【何之源-21个项目玩转深度学习】——Chapter2-2.1.2 CIFAR-10数据下载
本文主要讲用tensorflow框架下python代码实现CIFAR-10数据的下载;
主代码如下:
# coding:utf-8
# 引入当前目录中的已经编写好的cifar10模块
import cifar10
import tensorflow as tf
# tf.app.flags.FLAGS是TensorFlow内部的一个全局变量存储器,同时可以用于命令行参数的处理
FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS
# 在cifar10模块中预先定义了tf.app.flags.FLAGS.data_dir为CIFAR-10的数据路径
# 我们把这个路径改为cifar10_data
FLAGS.data_dir = 'cifar10_data/'
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('f', '', 'kernel') #亲测,不添加这行会报错
# 如果不存在数据文件,就会执行下载
cifar10.maybe_download_and_extract()其中cifar10的代码内容如下:
# Copyright 2015 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
"""Builds the CIFAR-10 network.
Summary of available functions:
# Compute input images and labels for training. If you would like to run
# evaluations, use inputs() instead.
inputs, labels = distorted_inputs()
# Compute inference on the model inputs to make a prediction.
predictions = inference(inputs)
# Compute the total loss of the prediction with respect to the labels.
loss = loss(predictions, labels)
# Create a graph to run one step of training with respect to the loss.
train_op = train(loss, global_step)
"""
# pylint: disable=missing-docstring
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import re
import sys
import tarfile
from six.moves import urllib
import tensorflow as tf
import cifar10_input
FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS
# Basic model parameters.
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('batch_size', 128,
"""Number of images to process in a batch.""")
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('data_dir', '/tmp/cifar10_data',
"""Path to the CIFAR-10 data directory.""")
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_boolean('use_fp16', False,
"""Train the model using fp16.""")
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('f','','kernel')
# Global constants describing the CIFAR-10 data set.
IMAGE_SIZE = cifar10_input.IMAGE_SIZE
NUM_CLASSES = cifar10_input.NUM_CLASSES
NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN = cifar10_input.NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN
NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_EVAL = cifar10_input.NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_EVAL
# Constants describing the training process.
MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY = 0.9999 # The decay to use for the moving average.
NUM_EPOCHS_PER_DECAY = 350.0 # Epochs after which learning rate decays.
LEARNING_RATE_DECAY_FACTOR = 0.1 # Learning rate decay factor.
INITIAL_LEARNING_RATE = 0.1 # Initial learning rate.
# If a model is trained with multiple GPUs, prefix all Op names with tower_name
# to differentiate the operations. Note that this prefix is removed from the
# names of the summaries when visualizing a model.
TOWER_NAME = 'tower'
DATA_URL = 'http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-10-binary.tar.gz'
def _activation_summary(x):
"""Helper to create summaries for activations.
Creates a summary that provides a histogram of activations.
Creates a summary that measures the sparsity of activations.
Args:
x: Tensor
Returns:
nothing
"""
# Remove 'tower_[0-9]/' from the name in case this is a multi-GPU training
# session. This helps the clarity of presentation on tensorboard.
tensor_name = re.sub('%s_[0-9]*/' % TOWER_NAME, '', x.op.name)
tf.summary.histogram(tensor_name + '/activations', x)
tf.summary.scalar(tensor_name + '/sparsity',
tf.nn.zero_fraction(x))
def _variable_on_cpu(name, shape, initializer):
"""Helper to create a Variable stored on CPU memory.
Args:
name: name of the variable
shape: list of ints
initializer: initializer for Variable
Returns:
Variable Tensor
"""
with tf.device('/cpu:0'):
dtype = tf.float16 if FLAGS.use_fp16 else tf.float32
var = tf.get_variable(name, shape, initializer=initializer, dtype=dtype)
return var
def _variable_with_weight_decay(name, shape, stddev, wd):
"""Helper to create an initialized Variable with weight decay.
Note that the Variable is initialized with a truncated normal distribution.
A weight decay is added only if one is specified.
Args:
name: name of the variable
shape: list of ints
stddev: standard deviation of a truncated Gaussian
wd: add L2Loss weight decay multiplied by this float. If None, weight
decay is not added for this Variable.
Returns:
Variable Tensor
"""
dtype = tf.float16 if FLAGS.use_fp16 else tf.float32
var = _variable_on_cpu(
name,
shape,
tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=stddev, dtype=dtype))
if wd is not None:
weight_decay = tf.multiply(tf.nn.l2_loss(var), wd, name='weight_loss')
tf.add_to_collection('losses', weight_decay)
return var
def distorted_inputs():
"""Construct distorted input for CIFAR training using the Reader ops.
Returns:
images: Images. 4D tensor of [batch_size, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3] size.
labels: Labels. 1D tensor of [batch_size] size.
