PCL_第13章_重建
一、resamping重采样
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/longyp/articles/7435547.html
https://blog.csdn.net/DLW__/article/details/102001232
测量较小的对象时产生一些误差,直接重建会使曲面不光滑或者有漏洞,为了建立完整的模型需要对表面进行平滑处理和漏洞修复.可通过数据重建来解决这一问题,重采样算法通过对周围数据点进行高阶多项式插值来重建表面缺少的部分.
由多个扫描配准后得到的数据直接拿来重建可能产生 "双墙"等重影,即拼接的区域出现重叠的两个曲面,重采样算法可以对此问题进行处理.
#include
#include
#include
#include //最小二乘平滑处理类定义
int
main (int argc, char** argv)
{
// Load input file into a PointCloud with an appropriate type
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud ());
// Load bun0.pcd -- should be available with the PCL archive in test
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("davi.pcd", *cloud);
// Create a KD-Tree
pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree);
// Output has the PointNormal type in order to store the normals calculated by MLS
pcl::PointCloud mls_points;
// Init object (second point type is for the normals, even if unused)
pcl::MovingLeastSquares mls;
// 设置在最小二乘计算中需要进行法线估计,不需要可跳过
mls.setComputeNormals (true);
// Set parameters
mls.setInputCloud (cloud);
mls.setPolynomialFit (true); //多项式拟合提高精度,可false 加快速度,或选择其他来控制平滑过程
mls.setSearchMethod (tree);
mls.setSearchRadius (3);
// Reconstruct
mls.process (mls_points);
// Save output
pcl::io::savePCDFile ("davi-mls.pcd", mls_points);
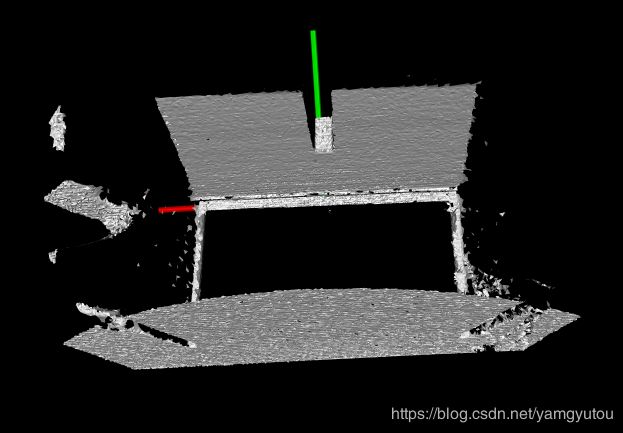
} 二、concave_hull_2d
本教程是为假设您正在寻找凹面而编写的。如果您想要平面模型的凸壳,只需在本教程的每一点用凸壳替换凹壳,包括源文件、文件名和CMakeLists.txt文件。您还需要注释掉setAlpha(),因为这不适用于凸包。
pcl::ConcaveHull
三、greedy projection 贪婪映射
pcl::GreedyProjectionTriangulation
程序支持两种文件格式:*.pcd和*.ply。
程序先读取点云文件;然后计算法向量,并将法向量和点云坐标放在一起;接着使用贪婪三角投影算法进行重构,最后显示结果。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int
main (int argc, char** argv)
{
// Load input file into a PointCloud with an appropriate type
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("table_scene_lms400_downsampled.pcd", *cloud);
//sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 cloud_blob;
//pcl::io::loadPCDFile ("table_scene_lms400_downsampled.pcd", cloud_blob);
//pcl::fromROSMsg (cloud_blob, *cloud);
//* the data should be available in cloud
// Normal estimation*
pcl::NormalEstimation n;
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr normals (new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree);
tree->setInputCloud (cloud);
n.setInputCloud (cloud);
n.setSearchMethod (tree);
n.setKSearch (20);
n.compute (*normals);
//* normals should not contain the point normals + surface curvatures
// Concatenate the XYZ and normal fields*
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_with_normals (new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::concatenateFields (*cloud, *normals, *cloud_with_normals);
//* cloud_with_normals = cloud + normals
// Create search tree*
pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr tree2 (new pcl::search::KdTree);
tree2->setInputCloud (cloud_with_normals);
// Initialize objects
pcl::GreedyProjectionTriangulation gp3;
pcl::PolygonMesh triangles;
// Set the maximum distance between connected points (maximum edge length)
