Otsu算法原理及实现
在图像处理中Otsu方法,是以 Nobuyuki otsu 的名字命名的(日本人,大津展之),常用于基于图像分割的聚类。该算法的理论依据是:假定图像包含两类像素(前景像素和背景像素),直方图为双峰直方图,然后计算使得两类像素能分开的最佳阈值(类内方差),或等价的间类间方差最大。
Otsu算法原理:
对于图像 I ( x , y ) I(x,y) I(x,y),前景(即目标)和背景的分割阈值记作 T T T,属于前景的像素点数占整幅图像的比例记为 ω 0 ω0 ω0,平均灰度为 μ 0 μ0 μ0;背景像素点数占整幅图像的比例为 ω 1 ω1 ω1,平均灰度为 μ 1 μ1 μ1;整幅图像的平均灰度记为 μ μ μ,类间方差记为 g g g。
假设图像大小为 M × N M×N M×N,图像中像素的灰度值小于阈值 T T T 的像素个数为 N 0 N0 N0,像素灰度大于阈值T的像素个数为 N 1 N1 N1,那么:
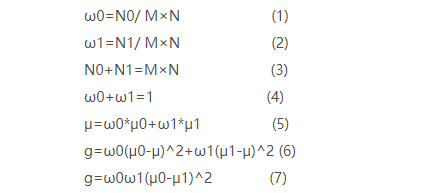
采用遍历的方法使得类间方差 g g g最大的阈值 T T T,即为所求。Ostu方法可以形象地理解为:求取直方图有两个峰值的图像中那两个峰值之间的低谷值 T T T 。
Otsu算法实现
matlab函数:
matlab中有现成的函数实现,函数名为: graythresh, 该函数便是用Ostu方法求分割阈值T。用法如下:
imgScr=imread('..');
T = graythresh(imgScr);
BW = im2bw(imgScr,T);
graythresh函数源码:
function [level em] = graythresh(I)
%GRAYTHRESH Global image threshold using Otsu's method.
% LEVEL = GRAYTHRESH(I) computes a global threshold (LEVEL) that can be
% used to convert an intensity image to a binary image with IM2BW. LEVEL
% is a normalized intensity value that lies in the range [0, 1].
% GRAYTHRESH uses Otsu's method, which chooses the threshold to minimize
% the intraclass variance of the thresholded black and white pixels.
%
% [LEVEL EM] = GRAYTHRESH(I) returns effectiveness metric, EM, as the
% second output argument. It indicates the effectiveness of thresholding
% of the input image and it is in the range [0, 1]. The lower bound is
% attainable only by images having a single gray level, and the upper
% bound is attainable only by two-valued images.
%
% Class Support
% -------------
% The input image I can be uint8, uint16, int16, single, or double, and it
% must be nonsparse. LEVEL and EM are double scalars.
%
% Example
% -------
% I = imread('coins.png');
% level = graythresh(I);
% BW = im2bw(I,level);
% figure, imshow(BW)
%
narginchk(1,1);
validateattributes(I,{'uint8','uint16','double','single','int16'},{'nonsparse'}, ...
mfilename,'I',1);
if ~isempty(I)
% Convert all N-D arrays into a single column. Convert to uint8 for
% fastest histogram computation.
I = im2uint8(I(:));
num_bins = 256;
counts = imhist(I,num_bins);
% Variables names are chosen to be similar to the formulas in
% the Otsu paper.
p = counts / sum(counts);
omega = cumsum(p);
mu = cumsum(p .* (1:num_bins)');
mu_t = mu(end);
sigma_b_squared = (mu_t * omega - mu).^2 ./ (omega .* (1 - omega));
% Find the location of the maximum value of sigma_b_squared.
% The maximum may extend over several bins, so average together the
% locations. If maxval is NaN, meaning that sigma_b_squared is all NaN,
% then return 0.
maxval = max(sigma_b_squared);
isfinite_maxval = isfinite(maxval);
if isfinite_maxval
idx = mean(find(sigma_b_squared == maxval));
% Normalize the threshold to the range [0, 1].
level = (idx - 1) / (num_bins - 1);
else
level = 0.0;
end
else
level = 0.0;
isfinite_maxval = false;
end
% compute the effectiveness metric
if nargout > 1
if isfinite_maxval
em = maxval/(sum(p.*((1:num_bins).^2)') - mu_t^2);
else
em = 0;
end
end
opencv函数实现:
getThreshVal_Otsu_8u( const Mat& _src )
{
Size size = _src.size();
if( _src.isContinuous() )
{
size.width *= size.height;
size.height = 1;
}
const int N = 256;
int i, j, h[N] = {0};
for( i = 0; i < size.height; i++ )
{
const uchar* src = _src.data + _src.step*i;
j = 0;
#if CV_ENABLE_UNROLLED
for( ; j <= size.width - 4; j += 4 )
{
int v0 = src[j], v1 = src[j+1];
h[v0]++; h[v1]++;
v0 = src[j+2]; v1 = src[j+3];
h[v0]++; h[v1]++;
}
#endif
for( ; j < size.width; j++ )
h[src[j]]++;
}
double mu = 0, scale = 1./(size.width*size.height);
for( i = 0; i < N; i++ )
mu += i*(double)h[i];
mu *= scale;
double mu1 = 0, q1 = 0;
double max_sigma = 0, max_val = 0;
for( i = 0; i < N; i++ )
{
double p_i, q2, mu2, sigma;
p_i = h[i]*scale;
mu1 *= q1;
q1 += p_i;
q2 = 1. - q1;
if( std::min(q1,q2) < FLT_EPSILON || std::max(q1,q2) > 1. - FLT_EPSILON )
continue;
mu1 = (mu1 + i*p_i)/q1;
mu2 = (mu - q1*mu1)/q2;
sigma = q1*q2*(mu1 - mu2)*(mu1 - mu2);
if( sigma > max_sigma )
{
max_sigma = sigma;
max_val = i;
}
}
return max_val;
}
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「Naruto_Q」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 by-sa版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/piaoxuezhong/article/details/78302893