DarkNet-YOLOv3训练自己的数据集(一)(过程超详细!!!)
本文是为了记录在公司实习的第一个手势识别的项目。
该项目数据集采用的是私有的手势照片,从1-10共十个类别,用手势对相机进行控制。
大部分相关工作在ubuntu上完成,后面具体实验步骤中会提到。
一、按照官网的步骤下载并编译darknet
- 直接clone darknet
git clone https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet
- 切换到darknet文件夹下,再编译,编译过程中会产生很多信息,只要没有error就可以了。
cd darknet
make
- 编译成功后,将已经训练好的权重文件下载下来,如果速度很慢,可以将链接复制到迅雷里面下载。下载好了之后,yolov3.weight 文件会在darknet目录下
wget https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights
- 接下来就可以试试看该权重的效果了,在darknet文件夹下会生成检测结果 predictions.jpg,
./darknet detect cfg/yolov3.cfg yolov3.weights data/dog.jpg
一般情况下,以上操作都不会出现什么问题,验证完之后,就可以训练自己的模型了。
二、制作数据集
- 用labelimg做标记,具体使用方法不细说
- 在darknet目录下新建VOCdevkit文件夹,该文件夹下包含如下文件夹目录:(这里截图是在windows下截的,ubuntu也一样建立相关文件夹目录就好了)
JPEGImages—放入自己的数据集
Annotations—放入数据集对应的xml文件
在VOC2007下新建creat_main.py文件,将下面代码拷贝进去运行,会在ImageSets下面的Main文件夹里面生成四个文件:train.txt,val.txt,test.txt和trainval.txt,数据集分割的百分比可以自己调整。
import os
import random
trainval_percent = 0.1
train_percent = 0.9
xmlfilepath = 'Annotations'
txtsavepath = 'ImageSets\Main'
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
ftrainval = open('ImageSets/Main/trainval.txt', 'w')
ftest = open('ImageSets/Main/test.txt', 'w')
ftrain = open('ImageSets/Main/train.txt', 'w')
fval = open('ImageSets/Main/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftest.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftrain.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()
生成如下四个.txt文件

3. 在darknet->scripts 文件夹下找到voc_label.py将该文件复制到VOCdevkit下,并在该文件夹下运行,会生成四个.txt文件,如下所示:

到此为止,数据集基本上就做完了,由于voc数据集的anchor不是特别适用于我们自己的数据集,因此接下来要对anchor重新聚类
三、重新聚类anchor
将下列代码写入voc_annotation.py,并运行,会生成和上图一样文件名的四个文件
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from os import getcwd
sets=[('2007', 'train'), ('2007', 'val'), ('2007', 'test')]
#根据自己的类别更改
classes = ["one","two","three","four","five","six","seven","eight","nine","ten"]
def convert_annotation(year, image_id, list_file):
in_file = open('VOCdevkit/VOC%s/Annotations/%s.xml'%(year, image_id))
tree=ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult)==1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (int(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), int(xmlbox.find('ymin').text), int(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), int(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
list_file.write(" " + ",".join([str(a) for a in b]) + ',' + str(cls_id))
wd = getcwd()
for year, image_set in sets:
image_ids = open('VOCdevkit/VOC%s/ImageSets/Main/%s.txt'%(year, image_set)).read().strip().split()
list_file = open('%s_%s.txt'%(year, image_set), 'w')
for image_id in image_ids:
list_file.write('%s/VOCdevkit/VOC%s/JPEGImages/%s.jpg'%(wd, year, image_id))
convert_annotation(year, image_id, list_file)
list_file.write('\n')
list_file.close()
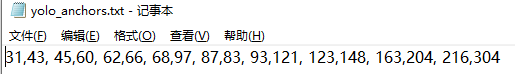
用下列代码对生成的2007_train.txt文件中的坐标进行聚类。聚类的anchor结果会保存到yolo_anchors.txt中。
import numpy as np
class YOLO_Kmeans:
def __init__(self, cluster_number, filename):
self.cluster_number = cluster_number
self.filename = "2007_train.txt"
def iou(self, boxes, clusters): # 1 box -> k clusters
n = boxes.shape[0]#box的数量
k = self.cluster_number#聚类中心的数量
box_area = boxes[:, 0] * boxes[:, 1]#box的面积
box_area = box_area.repeat(k)#重复k次
box_area = np.reshape(box_area, (n, k))#每行为每个gt的面积
cluster_area = clusters[:, 0] * clusters[:, 1]#得到的anchor的面积
cluster_area = np.tile(cluster_area, [1, n])#按1*n的大小横向纵向复制
cluster_area = np.reshape(cluster_area, (n, k))
box_w_matrix = np.reshape(boxes[:, 0].repeat(k), (n, k))
cluster_w_matrix = np.reshape(np.tile(clusters[:, 0], (1, n)), (n, k))
min_w_matrix = np.minimum(cluster_w_matrix, box_w_matrix)#对应位置比较,哪个小输出哪个
box_h_matrix = np.reshape(boxes[:, 1].repeat(k), (n, k))
cluster_h_matrix = np.reshape(np.tile(clusters[:, 1], (1, n)), (n, k))
min_h_matrix = np.minimum(cluster_h_matrix, box_h_matrix)
inter_area = np.multiply(min_w_matrix, min_h_matrix)
result = inter_area / (box_area + cluster_area - inter_area)
return result
def avg_iou(self, boxes, clusters):
accuracy = np.mean([np.max(self.iou(boxes, clusters), axis=1)])
return accuracy
def kmeans(self, boxes, k, dist=np.median):
box_number = boxes.shape[0]
distances = np.empty((box_number, k))
last_nearest = np.zeros((box_number,))
np.random.seed()
clusters = boxes[np.random.choice(
box_number, k, replace=False)] # init k clusters
while True:
distances = 1 - self.iou(boxes, clusters)
current_nearest = np.argmin(distances, axis=1)
if (last_nearest == current_nearest).all():
break # clusters won't change
for cluster in range(k):
clusters[cluster] = dist( # update clusters
boxes[current_nearest == cluster], axis=0)
last_nearest = current_nearest
return clusters
def result2txt(self, data):
f = open("yolo_anchors.txt", 'w')
row = np.shape(data)[0]
for i in range(row):
if i == 0:
x_y = "%d,%d" % (data[i][0], data[i][1])
else:
x_y = ", %d,%d" % (data[i][0], data[i][1])
f.write(x_y)
f.close()
def txt2boxes(self):
f = open(self.filename, 'r')
dataSet = []
for line in f:
infos = line.split(" ")
length = len(infos)
for i in range(1, length):
width = int(infos[i].split(",")[2]) - \
int(infos[i].split(",")[0])
height = int(infos[i].split(",")[3]) - \
int(infos[i].split(",")[1])
dataSet.append([width, height])
result = np.array(dataSet)
f.close()
return result
def txt2clusters(self):
all_boxes = self.txt2boxes()
result = self.kmeans(all_boxes, k=self.cluster_number)
result = result[np.lexsort(result.T[0, None])]
self.result2txt(result)
print("K anchors:\n {}".format(result))
print("Accuracy: {:.2f}%".format(
self.avg_iou(all_boxes, result) * 100))
if __name__ == "__main__":
cluster_number = 9 #聚类中心的个数
filename = "train.txt"
kmeans = YOLO_Kmeans(cluster_number, filename)# YOLO_Kmeans类实例化一个kmeans对象
kmeans.txt2clusters()#调用对象里面的方法