ORB_SLAM2源码解析-Tracking.cc
理论推导参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_30356613/article/details/80587649
代码来源:https://me.csdn.net/qq_30356613
/**
* This file is part of ORB-SLAM2.
*
* Copyright (C) 2014-2016 Raúl Mur-Artal (University of Zaragoza)
* For more information see
*
* ORB-SLAM2 is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* ORB-SLAM2 is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with ORB-SLAM2. If not, see
#include
#include"ORBmatcher.h"
#include"FrameDrawer.h"
#include"Converter.h"
#include"Map.h"
#include"Initializer.h"
#include"Optimizer.h"
#include"PnPsolver.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;
namespace ORB_SLAM2
{
/*******************************************************************************
* 函数属性:类Tracking的构造函数
* 函数功能:(1)加载相机相关参数(内参数矩阵K以及相机畸变矩阵DistCoef)
* (2)重定位最大失帧数
* (3)初始化ORB特征提取器
* 函数参数介绍:
* pSys:指定本系统
* pVoc:指定所用的词典
* pFrameDrawer:每一帧的观测器
* pKFDB:关键帧数据集
* pMapDrawer:地图的观测器
* pMap:指代整个地图
* strSettingPath:配置文件的路径(相机相关参数以及工程中所用到的参数)
* sensor:传感器类型
* 备注:NULL
*
******************************************************************************/
Tracking::Tracking(System *pSys, ORBVocabulary* pVoc, FrameDrawer *pFrameDrawer, MapDrawer *pMapDrawer, Map *pMap,
KeyFrameDatabase* pKFDB, const string &strSettingPath, const int sensor):
mState(NO_IMAGES_YET), mSensor(sensor), mbOnlyTracking(false), mbVO(false), mpORBVocabulary(pVoc),
mpKeyFrameDB(pKFDB), mpInitializer(static_cast(NULL)), mpSystem(pSys), mpViewer(NULL),
mpFrameDrawer(pFrameDrawer), mpMapDrawer(pMapDrawer), mpMap(pMap), mnLastRelocFrameId(0)
{
// Load camera parameters from settings file
//加载相机相关参数
cv::FileStorage fSettings(strSettingPath, cv::FileStorage::READ);
float fx = fSettings["Camera.fx"];
float fy = fSettings["Camera.fy"];
float cx = fSettings["Camera.cx"];
float cy = fSettings["Camera.cy"];
//相机内参数矩阵
cv::Mat K = cv::Mat::eye(3,3,CV_32F);
K.at(0,0) = fx;
K.at(1,1) = fy;
K.at(0,2) = cx;
K.at(1,2) = cy;
K.copyTo(mK);
//相机畸变矩阵 k1,k2,k3径向畸变 p1,p2切向畸变
cv::Mat DistCoef(4,1,CV_32F);
DistCoef.at(0) = fSettings["Camera.k1"];
DistCoef.at(1) = fSettings["Camera.k2"];
DistCoef.at(2) = fSettings["Camera.p1"];
DistCoef.at(3) = fSettings["Camera.p2"];
const float k3 = fSettings["Camera.k3"];
if(k3!=0)
{
DistCoef.resize(5);
DistCoef.at(4) = k3;
}
DistCoef.copyTo(mDistCoef);
//双目摄像头baseline*fx 50
mbf = fSettings["Camera.bf"];
//帧率,每秒钟所走过的帧数
float fps = fSettings["Camera.fps"];
if(fps==0)
fps=30;
// Max/Min Frames to insert keyframes and to check relocalisation
//插入关键帧和检测重定位的最小,最大帧,也就是说当连续有30帧没匹配到的时候进行重定位
mMinFrames = 0;
mMaxFrames = fps;
//打印一下刚刚配置的参数
cout << endl << "Camera Parameters: " << endl;
cout << "- fx: " << fx << endl;
cout << "- fy: " << fy << endl;
cout << "- cx: " << cx << endl;
cout << "- cy: " << cy << endl;
cout << "- k1: " << DistCoef.at(0) << endl;
cout << "- k2: " << DistCoef.at(1) << endl;
if(DistCoef.rows==5)
cout << "- k3: " << DistCoef.at(4) << endl;
cout << "- p1: " << DistCoef.at(2) << endl;
cout << "- p2: " << DistCoef.at(3) << endl;
cout << "- fps: " << fps << endl;
//配置图片是按照什么颜色顺序存储的RGB: 1 ;BGR: 0
int nRGB = fSettings["Camera.RGB"];
mbRGB = nRGB;
if(mbRGB)
cout << "- color order: RGB (ignored if grayscale)" << endl;
else
cout << "- color order: BGR (ignored if grayscale)" << endl;
// Load ORB parameters
//加载ORB的相关参数
//ORB特征点的数量
int nFeatures = fSettings["ORBextractor.nFeatures"];
//图像金字塔中相邻层的放大倍数
float fScaleFactor = fSettings["ORBextractor.scaleFactor"];
//图像金字塔有多少层
int nLevels = fSettings["ORBextractor.nLevels"];
// Image is divided in a grid. At each cell FAST are extracted imposing a minimum response.
// Firstly we impose iniThFAST. If no corners are detected we impose a lower value minThFAST
// You can lower these values if your images have low contrast
int fIniThFAST = fSettings["ORBextractor.iniThFAST"]; //提取fast特征点的默认阈值 20
int fMinThFAST = fSettings["ORBextractor.minThFAST"]; //如果默认阈值提取不出足够fast特征点,则使用最小阈值 8
// tracking过程都会用到mpORBextractorLeft作为特征点提取器
mpORBextractorLeft = new ORBextractor(nFeatures,fScaleFactor,nLevels,fIniThFAST,fMinThFAST);
// 如果是双目,tracking过程中还会用用到mpORBextractorRight作为右目特征点提取器
if(sensor==System::STEREO)
mpORBextractorRight = new ORBextractor(nFeatures,fScaleFactor,nLevels,fIniThFAST,fMinThFAST);
// 在单目初始化的时候,会用mpIniORBextractor来作为特征点提取器
if(sensor==System::MONOCULAR)
mpIniORBextractor = new ORBextractor(2*nFeatures,fScaleFactor,nLevels,fIniThFAST,fMinThFAST);
cout << endl << "ORB Extractor Parameters: " << endl;
cout << "- Number of Features: " << nFeatures << endl;
cout << "- Scale Levels: " << nLevels << endl;
cout << "- Scale Factor: " << fScaleFactor << endl;
cout << "- Initial Fast Threshold: " << fIniThFAST << endl;
cout << "- Minimum Fast Threshold: " << fMinThFAST << endl;
if(sensor==System::STEREO || sensor==System::RGBD)
{
// 判断一个3D点远/近的阈值 mbf * 35 / fx baseline*fx*35/fx = baseline*35
mThDepth = mbf*(float)fSettings["ThDepth"]/fx;
cout << endl << "Depth Threshold (Close/Far Points): " << mThDepth << endl;
}
if(sensor==System::RGBD)
{
// 深度相机disparity转化为depth时的因子
mDepthMapFactor = fSettings["DepthMapFactor"];
if(fabs(mDepthMapFactor)<1e-5)
mDepthMapFactor=1;
else
mDepthMapFactor = 1.0f/mDepthMapFactor;
}
}
//Tracking与LocalMapper线程相关联
void Tracking::SetLocalMapper(LocalMapping *pLocalMapper)
{
mpLocalMapper=pLocalMapper;
}
//Tracking与LoopClosing线程相关联
void Tracking::SetLoopClosing(LoopClosing *pLoopClosing)
{
mpLoopClosing=pLoopClosing;
}
//Tracking与Viewer线程相关联
void Tracking::SetViewer(Viewer *pViewer)
{
mpViewer=pViewer;
}
