BlockManager初始化和注册解密、BlockManagerMaster工作解密、BlockTransferService解密、本地数据读写解密、远程数据读写解密
1. BlockManager的注册和初始化
2. BlockManager里面的重要函数详细介绍
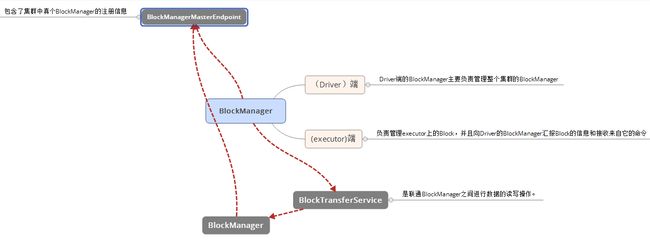
一:BlockManager初始化
1. BlockManager的实例对象调用initializes的时候才能正常工作。
启动initializes方法又两个作用:BlockTransferService(网络通信),ShuffleClient
/**
* Initializes the BlockManager with the given appId. This is not performed in the constructor as
* the appId may not be known at BlockManager instantiation time (in particular for the driver,
* where it is only learned after registration with the TaskScheduler).
*
* This method initializes the BlockTransferService and ShuffleClient, registers with the
* BlockManagerMaster, starts the BlockManagerWorker endpoint, and registers with a local shuffle
* service if configured.
*/在executor启动的时候通过BlockManager.initialize来实例化Executor的BlockManager。
if (!isLocal) {
env.metricsSystem.registerSource(executorSource)
env.blockManager.initialize(conf.getAppId)
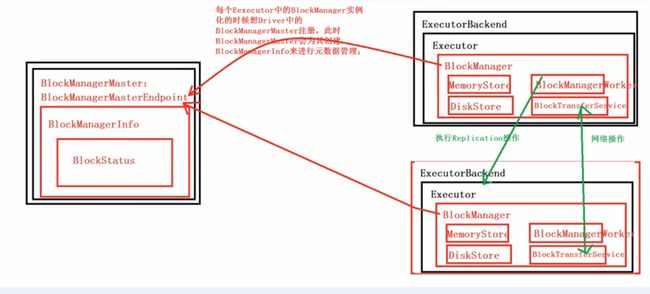
}BlockManager在启动的时候都会向BlockManagerMaster注册。
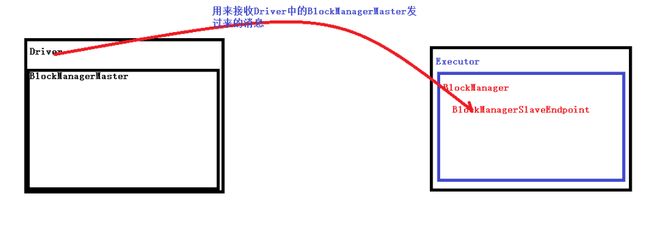
master.registerBlockManager(blockManagerId, maxMemory, slaveEndpoint)并且创建BlockManagerSlaveEndpoint这个消息循环体来接受Driver中的BlockManagerMaster发过来的指令,例如删除Block等;
private val slaveEndpoint = rpcEnv.setupEndpoint(
"BlockManagerEndpoint" + BlockManager.ID_GENERATOR.next,
new BlockManagerSlaveEndpoint(rpcEnv, this, mapOutputTracker))下面就具体看一下BlockManagerSlaveEndpoint,从注释里面可以看到, BlockManagerSlaveEndpoint接收BlockManagerMaster发过来的信息。
/**
* An RpcEndpoint to take commands from the master to execute options. For example,
* this is used to remove blocks from the slave's BlockManager.