gp3.setSearchRadius (0.025);
// Set typical values for the parameters
gp3.setMu (2.5);
gp3.setMaximumNearestNeighbors (100);
gp3.setMaximumSurfaceAngle(M_PI/4); // 45 degrees
gp3.setMinimumAngle(M_PI/18); // 10 degrees
gp3.setMaximumAngle(2*M_PI/3); // 120 degrees
gp3.setNormalConsistency(false);
// Get result
gp3.setInputCloud (cloud_with_normals);
gp3.setSearchMethod (tree2);
gp3.reconstruct (triangles);
// std::cout << triangles;
// Additional vertex information
std::vector parts = gp3.getPartIDs();
std::vector states = gp3.getPointStates();
boost::shared_ptr viewer (new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer ("3D Viewer"));
viewer->setBackgroundColor (0, 0, 0);
viewer->addPolygonMesh(triangles,"my");
viewer->addCoordinateSystem (1.0);
viewer->initCameraParameters ();
// 主循环
while (!viewer->wasStopped ())
{
viewer->spinOnce (100);
boost::this_thread::sleep (boost::posix_time::microseconds (100000));
}
// Finish
return (0);
}
四、Fitting trimmed B-splines unordered point clouds 无序点云B样条(B-spines)拟合
b样条曲线经常用于曲线的平滑处理
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?src=11×tamp=1589685829&ver=2343&signature=doeCJXnYVQzAYG1kNp7M2dqEgKlGLNIYx942W4tRE1yVwWD1M46JS9xyDiXOL*AZ-2hXEBZELPh*lIF*m7W486mK03u3S62w9s3-uZYdnxljZKoKNNqGy6-18XkMwuXM&new=1 贝塞尔曲线动图
这个教程讲解了如何在点云上利用b样条拟合算法获得一个平滑的参数化的表示。算法包括以下步骤:
(1)用pca初始化b样条表面,这里假设点云有两个主方向,例如它大致是一个平面。
(2)B样条曲面的细化和拟合。
(3)B样条曲线的循环初始化。这里我们假设点云是紧密的,即没有分离的簇。
(4)b样条曲线的拟合。
(5)修剪后的B样条曲面的三角剖分。
https://blog.csdn.net/shenziheng1/article/details/54411098 b样条 相关知识
非均匀有理B样条曲线,缩写NURBS。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace pcl::console;
typedef pcl::PointXYZ Point;
void
PointCloud2Vector3d (pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud, pcl::on_nurbs::vector_vec3d &data);
void
visualizeCurve (ON_NurbsCurve &curve,
ON_NurbsSurface &surface,
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer &viewer);
int
main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
std::string pcd_file, file_3dm;
if (argc < 2)
{
printf ("\nUsage: pcl_example_nurbs_fitting_surface pcd-in-file -o 3 -rn 4 -in 10 -mr 128 -td 1\n\n");
exit (0);
}
pcd_file = argv[1];
//file_3dm = argv[2];
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer ("点云库PCL学习教程第二版-B样条曲面拟合点云数据");
viewer.setBackgroundColor(255,255,255);
viewer.setSize (800, 600);
// ############################################################################
// load point cloud
printf (" loading %s\n", pcd_file.c_str ());
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PCLPointCloud2 cloud2;
pcl::on_nurbs::NurbsDataSurface data;
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile (pcd_file, cloud2) == -1)
throw std::runtime_error (" PCD file not found.");
fromPCLPointCloud2 (cloud2, *cloud);
PointCloud2Vector3d (cloud, data.interior);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom handler (cloud, 0, 255, 0);
viewer.addPointCloud (cloud, handler, "cloud_cylinder");
printf (" %lu points in data set\n", cloud->size ());
// ############################################################################