cv::Mat Tracking::GrabImageStereo(const cv::Mat &imRectLeft, const cv::Mat &imRectRight, const double ×tamp)
{
mImGray = imRectLeft;
cv::Mat imGrayRight = imRectRight;
if(mImGray.channels()==3)
{
if(mbRGB)
{
cvtColor(mImGray,mImGray,CV_RGB2GRAY);
cvtColor(imGrayRight,imGrayRight,CV_RGB2GRAY);
}
else
{
cvtColor(mImGray,mImGray,CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(imGrayRight,imGrayRight,CV_BGR2GRAY);
}
}
else if(mImGray.channels()==4)
{
if(mbRGB)
{
cvtColor(mImGray,mImGray,CV_RGBA2GRAY);
cvtColor(imGrayRight,imGrayRight,CV_RGBA2GRAY);
}
else
{
cvtColor(mImGray,mImGray,CV_BGRA2GRAY);
cvtColor(imGrayRight,imGrayRight,CV_BGRA2GRAY);
}
}
mCurrentFrame = Frame(mImGray,imGrayRight,timestamp,mpORBextractorLeft,mpORBextractorRight,mpORBVocabulary,mK,mDistCoef,mbf,mThDepth);
Track();
return mCurrentFrame.mTcw.clone();
}
/*******************************************************************************
* 函数属性:类Tracking的成员函数cv::Mat Tracking::GrabImageRGBD(const cv::Mat &imRGB,const cv::Mat &imD, const double ×tamp)
* 函数功能:(1)将彩色图转化为灰度图
* (2)用灰度图和彩色图初始化当前帧
* (3)进行线程追踪Track()
* 函数参数介绍:
* imRGB:彩色图像
* imD:灰度图像
* timestamp:该帧采集的时间戳
* 备注:NULL
*
******************************************************************************/
cv::Mat Tracking::GrabImageRGBD(const cv::Mat &imRGB,const cv::Mat &imD, const double ×tamp)
{
mImGray = imRGB;
cv::Mat imDepth = imD;
//将RGB图转换为灰度图
if(mImGray.channels()==3)
{
if(mbRGB)
cvtColor(mImGray,mImGray,CV_RGB2GRAY); //将RGB图转化为灰度图
else
cvtColor(mImGray,mImGray,CV_BGR2GRAY); //将BGR图转化为灰度图
}
else if(mImGray.channels()==4)
{
if(mbRGB)
cvtColor(mImGray,mImGray,CV_RGBA2GRAY); //将四通道的RGBA图转换为灰度图
else
cvtColor(mImGray,mImGray,CV_BGRA2GRAY);
}
//将灰度图转变到CV_32F型并且如果数据集中的数据有缩放的话需要将深度图进行变换
if((fabs(mDepthMapFactor-1.0f)>1e-5) || imDepth.type()!=CV_32F)
imDepth.convertTo(imDepth,CV_32F,mDepthMapFactor);
//初始化当前帧
mCurrentFrame = Frame(mImGray,imDepth,timestamp,mpORBextractorLeft,mpORBVocabulary,mK,mDistCoef,mbf,mThDepth);
Track();
return mCurrentFrame.mTcw.clone();
}
cv::Mat Tracking::GrabImageMonocular(const cv::Mat &im, const double ×tamp)
{
mImGray = im;
if(mImGray.channels()==3)
{
if(mbRGB)
cvtColor(mImGray,mImGray,CV_RGB2GRAY);
else
cvtColor(mImGray,mImGray,CV_BGR2GRAY);
}
else if(mImGray.channels()==4)
{
if(mbRGB)
cvtColor(mImGray,mImGray,CV_RGBA2GRAY);
else
cvtColor(mImGray,mImGray,CV_BGRA2GRAY);
}
if(mState==NOT_INITIALIZED || mState==NO_IMAGES_YET)
mCurrentFrame = Frame(mImGray,timestamp,mpIniORBextractor,mpORBVocabulary,mK,mDistCoef,mbf,mThDepth);
else
mCurrentFrame = Frame(mImGray,timestamp,mpORBextractorLeft,mpORBVocabulary,mK,mDistCoef,mbf,mThDepth);
Track();
return mCurrentFrame.mTcw.clone();
}
/*******************************************************************************
* 函数属性:类Tracking的成员函数Track() 跟踪线程有四个状态分别是 没有图片,未初始化(第一张图片),线程完好, 追踪线程失败
* 函数功能:检测当前系统状态是处于NO_IMAGES_YET,NOT_INITIALIZED,还是OK or LOST
* 1. 根据当前的跟踪状态来进行相机位姿的计算,处于NO_IMAGES_YET则将位姿状态转化为NOT_INITIALIZED
* 处在NOT_INITIALIZED则进行初始化程序,StereoInitialization() or MonocularInitialization()
* 处在LOST则进行重定位
* 处在OK状态,则通过TrackReferenceKeyFrame()和TrackWithMotionModel()进行相机位姿的计算
* TrackReferenceKeyFrame()是根据上一帧的位姿为初始位姿进行优化,匹配的是关键帧和当前帧得到匹配地图点
* TrackWithMotionModel()是根据上一帧的速度和上一帧的积来估算相机初始位姿,匹配的是上一帧和当前帧得到匹配地图点
* 2. 局部地图的跟踪,更新局部地图(局部地图点和局部关键帧)
* 3. 检测是否需要加入关键帧,将关键帧交给局部建图线程
* 4. 如果上述都顺利进行,则更新当前相机的最终位姿,存储完整的帧姿态信息以获取完整的相机轨迹
*
* 另: 仅线程追踪模式下只存在以前未开启仅线程追踪模式下的关键帧,不会添加新的关键帧,因此不会有新的地图点,仅仅追踪的是现有地图中的地图点
*
* 函数参数介绍:NULL
* 备注:追踪线程的主要成员函数,实现视觉里程计
* 仅线程追踪模式下只存在以前未开启仅线程追踪模式下的关键帧,不会添加新的关键帧,因此不会有新的地图点,仅仅追踪的是现有地图中的地图点
******************************************************************************/
void Tracking::Track()
{
if(mState==NO_IMAGES_YET)
{
mState = NOT_INITIALIZED;
}
// 更新上一次追踪状态
mLastProcessedState=mState;
// Get Map Mutex -> Map cannot be changed 锁住地图更新线程,同时也确保该段代码执行的时候不会有其他地图的更新操作
unique_lock lock(mpMap->mMutexMapUpdate);
if(mState==NOT_INITIALIZED)
{
if(mSensor==System::STEREO || mSensor==System::RGBD)
StereoInitialization(); //双目和rgbd地图的初始化
else
MonocularInitialization();// 单目初始化
mpFrameDrawer->Update(this); //更新帧的观测器
if(mState!=OK)
return;
}
else
{
// System is initialized. Track Frame.
bool bOK;
// Initial camera pose estimation using motion model or relocalization (if tracking is lost)
// 初始化相机位姿估计使用移动模型或者重定位
if(!mbOnlyTracking)
{
// Local Mapping is activated. This is the normal behaviour, unless
// you explicitly activate the "only tracking" mode. 局部建图线程被打开,这是一个正常的行为,除非你开启仅跟踪模式
if(mState==OK) //如果处于正常状态
{
// Local Mapping might have changed some MapPoints tracked in last frame
// 检查并更新上一帧被替换的MapPoints
// 更新Fuse函数和SearchAndFuse函数替换的MapPoints
CheckReplacedInLastFrame();
// 运动模型是空的或刚完成重定位
if(mVelocity.empty() || mCurrentFrame.mnId vpMPsMM;
vector vbOutMM;
cv::Mat TcwMM;
if(!mVelocity.empty())
{
bOKMM = TrackWithMotionModel(); //根据运动模型进行追踪
vpMPsMM = mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints;
vbOutMM = mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier;
TcwMM = mCurrentFrame.mTcw.clone();
}
bOKReloc = Relocalization(); //重定位获取相机位姿
if(bOKMM && !bOKReloc) // 跟踪成功,重定位失败
{
mCurrentFrame.SetPose(TcwMM);
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints = vpMPsMM;
mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier = vbOutMM;
if(mbVO) // 如果上一帧时在地图中找不到足够多的匹配内点
{
for(int i =0; iIncreaseFound(); //则将当前帧的检测到的地图点的查找次数增加
}
}
}
}
else if(bOKReloc) // 重定位成功 则整个跟踪进程正常进行
{
mbVO = false;
}
bOK = bOKReloc || bOKMM;
}
}
}
mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF = mpReferenceKF;
// If we have an initial estimation of the camera pose and matching. Track the local map.
