数据结构_之顺序队列_链式队列及队列的广泛应用
1.queue基本概念
队列是一种特殊的受限制的线性表。
队列(queue)是只允许在一端进行插入操作,而在另一端进行删除操作的线性表。
操作系统和客服系统中,都是应用了一种数据结构来实现先进先出的排队功能,这就是队列。
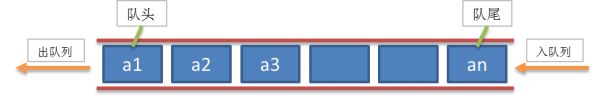
队列是一种先进先出的(First In First Out)的线性表,简称FIFO。允许插入的一端为队尾,允许删除的一端为队头。队列不允许在中间部位进行操作!假设队列是q=(a1,a2,……,an),那么a1就是队头元素,而an是队尾元素。这样我们就可以删除时,总是从a1开始,而插入时,总是在队列最后。这也比较符合我们通常生活中的习惯,排在第一个的优先出列,最后来的当然排在队伍最后。如下图:
队列在程序设计中用得非常频繁。前面我举了两个栗子,在比如用键盘进行各种字母或数字的输入并显示到显示器上,其实就是队列的典型。
2.queue常用操作
l 创建队列
l 销毁队列
l 清空队列
l 进队列
l 出队列
l 获取队头元素
l 获取队列的长度
队列的抽象数据类型:
ADT 队列(Queue) Data 通线性表。元素具有相同的类型,相邻元素具有前驱后继关系。 Operation // 初始化操作,建立一个空队列Q InitQueue(*Q); // 若队列Q存储,则销毁它。 DestroyQueue(*Q); // 将队列Q清空 ClearQueue(*Q); // 若队列为空则返回true,否则返回false QueueEmpty(Q); // 若队列Q存在且非空,用e返回队列Q的队头元素 GetHead(Q, *e); // 若队列Q存在,插入新元素e到队列Q中并成为队尾元素。 EnQueue(*Q, e); // 删除队列Q中的队头元素,并用e返回其值 DeQueue(*Q, *e); // 返回队列Q的元素个数 QueueLength(Q); endADT
接口:
1 #ifndef _MY_QUEUE_H_ 2 #define _MY_QUEUE_H_ 3 4 typedef void Queue; 5 6 Queue* Queue_Create(); 7 8 void Queue_Destroy(Queue* queue); 9 10 void Queue_Clear(Queue* queue); 11 12 int Queue_Append(Queue* queue, void* item); 13 14 void* Queue_Retrieve(Queue* queue); 15 16 void* Queue_Header(Queue* queue); 17 18 int Queue_Length(Queue* queue); 19 20 #endif //_MY_QUEUE_H_
3.队列模型和链表模型关系分析
4.队列的顺序存储设计与实现
1基本概念
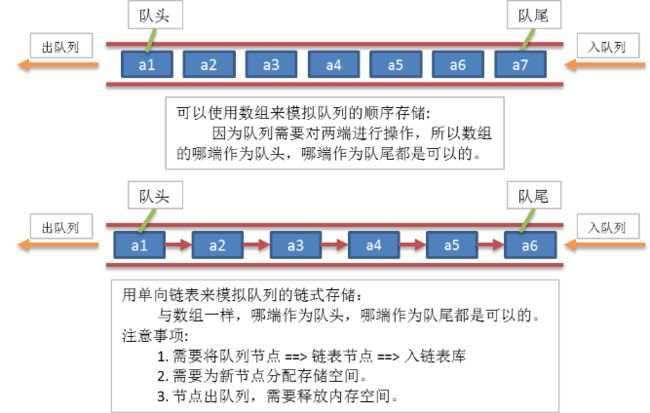
队列也是一种特殊的线性表;可以用线性表顺序存储来模拟队列。
2设计与实现
(1)用线性表顺序存储来模拟队列:
seqlist.h
#ifndef __MY_SEQLIST_H__ #define __MY_SEQLIST_H__ // #define ERR_BASE 0 // #define ERR_PARAM ERR_BASE -1; typedef void SeqList; typedef void SeqListNode; SeqList* SeqList_Create(int capacity); void SeqList_Destroy(SeqList* list); void SeqList_Clear(SeqList* list); int SeqList_Length(SeqList* list); int SeqList_Capacity(SeqList* list); int SeqList_Insert(SeqList* list, SeqListNode* node, int pos); SeqListNode* SeqList_Get(SeqList* list, int pos); SeqListNode* SeqList_Delete(SeqList* list, int pos); #endif //__MY_SEQLIST_H__
seqqueue.h
1 #ifndef _MY_SEQQUEUE_H_ 2 #define _MY_SEQQUEUE_H_ 3 4 typedef void SeqQueue; 5 6 SeqQueue* SeqQueue_Create(int capacity); 7 8 void SeqQueue_Destroy(SeqQueue* queue); 9 10 void SeqQueue_Clear(SeqQueue* queue); 11 12 int SeqQueue_Append(SeqQueue* queue, void* item); 13 14 void* SeqQueue_Retrieve(SeqQueue* queue); 15 16 void* SeqQueue_Header(SeqQueue* queue); 17 18 int SeqQueue_Length(SeqQueue* queue); 19 20 int SeqQueue_Capacity(SeqQueue* queue); 21 22 #endif //_MY_SEQQUEUE_H_
seqlist.c
