linux文件系统与模型【笔记】 surper block/inode/dentry/file
因为有文件,所以有管理文件的系统=>因为有很多种文件系统,所以有虚拟文件系统对它们进行封装,让上层的程序只需要调用简单的接口。
文件系统是存储和组织信息的机制,它的目的是管理各种存储设备,所谓的管理是指:存储/操作等。
文件系统管理的对象不同,对应的文件就不同:普通文件,socket文件,目录文件,链接文件,设备文件,管道文件。
文件系统分类:磁盘文件系统,如ext3,ext4;网络文件系统,如NFS;特殊文件系统,这类系统不管理本地或者远程的磁盘,如/proc。
linux支持的文件系统可以查看源码中的fs文件夹,如下:
norton@norton-laptop:~/linuxKernel/linux-2.6.34/fs$ ls
9p bio.c dlm fs_struct.c Kconfig notify select.c
adfs bio-integrity.c drop_caches.c fs-writeback.c Kconfig.binfmt ntfs seq_file.c
affs block_dev.c ecryptfs fuse libfs.c ocfs2 signalfd.c
afs btrfs efs generic_acl.c lockd omfs smbfs
aio.c buffer.c eventfd.c gfs2 locks.c open.c splice.c
anon_inodes.c cachefiles eventpoll.c hfs logfs openpromfs squashfs
attr.c ceph exec.c hfsplus Makefile partitions stack.c
autofs char_dev.c exofs hostfs mbcache.c pipe.c stat.c
autofs4 cifs exportfs hpfs minix pnode.c super.c
bad_inode.c coda ext2 hppfs mpage.c pnode.h sync.c
befs compat_binfmt_elf.c ext3 hugetlbfs namei.c posix_acl.c sysfs
bfs compat.c ext4 inode.c namespace.c proc sysv
binfmt_aout.c compat_ioctl.c fat internal.h ncpfs qnx4 timerfd.c
binfmt_elf.c configfs fcntl.c ioctl.c nfs quota ubifs
binfmt_elf_fdpic.c cramfs fifo.c ioprio.c nfs_common ramfs udf
binfmt_em86.c dcache.c file.c isofs nfsctl.c readdir.c ufs
binfmt_flat.c dcookies.c filesystems.c jbd nfsd read_write.c utimes.c
binfmt_misc.c debugfs file_table.c jbd2 nilfs2 read_write.h xattr_acl.c
binfmt_script.c devpts freevxfs jffs2 nls reiserfs xattr.c
binfmt_som.c direct-io.c fscache jfs no-block.c romfs xfs
虚拟文件系统VFS
是建立在各个文件系统上的抽象层,屏蔽了不同文件系统的差异。它之所以有这样的功能是因为它提供了一个“通用的文件系统模型”。该通用模型能够表示很多(即它支持的了)的文件系统。它只提供API接口,桥接实际的文件系统和具体的应用,不会做任何处理文件相关的决策。
VFS采用面向对象的设计思路,将一系列概念抽象出来的同时,也包括处理这些对象的方法。
VFS对象模型
代表一个已经安装的文件系统。如果是基于磁盘的文件系统,则存放在磁盘扇区。如果不是和基于磁盘的文件系统,如sysfs是基于内存的文件系统,则super_block存放在内存中。
2.索引节点(struct inode)
代表存储设备上的一个实际文件,存储文件相关的信息。linux把文件和文件信息分离出来,文件的相关信息又称为文件的“元数据”,文件信息包括:访问权限,大小,创建时间等。inode结构里面有hash链表,因为inode节点很多,查找效率低,需要借助hash表提高效率。相同hash值的inode节点会被放到一起。
3.目录项(struct dentry)
描述文件系统的层次结构,目录和文件(如.c文件)本身也是“目录项”的对象。通过目录项去找inode。它只存在内存中,不存在磁盘里,具体存在directory cache。它的存在是为了提高系统性能。定义在/include/linux/dcache.h中。
4.文件(struct file)
代表已经被打开(open)的文件。主要用于建立“进程”和文件之间的关系。一个物理文件可能对应多个“文件对象”,但只有唯一的对应的inode。file的结构体中有一个union,用了rcu链表,所以我转载了关于rcu机制的文章,不知道是不是这个rcu机制,仅供参考:http://blog.csdn.net/xzongyuan/article/details/20382995。
总结下4个模型的特征:
1.超级块是磁盘或者内存的抽象,通过超级块,我们可以访问磁盘或内存的具体位置;
3.目录项,它是一个抽象概念的模型,抽象的是文件的层次逻辑关系。它主要用来构建文件系统的层次性,因此它不代表具体某个对象。
4.文件。真正的文件对象,进程需要通过它来处理文件数据。该文件模型使得进程有能力通过目录项/索引节点/超级块来访问磁盘和内存。
/include/linux/fs.h
struct file {
/*
* fu_list becomes invalid after file_free is called and queued via
* fu_rcuhead for RCU freeing
*/
union {
struct list_head fu_list;
struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead;
} f_u;
struct path f_path;
#define f_dentry f_path.dentry
#define f_vfsmnt f_path.mnt
const struct file_operations *f_op;
spinlock_t f_lock; /* f_ep_links, f_flags, no IRQ */
atomic_long_t f_count;
unsigned int f_flags;
fmode_t f_mode;
loff_t f_pos;