// 如果不处于仅追踪模式下 则追踪局部地图并更新tracking线程中局部地图
if(!mbOnlyTracking)
{
if(bOK)
bOK = TrackLocalMap();
}
else
{
// mbVO true means that there are few matches to MapPoints in the map. We cannot retrieve
// a local map and therefore we do not perform TrackLocalMap(). Once the system relocalizes
// the camera we will use the local map again. 如果处于仅追踪模式下,并且有当前帧足够多的地图点,则追踪局部地图
if(bOK && !mbVO)
bOK = TrackLocalMap();
}
if(bOK)
mState = OK;
else
mState=LOST;
// Update drawer 更新帧观测器
mpFrameDrawer->Update(this);
// If tracking were good, check if we insert a keyframe 如果追踪线程是好的,检测你是否该加入关键帧
if(bOK)
{
// Update motion model 更新运动模型
if(!mLastFrame.mTcw.empty())
{
//上一帧的位姿变换矩阵
cv::Mat LastTwc = cv::Mat::eye(4,4,CV_32F);
mLastFrame.GetRotationInverse().copyTo(LastTwc.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3));
mLastFrame.GetCameraCenter().copyTo(LastTwc.rowRange(0,3).col(3));
mVelocity = mCurrentFrame.mTcw*LastTwc; //运动速度 上一帧到这一帧的位姿变换矩阵
}
else //第一帧
mVelocity = cv::Mat();
mpMapDrawer->SetCurrentCameraPose(mCurrentFrame.mTcw);
// Clean VO matches 清理那些据外点和冗余地图点
for(int i=0; iObservations()<1)
{
mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i] = false;
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=static_cast(NULL);
}
}
// Delete temporal MapPoints 清除临时地图点
for(list::iterator lit = mlpTemporalPoints.begin(), lend = mlpTemporalPoints.end(); lit!=lend; lit++)
{
MapPoint* pMP = *lit;
delete pMP;
}
mlpTemporalPoints.clear(); //临时地图点清空
// Check if we need to insert a new keyframe 判断是否需要插入该帧到关键帧中
if(NeedNewKeyFrame())
CreateNewKeyFrame();
// We allow points with high innovation (considererd outliers by the Huber Function)
// pass to the new keyframe, so that bundle adjustment will finally decide
// if they are outliers or not. We don't want next frame to estimate its position
// with those points so we discard them in the frame.
//我们允许用更多的点和关键帧匹配,因此BA优化将会决定这些点哪些是外点 我们不想通过这些点来估计下一帧的位姿,因此我们删除这些地图点
for(int i=0; i(NULL);
}
}
// Reset if the camera get lost soon after initialization 如果追踪线程丢失并且此时在初始化后不久则复位该线程
if(mState==LOST)
{
if(mpMap->KeyFramesInMap()<=5)
{
cout << "Track lost soon after initialisation, reseting..." << endl;
mpSystem->Reset();
return;
}
}
if(!mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF)//如果当前帧没有参考关键帧 则我们将当前关键帧设为当前帧的参考关键帧
mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF = mpReferenceKF;
mLastFrame = Frame(mCurrentFrame); //将上一帧更新为当前帧
}
// Store frame pose information to retrieve the complete camera trajectory afterward存储完整的帧姿态信息以获取完整的相机轨迹
//每个关键帧都有三个坐标系下的变换矩阵,世界坐标系相对于相机坐标系的变换矩阵,相机坐标系相对于参考帧相机坐标系的变换矩阵,参考帧相机坐标系相对于世界坐标系的变换矩阵
if(!mCurrentFrame.mTcw.empty()) //如果当前帧的世界坐标系下的变换矩阵不为空 即未丢失,跟踪成功
{
cv::Mat Tcr = mCurrentFrame.mTcw*mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF->GetPoseInverse(); //计算当前帧相对于参考帧的变换矩阵
mlRelativeFramePoses.push_back(Tcr);
mlpReferences.push_back(mpReferenceKF); //将当前参考关键帧存入到参考帧列表中
mlFrameTimes.push_back(mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp); //将当前帧的时间戳存入mlFrameTimes
mlbLost.push_back(mState==LOST); //存储当前帧的状态,是否丢失
}
else
{
// This can happen if tracking is lost 如果追踪丢失,将保持原参考数据不变,并将该帧定义为LOST帧
mlRelativeFramePoses.push_back(mlRelativeFramePoses.back());
mlpReferences.push_back(mlpReferences.back());
mlFrameTimes.push_back(mlFrameTimes.back());
mlbLost.push_back(mState==LOST);
}
}
/*******************************************************************************
* 函数属性:类Tracking的成员函数StereoInitialization()
* 函数功能:(1)设定初始化位姿
* (2)将当前帧构造为初始关键帧
* (3)在地图中添加该初始关键帧
* (4)为每个特征点构造mappoint
* (5)在局部地图中添加该初始关键帧
* 函数参数介绍:NULL
* 备注:双目或者RGBDSLAM的第一帧处理函数,地图初始化
*
******************************************************************************/
void Tracking::StereoInitialization()
{
if(mCurrentFrame.N>500) //当前帧关键点的数量大于500,才将此帧作为初始帧并认为其为关键帧
{
// Set Frame pose to the origin 设置初始帧的位姿
mCurrentFrame.SetPose(cv::Mat::eye(4,4,CV_32F));
// Create KeyFrame 将当前帧(第一帧)作为初始关键帧(调用关键帧的构造函数)
KeyFrame* pKFini = new KeyFrame(mCurrentFrame,mpMap,mpKeyFrameDB);
// Insert KeyFrame in the map 将关键帧插入地图中. KeyFrame中包含了地图、反过来地图中也包含了KeyFrame,相互包含
mpMap->AddKeyFrame(pKFini);
// Create MapPoints and asscoiate to KeyFrame 创建地图点并将其与关键帧建立联系
for(int i=0; i0)
{
cv::Mat x3D = mCurrentFrame.UnprojectStereo(i); //将当前帧的第i个特征点反投影到3D世界坐标系下
MapPoint* pNewMP = new MapPoint(x3D,pKFini,mpMap); //用该特征点构造新的地图点
pNewMP->AddObservation(pKFini,i); //地图点添加关键帧 说明该地图点属于哪一关键帧
pKFini->AddMapPoint(pNewMP,i); //关键帧添加地图点 表明在该关键帧下可以看到该地图点
pNewMP->ComputeDistinctiveDescriptors(); //从众多观测到该MapPoint的特征点中挑选区分读最高的描述子
pNewMP->UpdateNormalAndDepth(); //更新该MapPoint平均观测方向以及观测距离的范围
mpMap->AddMapPoint(pNewMP); //将新的地图点加入到地图中
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=pNewMP; // 将地图点加入到当前针的mvpMapPoints中,为当前Frame的特征点与MapPoint之间建立联系
}
}
cout << "New map created with " << mpMap->MapPointsInMap() << " points" << endl;
//在局部地图中添加该初始关键帧
mpLocalMapper->InsertKeyFrame(pKFini); //将该帧插入局部地图
//更新上一帧为当前帧
mLastFrame = Frame(mCurrentFrame);
mnLastKeyFrameId=mCurrentFrame.mnId;
// 更新上一关键帧为当前关键帧
mpLastKeyFrame = pKFini;
mvpLocalKeyFrames.push_back(pKFini); //将初始关键帧加入到局部地图的关键帧
mvpLocalMapPoints=mpMap->GetAllMapPoints(); //将全部地图点加入到当前局部地图点
mpReferenceKF = pKFini; //将当前关键帧作为参考关键帧
mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF = pKFini; //将该关键帧作为当前帧的参考关键帧
mpMap->SetReferenceMapPoints(mvpLocalMapPoints); //将当前局部地图点作为整个地图参考地图点,用于画图
mpMap->mvpKeyFrameOrigins.push_back(pKFini); //将关键帧加入地图的原始的关键帧
mpMapDrawer->SetCurrentCameraPose(mCurrentFrame.mTcw); //将当前帧加入到地图观测器
mState=OK;
}
}
/****************************************************************************
* 单目相机的初始化
* 单目相机初始化至少需要两帧
* 如果是第一帧初始化帧 则建立好初始化器
* 如果已经建立好初始化器并且有初始化的参考帧, 则
* 匹配当前帧和初始化帧
* 计算两帧之间的位姿(H矩阵和F矩阵)
* 如果初始化成功 ,则更新初始化地图,将地图点加入初始化地图中,并更新关键帧,将关键帧加入到局部建图中
***************************************************************************/
void Tracking::MonocularInitialization()
{
// 如果单目初始化器没有被创建,则创建单目初始化器
if(!mpInitializer)
{
// Set Reference Frame 如果当前帧的特征点数量大于100 则可以将其设为初始化的参考帧
if(mCurrentFrame.mvKeys.size()>100)