1 #include "stdlib.h" 2 #include "stdio.h" 3 #include "string.h" 4 #include "seqlist.h" 5 6 typedef struct _tag_SeqList 7 { 8 int capacity; 9 int length; 10 unsigned int *node ; // unsigned int nodeAarry[100] 11 //void *node ; 12 }TSeqList; 13 14 //typdef的意思 把void 重新命名成SeqList 15 16 /* 17 void * SeqList_Create2(int capacity) 18 { 19 TSeqList *ret = NULL; 20 ret = (TSeqList *)malloc(sizeof(TSeqList)); 21 if (ret == NULL) 22 { 23 return NULL; 24 } 25 ret->capacity = capacity; 26 ret->node = (unsigned int *)malloc(sizeof(unsigned int ) * capacity); 27 if (ret->node == NULL) 28 { 29 return NULL; 30 } 31 ret->length = 0; 32 return ret; 33 } 34 */ 35 36 void * SeqList_Create(int capacity) 37 { 38 TSeqList *ret = NULL; 39 40 if (capacity <= 0) 41 { 42 return NULL; 43 } 44 ret = (TSeqList *)malloc(sizeof(TSeqList) + sizeof(unsigned int ) * capacity ); 45 if (ret == NULL) 46 { 47 return NULL; 48 } 49 ret->capacity = capacity; 50 ret->node = (unsigned int *)(ret + 1); 51 52 ret->length = 0; 53 return ret; 54 } 55 56 void SeqList_Destroy(SeqList* list) 57 { 58 if (list == NULL) 59 { 60 return ; 61 } 62 free(list); 63 return ; 64 } 65 66 void SeqList_Clear(SeqList* list) 67 { 68 TSeqList *tlist = NULL; 69 if (list == NULL) 70 { 71 return ; 72 } 73 tlist = (TSeqList *)list; 74 75 tlist->length = 0; 76 return ; 77 } 78 79 int SeqList_Length(SeqList* list) 80 { 81 TSeqList *tlist = list; 82 if (list == NULL) 83 { 84 return -1; 85 } 86 return tlist->length; 87 } 88 89 int SeqList_Capacity(SeqList* list) 90 { 91 TSeqList *tlist = list; 92 if (list == NULL) 93 { 94 return -1; 95 } 96 return tlist->capacity; 97 } 98 99 int SeqList_Insert(SeqList* list, SeqListNode* node, int pos) 100 { 101 int i = 0; 102 TSeqList *tlist = list; 103 104 if (list == NULL || node== NULL ) 105 { 106 return -1; 107 } 108 109 if (pos<0 || pos>=tlist->capacity ) 110 { 111 return -2; 112 } 113 114 //判断是否已经man 115 if (tlist->length >= tlist->capacity) 116 { 117 return -3; 118 } 119 120 //容错 121 if (pos > tlist->length) 122 { 123 pos = tlist->length; 124 } 125 126 //插入算法 有两步 127 //从插入的位置 后移元素 128 //注意length能表示出现在数组的最后元素位置 129 //最后元素的下标为 tlist->node[length-1]; 130 for (i=tlist->length; i>pos; i--) 131 { 132 tlist->node[i] = tlist->node[i-1]; 133 } 134 //在pos位置插入元素 135 tlist->node[pos] = (unsigned int)node; //20140514这个地方不能加 (unsigned int *) 136 //如果你加*,说明你对 unsigned int *node ; // unsigned int nodeAarry[100]还没有理解 137 tlist->length ++; 138 139 return 0; 140 } 141 142 SeqListNode* SeqList_Get(SeqList* list, int pos) 143 { 144 int i = 0; 145 TSeqList *tlist = list; 146 //if (list== NULL || pos<0 || pos>=tlist->length) 147 if (list== NULL || pos<0 || pos>tlist->length) 148 { 149 return NULL; 150 } 151 return (SeqListNode*)tlist->node[pos]; 152 } 153 154 SeqListNode* SeqList_Delete(SeqList* list, int pos) 155 { 156 int i = 0; 157 TSeqList *tlist = list; 158 SeqListNode* ret = NULL; 159 if (list == NULL || pos<0 || pos>tlist->length) 160 { 161 return NULL; 162 } 163 //缓存要删除的结点 164 ret = (SeqListNode*)tlist->node[pos]; 165 //对链表进行移动 166 for (i=pos+1; ilength; i++) 167 { 168 tlist->node[i-1] = tlist->node[i]; 169 } 170 tlist->length --; 171 return ret; 172 }
seqqueue.c