Raises:
ValueError: If no data_dir
"""
if not FLAGS.data_dir:
raise ValueError('Please supply a data_dir')
data_dir = os.path.join(FLAGS.data_dir, 'cifar-10-batches-bin')
images, labels = cifar10_input.distorted_inputs(data_dir=data_dir,
batch_size=FLAGS.batch_size)
if FLAGS.use_fp16:
images = tf.cast(images, tf.float16)
labels = tf.cast(labels, tf.float16)
return images, labels
def inputs(eval_data):
"""Construct input for CIFAR evaluation using the Reader ops.
Args:
eval_data: bool, indicating if one should use the train or eval data set.
Returns:
images: Images. 4D tensor of [batch_size, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3] size.
labels: Labels. 1D tensor of [batch_size] size.
Raises:
ValueError: If no data_dir
"""
if not FLAGS.data_dir:
raise ValueError('Please supply a data_dir')
data_dir = os.path.join(FLAGS.data_dir, 'cifar-10-batches-bin')
images, labels = cifar10_input.inputs(eval_data=eval_data,
data_dir=data_dir,
batch_size=FLAGS.batch_size)
if FLAGS.use_fp16:
images = tf.cast(images, tf.float16)
labels = tf.cast(labels, tf.float16)
return images, labels
def inference(images):
"""Build the CIFAR-10 model.
Args:
images: Images returned from distorted_inputs() or inputs().
Returns:
Logits.
"""
# We instantiate all variables using tf.get_variable() instead of
# tf.Variable() in order to share variables across multiple GPU training runs.
# If we only ran this model on a single GPU, we could simplify this function
# by replacing all instances of tf.get_variable() with tf.Variable().
#
# conv1
with tf.variable_scope('conv1') as scope:
kernel = _variable_with_weight_decay('weights',
shape=[5, 5, 3, 64],
stddev=5e-2,
wd=0.0)
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = _variable_on_cpu('biases', [64], tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name)
_activation_summary(conv1)
# pool1
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME', name='pool1')
# norm1
norm1 = tf.nn.lrn(pool1, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75,
name='norm1')
# conv2
with tf.variable_scope('conv2') as scope:
kernel = _variable_with_weight_decay('weights',
shape=[5, 5, 64, 64],
stddev=5e-2,
wd=0.0)
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(norm1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = _variable_on_cpu('biases', [64], tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name)
_activation_summary(conv2)
# norm2
norm2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75,
name='norm2')
# pool2
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(norm2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME', name='pool2')
# local3
with tf.variable_scope('local3') as scope:
# Move everything into depth so we can perform a single matrix multiply.
reshape = tf.reshape(pool2, [FLAGS.batch_size, -1])
dim = reshape.get_shape()[1].value
weights = _variable_with_weight_decay('weights', shape=[dim, 384],
stddev=0.04, wd=0.004)
biases = _variable_on_cpu('biases', [384], tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
local3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshape, weights) + biases, name=scope.name)
_activation_summary(local3)
# local4
with tf.variable_scope('local4') as scope:
weights = _variable_with_weight_decay('weights', shape=[384, 192],
stddev=0.04, wd=0.004)
biases = _variable_on_cpu('biases', [192], tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
local4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(local3, weights) + biases, name=scope.name)
_activation_summary(local4)
# linear layer(WX + b),
# We don't apply softmax here because
# tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits accepts the unscaled logits
# and performs the softmax internally for efficiency.
with tf.variable_scope('softmax_linear') as scope:
weights = _variable_with_weight_decay('weights', [192, NUM_CLASSES],
stddev=1/192.0, wd=0.0)
biases = _variable_on_cpu('biases', [NUM_CLASSES],
tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
softmax_linear = tf.add(tf.matmul(local4, weights), biases, name=scope.name)
_activation_summary(softmax_linear)
return softmax_linear
def loss(logits, labels):
"""Add L2Loss to all the trainable variables.
Add summary for "Loss" and "Loss/avg".
Args:
logits: Logits from inference().
labels: Labels from distorted_inputs or inputs(). 1-D tensor
of shape [batch_size]
Returns:
Loss tensor of type float.
"""
# Calculate the average cross entropy loss across the batch.
labels = tf.cast(labels, tf.int64)
cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=labels, logits=logits, name='cross_entropy_per_example')
cross_entropy_mean = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='cross_entropy')
tf.add_to_collection('losses', cross_entropy_mean)
# The total loss is defined as the cross entropy loss plus all of the weight
# decay terms (L2 loss).
return tf.add_n(tf.get_collection('losses'), name='total_loss')
def _add_loss_summaries(total_loss):
"""Add summaries for losses in CIFAR-10 model.
Generates moving average for all losses and associated summaries for
visualizing the performance of the network.