{
mInitialFrame = Frame(mCurrentFrame);
mLastFrame = Frame(mCurrentFrame);
mvbPrevMatched.resize(mCurrentFrame.mvKeysUn.size());
for(size_t i=0; i(NULL);
fill(mvIniMatches.begin(),mvIniMatches.end(),-1);
return;
}
// Find correspondences 寻找匹配点 为地图初始化寻找匹配对
ORBmatcher matcher(0.9,true);
int nmatches = matcher.SearchForInitialization(mInitialFrame,mCurrentFrame,mvbPrevMatched,mvIniMatches,100);
// Check if there are enough correspondences 如果匹配点太少,则删除初始化器,重新进行初始化
if(nmatches<100)
{
delete mpInitializer;
mpInitializer = static_cast(NULL);
return;
}
// Current Camera Rotation 当前相机的旋转矩阵
cv::Mat Rcw;
// Current Camera Translation 当前相机的平移矩阵
cv::Mat tcw;
// Triangulated Correspondences (mvIniMatches) 能被三角化的匹配点(两相机下的视角非平行)
vector vbTriangulated;
// 根据当前帧和初始化参考帧进行三角化
if(mpInitializer->Initialize(mCurrentFrame, mvIniMatches, Rcw, tcw, mvIniP3D, vbTriangulated))
{
for(size_t i=0, iend=mvIniMatches.size(); i=0 && !vbTriangulated[i])
{
mvIniMatches[i]=-1;
nmatches--;
}
}
// Set Frame Poses 设置相机的位姿 初始化帧相机的位姿 当前帧的相机位姿
mInitialFrame.SetPose(cv::Mat::eye(4,4,CV_32F));
cv::Mat Tcw = cv::Mat::eye(4,4,CV_32F);
Rcw.copyTo(Tcw.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3));
tcw.copyTo(Tcw.rowRange(0,3).col(3));
mCurrentFrame.SetPose(Tcw);
CreateInitialMapMonocular();
}
}
}
// 构建单目初始化地图,创建地图点,创建关键帧,更新地图,更新局部地图线程关键帧等等,归一化位移向量,归一化地图点
void Tracking::CreateInitialMapMonocular()
{
// Create KeyFrames 根据当前参考帧和当前帧构建关键帧
KeyFrame* pKFini = new KeyFrame(mInitialFrame,mpMap,mpKeyFrameDB);
KeyFrame* pKFcur = new KeyFrame(mCurrentFrame,mpMap,mpKeyFrameDB);
// 计算关键帧的BOW向量
pKFini->ComputeBoW();
pKFcur->ComputeBoW();
// Insert KFs in the map 将关键帧加入地图中
mpMap->AddKeyFrame(pKFini);
mpMap->AddKeyFrame(pKFcur);
// Create MapPoints and asscoiate to keyframes 创建地图点,并与关键帧关联
for(size_t i=0; iAddMapPoint(pMP,i);
pKFcur->AddMapPoint(pMP,mvIniMatches[i]);
// 地图点关联关键帧
pMP->AddObservation(pKFini,i);
pMP->AddObservation(pKFcur,mvIniMatches[i]);
// 计算该地图点的最优描述子,并计算该地图点的平均观测方向和观测深度范围
pMP->ComputeDistinctiveDescriptors();
pMP->UpdateNormalAndDepth();
//Fill Current Frame structure 填充当前帧的地图点和局外点
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[mvIniMatches[i]] = pMP;
mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[mvIniMatches[i]] = false;
//Add to Map 将地图点添加到地图
mpMap->AddMapPoint(pMP);
}
// Update Connections
pKFini->UpdateConnections();
pKFcur->UpdateConnections();
// Bundle Adjustment
cout << "New Map created with " << mpMap->MapPointsInMap() << " points" << endl;
Optimizer::GlobalBundleAdjustemnt(mpMap,20);
// Set median depth to 1
float medianDepth = pKFini->ComputeSceneMedianDepth(2);
float invMedianDepth = 1.0f/medianDepth;
// 当前地图点的深度中值<0 或者关键帧的地图点被观察到一次以上的个数小于100 则初始化失败,重启
if(medianDepth<0 || pKFcur->TrackedMapPoints(1)<100)
{
cout << "Wrong initialization, reseting..." << endl;
Reset();
return;
}
// Scale initial baseline 尺度归一化,把初始化的两帧之间的位移作为单位位移,由于单目相机的尺度是不确定的!所以我们假设了初始化两帧之间的位移为单位长度
cv::Mat Tc2w = pKFcur->GetPose();
Tc2w.col(3).rowRange(0,3) = Tc2w.col(3).rowRange(0,3)*invMedianDepth;
pKFcur->SetPose(Tc2w);
// Scale points 地图点归一化 ,把地图点的深度也归一化
vector vpAllMapPoints = pKFini->GetMapPointMatches();
for(size_t iMP=0; iMPSetWorldPos(pMP->GetWorldPos()*invMedianDepth);
}
}
//将关键帧插入局部地图线程
mpLocalMapper->InsertKeyFrame(pKFini);
mpLocalMapper->InsertKeyFrame(pKFcur);
// 更新当前帧和上一帧关键帧
mCurrentFrame.SetPose(pKFcur->GetPose());
mnLastKeyFrameId=mCurrentFrame.mnId;
mpLastKeyFrame = pKFcur;
// 更新局部地图关键帧
mvpLocalKeyFrames.push_back(pKFcur);
mvpLocalKeyFrames.push_back(pKFini);
mvpLocalMapPoints=mpMap->GetAllMapPoints();
mpReferenceKF = pKFcur;
mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF = pKFcur;
mLastFrame = Frame(mCurrentFrame);
mpMap->SetReferenceMapPoints(mvpLocalMapPoints); // 将局部地图点加入地图,用于作图
mpMapDrawer->SetCurrentCameraPose(pKFcur->GetPose());
mpMap->mvpKeyFrameOrigins.push_back(pKFini);
mState=OK;
}
//检测上一帧中的所有地图点,看是否已有其他地图点可以代替该地图点,如果可以代替则将其替代掉
void Tracking::CheckReplacedInLastFrame()
{
for(int i =0; iGetReplaced(); //找到该地图点的可代替其他地图点
if(pRep) //检测上一帧中的地图点是否可以找到被代替的其他地图点
{
mLastFrame.mvpMapPoints[i] = pRep;
}
}
}
}
/*******************************************************************************
* 函数属性:类Tracking的成员函数TrackReferenceKeyFrame()
* 函数功能:
* 1. 计算当前帧的词包,将当前帧的特征点分到特定层的nodes上
* 2. 对属于同一node的描述子进行匹配
* 3. 根据匹配对估计当前帧的姿态
* 4. 根据位姿估计下的模型判断是否为内点来剔除误匹配
* 5. 返回当前优化位姿模型下内点数量是否大于10 大于10证明当前位姿估计模型是好的,否则是差的
* 函数参数介绍:NULL
* 备注:
* 根据上一帧的位姿作为初始位姿进行位姿优化得到当前帧的位姿
******************************************************************************/
bool Tracking::TrackReferenceKeyFrame()
{
// Compute Bag of Words vector
// 将当前帧描述子转化为BoW向量
mCurrentFrame.ComputeBoW();
// We perform first an ORB matching with the reference keyframe
// If enough matches are found we setup a PnP solver
ORBmatcher matcher(0.7,true);
vector vpMapPointMatches;
//根据BoW进行将参考帧和当前帧进行特征匹配 将匹配点存储到vpMapPointMatches中 返回的是匹配点的数量
int nmatches = matcher.SearchByBoW(mpReferenceKF,mCurrentFrame,vpMapPointMatches);
//匹配点数量小于15无法进行优化,证明不是一个有效的匹配
if(nmatches<15)
return false;
//设置初始位姿为上一帧的位姿,优化节点为vpMapPointMatches中的匹配点
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints = vpMapPointMatches;
mCurrentFrame.SetPose(mLastFrame.mTcw);
//进行位姿优化,从而获得准确的相机位姿
Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);
// Discard outliers 剔除优化后的局外匹配点
int nmatchesMap = 0;
for(int i =0; i(NULL);
mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i]=false;
pMP->mbTrackInView = false;
pMP->mnLastFrameSeen = mCurrentFrame.mnId;
nmatches--;
}
else if(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]->Observations()>0) //否则说明是当前帧和参考帧的好匹配点
nmatchesMap++;//匹配点数量加1
}
}
return nmatchesMap>=10; //如果匹配点数量足够,则证明此次位姿估计是好的
}
/***********************************************************
* 更新上一帧
* 1 根据参考关键帧相对于初始帧的相机位姿和上一帧相对于参考关键帧的相机位姿来计算上一帧相对于初始帧的相机位姿
* 2 如果上一帧不为关键帧并且当前不是单目相机并且是在仅追踪模式下,则
* 1.创建视觉里程计的地图点 根据测量他们的地图点深度排序这些点
* 2.创建视觉里程计的地图点 根据测量他们的地图点深度排序这些点
****************************************************************/
void Tracking::UpdateLastFrame()