*/BlockManager注册
1. 通过RegisterBlockManager注册BlockManager
/** Register the BlockManager's id with the driver. */
def registerBlockManager(
blockManagerId: BlockManagerId, maxMemSize: Long, slaveEndpoint: RpcEndpointRef): Unit = {
logInfo("Trying to register BlockManager")
tell(RegisterBlockManager(blockManagerId, maxMemSize, slaveEndpoint))
logInfo("Registered BlockManager")
}2.Tell就将此方法发送给Driver端。
/** Send a one-way message to the master endpoint, to which we expect it to reply with true. */
private def tell(message: Any) {
if (!driverEndpoint.askWithRetry[Boolean](message)) {
throw new SparkException("BlockManagerMasterEndpoint returned false, expected true.")
}
}3.当BlockManagerSlaveEndpoint实例化后,Executor上的BlockManager需要向Driver上的BlockManagerMasterEndpoint注册。
master.registerBlockManager(blockManagerId, maxMemory, slaveEndpoint)4.BlockManagerMasterEndpoint接收到Executor上的注册信息并进行处理。
BlockManagerMasterEndpoint:
/**
* BlockManagerMasterEndpoint is an [[ThreadSafeRpcEndpoint]] on the master node to track statuses
* of all slaves' block managers.
*/
override def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case RegisterBlockManager(blockManagerId, maxMemSize, slaveEndpoint) =>
register(blockManagerId, maxMemSize, slaveEndpoint)
context.reply(true)下面具体分析register方法:
private def register(id: BlockManagerId, maxMemSize: Long, slaveEndpoint: RpcEndpointRef) {
val time = System.currentTimeMillis()
if (!blockManagerInfo.contains(id)) {
blockManagerIdByExecutor.get(id.executorId) match {5.分析里面的参数blockManagerInfo,blockManagerMaster会为每一个executor创建一个blockManagerInfo,blockManagerInfo是Driver端为了管理ExecutorBackend中的BlockManager上面的所有元数据而设立的。
// Mapping from block manager id to the block manager's information.
private val blockManagerInfo = new mutable.HashMap[BlockManagerId, BlockManagerInfo]根据BlockManagerId来映射BlockManager的信息。
private[spark] class BlockManagerInfo(
val blockManagerId: BlockManagerId,//获得BlockManager的Id
timeMs: Long,
val maxMem: Long,
val slaveEndpoint: RpcEndpointRef) 6.根据获得的BlockManagerId来判断此时的BlockManager是否被注册过,如果注册过了那么就将此BlockManager,remove掉。
private def register(id: BlockManagerId, maxMemSize: Long, slaveEndpoint: RpcEndpointRef) {
val time = System.currentTimeMillis()
if (!blockManagerInfo.contains(id)) {
blockManagerIdByExecutor.get(id.executorId) match {
case Some(oldId) =>
// A block manager of the same executor already exists, so remove it (assumed dead)
logError("Got two different block manager registrations on same executor - "
+ s" will replace old one $oldId with new one $id")
removeExecutor(id.executorId)//此时的executorId是从blockManagerId中获取的。
case None =>
}根据blockManagerIdByExecutor将executor ID从映射block manager ID,从而就获取了executor ID。
// Mapping from executor ID to block manager ID.
private val blockManagerIdByExecutor = new mutable.HashMap[String, BlockManagerId]7.下面我们看一下具体是怎么removeExecutor掉的,以及remove掉了什么?
调用removeExecutor来remove掉Executor。
private def removeExecutor(execId: String) {
logInfo("Trying to remove executor " + execId + " from BlockManagerMaster.")
blockManagerIdByExecutor.get(execId).foreach(removeBlockManager)
}removeBlockManager具体实现blockManager的删除。
private def removeBlockManager(blockManagerId: BlockManagerId) {
val info = blockManagerInfo(blockManagerId)//先得到BlockManagerInfo
// Remove the block manager from blockManagerIdByExecutor.
blockManagerIdByExecutor -= blockManagerId.executorId
//blockManager管理的对象是Block
// Remove it from blockManagerInfo and remove all the blocks.