// fit B-spline surface
// parameters
unsigned order (3);
unsigned refinement (4);
unsigned iterations (10);
unsigned mesh_resolution (128);
bool two_dim=true;
parse_argument (argc, argv, "-o", order);
parse_argument (argc, argv, "-rn", refinement);
parse_argument (argc, argv, "-in", iterations);
parse_argument (argc, argv, "-mr", mesh_resolution);
parse_argument (argc, argv, "-td", two_dim);
pcl::on_nurbs::FittingSurface::Parameter params;
params.interior_smoothness = 0.2;
params.interior_weight = 1.0;
params.boundary_smoothness = 0.2;
params.boundary_weight = 0.0;
// initialize
printf (" surface fitting ...\n");
ON_NurbsSurface nurbs = pcl::on_nurbs::FittingSurface::initNurbsPCABoundingBox (order, &data);
pcl::on_nurbs::FittingSurface fit (&data, nurbs);
// fit.setQuiet (false); // enable/disable debug output
// mesh for visualization
pcl::PolygonMesh mesh;
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr mesh_cloud (new pcl::PointCloud);
std::vector mesh_vertices;
std::string mesh_id = "mesh_nurbs";
pcl::on_nurbs::Triangulation::convertSurface2PolygonMesh (fit.m_nurbs, mesh, mesh_resolution);
viewer.addPolygonMesh (mesh, mesh_id);
std::cout<<"Before refine"< (mesh_cloud, mesh_vertices, mesh_id);
viewer.spinOnce (3000);
std::cout<<"refine: "< (mesh_cloud, mesh_vertices, mesh_id);
viewer.spinOnce (3000);
std::cout<<"iterations: "<::Ptr cloud, pcl::on_nurbs::vector_vec3d &data)
{
for (unsigned i = 0; i < cloud->size (); i++)
{
Point &p = cloud->at (i);
if (!pcl_isnan (p.x) && !pcl_isnan (p.y) && !pcl_isnan (p.z))
data.push_back (Eigen::Vector3d (p.x, p.y, p.z));
}
}
void
visualizeCurve (ON_NurbsCurve &curve, ON_NurbsSurface &surface, pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer &viewer)
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr curve_cloud (new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::on_nurbs::Triangulation::convertCurve2PointCloud (curve, surface, curve_cloud, 4);
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < curve_cloud->size () - 1; i++)
{
pcl::PointXYZRGB &p1 = curve_cloud->at (i);
pcl::PointXYZRGB &p2 = curve_cloud->at (i + 1);
std::ostringstream os;
os << "line" << i;
viewer.removeShape (os.str ());
viewer.addLine (p1, p2, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, os.str ());
}
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr curve_cps (new pcl::PointCloud);
for (int i = 0; i < curve.CVCount (); i++)
{
ON_3dPoint p1;
curve.GetCV (i, p1);
double pnt[3];
surface.Evaluate (p1.x, p1.y, 0, 3, pnt);
pcl::PointXYZRGB p2;
p2.x = float (pnt[0]);
p2.y = float (pnt[1]);
p2.z = float (pnt[2]);
p2.r = 255;
p2.g = 0;
p2.b = 0;
curve_cps->push_back (p2);
}
viewer.removePointCloud ("cloud_cps");
viewer.addPointCloud (curve_cps, "cloud_cps");
} error:“Expression:vector subscript out of range”
解决:https://blog.csdn.net/zfjBIT/article/details/95348002
https://blog.csdn.net/zhang010206/article/details/39642827
将curve_param.accuracy改成一
实验结果:https://blog.csdn.net/zfjBIT/article/details/95354801
五、2Dfitting 2D拟合