1 #include "stdio.h" 2 #include "string.h" 3 #include "stdio.h" 4 #include "seqqueue.h" 5 #include "seqlist.h" 6 7 //java ssh 8 //创建队列,相当于创建一个线性表 9 SeqQueue* SeqQueue_Create(int capacity) 10 { 11 return SeqList_Create(capacity); 12 } 13 14 void SeqQueue_Destroy(SeqQueue* queue) 15 { 16 SeqList_Destroy(queue); 17 } 18 19 void SeqQueue_Clear(SeqQueue* queue) 20 { 21 SeqList_Clear(queue); 22 } 23 24 //向队列中添加元素,相当于 向线性表中,尾部插入元素 25 int SeqQueue_Append(SeqQueue* queue, void* item) 26 { 27 return SeqList_Insert(queue, item, SeqList_Length(queue)); 28 } 29 30 //从队列中删除元素,相当于从线性表中删除第一个元素 31 void* SeqQueue_Retrieve(SeqQueue* queue) 32 { 33 return SeqList_Delete(queue, 0); 34 } 35 36 void* SeqQueue_Header(SeqQueue* queue) 37 { 38 return SeqList_Get(queue, 0); 39 } 40 41 int SeqQueue_Length(SeqQueue* queue) 42 { 43 return SeqList_Length(queue); 44 } 45 46 int SeqQueue_Capacity(SeqQueue* queue) 47 { 48 return SeqList_Capacity(queue); 49 }
seqqueue业务集成测试.c
1 #include "stdio.h" 2 #include "string.h" 3 #include "stdio.h" 4 #include "seqqueue.h" 5 6 void main() 7 { 8 int i, a[10]; 9 SeqQueue *queue = NULL; 10 11 queue = SeqQueue_Create(10); 12 13 //向队列中放元素 14 for (i=0; i<10; i++) 15 { 16 a[i] = i+1; 17 SeqQueue_Append(queue, &a[i]); 18 } 19 20 printf("the header of queue: %d \n", *((int *)SeqQueue_Header(queue)) ); 21 printf("the length of queue: %d \n", SeqQueue_Length(queue)); 22 printf("the capacity of queue: %d \n", SeqQueue_Capacity(queue)); 23 24 //删除队列 25 while (SeqQueue_Length(queue) > 0) 26 { 27 printf("%d \n", *( (int *)SeqQueue_Retrieve(queue) ) ); 28 } 29 30 // 31 SeqQueue_Destroy(queue); 32 33 system("pause"); 34 }
(2)不用线性表顺序存储来模拟队列:
SeqQueue.h
#ifndef SEQQUEUE_H #define SEQQUEUE_H #include#include #define MAX_SIZE 1024 //顺序队列结构体 typedef struct SEQQUEUE{ void* data[MAX_SIZE]; int size; }SeqQueue; //初始化 SeqQueue* Init_SeqQueue(); //入队 void Push_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue,void* data); //返回队头元素 void* Front_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue); //出队 void Pop_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue); //返回队尾元素 void* Back_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue); //返回大小 int Size_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue); //清空队列 void Clear_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue); //销毁 void FreeSpace_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue); #endif
SeqQueue.c
#include "SeqQueue.h" //初始化 SeqQueue* Init_SeqQueue() { SeqQueue* queue = (SeqQueue*)malloc(sizeof(SeqQueue)); for (int i = 0; i < MAX_SIZE;i ++){ queue->data[i] = NULL; } queue->size = 0; return queue; } //入队 void Push_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue, void* data){ //数组左边当做队头 if (queue == NULL){ return; } if (data == NULL){ return; } if (queue->size == MAX_SIZE){ return; } queue->data[queue->size] = data; queue->size++; } //返回队头元素 void* Front_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue){ if (queue == NULL){ return NULL; } if (queue->size ==0){ return NULL; } return queue->data[0]; } //出队 void Pop_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue){ //需要移动元素 if (queue == NULL){ return; } if (queue->size == 0){ return; } for (int i = 0; i < queue->size - 1;i ++){ queue->data[i] = queue->data[i + 1]; } queue->size--; } //返回队尾元素 void* Back_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue){ if (queue == NULL){ return NULL; } if (queue->size == 0){ return NULL; } return queue->data[queue->size-1]; } //返回大小 int Size_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue){ if (queue == NULL){ return -1; } return queue->size; } //清空队列 void Clear_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue){ if (queue == NULL){ return; } queue->size = 0; } //销毁 void FreeSpace_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue){ if (queue == NULL){ return; } free(queue); }
队列的顺序存储.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include#include #include <string.h> #include "SeqQueue.h" typedef struct PERSON{ char name[64]; int age; }Person; int main(void){ //创建队列 SeqQueue* queue = Init_SeqQueue(); //创建数据 Person p1 = { "aaa", 10 }; Person p2 = { "bbb", 20 }; Person p3 = { "ccc", 30 }; Person p4 = { "ddd", 40 }; Person p5 = { "eee", 50 }; //数据入队列 Push_SeqQueue(queue, &p1); Push_SeqQueue(queue, &p2); Push_SeqQueue(queue, &p3); Push_SeqQueue(queue, &p4); Push_SeqQueue(queue, &p5); //输出队尾元素 Person* backPerson = (Person*)Back_SeqQueue(queue); printf("Name:%s Age:%d\n",backPerson->name,backPerson->age); //输出 while (Size_SeqQueue(queue) > 0){ //取出队头元素 Person* p = (Person*)Front_SeqQueue(queue); printf("Name:%s Age:%d\n",p->name,p->age); //从队头弹出元素 Pop_SeqQueue(queue); } //销毁队列 FreeSpace_SeqQueue(queue); system("pause"); return 0; }
5.队列的链式存储设计与实现
1基本概念
队列也是一种特殊的线性表;可以用线性表链式存储来模拟队列的链式存储。
2设计与实现
(1)线性表链式存储来模拟队列的链式存储
linklist.h
1 #ifndef _MYLINKLIST_H_ 2 #define _MYLINKLIST_H_ 3 4 typedef void LinkList; 5 /* 6 typedef struct _tag_LinkListNode LinkListNode; 7 struct _tag_LinkListNode 8 { 9 LinkListNode* next; 10 }; 11 */ 12 typedef struct _tag_LinkListNode 13 { 14 struct _tag_LinkListNode* next; 15 }LinkListNode; 16 17 LinkList* LinkList_Create(); 18 19 void LinkList_Destroy(LinkList* list); 20 21 void LinkList_Clear(LinkList* list); 22 23 int LinkList_Length(LinkList* list); 24 25 int LinkList_Insert(LinkList* list, LinkListNode* node, int pos); 26 27 LinkListNode* LinkList_Get(LinkList* list, int pos); 28 29 LinkListNode* LinkList_Delete(LinkList* list, int pos); 30 31 #endif
linkqueue.h
1 #ifndef _MY_LINKQUEUE_H_ 2 #define _MY_LINKQUEUE_H_ 3 4 typedef void LinkQueue; 5 6 LinkQueue* LinkQueue_Create(); 7 8 void LinkQueue_Destroy(LinkQueue* queue); 9 10 void LinkQueue_Clear(LinkQueue* queue); 11 12 int LinkQueue_Append(LinkQueue* queue, void* item); 13 14 void* LinkQueue_Retrieve(LinkQueue* queue); 15 16 void* LinkQueue_Header(LinkQueue* queue); 17 18 int LinkQueue_Length(LinkQueue* queue); 19 20 #endif //_MY_LINKQUEUE_H_