{
// Update pose according to reference keyframe
KeyFrame* pRef = mLastFrame.mpReferenceKF;
cv::Mat Tlr = mlRelativeFramePoses.back();
mLastFrame.SetPose(Tlr*pRef->GetPose());
//如果上一帧为关键帧或者当前是单目相机或者是不在仅追踪模式下 则返回
if(mnLastKeyFrameId==mLastFrame.mnId || mSensor==System::MONOCULAR || !mbOnlyTracking)
return;
// Create "visual odometry" MapPoints
// We sort points according to their measured depth by the stereo/RGB-D sensor
// 创建视觉里程计的地图点 根据测量他们的地图点深度排序这些点
vector > vDepthIdx;
vDepthIdx.reserve(mLastFrame.N);
for(int i=0; i0)
{
vDepthIdx.push_back(make_pair(z,i));
}
}
if(vDepthIdx.empty())
return;
sort(vDepthIdx.begin(),vDepthIdx.end());
// We insert all close points (depthObservations()<1)
{
bCreateNew = true;
}
if(bCreateNew)
{
cv::Mat x3D = mLastFrame.UnprojectStereo(i);
MapPoint* pNewMP = new MapPoint(x3D,mpMap,&mLastFrame,i);
mLastFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=pNewMP;
mlpTemporalPoints.push_back(pNewMP);
nPoints++;
}
else
{
nPoints++;
}
if(vDepthIdx[j].first>mThDepth && nPoints>100)
break;
}
}
/******************************************************************************
* 根据运动模型来进行位姿计算 并完成追踪
* 1 更新上一帧的相机位姿 根据上一帧相机位姿以及上一帧相机位姿变化的速度来估算当前位姿
* 2 通过映射的方式匹配当前帧和上一帧,并追踪上一帧的地图点
* 3 优化当前帧的相机位姿
* 4 去除局外点,如果当前模型下的局内点数量大于10 则返回成功追踪
* 5 仅追踪模式下地图内的匹配点数量小于10将mbVO置1 表明地图内匹配内点数量不足 返回局内点数量是否大于20
***********************************************************************/
bool Tracking::TrackWithMotionModel()
{
ORBmatcher matcher(0.9,true);
// Update last frame pose according to its reference keyframe
// Create "visual odometry" points if in Localization Mode
UpdateLastFrame();
//将当前帧的初始位姿设为上一帧位姿乘上一帧位姿的变化速度
mCurrentFrame.SetPose(mVelocity*mLastFrame.mTcw);
//将当前帧的地图点清空
fill(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.begin(),mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.end(),static_cast(NULL));
// Project points seen in previous frame 通过映射来计算匹配
int th;
if(mSensor!=System::STEREO)
th=15;
else
th=7;
// 匹配局内点的数量
int nmatches = matcher.SearchByProjection(mCurrentFrame,mLastFrame,th,mSensor==System::MONOCULAR);
// If few matches, uses a wider window search 如果匹配点不足够多,则增大筛选阈值
if(nmatches<20)
{
fill(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.begin(),mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.end(),static_cast(NULL));
nmatches = matcher.SearchByProjection(mCurrentFrame,mLastFrame,2*th,mSensor==System::MONOCULAR);
}
if(nmatches<20)
return false;
// Optimize frame pose with all matches 优化位姿并将地图点分为局外点和局内点
Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);
// Discard outliers 匹配点在地图点中的数量
int nmatchesMap = 0;
for(int i =0; i(NULL);
mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i]=false;
pMP->mbTrackInView = false;
pMP->mnLastFrameSeen = mCurrentFrame.mnId;
nmatches--;
}
else if(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]->Observations()>0) // 在其他关键帧中也能看到该地图点
nmatchesMap++;
}
}
if(mbOnlyTracking)//仅追踪模式下地图内的匹配点数量小于10将mbVO置1 表明地图内匹配内点数量不足 局内点数量是否大于20
{
mbVO = nmatchesMap<10;
return nmatches>20;
}
return nmatchesMap>=10; //返回局内点是否大于10
}
/*****************************************************************************
* 追踪局部地图
* 1. 更新局部地图(更新局部关键帧和局部地图点)
* 2. 在局部地图点中寻找在当前帧的视野范围内的点,匹配视野范围内的点与当前帧,匹配点存储到当前帧的地图点容器中
* 3. 根据新得到的匹配点重新优化相机位姿并得到匹配内点, 通过匹配内点的数量来判断当前局部地图是否追踪成功
****************************************************************************/
bool Tracking::TrackLocalMap()
{
// We have an estimation of the camera pose and some map points tracked in the frame.
// We retrieve the local map and try to find matches to points in the local map.
// 更新局部地图
UpdateLocalMap();
// 匹配局部地图点与当前帧的地图点
SearchLocalPoints();
// Optimize Pose 根据新更新的匹配局部地图点进行当前帧的位姿优化
Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);
mnMatchesInliers = 0;
// Update MapPoints Statistics 根据优化后的位姿重新更新匹配点的内点和外点
for(int i=0; iIncreaseFound();// 当前帧的被查找次数+1
if(!mbOnlyTracking)
{
if(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]->Observations()>0)
mnMatchesInliers++;
}
else
mnMatchesInliers++;
}
else if(mSensor==System::STEREO)
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i] = static_cast(NULL);
}
}
// Decide if the tracking was succesful
// More restrictive if there was a relocalization recently
if(mCurrentFrame.mnIdisStopped() || mpLocalMapper->stopRequested())
return false;
//得到整个地图中关键帧的数量
const int nKFs = mpMap->KeyFramesInMap();
// Do not insert keyframes if not enough frames have passed from last relocalisation 如果在上次重定位后还没有足够的帧通过 则不插入关键帧
if(mCurrentFrame.mnIdmMaxFrames)
return false;
// Tracked MapPoints in the reference keyframe 在参考关键帧中追踪地图点
int nMinObs = 3;
if(nKFs<=2)
nMinObs=2;
// 参考关键帧中所有地图点被观察到的次数大于2或3次的地图点数量
int nRefMatches = mpReferenceKF->TrackedMapPoints(nMinObs);
// Local Mapping accept keyframes? 局部地图是否接收关键帧
bool bLocalMappingIdle = mpLocalMapper->AcceptKeyFrames();
// Check how many "close" points are being tracked and how many could be potentially created. 检测有多少近点被追踪
// 未被追踪的近点数量
int nNonTrackedClose = 0;
// 被追踪的近点的数量
int nTrackedClose= 0;
if(mSensor!=System::MONOCULAR) //非单目相机 检测每一特征点是否是近点 有多少近点中局内点数量,有近点中局外点数量
{
for(int i =0; i0 && mCurrentFrame.mvDepth[i]70);
// Thresholds 设置阈值 参考比率(当前帧内点数量/参考关键帧中所有地图点被观察到的次数大于2或3次的地图点数量)
float thRefRatio = 0.75f;
if(nKFs<2)//如果整个地图中关键帧的数量小于2 则阈值设为0.4
thRefRatio = 0.4f;
if(mSensor==System::MONOCULAR)// 如果是单目相机 比例设为0.9
thRefRatio = 0.9f;
// Condition 1a: More than "MaxFrames" have passed from last keyframe insertion 此帧距离上次插入关键帧已经超过了最大的帧数
const bool c1a = mCurrentFrame.mnId>=mnLastKeyFrameId+mMaxFrames;
// Condition 1b: More than "MinFrames" have passed and Local Mapping is idle 此帧距离上次插入关键帧已经超过了最小帧数并且此时局部地图线程处于空闲状态
const bool c1b = (mCurrentFrame.mnId>=mnLastKeyFrameId+mMinFrames && bLocalMappingIdle);
//Condition 1c: tracking is weak 如果传感器不是单目 并且(匹配到的内点小于好地图点的0.25倍或者 近点中局内点数量小于100 并且局外点大于70) 追踪线程是比较弱的
const bool c1c = mSensor!=System::MONOCULAR && (mnMatchesInliers15);
if((c1a||c1b||c1c)&&c2)
{
// If the mapping accepts keyframes, insert keyframe.