Args:
total_loss: Total loss from loss().
Returns:
loss_averages_op: op for generating moving averages of losses.
"""
# Compute the moving average of all individual losses and the total loss.
loss_averages = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(0.9, name='avg')
losses = tf.get_collection('losses')
loss_averages_op = loss_averages.apply(losses + [total_loss])
# Attach a scalar summary to all individual losses and the total loss; do the
# same for the averaged version of the losses.
for l in losses + [total_loss]:
# Name each loss as '(raw)' and name the moving average version of the loss
# as the original loss name.
tf.summary.scalar(l.op.name + ' (raw)', l)
tf.summary.scalar(l.op.name, loss_averages.average(l))
return loss_averages_op
def train(total_loss, global_step):
"""Train CIFAR-10 model.
Create an optimizer and apply to all trainable variables. Add moving
average for all trainable variables.
Args:
total_loss: Total loss from loss().
global_step: Integer Variable counting the number of training steps
processed.
Returns:
train_op: op for training.
"""
# Variables that affect learning rate.
num_batches_per_epoch = NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN / FLAGS.batch_size
decay_steps = int(num_batches_per_epoch * NUM_EPOCHS_PER_DECAY)
# Decay the learning rate exponentially based on the number of steps.
lr = tf.train.exponential_decay(INITIAL_LEARNING_RATE,
global_step,
decay_steps,
LEARNING_RATE_DECAY_FACTOR,
staircase=True)
tf.summary.scalar('learning_rate', lr)
# Generate moving averages of all losses and associated summaries.
loss_averages_op = _add_loss_summaries(total_loss)
# Compute gradients.
with tf.control_dependencies([loss_averages_op]):
opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(lr)
grads = opt.compute_gradients(total_loss)
# Apply gradients.
apply_gradient_op = opt.apply_gradients(grads, global_step=global_step)
# Add histograms for trainable variables.
for var in tf.trainable_variables():
tf.summary.histogram(var.op.name, var)
# Add histograms for gradients.
for grad, var in grads:
if grad is not None:
tf.summary.histogram(var.op.name + '/gradients', grad)
# Track the moving averages of all trainable variables.
variable_averages = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(
MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY, global_step)
variables_averages_op = variable_averages.apply(tf.trainable_variables())
with tf.control_dependencies([apply_gradient_op, variables_averages_op]):
train_op = tf.no_op(name='train')
return train_op
def maybe_download_and_extract():
"""Download and extract the tarball from Alex's website."""
dest_directory = FLAGS.data_dir
if not os.path.exists(dest_directory):
os.makedirs(dest_directory)
filename = DATA_URL.split('/')[-1]
filepath = os.path.join(dest_directory, filename)
if not os.path.exists(filepath):
def _progress(count, block_size, total_size):
sys.stdout.write('\r>> Downloading %s %.1f%%' % (filename,
float(count * block_size) / float(total_size) * 100.0))
sys.stdout.flush()
filepath, _ = urllib.request.urlretrieve(DATA_URL, filepath, _progress)
print()
statinfo = os.stat(filepath)
print('Successfully downloaded', filename, statinfo.st_size, 'bytes.')
extracted_dir_path = os.path.join(dest_directory, 'cifar-10-batches-bin')
if not os.path.exists(extracted_dir_path):
tarfile.open(filepath, 'r:gz').extractall(dest_directory)
主代码中用到了cifar10中的maybe_download_and_extract()函数。
下面针对这个函数做讲解:
指定数据下载路径为cifar10_data文件夹,如没有则创建;对下载的URL链接名分割得到filename是cifar-10-binary.tar.gz
那么文件路径就是cifar10_data/cifar-10-binary.tar.gz, 当文件没下载好时,定义了一个进度状态信息来显示下载情况。其中sys.stdout.flush()函数用于刷新stdout,这样就能每隔一定时间输出下载状态。可以用在网络程序中多线程程序,多个线程后台运行,同时要能在屏幕上实时看到输出信息。(sys.stdout.flush())
下载完成后会显示成功下载信息;
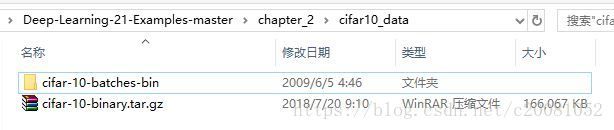
将下载后的压缩文件进行解压,解压目录在cifar10_data/cifar-10-batches-bin .
下载以及解压结果如下:
解压出来的文件有数据集类别描述:batches.meta.txt;(包含10类标签:
airplane
automobile
bird
cat
deer
dog
frog
horse
ship
truck)
训练的数据集:
data_batch_1.bin
data_batch_2.bin
data_batch_3.bin
data_batch_4.bin
data_batch_5.bin
测试数据集:
test_batch.bin