blockManagerInfo.remove(blockManagerId)
val iterator = info.blocks.keySet.iterator
while (iterator.hasNext) { //重复注册的话,会将所有的Block,删除掉
val blockId = iterator.next
val locations = blockLocations.get(blockId)
locations -= blockManagerId
if (locations.size == 0) {
blockLocations.remove(blockId)
}
}
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerBlockManagerRemoved(System.currentTimeMillis(), blockManagerId))
logInfo(s"Removing block manager $blockManagerId")
}下面来详细的看一下BlockManager里面的重要的方法:

8.Executor上的BlockManager注册完成之后,BlockManager会不断的向Driver汇报executor上的Block的状态。
private def reportAllBlocks(): Unit = {
logInfo(s"Reporting ${blockInfo.size} blocks to the master.")
for ((blockId, info) <- blockInfo) {
val status = getCurrentBlockStatus(blockId, info)
if (!tryToReportBlockStatus(blockId, info, status)) {
logError(s"Failed to report $blockId to master; giving up.")
return
}
}
}9.获得Block的位置,就要发消息给DriverEndpoint,向Driver端索取Block的位置信息。
/**
* Get locations of an array of blocks.
*/
private def getLocationBlockIds(blockIds: Array[BlockId]): Array[Seq[BlockManagerId]] = {
val startTimeMs = System.currentTimeMillis
val locations = master.getLocations(blockIds).toArray
logDebug("Got multiple block location in %s".format(Utils.getUsedTimeMs(startTimeMs)))
locations
}具体实现是在BlockManagerMaster,因为BlockManagerMaster拥有所有BlockManager的信息。
/** Get locations of multiple blockIds from the driver */
def getLocations(blockIds: Array[BlockId]): IndexedSeq[Seq[BlockManagerId]] = {
driverEndpoint.askWithRetry[IndexedSeq[Seq[BlockManagerId]]](
GetLocations MultipleBlockIds(blockIds))
}10.通过getLocationsMultipleBlockIds来从BlockManagerMasterEndpoint中获得BlockId的位置。
private def getLocationsMultipleBlockIds(
blockIds: Array[BlockId]): IndexedSeq[Seq[BlockManagerId]] = {
blockIds.map(blockId => getLocations(blockId))
}getLocations首先会判断内存缓冲区中是否有BlockId如果有则直接返回。
private def getLocations(blockId: BlockId): Seq[BlockManagerId] = {
if (blockLocations.containsKey(blockId)) blockLocations.get(blockId).toSeq else Seq.empty
}blockLocations中的V为啥是一个HashSet?
// Mapping from block id to the set of block managers that have the block.
private val blockLocations = new JHashMap[BlockId, mutable.HashSet[BlockManagerId]]因为一个Block一般会有副本,并且副本存储在不同机器上,不同机器上的BlockManager一定是不一样的,则BlockId肯定是不一样的,因此要返回HashSet.
11.通过getLocal从本地来获得Block信息。
/**
* Get block from local block manager.
*/
def getLocal(blockId: BlockId): Option[BlockResult] = {
logDebug(s"Getting local block $blockId")
doGetLocal(blockId, asBlockResult = true).asInstanceOf[Option[BlockResult]]
}具体看一下doGetLocal实现。
private def doGetLocal(blockId: BlockId, asBlockResult: Boolean): Option[Any] = {
val info = blockInfo.get(blockId).orNull
if (info != null) {
info.synchronized {为啥里面用了synchronized?不同的线程去操作一块数据,JVM是多线程操作的数据,所以用了一个同步代码块来防止资源竞争。
如果有其他线程正在操作,所以该线程就要等待,为了保证数据的一致性。
// If another thread is writing the block, wait for it to become ready.
if (!info.waitForReady()) { //所以要等待
// If we get here, the block write failed.
logWarning(s"Block $blockId was marked as failure.")