// Otherwise send a signal to interrupt BA
if(bLocalMappingIdle) //如果局部建图线程处于空闲状态则返回真
{
return true;
}
else //否则中断BA优化
{
mpLocalMapper->InterruptBA();
if(mSensor!=System::MONOCULAR)
{
if(mpLocalMapper->KeyframesInQueue()<3)// 如果关键帧队列中关键帧数量小于3 则添加关键帧
return true;
else
return false;
}
else
return false;
}
}
else
return false;
}
// 添加新的关键帧
// 建立关键帧中的地图点加入全局map中(非单目情况下),并且将关键帧传递给localmapping线程
void Tracking::CreateNewKeyFrame()
{
if(!mpLocalMapper->SetNotStop(true)) // 如果局部建图线程被暂停
return;
KeyFrame* pKF = new KeyFrame(mCurrentFrame,mpMap,mpKeyFrameDB);
mpReferenceKF = pKF; //更新参考关键帧为当前新添加的关键帧
mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF = pKF; //当前帧的参考关键帧设为该帧
if(mSensor!=System::MONOCULAR) // 双目或rgbd 添加地图点到地图中
{
mCurrentFrame.UpdatePoseMatrices();
// We sort points by the measured depth by the stereo/RGBD sensor.
// We create all those MapPoints whose depth < mThDepth.
// If there are less than 100 close points we create the 100 closest.
// 通过深度对点进行排序 将100个近点插入到地图中
vector > vDepthIdx;
vDepthIdx.reserve(mCurrentFrame.N);
for(int i=0; i0)
{
vDepthIdx.push_back(make_pair(z,i));
}
}
if(!vDepthIdx.empty())
{
sort(vDepthIdx.begin(),vDepthIdx.end());
int nPoints = 0;
for(size_t j=0; jObservations()<1)
{
bCreateNew = true;
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i] = static_cast(NULL);
}
if(bCreateNew)
{
cv::Mat x3D = mCurrentFrame.UnprojectStereo(i);
MapPoint* pNewMP = new MapPoint(x3D,pKF,mpMap);
pNewMP->AddObservation(pKF,i);
pKF->AddMapPoint(pNewMP,i);
pNewMP->ComputeDistinctiveDescriptors();
pNewMP->UpdateNormalAndDepth();
mpMap->AddMapPoint(pNewMP); // 将地图点添加进全局地图mpMap中
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=pNewMP;
nPoints++;
}
else
{
nPoints++;
}
// 如果地图点的深度大于阈值(远点)并且当前添加的地图点数量已经大于100 则不再继续添加地图点了
if(vDepthIdx[j].first>mThDepth && nPoints>100)
break;
}
}
}
// 局部地图加入关键帧
mpLocalMapper->InsertKeyFrame(pKF);
mpLocalMapper->SetNotStop(false);
mnLastKeyFrameId = mCurrentFrame.mnId;
mpLastKeyFrame = pKF;
}
/**
* @brief 对Local MapPoints进行跟踪
*
* 在局部地图中查找在当前帧视野范围内的点,将视野范围内的点和当前帧的特征点进行投影匹配
*/
void Tracking::SearchLocalPoints()
{
// Do not search map points already matched 不去匹配已经匹配过的点(在tracking的位姿计算过程中(按照运动模型计算和根据关键帧进行计算))
for(vector::iterator vit=mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.begin(), vend=mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.end(); vit!=vend; vit++)
{
MapPoint* pMP = *vit;
if(pMP)
{
if(pMP->isBad())
{
*vit = static_cast(NULL);
}
else
{
pMP->IncreaseVisible();
pMP->mnLastFrameSeen = mCurrentFrame.mnId;
pMP->mbTrackInView = false;
}
}
}
int nToMatch=0;
// Project points in frame and check its visibility 将局部地图中的点投影到当前帧的视锥中,然后将当前帧和当前局部地图点进行匹配
for(vector::iterator vit=mvpLocalMapPoints.begin(), vend=mvpLocalMapPoints.end(); vit!=vend; vit++)
{
MapPoint* pMP = *vit;
if(pMP->mnLastFrameSeen == mCurrentFrame.mnId) //不去匹配已经匹配过的点(在tracking的位姿计算过程中(按照运动模型计算和根据关键帧进行计算))
continue;
if(pMP->isBad())
continue;
// Project (this fills MapPoint variables for matching)
if(mCurrentFrame.isInFrustum(pMP,0.5))
{
pMP->IncreaseVisible();
nToMatch++;
}
}
if(nToMatch>0)
{
ORBmatcher matcher(0.8);
int th = 1;
if(mSensor==System::RGBD)
th=3;
// If the camera has been relocalised recently, perform a coarser search
if(mCurrentFrame.mnIdSetReferenceMapPoints(mvpLocalMapPoints);
// Update 更新局部关键帧和局部地图点
UpdateLocalKeyFrames();
UpdateLocalPoints();
}
// 更新局部地图点
// 将局部关键帧中的所有关键帧的地图点加入局部地图点中(没有局部关键帧就没有局部地图点)
void Tracking::UpdateLocalPoints()
{
mvpLocalMapPoints.clear();
// 将局部关键帧中的所有关键帧的地图点加入局部地图点中
for(vector::const_iterator itKF=mvpLocalKeyFrames.begin(), itEndKF=mvpLocalKeyFrames.end(); itKF!=itEndKF; itKF++)
{
KeyFrame* pKF = *itKF;
const vector vpMPs = pKF->GetMapPointMatches();
for(vector::const_iterator itMP=vpMPs.begin(), itEndMP=vpMPs.end(); itMP!=itEndMP; itMP++)
{
MapPoint* pMP = *itMP;
if(!pMP)
continue;
if(pMP->mnTrackReferenceForFrame==mCurrentFrame.mnId)
continue;
if(!pMP->isBad())
{
mvpLocalMapPoints.push_back(pMP);
pMP->mnTrackReferenceForFrame=mCurrentFrame.mnId;
}
}
}
}
/************
* 更新局部关键帧
* 添加的关键帧为:1 当前帧的所有地图点还在哪些关键帧中看到 将这些关键帧加入局部关键帧
* 2 将所有看到地图点的所有关键帧的共视关键帧添加到局部地图中
* 3 将所有看到地图点的所有关键帧的父关键帧和子关键帧添加到局部地图中
* 更新参考关键帧为局部关键帧中看到最多当前帧地图点的关键帧
********/
void Tracking::UpdateLocalKeyFrames()
{
// Each map point vote for the keyframes in which it has been observed
// 每一个地图点为看到该地图点的关键帧投票 并将看到地图点的关键帧和该关键帧看到当前帧地图点的数量放到keyframeCounter容器中
map keyframeCounter;
for(int i=0; iisBad())
