20200730Java集合练习
一、选择
1.下列不属于Collection子接口的是 B
A. List
B. Map
C. Queue
D. Set
2.已知ArrayList的对象是list,以下哪个方法是判断ArrayList中是否包含"dodoke" A
A. list.contains(“dodoke”);
B. list.add(“dodoke”);
C. list.remove(“dodoke”);
D. list.remove(“dodoke”);
3.下列哪个方法可以获取列表指定位置处的元素 D
A. add(E e)
B. remove()
C. size()
D. get(int index)
4.下列有关HashSet的描述正确的是(多选) AC
A. HashSet是Set的一个重要实现类
B. HashSet中的元素无序但可以重复
C. HashSet中只允许一个null元素
D. 不适用于存取和查找
5.以下关于Set对象的创建错误的是 A
A. Set set=new Set();
B. Set set=new HashSet();
C. HashSet set=new HashSet();
D. Set set=new HashSet(10);
6.关于Iterator的描述错误的是 D
A. Iterator可以对集合Set中的元素进行遍历
B. hasNext()方法用于检查集合中是否还有下一个元素
C. next()方法返回集合中的下一个元素
D. next()方法的返回值为false时,表示集合中的元素已经遍历完毕
7.定义一个Worker类,关于hashCode()方法的说法正确的是? C
A. 在Worker类中,hashCode()方法必须被重写
B. 如果hashCode的值相同,则两个Worker类的对象就认为是相等的
C. hashCode的值不同时,则两个对象必定不同
D. 以上说法均正确
8.下列相关迭代器描述正确的是 ABC
A. Iterator接口可以以统一的方式对各种集合元素进行遍历
B. hasNext()是Iterator接口的一个方法,是用来检测集合中是否还有下一个元素
C. next()是Iterator接口的一个方法,是用来返回集合中的下一个元素
D. hasNext()是Iterator接口的一个方法,是用来返回集合中的下一个元素
9.HashMap的数据是以key-value的形式存储的,以下关于HashMap的说法正确的是 C
A. HashMap中的键不能为null
B. HashMap中的Entry对象是有序排列的
C. key值不允许重复
D. value值不允许重复
10.已知HashMap对象,横线处应添加的语句是? A

A. hashMap.get(key);
B. hasMap.getValue();
C. hashMap.getKey();
D. hashMap.Value();
11.以下关于Set和List的说法,正确的是 C
A. Set中的元素是可以重复的
B. List中的元素是无序的
C. HashSet中只允许有一个null元素
D. List中的元素是不可以重复的
二、编程
1.使用集合ArrayList对字符串进行存储和管理。
运行效果图:

任务:
定义ArrayList对象
存储学科名称,见运行效果图
输出集合中元素的个数
遍历输出集合中的所有元素
编程:
public class ArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用ArrayList存储学科的名称
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("语文");
list.add("数学");
list.add("英语");
list.add("化学");
list.add("物理");
list.add("生物");
//输出列表中元素的个数
System.out.println("列表中元素的个数为:" + list.size());
//遍历输出所有列表元素
for (String str : list) {
System.out.println("第" + (list.indexOf(str)+1) + "个为" + str);
}
}
}
2.定义一个员工信息类Employee,使用ArrayList对员工信息进行添加和显示。
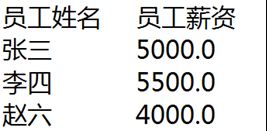
运行效果图:
任务:
1、实现员工信息类Employee
成员变量:编号id(int),姓名name(String),薪资salary(double)
方法:构造方法和相关的get和set方法
2、定义三条员工信息添加到ArrayList中
3、将所有员工的姓名和薪资输出,见效果图
编程:
public class Employee {
//成员变量
private int id;
private String name;
private double salary;
//构造器
public Employee() {
super();
}
public Employee(int id, String name, double salary) {
super();
this.setId(id);
this.setName(name);
this.setSalary(salary);
}
//getters&setters
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
public class EmployeeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义ArrayList对象
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<>();
//创建三个Employee类的对象
Employee e1 = new Employee(1, "张三", 5000.0);
Employee e2 = new Employee(2, "李四", 5500.0);
Employee e3 = new Employee(3, "赵六", 4000.0);
//添加员工信息到ArrayList中
list.add(e1);
list.add(e2);
list.add(e3);
//显示员工的姓名和薪资
System.out.println("员工姓名 员工薪资");
for (Employee e : list) {
System.out.println(e.getName() + " " + e.getSalary());
}
}
}
3.定义一个学生类,使用HashSet对学生类的对象进行管理:执行添加操作,然后解决重复数据的添加问题。
运行效果图:

