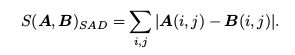建图——单目稠密重建
目录
- 立体视觉
- 极线搜索与块匹配
- 高斯分布的深度滤波器
- 实践:
立体视觉
在稠密重建,我们需要知道每一个像素点(或大部分像素点)的距离,那么大致上有以下几种解决方案:
- 使用单目相机,利用移动相机之后进行三角化,测量像素的距离。
- 使用双目相机,利用左右目的视差计算像素的距离(多目原理相同)。
- 使用 RGB-D 相机直接获得像素距离。
极线搜索与块匹配
-
左边的相机观测到了某个像素 p 1 p_1 p1 。由于这是一个单目相机,无从知道它的深度,所以假设这个深度可能在某个区域之内,不妨说是某最小值到无穷远之间:(d min , +∞)。因此,该像素对应的空间点就分布在某条线段上。在另一个视角(右侧相机)看来,这条线段的投影也形成图像平面上的一条线,称为极线。当我们知道两个相机间的运动时,这条极线也是能够确定的。
-
在特征点法中,通过特征匹配得到p2的位置,然而现在没有描述子,只能在极线上搜索和p1想的比较相似的点。(可能沿着极线一直走比较每个像素与p1的相似程度。)
块匹配
- 在 p 1 p_1 p1周围取一个大小为w*w的小块,然后在极线上也取很多同样大小的小块进行比较,就可以在一定程度上提高区分性。这就是所谓的块匹配(只有假设在不同图像间整个小块的灰度值不变)。
取了 p 1 p_1 p1周围的小块,并且在极线上也取了很多个小块。不妨把p1周围的小块记成 A ∈ R w × w A ∈ R^{w×w} A∈Rw×w,把极线上的n个小块记成 B i , i = 1... n B_i,i=1...n Bi,i=1...n。几种不同的方法计算小块与小块间的差异:
-
NCC(Normalized Cross Correlation)(归一化互相关),计算的是两个小块的相关性:
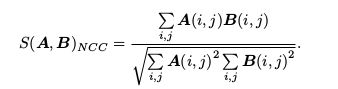
除了这些简单的版本外,我们可以先把每个小块的均值去掉。去掉均值后,我们准许像“小块B比A整体上亮一些,但仍然很相似”这样的情况。因此比之前的更加可靠一些。
高斯分布的深度滤波器
对像素点深度的估计,本身亦可建模为一个状态估计问题,存在滤波器与非线性优化两种求解思路,采用计算量较少的滤波器方式。
下面介绍并演示高斯分布假设下的深度滤波器:
设某个像素点的深度 d 服从:

而每当新的数据到来,我们都会观测到它的深度。同样的,假设这次观测亦是一个高斯分布:
![]()
由于我们仅有观测方程而没有运动方程,所以这里深度仅用到了信息融合部分。设融合后的 d的分布为 N ( μ f u s e , σ f u s e 2 N(μ_{f use} , σ_{fuse}^2 N(μfuse,σfuse2 ),有:

只考虑由几何关系带来的不确定性(不考虑光度不确定性等),计算深度不确定性 σ o b s 2 σ_{obs}^2 σobs2
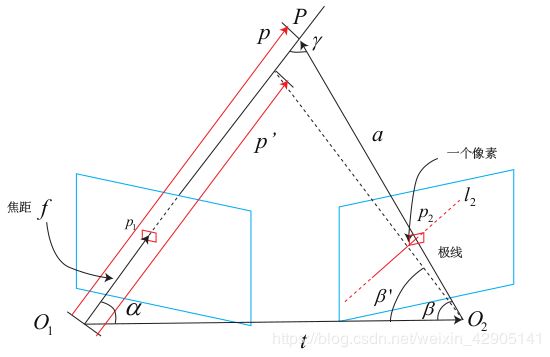
考虑某次极线搜索,我们找到了p1对应的p2点,从而观测到了p1的深度值,认为p1对应的三维点为P。
记 O 1 P O_1P O1P 为 p, O 1 O 2 O_1O_2 O1O2 为相机的平移 t , O 2 P O_2P O2P 记为 a。并且,把这个三角形的下面两个角记作 α, β。现在,考虑极线 l 2 l_2 l2 上存在着一个像素大小的误差,使得 β 角变成了 β ′ ,而 p 也变成了 p ′ ,并记上面那个角为 γ。我们要问的是,这一个像素的误差,会导致 p ′ 与 p 产生多大的差距呢?
由集合关系得:
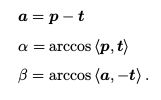
对 p 2 p_2 p2 扰动一个像素,将使得 β 产生一个变化量 δβ,由于相机焦距为 f ,于是:

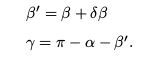
p ′ 的大小可以求得:
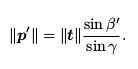
由此,我们确定了由单个像素的不确定引起的深度不确定性。如果认为极线搜索的块
匹配仅有一个像素的误差,那么就可以设:
![]()
如果极线搜索的不确定性大于一个像素,我们亦可按照此推导来放大这个不确定性。
估计稠密深度的一个完整的过程:
-
假设所有像素的深度满足某个初始的高斯分布。
-
当新数据产生时,通过极线搜索和块匹配确定投影点位置。
-
根据几何关系计算三角化后的深度及不确定性。
-
将当前观测融合进上一次的估计中。若收敛则停止计算,否则返回第2步。
实践:
#include 注解: