第十四周项目一~~验证各算法
/*问题及代码
*Copyright(c)2015,烟台大学计算机学院
*All right reserved.
*文件名称:验证算法.cpp
*作者:李浩
*时间:11月30日
*版本号;v1.0
*问题描述:
认真阅读并验证折半查找算法。
认真阅读并验证分块查找算法。
认真阅读并验证二叉排序树相关算法。
认真阅读并验证平衡二叉树相关算法。
*输入描述:无
*程序输出:根据要求输出
*/#include
#define MAXL 100
typedef int KeyType;
typedef char InfoType[10];
typedef struct
{
KeyType key; //KeyType为关键字的数据类型
InfoType data; //其他数据
} NodeType;
typedef NodeType SeqList[MAXL]; //顺序表类型
int BinSearch(SeqList R,int n,KeyType k)
{
int low=0,high=n-1,mid;
while (low<=high)
{
mid=(low+high)/2;
if (R[mid].key==k) //查找成功返回
return mid+1;
if (R[mid].key>k) //继续在R[low..mid-1]中查找
high=mid-1;
else
low=mid+1; //继续在R[mid+1..high]中查找
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int i,n=10;
int result;
SeqList R;
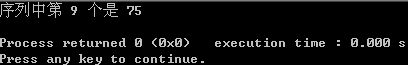
KeyType a[]= {1,3,9,12,32,41,45,62,75,77},x=75;
for (i=0; i0)
printf("序列中第 %d 个是 %d\n",result, x);
else
printf("木有找到!\n");
return 0;
}
递归折半#include
#define MAXL 100
typedef int KeyType;
typedef char InfoType[10];
typedef struct
{
KeyType key; //KeyType为关键字的数据类型
InfoType data; //其他数据
} NodeType;
typedef NodeType SeqList[MAXL]; //顺序表类型
int BinSearch1(SeqList R,int low,int high,KeyType k)
{
int mid;
if (low<=high) //查找区间存在一个及以上元素
{
mid=(low+high)/2; //求中间位置
if (R[mid].key==k) //查找成功返回其逻辑序号mid+1
return mid+1;
if (R[mid].key>k) //在R[low..mid-1]中递归查找
BinSearch1(R,low,mid-1,k);
else //在R[mid+1..high]中递归查找
BinSearch1(R,mid+1,high,k);
}
else
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int i,n=10;
int result;
SeqList R;
KeyType a[]= {1,3,9,12,32,41,45,62,75,77},x=75;
for (i=0; i0)
printf("序列中第 %d 个是 %d\n",result, x);
else
printf("木有找到!\n");
return 0;
}
运行结果
#include
#define MAXL 100 //数据表的最大长度
#define MAXI 20 //索引表的最大长度
typedef int KeyType;
typedef char InfoType[10];
typedef struct
{
KeyType key; //KeyType为关键字的数据类型
InfoType data; //其他数据
} NodeType;
typedef NodeType SeqList[MAXL]; //顺序表类型
typedef struct
{
KeyType key; //KeyType为关键字的类型
int link; //指向对应块的起始下标
} IdxType;
typedef IdxType IDX[MAXI]; //索引表类型
int IdxSearch(IDX I,int m,SeqList R,int n,KeyType k)
{
int low=0,high=m-1,mid,i;
int b=n/m; //b为每块的记录个数
while (low<=high) //在索引表中进行二分查找,找到的位置存放在low中
{
mid=(low+high)/2;
if (I[mid].key>=k)
high=mid-1;
else
low=mid+1;
}
//应在索引表的high+1块中,再在线性表中进行顺序查找
i=I[high+1].link;
while (i<=I[high+1].link+b-1 && R[i].key!=k) i++;
if (i<=I[high+1].link+b-1)
return i+1;
else
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int i,n=25,m=5,j;
SeqList R;
IDX I= {{14,0},{34,5},{66,10},{85,15},{100,20}};
KeyType a[]= {8,14,6,9,10,22,34,18,19,31,40,38,54,66,46,71,78,68,80,85,100,94,88,96,87};
KeyType x=85;
for (i=0; i 运行结果
#include
#include
typedef int KeyType;
typedef char InfoType[10];
typedef struct node //记录类型
{
KeyType key; //关键字项
InfoType data; //其他数据域
struct node *lchild,*rchild; //左右孩子指针
} BSTNode;
//在p所指向的二叉排序树中,插入值为k的节点
int InsertBST(BSTNode *&p,KeyType k)
{
if (p==NULL) //原树为空, 新插入的记录为根结点
{
p=(BSTNode *)malloc(sizeof(BSTNode));
p->key=k;
p->lchild=p->rchild=NULL;
return 1;
}
else if (k==p->key) //树中存在相同关键字的结点,返回0
return 0;
else if (kkey)
return InsertBST(p->lchild,k); //插入到*p的左子树中
else
return InsertBST(p->rchild,k); //插入到*p的右子树中
}
//由有n个元素的数组A,创建一个二叉排序树
BSTNode *CreateBST(KeyType A[],int n) //返回BST树根结点指针
{
BSTNode *bt=NULL; //初始时bt为空树
int i=0;
while (ikey);
if (bt->lchild!=NULL || bt->rchild!=NULL)
{
printf("("); //有孩子结点时才输出(
DispBST(bt->lchild); //递归处理左子树
if (bt->rchild!=NULL) printf(","); //有右孩子结点时才输出,
DispBST(bt->rchild); //递归处理右子树
printf(")"); //有孩子结点时才输出)
}
}
}
//在bt指向的节点为根的排序二叉树中,查找值为k的节点。找不到返回NULL
BSTNode *SearchBST(BSTNode *bt,KeyType k)
{
if (bt==NULL || bt->key==k) //递归终结条件
return bt;
if (kkey)
return SearchBST(bt->lchild,k); //在左子树中递归查找
else
return SearchBST(bt->rchild,k); //在右子树中递归查找
}
//二叉排序树中查找的非递归算法
BSTNode *SearchBST1(BSTNode *bt,KeyType k)
{
while (bt!=NULL)
{
if (k==bt->key)
return bt;
else if (kkey)
bt=bt->lchild;
else
bt=bt->rchild;
}
return NULL;
}
void Delete1(BSTNode *p,BSTNode *&r) //当被删*p结点有左右子树时的删除过程
{
BSTNode *q;
if (r->rchild!=NULL)
Delete1(p,r->rchild); //递归找最右下结点
else //找到了最右下结点*r
{
p->key=r->key; //将*r的关键字值赋给*p
q=r;
r=r->lchild; //直接将其左子树的根结点放在被删结点的位置上
free(q); //释放原*r的空间
}
}
void Delete(BSTNode *&p) //从二叉排序树中删除*p结点
{
BSTNode *q;
if (p->rchild==NULL) //*p结点没有右子树的情况
{
q=p;
p=p->lchild; //直接将其右子树的根结点放在被删结点的位置上
free(q);
}
else if (p->lchild==NULL) //*p结点没有左子树的情况
{
q=p;
p=p->rchild; //将*p结点的右子树作为双亲结点的相应子树
free(q);
}
else Delete1(p,p->lchild); //*p结点既没有左子树又没有右子树的情况
}
int DeleteBST(BSTNode *&bt, KeyType k) //在bt中删除关键字为k的结点
{
if (bt==NULL)
return 0; //空树删除失败
else
{
if (kkey)
return DeleteBST(bt->lchild,k); //递归在左子树中删除为k的结点
else if (k>bt->key)
return DeleteBST(bt->rchild,k); //递归在右子树中删除为k的结点
else
{
Delete(bt); //调用Delete(bt)函数删除*bt结点
return 1;
}
}
}
int main()
{
BSTNode *bt;
int n=12,x=46;
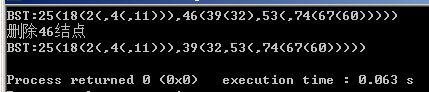
KeyType a[]= {25,18,46,2,53,39,32,4,74,67,60,11};
bt=CreateBST(a,n);
printf("BST:");
DispBST(bt);
printf("\n");
printf("删除%d结点\n",x);
if (SearchBST(bt,x)!=NULL)
{
DeleteBST(bt,x);
printf("BST:");
DispBST(bt);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
#include
#include
typedef int KeyType; //定义关键字类型
typedef char InfoType;
typedef struct node //记录类型
{
KeyType key; //关键字项
int bf; //平衡因子
InfoType data; //其他数据域
struct node *lchild,*rchild; //左右孩子指针
} BSTNode;
void LeftProcess(BSTNode *&p,int &taller)
//对以指针p所指结点为根的二叉树作左平衡旋转处理,本算法结束时,指针p指向新的根结点
{
BSTNode *p1,*p2;
if (p->bf==0) //原本左、右子树等高,现因左子树增高而使树增高
{
p->bf=1;
taller=1;
}
else if (p->bf==-1) //原本右子树比左子树高,现左、右子树等高
{
p->bf=0;
taller=0;
}
else //原本左子树比右子树高,需作左子树的平衡处理
{
p1=p->lchild; //p指向*p的左子树根结点
if (p1->bf==1) //新结点插入在*b的左孩子的左子树上,要作LL调整
{
p->lchild=p1->rchild;
p1->rchild=p;
p->bf=p1->bf=0;
p=p1;
}
else if (p1->bf==-1) //新结点插入在*b的左孩子的右子树上,要作LR调整
{
p2=p1->rchild;
p1->rchild=p2->lchild;
p2->lchild=p1;
p->lchild=p2->rchild;
p2->rchild=p;
if (p2->bf==0) //新结点插在*p2处作为叶子结点的情况
p->bf=p1->bf=0;
else if (p2->bf==1) //新结点插在*p2的左子树上的情况
{
p1->bf=0;
p->bf=-1;
}
else //新结点插在*p2的右子树上的情况
{
p1->bf=1;
p->bf=0;
}
p=p2;
p->bf=0; //仍将p指向新的根结点,并置其bf值为0
}
taller=0;
}
}
void RightProcess(BSTNode *&p,int &taller)
//对以指针p所指结点为根的二叉树作右平衡旋转处理,本算法结束时,指针p指向新的根结点
{
BSTNode *p1,*p2;
if (p->bf==0) //原本左、右子树等高,现因右子树增高而使树增高
{
p->bf=-1;
taller=1;
}
else if (p->bf==1) //原本左子树比右子树高,现左、右子树等高
{
p->bf=0;
taller=0;
}
else //原本右子树比左子树高,需作右子树的平衡处理
{
p1=p->rchild; //p指向*p的右子树根结点
if (p1->bf==-1) //新结点插入在*b的右孩子的右子树上,要作RR调整
{
p->rchild=p1->lchild;
p1->lchild=p;
p->bf=p1->bf=0;
p=p1;
}
else if (p1->bf==1) //新结点插入在*p的右孩子的左子树上,要作RL调整
{
p2=p1->lchild;
p1->lchild=p2->rchild;
p2->rchild=p1;
p->rchild=p2->lchild;
p2->lchild=p;
if (p2->bf==0) //新结点插在*p2处作为叶子结点的情况
p->bf=p1->bf=0;
else if (p2->bf==-1) //新结点插在*p2的右子树上的情况
{
p1->bf=0;
p->bf=1;
}
else //新结点插在*p2的左子树上的情况
{
p1->bf=-1;
p->bf=0;
}
p=p2;
p->bf=0; //仍将p指向新的根结点,并置其bf值为0
}
taller=0;
}
}
int InsertAVL(BSTNode *&b,KeyType e,int &taller)
/*若在平衡的二叉排序树b中不存在和e有相同关键字的结点,则插入一个
数据元素为e的新结点,并返回1,否则返回0。若因插入而使二叉排序树
失去平衡,则作平衡旋转处理,布尔变量taller反映b长高与否*/
{
if(b==NULL) //原为空树,插入新结点,树“长高”,置taller为1
{
b=(BSTNode *)malloc(sizeof(BSTNode));
b->key=e;
b->lchild=b->rchild=NULL;
b->bf=0;
taller=1;
}
else
{
if (e==b->key) //树中已存在和e有相同关键字的结点则不再插入
{
taller=0;
return 0;
}
if (ekey) //应继续在*b的左子树中进行搜索
{
if ((InsertAVL(b->lchild,e,taller))==0) //未插入
return 0;
if (taller==1) //已插入到*b的左子树中且左子树“长高”
LeftProcess(b,taller);
}
else //应继续在*b的右子树中进行搜索
{
if ((InsertAVL(b->rchild,e,taller))==0) //未插入
return 0;
if (taller==1) //已插入到b的右子树且右子树“长高”
RightProcess(b,taller);
}
}
return 1;
}
void DispBSTree(BSTNode *b) //以括号表示法输出AVL
{
if (b!=NULL)
{
printf("%d",b->key);
if (b->lchild!=NULL || b->rchild!=NULL)
{
printf("(");
DispBSTree(b->lchild);
if (b->rchild!=NULL) printf(",");
DispBSTree(b->rchild);
printf(")");
}
}
}
void LeftProcess1(BSTNode *&p,int &taller) //在删除结点时进行左处理
{
BSTNode *p1,*p2;
if (p->bf==1)
{
p->bf=0;
taller=1;
}
else if (p->bf==0)
{
p->bf=-1;
taller=0;
}
else //p->bf=-1
{
p1=p->rchild;
if (p1->bf==0) //需作RR调整
{
p->rchild=p1->lchild;
p1->lchild=p;
p1->bf=1;
p->bf=-1;
p=p1;
taller=0;
}
else if (p1->bf==-1) //需作RR调整
{
p->rchild=p1->lchild;
p1->lchild=p;
p->bf=p1->bf=0;
p=p1;
taller=1;
}
else //需作RL调整
{
p2=p1->lchild;
p1->lchild=p2->rchild;
p2->rchild=p1;
p->rchild=p2->lchild;
p2->lchild=p;
if (p2->bf==0)
{
p->bf=0;
p1->bf=0;
}
else if (p2->bf==-1)
{
p->bf=1;
p1->bf=0;
}
else
{
p->bf=0;
p1->bf=-1;
}
p2->bf=0;
p=p2;
taller=1;
}
}
}
void RightProcess1(BSTNode *&p,int &taller) //在删除结点时进行右处理
{
BSTNode *p1,*p2;
if (p->bf==-1)
{
p->bf=0;
taller=-1;
}
else if (p->bf==0)
{
p->bf=1;
taller=0;
}
else //p->bf=1
{
p1=p->lchild;
if (p1->bf==0) //需作LL调整
{
p->lchild=p1->rchild;
p1->rchild=p;
p1->bf=-1;
p->bf=1;
p=p1;
taller=0;
}
else if (p1->bf==1) //需作LL调整
{
p->lchild=p1->rchild;
p1->rchild=p;
p->bf=p1->bf=0;
p=p1;
taller=1;
}
else //需作LR调整
{
p2=p1->rchild;
p1->rchild=p2->lchild;
p2->lchild=p1;
p->lchild=p2->rchild;
p2->rchild=p;
if (p2->bf==0)
{
p->bf=0;
p1->bf=0;
}
else if (p2->bf==1)
{
p->bf=-1;
p1->bf=0;
}
else
{
p->bf=0;
p1->bf=1;
}
p2->bf=0;
p=p2;
taller=1;
}
}
}
void Delete2(BSTNode *q,BSTNode *&r,int &taller)
//由DeleteAVL()调用,用于处理被删结点左右子树均不空的情况
{
if (r->rchild==NULL)
{
q->key=r->key;
q=r;
r=r->lchild;
free(q);
taller=1;
}
else
{
Delete2(q,r->rchild,taller);
if (taller==1)
RightProcess1(r,taller);
}
}
int DeleteAVL(BSTNode *&p,KeyType x,int &taller) //在AVL树p中删除关键字为x的结点
{
int k;
BSTNode *q;
if (p==NULL)
return 0;
else if (xkey)
{
k=DeleteAVL(p->lchild,x,taller);
if (taller==1)
LeftProcess1(p,taller);
return k;
}
else if (x>p->key)
{
k=DeleteAVL(p->rchild,x,taller);
if (taller==1)
RightProcess1(p,taller);
return k;
}
else //找到了关键字为x的结点,由p指向它
{
q=p;
if (p->rchild==NULL) //被删结点右子树为空
{
p=p->lchild;
free(q);
taller=1;
}
else if (p->lchild==NULL) //被删结点左子树为空
{
p=p->rchild;
free(q);
taller=1;
}
else //被删结点左右子树均不空
{
Delete2(q,q->lchild,taller);
if (taller==1)
LeftProcess1(q,taller);
p=q;
}
return 1;
}
}
int main()
{
BSTNode *b=NULL;
int i,j,k;
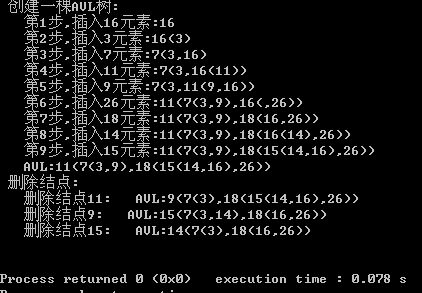
KeyType a[]= {16,3,7,11,9,26,18,14,15},n=9; //例10.5
printf(" 创建一棵AVL树:\n");
for(i=0; i 所有的查找方法都是以判断是否能查找所制定数字为目的,采用的一系列降低复杂度的方法。对于折半,递归折半,分块等方法其实并不难,关键是真正能理解其降低复杂度的方法,很少的数据不能体现其简单性,数据多了就能体现了。
而对于二叉树和平衡二叉树则是更加方便的利用折半的方式将所有的数字变成二叉树的形式,平衡二叉树关键是理解哪里不平衡就改哪里,是一个解决问题的过程,画画图寻思寻思就好了
学习心得
还是说遇到硬骨头不能软掉,硬着头皮去做就办了,关键是看视频看书,坚持不懈得去看我觉得没有过不去的坎儿。