linklist.c
1 #include2 #include "stdlib.h" 3 #include "string.h" 4 5 #include "linklist.h" 6 7 typedef struct _tag_LinkList 8 { 9 //这个句柄里面,需要保存所有节点信息。需要有一个起始点 10 //就是带头节点的链表。。。 11 LinkListNode header; 12 int length; 13 }TLinkList; 14 15 LinkList* LinkList_Create() 16 { 17 TLinkList *ret = (TLinkList *)malloc(sizeof(TLinkList)); 18 if (ret == NULL) 19 { 20 return NULL; 21 } 22 //memset(ret, 0, sizeof(TLinkList)); 23 ret->header.next = NULL; 24 ret->length = 0; 25 return ret; 26 } 27 28 void LinkList_Destroy(LinkList* list) 29 { 30 if (list == NULL) 31 { 32 return ; 33 } 34 free(list); 35 return ; 36 } 37 38 void LinkList_Clear(LinkList* list) 39 { 40 41 TLinkList *tList =NULL; 42 43 if (list == NULL) 44 { 45 return ; 46 } 47 tList = (TLinkList *)list; 48 tList->length = 0; 49 tList->header.next = NULL; 50 return ; 51 } 52 53 int LinkList_Length(LinkList* list) 54 { 55 56 TLinkList *tList = (TLinkList *)list; 57 if (tList == NULL) 58 { 59 return -1; 60 } 61 62 return tList->length; 63 } 64 65 int LinkList_Insert(LinkList* list, LinkListNode* node, int pos) 66 { 67 int i = 0; 68 69 TLinkList *tList = NULL; 70 LinkListNode *current = NULL; 71 72 tList = (TLinkList *)list; 73 //准备环境让辅助指针变量 指向链表头节点 74 current = &tList->header; 75 for (i=0; i next!=NULL); i++) 76 { 77 current = current->next; 78 } 79 80 //让node节点链接后续链表 81 node->next = current->next ; 82 //让前边的链表。链接node 83 current->next = node; 84 tList->length ++; 85 return 0; 86 } 87 88 LinkListNode* LinkList_Get(LinkList* list, int pos) 89 { 90 91 int i = 0; 92 93 TLinkList *tList = NULL; 94 LinkListNode *current = NULL; 95 LinkListNode *ret = NULL; 96 tList = (TLinkList *)list; 97 98 if (list == NULL || pos <0 ||pos>=tList->length) 99 { 100 return NULL; 101 } 102 //准备环境让辅助指针变量 指向链表头节点 103 current = &tList->header; 104 for (i=0; i next!=NULL); i++) 105 { 106 current = current->next; 107 } 108 ret = current->next; 109 110 return ret; 111 } 112 113 LinkListNode* LinkList_Delete(LinkList* list, int pos) 114 { 115 int i = 0; 116 117 TLinkList *tList = NULL; 118 LinkListNode *current = NULL; 119 LinkListNode *ret = NULL; 120 tList = (TLinkList *)list; 121 122 if (list == NULL || pos <0 ||pos>=tList->length) 123 { 124 return NULL; 125 } 126 //准备环境让辅助指针变量 指向链表头节点 127 current = &tList->header; 128 for (i=0; i next!=NULL); i++) 129 { 130 current = current->next; 131 } 132 ret = current->next; 133 134 //删除算法 135 current->next =ret->next; 136 tList->length--; 137 138 return ret; 139 }
linkqueue.c