{
const map observations = pMP->GetObservations();
for(map::const_iterator it=observations.begin(), itend=observations.end(); it!=itend; it++)
keyframeCounter[it->first]++;
}
else
{
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=NULL;
}
}
}
if(keyframeCounter.empty())
return;
int max=0;
KeyFrame* pKFmax= static_cast(NULL);
mvpLocalKeyFrames.clear();
mvpLocalKeyFrames.reserve(3*keyframeCounter.size());
// All keyframes that observe a map point are included in the local map. Also check which keyframe shares most points
// 将所有看到地图点的所有关键帧添加到局部地图中 并且检查哪个关键帧能看到最多的地图点
for(map::const_iterator it=keyframeCounter.begin(), itEnd=keyframeCounter.end(); it!=itEnd; it++)
{
KeyFrame* pKF = it->first;
if(pKF->isBad())
continue;
if(it->second>max)
{
max=it->second;
pKFmax=pKF;
}
mvpLocalKeyFrames.push_back(it->first);
pKF->mnTrackReferenceForFrame = mCurrentFrame.mnId;
}
// Include also some not-already-included keyframes that are neighbors to already-included keyframes
// 如果局部关键帧不足够的话将这些关键帧的共视关键帧也加入进来
for(vector::const_iterator itKF=mvpLocalKeyFrames.begin(), itEndKF=mvpLocalKeyFrames.end(); itKF!=itEndKF; itKF++)
{
// Limit the number of keyframes 限制关键帧的数量
if(mvpLocalKeyFrames.size()>80)
break;
KeyFrame* pKF = *itKF;
const vector vNeighs = pKF->GetBestCovisibilityKeyFrames(10);
for(vector::const_iterator itNeighKF=vNeighs.begin(), itEndNeighKF=vNeighs.end(); itNeighKF!=itEndNeighKF; itNeighKF++)
{
KeyFrame* pNeighKF = *itNeighKF;
if(!pNeighKF->isBad())
{
if(pNeighKF->mnTrackReferenceForFrame!=mCurrentFrame.mnId)
{
mvpLocalKeyFrames.push_back(pNeighKF);
pNeighKF->mnTrackReferenceForFrame=mCurrentFrame.mnId;
break;
}
}
}
// 将这些关键帧的孩子加入到局部关键帧中 自关键帧为本关键帧为哪些关键帧的最大关联关键帧
const set spChilds = pKF->GetChilds();
for(set::const_iterator sit=spChilds.begin(), send=spChilds.end(); sit!=send; sit++)
{
KeyFrame* pChildKF = *sit;
if(!pChildKF->isBad())
{
if(pChildKF->mnTrackReferenceForFrame!=mCurrentFrame.mnId)
{
mvpLocalKeyFrames.push_back(pChildKF);
pChildKF->mnTrackReferenceForFrame=mCurrentFrame.mnId;
break;
}
}
}
// 将这些关键帧的父辈加入到局部关键帧中 父关键帧为本关键帧的最大关联关键帧
KeyFrame* pParent = pKF->GetParent();
if(pParent)
{
if(pParent->mnTrackReferenceForFrame!=mCurrentFrame.mnId)
{
mvpLocalKeyFrames.push_back(pParent);
pParent->mnTrackReferenceForFrame=mCurrentFrame.mnId;
break;
}
}
}
if(pKFmax) // 将能看到当前帧最多地图点的关键帧设为参考关键帧,并更新当前帧的参考关键帧为该帧
{
mpReferenceKF = pKFmax;
mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF = mpReferenceKF;
}
}
/*******************************************************************************
* 函数属性:类Tracking的成员函数Relocalization()
* 函数功能:(1)计算当前帧的BoW映射
* (2)找到与当前帧相似的候选关键帧
* (3)匹配当前帧与找到的候选关键帧,计算相机位姿Tcw
* (4)优化相机位姿Tcw
* 首先进行优化,将优化的结果存到nGood中,
* 如果优化结果不理想进行映射匹配,然后再进行优化
* 如果优化结果还不理想缩小映射窗口后在进行匹配并优化
* 此时若还不理想就判定该候选关键帧不能与本帧形成匹配,继续进行下一关键帧的匹配;如果可以,则证明已经进行重定位或者找到回环,退出循环
* 函数参数介绍:NULL
* 备注:重定位函数,用于失帧重定位和回环检测函数中
*
******************************************************************************/
bool Tracking::Relocalization()
{
// Compute Bag of Words Vector 计算当前帧的BoW向量和Feature向量
mCurrentFrame.ComputeBoW();
// Relocalization is performed when tracking is lost
// Track Lost: Query KeyFrame Database for keyframe candidates for relocalisation
// 当追踪线程丢失时进行重定位
// 找到当前帧相似的候选关键帧
vector vpCandidateKFs = mpKeyFrameDB->DetectRelocalizationCandidates(&mCurrentFrame);
if(vpCandidateKFs.empty()) //如果当前帧找不到相似候选关键帧
return false;
const int nKFs = vpCandidateKFs.size(); //得到候选关键帧的数量
// We perform first an ORB matching with each candidate
// If enough matches are found we setup a PnP solver 对于没一个候选关键帧与当前帧进行匹配,如果发现匹配点数量足够的话,我们进行PnP求解相机位姿
ORBmatcher matcher(0.75,true);
vector vpPnPsolvers;
vpPnPsolvers.resize(nKFs);
vector > vvpMapPointMatches;
vvpMapPointMatches.resize(nKFs);
vector vbDiscarded;
vbDiscarded.resize(nKFs);
// 候选关键帧数量
int nCandidates=0;
// 匹配当前帧与找到的候选关键帧,并将每一候选关键帧匹配到的地图点存储到vvpMapPointMatches容器中,并记录每一候选关键帧是否的到满意的匹配,储存到vbDiscarded容器中
// 根据匹配到的地图点和当前帧建立PNP解决器将其存储到vpPnPsolvers容器中
for(int i=0; iisBad())
vbDiscarded[i] = true;
else
{
//当前帧和候选关键帧通过BoW进行匹配 vvpMapPointMatches数组存储该候选关键帧与该帧匹配到的地图点
int nmatches = matcher.SearchByBoW(pKF,mCurrentFrame,vvpMapPointMatches[i]);
if(nmatches<15) //如果匹配点数量小于15 ,那么就说明该匹配是失败的
{
vbDiscarded[i] = true;
continue;
}
else //否则建立PNPsolver
{
PnPsolver* pSolver = new PnPsolver(mCurrentFrame,vvpMapPointMatches[i]);
pSolver->SetRansacParameters(0.99,10,300,4,0.5,5.991); //设置PNP求解器的相关参数
vpPnPsolvers[i] = pSolver;
nCandidates++;
}
}
}
// Alternatively perform some iterations of P4P RANSAC
// Until we found a camera pose supported by enough inliers
bool bMatch = false; //该标志量表示是否完成重定位
ORBmatcher matcher2(0.9,true);
while(nCandidates>0 && !bMatch)
{
for(int i=0; i vbInliers;
int nInliers;
bool bNoMore;
PnPsolver* pSolver = vpPnPsolvers[i];
cv::Mat Tcw = pSolver->iterate(5,bNoMore,vbInliers,nInliers); //用PNP计算位姿 bNoMore是否达到最大迭代次数 vbInliers表示该点是否为内点 nInliers内点数量
// If Ransac reachs max. iterations discard keyframe 如果RANSAC迭代达到最大则取消迭代,认为该帧不能与该关键帧匹配
if(bNoMore)
{
vbDiscarded[i]=true;
nCandidates--;
}
// If a Camera Pose is computed, optimize 如果相机位姿被计算出,进行优化
if(!Tcw.empty())
{
Tcw.copyTo(mCurrentFrame.mTcw);
set sFound;
const int np = vbInliers.size(); //该帧与当前匹配关键帧之间的匹配地图点数量
for(int j=0; j(NULL);
// If few inliers, search by projection in a coarse window and optimize again 如果有很少的内点,那么通过仿射进行再次优化
if(nGood<50)
{
int nadditional =matcher2.SearchByProjection(mCurrentFrame,vpCandidateKFs[i],sFound,10,100); //通过投影的方式进行再次匹配,增加匹配点
if(nadditional+nGood>=50) //如果投影匹配和BOW匹配得到的内点大于50
{
nGood = Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame); //进行再次优化
// If many inliers but still not enough, search by projection again in a narrower window
// the camera has been already optimized with many points
//如果有许多内点但是还不足够,那么就再次通过缩小窗口进行投影 进行再次优化
if(nGood>30 && nGood<50)
{
sFound.clear();
for(int ip =0; ip=50)
{
nGood = Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame); //最终优化
for(int io =0; io=50)
{
bMatch = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
if(!bMatch)
{
return false;
}
else
{
mnLastRelocFrameId = mCurrentFrame.mnId; //重定位成功,将上次重定位的ID设为本帧的ID
return true;
}
}
void Tracking::Reset()
{
cout << "System Reseting" << endl;
if(mpViewer)
{
mpViewer->RequestStop();
while(!mpViewer->isStopped())
usleep(3000);
}
// Reset Local Mapping
cout << "Reseting Local Mapper...";
mpLocalMapper->RequestReset();
cout << " done" << endl;
// Reset Loop Closing
cout << "Reseting Loop Closing...";
mpLoopClosing->RequestReset();
cout << " done" << endl;
// Clear BoW Database
cout << "Reseting Database...";
mpKeyFrameDB->clear();
cout << " done" << endl;
// Clear Map (this erase MapPoints and KeyFrames)
mpMap->clear();
KeyFrame::nNextId = 0;
Frame::nNextId = 0;
mState = NO_IMAGES_YET;
if(mpInitializer)
{
delete mpInitializer;
mpInitializer = static_cast(NULL);
}
mlRelativeFramePoses.clear();
mlpReferences.clear();
mlFrameTimes.clear();
mlbLost.clear();
if(mpViewer)
mpViewer->Release();
}
void Tracking::ChangeCalibration(const string &strSettingPath)
{
cv::FileStorage fSettings(strSettingPath, cv::FileStorage::READ);
float fx = fSettings["Camera.fx"];
float fy = fSettings["Camera.fy"];
float cx = fSettings["Camera.cx"];
float cy = fSettings["Camera.cy"];
cv::Mat K = cv::Mat::eye(3,3,CV_32F);
K.at(0,0) = fx;
K.at(1,1) = fy;
K.at(0,2) = cx;
K.at(1,2) = cy;
K.copyTo(mK);
cv::Mat DistCoef(4,1,CV_32F);
DistCoef.at(0) = fSettings["Camera.k1"];
DistCoef.at(1) = fSettings["Camera.k2"];
DistCoef.at(2) = fSettings["Camera.p1"];
DistCoef.at(3) = fSettings["Camera.p2"];
const float k3 = fSettings["Camera.k3"];
if(k3!=0)
{
DistCoef.resize(5);
DistCoef.at(4) = k3;
}
DistCoef.copyTo(mDistCoef);
mbf = fSettings["Camera.bf"];
Frame::mbInitialComputations = true;
}
//通知仅仅进行Tracking线程 mbOnlyTracking 仅定位模式标志量
void Tracking::InformOnlyTracking(const bool &flag)
{
mbOnlyTracking = flag;
}
} //namespace ORB_SLAM
首先跟踪线程有四种状态,没有图片、未初始化、线程完好和追踪线程失败,如果没有图片或没有初始化则进行初始化,単目和其他的初始化是不一样的这里要注意一下,我们以RGBD相机来看初始化。
首先需要判断当前帧图像的关键点的个数是否大于500,大于500就开始进行初始化,接着设置初始帧的位姿为一个4*4的矩阵,将当前帧也就是第一帧作为初始关键帧,将关键帧插入地图中(KeyFrame中包含了地图,反过来地图中也包含了KeyFrame),然后创建地图点并将其与关键帧建立联系,接着获取深度值,并将该特征点反向投影到3D世界坐标系下。最后是将上一帧设为当前帧,当前上一关键帧为当前关键帧。(具体的看代码中的注释)
如果定位和建图同时存在的模式,局部建图线程被打开。检查并更新上一帧被替换的MapPoints.如果运动模型是空的或刚完成重定位, 将上一帧的位姿作为当前帧的初始位姿,通过BoW的方式在参考帧中找当前帧特征点的匹配点,优化每个特征点都对应3D点重投影误差即可得到位姿(常规的方法)。根据恒速模型设定当前帧的初始位姿,通过投影的方式在参考帧中找当前帧特征点的匹配点,优化每个特征点所对应3D点的投影误差即可得到位姿。如果不能根据固定运动速度模型预测当前帧的位姿态,可以通过bow加速匹配(SearchByBow)最后通过优化得到优化后的位姿。如果当前跟踪丢失,就重新定位。
如果在仅仅定位的模式下,那么地图构建线程被停止,
如果匹配的3D点比较多,首先判断是否可以计算出当前速度,然后根据运动模型来进行位姿计算 并完成追踪。否则就需要根据上一个参考帧完成跟踪。如果可匹配的点较少,就需要既做跟踪又做定位。需要计算两个相机位姿,一个来自于运动模型,另一个来自于重定位,如果重定位成功我们选择这种方法,否则我们选择视觉里程计方法。如果跟踪成功,重定位失败,重定位成功 则整个跟踪进程正常进行。
如果追踪线程是好的,就检查是否要加入关键帧,然后更新运动模型,获取上一帧到当前帧的位姿变换矩阵。剩下的就看代码中的注释了。ps:原文章的SLAM系列写的真的很详细,链接在最上面。
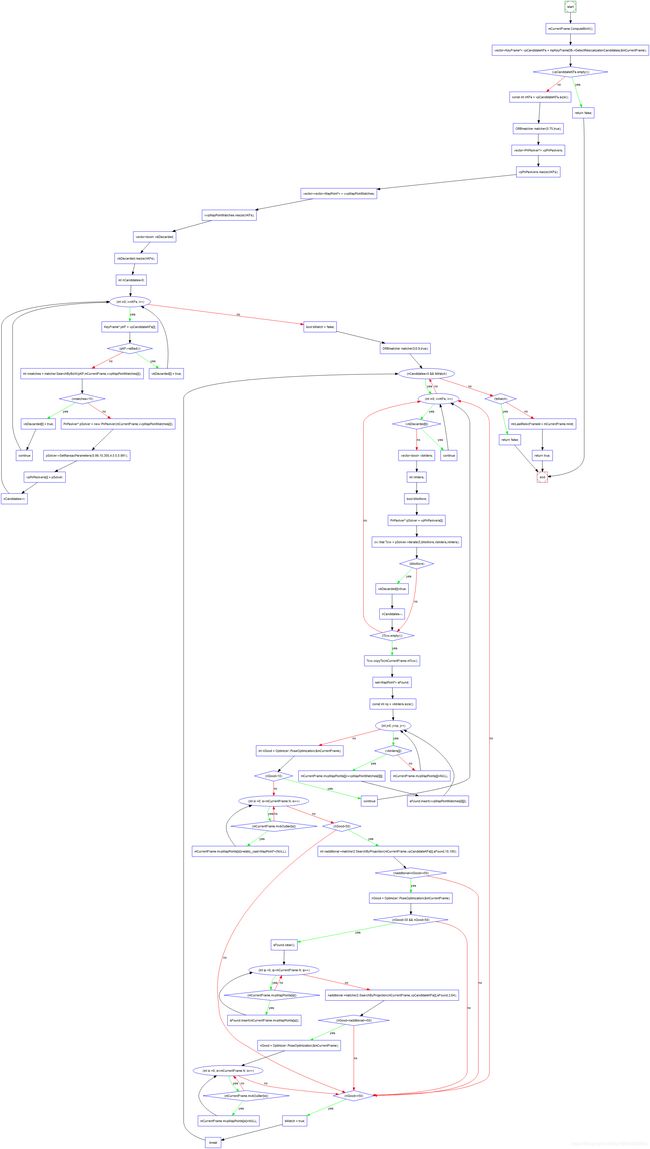
附上一张Track()函数的流程图:
在附上一张relocalization函数的流程图