess = K.get_session()
#开启交互绘图模式
plt.ion()
# 逐帧处理
while True:
# 开始计时
start = timer()
# 获取数据
(ret, frame) = camera.read()
# 将像素数据转换为图像
image = Image.fromarray(frame)
if not ret:
break
# 图像数据预处理
image_data = np.array(frame, dtype='float32')
image_data /= 255.
image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, 0) # Add batch dimension.
# 运行tensorflow会话
out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = sess.run(
[boxes, scores, classes],
feed_dict={
yolo_model.input: image_data,
input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]],
K.learning_phase(): 0
})
font = ImageFont.truetype(font='font/FiraMono-Medium.otf',
size=np.floor(3e-2 * image.size[1] + 0.5).astype('int32'))
thickness = (image.size[0] + image.size[1]) // 300
# 在原图像的基础上绘制
for i, c in reversed(list(enumerate(out_classes))):
predicted_class = class_names[c]
box = out_boxes[i]
score = out_scores[i]
# 计算识别内容所在区域
label = '{} {:.2f}'.format(predicted_class, score)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
label_size = draw.textsize(label, font)
top, left, bottom, right = box
top = max(0, np.floor(top + 0.5).astype('int32'))
left = max(0, np.floor(left + 0.5).astype('int32'))
bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom + 0.5).astype('int32'))
right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right + 0.5).astype('int32'))
if top - label_size[1] >= 0:
text_origin = np.array([left, top - label_size[1]])
else:
text_origin = np.array([left, top + 1])
# 绘制识别内容所在区域
for i in range(thickness):
draw.rectangle(
[left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],
outline=colors[c])
draw.rectangle(
[tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)],
fill=colors[c])
draw.text(text_origin, label, fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)
del draw
end = timer()
print(end - start)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis('off')#关闭坐标轴显示
plt.show()
plt.pause(2)
# 释放资源并关闭所有窗口
plt.ioff() #关闭interactive模式,否则后面的plt.show()也会一闪而过
camera.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()由于电脑配置的问题,处理一帧数据需要5s左右。因此,会显得不流畅。
10.776641618602282
4.792536805818951
4.796147291389371
5.000113367100862
4.962706422596163
5.18331226944607
5.804779053118786
5.265706358681378
5.215022867030655
4.780028169158641
4.718418981478251
4.7511960695672855
4.864659742409415
5.245915635282643
5.4219901384618225附代码地址:keras-yolo3 实时目标检测、原始项目的github地址。注意,由于模型文件过大,所以没有上传,有需要的可以在评论区留言。