return None
}在内存中寻找Block。
// Look for the block in memory
if (level.useMemory) { //useMemory是Block的存储级别中的内存
logDebug(s"Getting block $blockId from memory")
val result = if (asBlockResult) {//如果有则返回结果
memoryStore.getValues(blockId).map(new BlockResult(_, DataReadMethod.Memory, info.size))
} else {
memoryStore.getBytes(blockId)
}
result match {
case Some(values) =>
return result
case None =>
logDebug(s"Block $blockId not found in memory")
}
}如果存储的数据在磁盘中,则会将磁盘中的数据存储到内存中。
// Look for block on disk, potentially storing it back in memory if required
if (level.useDisk) {
logDebug(s"Getting block $blockId from disk")
val bytes: ByteBuffer = diskStore.getBytes(blockId) match {
case Some(b) => b
case None =>
throw new BlockException(
blockId, s"Block $blockId not found on disk, though it should be")
}
assert(0 == bytes.position())
if (!level.useMemory) {
// If the block shouldn't be stored in memory, we can just return it
if (asBlockResult) {
return Some(new BlockResult(dataDeserialize(blockId, bytes), DataReadMethod.Disk,
info.size))
} else {
return Some(bytes)
}
} else {
// Otherwise, we also have to store something in the memory store
if (!level.deserialized || !asBlockResult) {
/* We'll store the bytes in memory if the block's storage level includes
* "memory serialized", or if it should be cached as objects in memory
* but we only requested its serialized bytes. */
//将数据存储到内存中
memoryStore.putBytes(blockId, bytes.limit, () => {12.getRemote从远程获取数据。
/**
* Get block from remote block managers.
*/
def getRemote(blockId: BlockId): Option[BlockResult] = {
logDebug(s"Getting remote block $blockId")
doGetRemote(blockId, asBlockResult = true).asInstanceOf[Option[BlockResult]]
}BlockId对于的Block一般是有多个副本,只需要读取一个副本上的数据即可。
private def doGetRemote(blockId: BlockId, asBlockResult: Boolean): Option[Any] = {
require(blockId != null, "BlockId is null")
//通过BlockId,master就可以获取BlockdId所对应的不同节点上的block副本,然后再对结果进行Shuffle一下。此时的Shuffle只是为了负载均衡。
val locations = Random.shuffle(master.getLocations(blockId))通过BlockTransforService来获取不同节点上的副本。
var numFetchFailures = 0
for (loc <- locations) {
logDebug(s"Getting remote block $blockId from $loc")
val data = try {
blockTransferService.fetchBlockSync(
loc.host, loc.port, loc.executorId, blockId.toString).nioByteBuffer()
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) =>
numFetchFailures += 1
if (numFetchFailures == locations.size) {//获取副本的时候可能会失败。
//所以下面会有失败次数的限制
// An exception is thrown while fetching this block from all locations
throw new BlockFetchException(s"Failed to fetch block from" +
s" ${locations.size} locations. Most recent failure cause:",BlockTransforService获取副本是通过具体实现的。
val data = try {
blockTransferService.fetchBlockSync(
loc.host, loc.port, loc.executorId, blockId.toString).nioByteBuffer()13.Drop的block有可能放到disk上,此可能只有一种就是Memory and Disk的时候,而此时的Memory不够的时候,才会将block放到Disk中。
其次,如果你的数据并没有指定Memory and Disk的时候,数据就直接丢弃了,这时候如果你曾经进行了cache,那再次获取的时候就需要重新计算。
Drop:是指当我们的内存不够的时候,尝试释放一部分内存,给要使用内存的应用或者操作。
这个时候就会有权衡,如果直接丢弃的话,下回再次用的时候就要重新计算,如果cache的话,下次用直接调用。
/**
* Drop a block from memory, possibly putting it on disk if applicable. Called when the memory
* store reaches its limit and needs to free up space.
*
* If `data` is not put on disk, it won't be created.
*
* Return the block status if the given block has been updated, else None.
*/总结: 通过源码的方式对BlockManager进行了详细的分析,但是对象持久化和消息通信方面接下来几篇将会详细剖析。