1 #include "stdio.h" 2 #include "string.h" 3 #include "stdlib.h" 4 #include "linkqueue.h" 5 #include "linklist.h" 6 7 typedef struct _tag_LinkQueueNode 8 { 9 LinkListNode node; 10 void *item;//承载业务结点 11 }TLinkQueueNode; 12 //思想:用线性表来模拟队列 13 14 //创建一个队列,相当于创建一个线性表 15 LinkQueue* LinkQueue_Create() //O(1) 16 { 17 return LinkList_Create(); 18 } 19 20 void LinkQueue_Destroy(LinkQueue* queue) //O(1) 21 { 22 LinkQueue_Clear(queue); 23 LinkList_Destroy(queue); 24 return ; 25 } 26 27 void LinkQueue_Clear(LinkQueue* queue) //O(n) 28 { 29 while (LinkQueue_Length(queue) > 0) 30 { 31 LinkQueue_Retrieve(queue); 32 } 33 //LinkQueue_Clear(queue); 34 return ; 35 } 36 37 //向队列中添加元素,相当于向队列的尾部插入元素 38 int LinkQueue_Append(LinkQueue* queue, void* item) //O(n) 39 { 40 int ret = 0; 41 TLinkQueueNode *node = NULL; 42 //需要向linklist中添加业务节点,需要在业务节点中包含链表结点 43 //需要让链表结点放在业务节点的第一个成员域。 44 45 //把形参item,转换为 linklist识别的业务节点 46 node = (TLinkQueueNode *)malloc(sizeof(TLinkQueueNode)); 47 if (node == NULL) 48 { 49 return -1; 50 } 51 memset(node, 0, sizeof(TLinkQueueNode)); 52 node->item = item; 53 54 ret = LinkList_Insert(queue, (LinkListNode *)node, LinkList_Length(queue)); 55 if (ret != 0) 56 { 57 free(node); 58 return ret; 59 } 60 61 return ret; 62 } 63 64 //从队列删除元素,相当于从队列的头部拿元素 65 void* LinkQueue_Retrieve(LinkQueue* queue) //O(1) 66 { 67 int ret = 0; 68 void *item = NULL; 69 TLinkQueueNode *node = NULL; 70 //需要向linklist中添加业务节点,需要在业务节点中包含链表结点 71 node = (TLinkQueueNode *)LinkList_Delete(queue, 0); 72 if (node == NULL) 73 { 74 return -1; 75 } 76 item = node->item; 77 if (node != NULL) 78 { 79 free(node); 80 node = NULL; 81 } 82 return item; 83 } 84 85 //获取队列头元素,相当于从队列0位置拿元素 86 void* LinkQueue_Header(LinkQueue* queue) //O(1) 87 { 88 int ret = 0; 89 void *item = NULL; 90 TLinkQueueNode *node = NULL; 91 node = (TLinkQueueNode *)LinkList_Get(queue, 0); 92 if (node == NULL) 93 { 94 return NULL; 95 } 96 item = node->item; 97 return item; 98 } 99 100 int LinkQueue_Length(LinkQueue* queue) 101 { 102 return LinkList_Length(queue); 103 }
linkqueue业务集成测试.c
1 #include "stdio.h" 2 #include "string.h" 3 #include "stdlib.h" 4 5 #include "linkqueue.h" 6 7 void main(void) 8 { 9 int i , a[10]; 10 LinkQueue* queue = NULL; 11 12 queue = LinkQueue_Create(); 13 14 //向队列中添加元素 15 for (i=0; i<10; i++) 16 { 17 a[i] = i + 1; 18 LinkQueue_Append(queue, &a[i]); 19 } 20 21 // 22 printf("the length of queue: %d \n", LinkQueue_Length(queue)); 23 printf("the header of queue: %d \n", *( (int *)LinkQueue_Header(queue) ) ); 24 25 while (LinkQueue_Length(queue) > 0) 26 { 27 printf("%d \n", *((int *)LinkQueue_Retrieve(queue)) ); 28 } 29 30 LinkQueue_Destroy(queue); 31 32 system("pause"); 33 }
(2)不线性表链式存储来模拟队列的链式存储
LinkQueue.h
#ifndef _LINKQUEUE_H #define _LINKQUEUE_H typedef struct _NODE { struct _NODE* next; }Node; typedef struct { // 长度 int length; // 尾节点指针 Node *real; // 头结点指针 Node *front; }LinkQueue; // 初始化操作,建立一个空队列Q void InitQueue(LinkQueue *Q); // 将队列Q清空 void ClearQueue(LinkQueue *Q); // 若队列为空则返回true,否则返回false int QueueEmpty(LinkQueue Q); // 若队列Q存在且非空,用e返回队列Q的队头元素 void GetHead(LinkQueue Q, Node** e); // 若队列Q存在,插入新元素e到队列Q中并成为队尾元素。 void EnQueue(LinkQueue *Q, Node* e); // 删除队列Q中的队头元素,并用e返回其值 void DeQueue(LinkQueue *Q, Node** e); // 返回队列Q的元素个数 int QueueLength(LinkQueue Q); #endif //_LINKQUEUE_H