任务:
定义一个学生类Student
(1)属性为:学号stuId(int),姓名name(String),成绩score(float)
(2)方法为:构造方法,getter和setter方法,toString方法
(3)重写hashCode()和equals()方法,equals方法的判断依据是学号和姓名相等
定义三个Student类的对象,添加到HashSet中
显示HashSet中元素的内容
添加一个重复数据到Set中,观察输出结果
编程:
public class Student {
//成员属性
private int stuId;
private String name;
private float score;
//构造器
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(int stuId, String name, float score) {
super();
this.setStuId(stuId);
this.setName(name);
this.setScore(score);
}
//getters&setters
public int getStuId() {
return stuId;
}
public void setStuId(int stuId) {
this.stuId = stuId;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public float getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(float score) {
this.score = score;
}
//toString重写
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [学号:" + getStuId() + ", 姓名:" + getName() + ", 成绩:" + getScore() + "]";
}
//hashCode重写
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + getStuId();
result = prime * result + ((getName() == null) ? 0 : getName().hashCode());
return result;
}
//equals重写
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (obj.getClass() == Student.class) {
Student stu = (Student)obj;
return stu.getName().equals(this.getName()) && (stu.getStuId() == this.getStuId());
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义三个Student类的对象及一个HashSet类的对象
Student stu1 = new Student(3, "William", 65.0F);
Student stu2 = new Student(1, "Tom", 87.0F);
Student stu3 = new Student(2, "Lucy", 95.0F);
Set<Student> stu = new HashSet<>();
//将Student类的对象添加到集合中
stu.add(stu1);
stu.add(stu2);
stu.add(stu3);
//使用迭代器显示Student类的对象中的内容
Iterator<Student> it = stu.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
//添加一个重复数据到Set中,观察输出结果
Student stu4 = new Student(2, "Lucy", 55.0F);
stu.add(stu4);
Iterator<Student> it2 = stu.iterator();
while (it2.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it2.next());
}
}
}
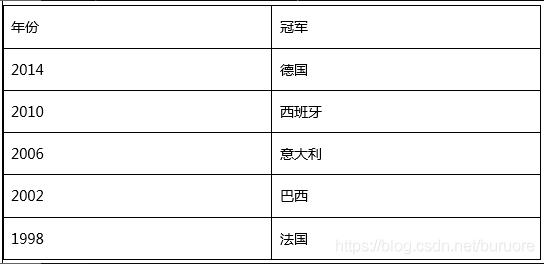
4.已知如下数据:世界杯冠军及夺冠年份。
将夺冠年份作为key值,冠名队名作为value值,存储至少三条数据到HashMap中,并循环打印输出。
运行效果图:

任务:
1、将夺冠年份和冠军队名以key-value形式存储到HashMap中
2、使用迭代器和EntrySet两种方式遍历输出HashMap中的key和value
编程:
public class FootballDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义HashMap的对象并添加数据
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(2014, "德国");
map.put(2010, "西班牙");
map.put(2006, "意大利");
map.put(2002, "巴西");
map.put(1998, "法国");
//使用迭代器的方式遍历
Iterator<String> it = map.values().iterator();
System.out.println("使用迭代器方式进行输出:");
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
//使用EntrySet同时获取key和value
Set<Entry<Integer, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
System.out.println("使用EntrySet进行输出:");
for (Entry<Integer, String> entry : entrySet) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "-" + entry.getValue());
}
}
}