struct fown_struct f_owner;
const struct cred *f_cred;
struct file_ra_state f_ra;
u64 f_version;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *f_security;
#endif
/* needed for tty driver, and maybe others */
void *private_data;
#ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL
/* Used by fs/eventpoll.c to link all the hooks to this file */
struct list_head f_ep_links;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL */
struct address_space *f_mapping;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_WRITECOUNT
unsigned long f_mnt_write_state;
#endif
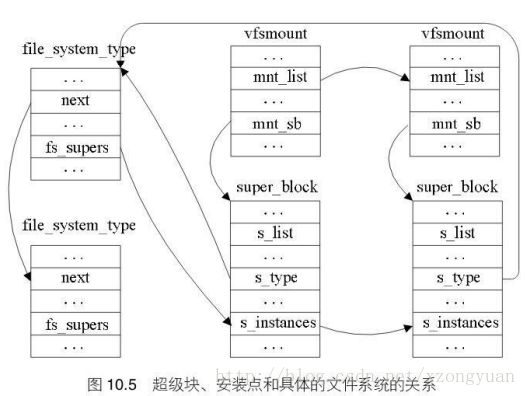
};5.其它。还有很多VFS对象,如表示文件系统类型的对象file_system_type,表示挂载点的对象vfsmount。不同的文件类型(file_system_type)通过next关联,相同文件类型的superblock通过s_instance(super block实例)字段链接在一起。所有的相同文件类型的vfsmount通过mnt_list连接在一起。
代码在include/linux/fs.h和include/linux/mount.h中。
struct file_system_type {
const char *name;
int fs_flags;
int (*get_sb) (struct file_system_type *, int,
const char *, void *, struct vfsmount *);
void (*kill_sb) (struct super_block *);
struct module *owner;
struct file_system_type * next;
struct list_head fs_supers;
struct lock_class_key s_lock_key;
struct lock_class_key s_umount_key;
struct lock_class_key i_lock_key;
struct lock_class_key i_mutex_key;
struct lock_class_key i_mutex_dir_key;
struct lock_class_key i_alloc_sem_key;
}struct vfsmount {
struct list_head mnt_hash;
struct vfsmount *mnt_parent; /* fs we are mounted on */
struct dentry *mnt_mountpoint; /* dentry of mountpoint */
struct dentry *mnt_root; /* root of the mounted tree */
struct super_block *mnt_sb; /* pointer to superblock */
struct list_head mnt_mounts; /* list of children, anchored here */
struct list_head mnt_child; /* and going through their mnt_child */
int mnt_flags;
/* 4 bytes hole on 64bits arches */
const char *mnt_devname; /* Name of device e.g. /dev/dsk/hda1 */
struct list_head mnt_list;
struct list_head mnt_expire; /* link in fs-specific expiry list */
struct list_head mnt_share; /* circular list of shared mounts */
struct list_head mnt_slave_list;/* list of slave mounts */
struct list_head mnt_slave; /* slave list entry */
struct vfsmount *mnt_master; /* slave is on master->mnt_slave_list */
struct mnt_namespace *mnt_ns; /* containing namespace */
int mnt_id; /* mount identifier */
int mnt_group_id; /* peer group identifier */
/*
* We put mnt_count & mnt_expiry_mark at the end of struct vfsmount
* to let these frequently modified fields in a separate cache line
* (so that reads of mnt_flags wont ping-pong on SMP machines)
*/
atomic_t mnt_count;
int mnt_expiry_mark; /* true if marked for expiry */
int mnt_pinned;
int mnt_ghosts;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
int __percpu *mnt_writers;
#else
int mnt_writers;
#endif
};
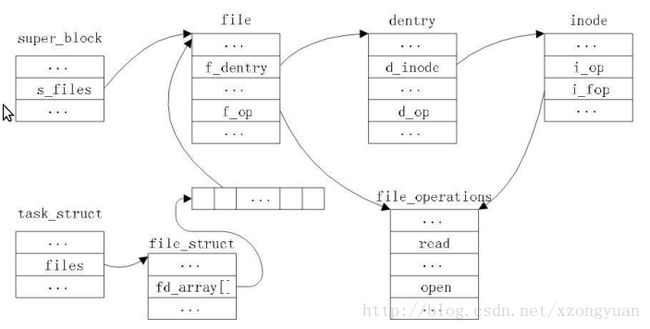
VFS对象之间不是孤立的,其关系如下。
进程描述符task_struct的files字段描述了所有打开的文件,存放在fd_array数组里。通过该数组找到file对象(该file对象实际存放在super_block指定的文件系统中),可以找到dentry项,从而找到inode。这件就建立了文件对象和物理文件之间的关联。
Linux以一组通用的对象看待所有文件系统:super block,inode,dentry和file。