LinkQueue.c
#include "LinkQueue.h" #includevoid InitQueue(LinkQueue *Q) { Q->length = 0; Q->real = NULL; Q->front = NULL; } void ClearQueue(LinkQueue *Q) { while (Q->length) { Node* p; DeQueue(Q, &p); } } int QueueEmpty(LinkQueue Q) { if (Q.length == 0) { return 1; } return 0; } // 链表的头部为队头, 尾部为队尾 void GetHead(LinkQueue Q, Node** e) { // 错误处理 if (Q.length == 0) { return; } *e = Q.front; } void EnQueue(LinkQueue *Q, Node* e) { if (Q->length == 0) { // 空链表 Q->real = Q->front = e; } else { // 新节点放到队尾 Q->real->next = e; // rear指向最后一个节点 Q->real = e; } // 长度 Q->length++; } void DeQueue(LinkQueue *Q, Node** e) { if (Q->length == 0) { // 空链表 return; } // 赋值 *e = Q->front; // front指针后移 Q->front = Q->front->next; // 长度 Q->length--; if (Q->length == 0) { // 删除最后一个节点的时候, 尾指针需要指向NULL Q->real = NULL; } } int QueueLength(LinkQueue Q) { return Q.length; }
main.c
#include#include #include "LinkQueue.h" void main() { #if 0 int array[10]; // 创建队列变量 SqQueue q; // 初始化队列 InitQueue(&q); // for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) { array[i] = i + 10; // 入队列 EnQueue(&q, (void*)&array[i]); } printf("Queeu size = %d\n", QueueLength(q)); // 全部都出队列 while (QueueEmpty(q) != 1) { int* tmp; GetHead(q, (void**)&tmp); printf("Queue head value = %d\n", *tmp); // 出队列 DeQueue(&q, (void**)&tmp); printf("Delete elem value = %d\n", *tmp); } #else // 业务节点 typedef struct _tag_value { // 包含一个链表节点 Node node; // 数据 int v; }Value; Value val[5]; // 队列变量 LinkQueue q; // init InitQueue(&q); // for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) { val[i].v = i + 20; // 入队列 EnQueue(&q, &val[i].node); } printf("Queue size = %d\n", QueueLength(q)); // 删除全部节点 while (QueueEmpty(q) != 1) { // 取出队头元素 Node* p; GetHead(q, &p); Value* pp = (Value*)p; printf("Queue head value = %d\n", pp->v); // 出队列 DeQueue(&q, &p); pp = (Value*)p; printf("Delete Queue head value = %d\n", pp->v); } #endif system("pause"); }
6.队列应用实例:农夫过河问题
题目:农夫要把狼、羊、菜和自己运到河对岸去,只有农夫能够划船,农夫每次只能运一种东西,就是如果没有农夫看着,羊会偷吃菜,狼会吃羊。
详细解释:
设一个农夫过河带着一条狼、一只羊和一棵白菜,身处河的南岸。现在他要把这些西全部运到北岸,现在问题是他面前只有一条小船,船小到只能容下他和一件物品,另外只有农夫能撑船。当农夫在场的时候,这三样东西相安无事.一旦农夫不在,狼会吃羊,羊会吃白菜。根据原题的描述我们知道,单独留下白菜和羊,或单独留下狼和羊在某一岸的状态是不安全的。白菜和狼相处没事,把它看作个重要关系的,通过位置分布的代码来判断状态是否安全。然后设计一个方案, 模拟农夫能安全地将这三样东西带过河。
思路:
要模拟农夫过河问题,首先需要选择一个对问题中每个角色的位置进行描述的方法。一个很方便的办法是用四位二进制数顺序分别表示农夫、狼、白菜和羊的位置。例如用0表示农夫或者某东西在河的南岸,1表示在河的北岸。因此整数5(其二进制表示为0101) 表示农夫和白菜在河的南岸,而狼和羊在北岸。确定每个角色位置的函数,用整数location表示上述四位二进制描述的状态,用下面的四个函数从上述状态中得到每个角色所在位置的代码。函数返回值为真表示所考察的人或物在河的北岸,否则在南岸。从初始状态二进制0000(全部在河的南岸) 出发,寻找一种全部由安全状态构成的状态序列,它以二进制1111(全部到达河的北岸) 为最终目标,并且在序列中的每一个状态都可以从前一状态通过农夫(可以带一样东西)划船过河的动作到达。
1.确定每个角色位置,,用整数location表示狼、羊、农夫、白菜的二进制来描述所在位置的代码.
2.初始状态二进制0000(全部在河的南岸) 出发。
3.寻找一种全部由安全状态构成的状态序列
4.在寻找安全路径的同时,要考虑其他安全状态,若出现相同状态路径要记录下来,防止重复。
5.本程序不断寻找安全的状态,它以二进制1111(全部到达河的北岸) 为最终目标,程序结束。
参考代码:
farmer_queue.c
1 /* 用队列解决农夫过河问题的算法*/ 2 3 4 #include5 #include 6 7 #define MAXNUM 20 8 9 typedef int DataType; 10 struct SeqQueue { /* 顺序队列类型定义 */ 11 int f, r; 12 DataType q[MAXNUM]; 13 }; 14 15 typedef struct SeqQueue *PSeqQueue; /* 顺序队列类型的指针类型 */ 16 17 PSeqQueue createEmptyQueue_seq( void ) { 18 PSeqQueue paqu = (PSeqQueue)malloc(sizeof(struct SeqQueue)); 19 if (paqu == NULL) 20 printf("Out of space!! \n"); 21 else 22 paqu->f = paqu->r = 0; 23 return (paqu); 24 } 25 26 int isEmptyQueue_seq( PSeqQueue paqu ) { 27 return paqu->f == paqu->r; 28 } 29 30 /* 在队列中插入一元素x */ 31 void enQueue_seq( PSeqQueue paqu, DataType x ) { 32 if ( (paqu->r + 1) % MAXNUM == paqu->f ) 33 printf( "Full queue.\n" ); 34 else { 35 paqu->q[paqu->r] = x; 36 paqu->r = (paqu->r + 1) % MAXNUM; 37 } 38 } 39 40 /* 删除队列头部元素 */ 41 void deQueue_seq( PSeqQueue paqu ) { 42 if( paqu->f == paqu->r ) 43 printf( "Empty Queue.\n" ); 44 else 45 paqu->f = (paqu->f + 1) % MAXNUM; 46 } 47 48 /* 对非空队列,求队列头部元素 */ 49 DataType frontQueue_seq( PSeqQueue paqu ) { 50 return (paqu->q[paqu->f]); 51 } 52 53 int farmer(int location) { 54 return 0 != (location & 0x08); 55 } 56 57 int wolf(int location) { 58 return 0 != (location & 0x04); 59 } 60 61 int cabbage(int location) { 62 return 0 != (location & 0x02); 63 } 64 65 int goat(int location) { 66 return 0 !=(location & 0x01); 67 } 68 69 /* 若状态安全则返回true */ 70 int safe(int location) { 71 /* 羊吃白菜 */ 72 if ((goat(location) == cabbage(location)) && 73 (goat(location) != farmer(location)) ) 74 return 0; 75 /* 狼吃羊 */ 76 if ((goat(location) == wolf(location)) && 77 (goat(location) != farmer(location))) 78 return 0; 79 return 1; /* 其他状态是安全的 */ 80 } 81 82 83 void farmerProblem( ) { 84 int movers, i, location, newlocation; 85 int route[16]; /*记录已考虑的状态路径*/ 86 PSeqQueue moveTo; 87 /*准备初值*/ 88 moveTo = createEmptyQueue_seq( ); 89 enQueue_seq(moveTo, 0x00); 90 for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) route[i] = -1; 91 route[0]=0; 92 93 /*开始移动*/ 94 while (!isEmptyQueue_seq(moveTo)&&(route[15] == -1)) { 95 /*得到现在的状态*/ 96 location = frontQueue_seq(moveTo); 97 deQueue_seq(moveTo); 98 for (movers = 1; movers <= 8; movers <<= 1) { 99 /* 农夫总是在移动,随农夫移动的也只能是在农夫同侧的东西 */ 100 if ((0 != (location & 0x08)) == (0 != (location & movers))) { 101 newlocation = location^(0x08|movers); 102 if (safe(newlocation) && (route[newlocation] == -1)) { 103 route[newlocation] = location; 104 enQueue_seq(moveTo, newlocation); 105 } 106 } 107 } 108 } 109 110 /* 打印出路径 */ 111 if(route[15] != -1) { 112 printf("The reverse path is : \n"); 113 for(location = 15; location >= 0; location = route[location]) { 114 printf("The location is : %d\n",location); 115 if (location == 0) return; 116 } 117 } 118 else 119 printf("No solution.\n"); 120 } 121 122 123 int main() { 124 farmerProblem( ); 125 return 0; 126 }
截图:
以上资料,来源于网络,和自己的简介,如有雷同,纯属巧合,欢迎转载,并注明出处。
还有不足,待补充。