数据结构——斐波那契堆FibonacciHeap(C语言)
前一篇博文记录了二项堆的一些操作,本文介绍与之相似的堆结构——斐波那契堆。
斐波那契堆是可合并堆,一些操作可以在常数滩还时间内完成,而二项堆中的一些操作需要O(lgn);
定义
一个斐波那契堆是一序列具有最小堆序的有根树的集合。也就会说,每棵树都遵循最小堆性质:每个节点的关键字不小于它父节点的关键字。
注:斐波那契堆里的树可以不是二项树,并且根链表是无序的。
结构
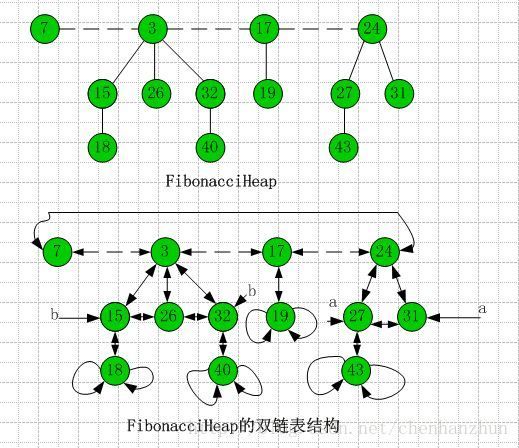
斐波那契堆是由一组最小堆有序树构成的。每个节点的度数为其子节点的数目。树的度数为其根节点的度数。
斐波那契堆中的树都是有根的但是无序。每个节点x包含指向父节点的指针p[x]和指向任意一个子结点的child[x]。x的所有子节点都用双向循环链表链接起来,叫做x的子链表。子链表中的每一个节点y都有指向它的左兄弟的left[y]和右兄弟的right[y]。如果节点y是x仅有的子节点,则left[y]=right[y]=y。
斐波那契堆中所有树的根节点也用一个双向循环链表链接起来。
每个节点x的域
- 父节点p[x]
- 指向任一子女的指针child[x]——结点x的子女被链接成一个环形双链表,称为x的子女表
- 左兄弟left[x]
- 右兄弟right[x]——当left[x] = right[x] = x时,说明x是独子。
- 子女的个数degree[x]
- 布尔值域mark[x]——标记是否失去了一个孩子
操作
1、初始化
/*创建并返回一个空的FibonacciHeap*/
FibHeap Make_FibHeap()
{
FibHeap heap=NULL;
heap=(FibHeap)malloc(sizeof(FiboHeap));
if(NULL==heap)
{
printf("malloc heap is failed.\n");
exit(1);
}
memset(heap,0,sizeof(FiboHeap));
return heap;
}
/*初始化节点*/
FibHeapNode intial_Node()
{
FibHeapNode x=NULL;
x=(FibHeapNode)malloc(sizeof(FibNode));
if(NULL==x)
{
printf("malloc the node of x is failed.\n");
exit(1);
}
memset(x,0,sizeof(FibNode));
x->left=x->right=x;
return x;
}2、插入节点
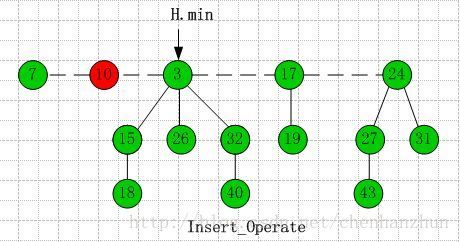
首先初始化要插入的节点,赋予节点关键字值,构造自身的环形双向链表,然后把它插入到最小根节点之前,若堆为空,直接把最小头结点指向该节点即可,否则利用双向链表的插入操作把节点插入到最小根节点之前。
Fibonacci-Heap-Insert(H,x)
degree[x] := 0
p[x] := NIL
child[x] := NIL
left[x] := x
right[x] := x
mark[x] := FALSE
concatenate the root list containing x with root list H
if min[H] = NIL or key[x]此合并操纵比较简单,只需把两个斐波那契堆H1和H2的根链表利用双向循环链表的知识链接即可,即把两个根链表的首尾循环相接。
Fibonacci-Heap-Union(H1,H2)
H := Make-Fibonacci-Heap()
min[H] := min[H1]
Concatenate the root list of H2 with the root list of H
if (min[H1] = NIL) or (min[H2] <> NIL and min[H2] < min[H1])
then min[H] := min[H2]
n[H] := n[H1] + n[H2]
free the objects H1 and H2
return H4、抽取最小关键字
抽取最小关键字的操作比较复杂一点,因为斐波那契堆的树遵循最小堆的性质,则最小关键字节点即是堆的头节点H[min],
首先,删除最小关键字节点,把堆新的头节点指向被删除节点的右兄弟即H[min]->right;并判断被删除节点是否有儿子节点,
若存在儿子节点,把儿子节点作为一个新的堆的根节点,组成新的根链表ChildHeap;接下来将新的根链表ChildHeap与原来根链表剩下的根链表heap进行合并操作,组成最新的根链表heap,最后对新的根链表heap中含有相同度数的树进行合并操作Consolidate();具体步骤详见源程序。
抽取最小关键字的操作过程比较复杂,操作过程的流图就不画了,很多参考书都给出详细的操作过程及其解说。
Fibonacci-Heap-Extract-Min(H)
z:= min[H]
if x <> NIL
then for each child x of z
do add x to the root list of H
p[x]:= NIL
remove z from the root list of H
if z = right[z]
then min[H]:=NIL
else min[H]:=right[z]
CONSOLIDATE(H)
n[H] := n[H]-1
return z
CONSOLIDATE(H)
for i:=0 to D(n[H])
Do A[i] := NIL
for each node w in the root list of H
do x:= w
d:= degree[x]
while A[d] <> NIL
do y:=A[d]
if key[x]>key[y]
then exchange x<->y
Fibonacci-Heap-Link(H, y, x)
A[d]:=NIL
d:=d+1
A[d]:=x
min[H]:=NIL
for i:=0 to D(n[H])
do if A[i]<> NIL
then add A[i] to the root list of H
if min[H] = NIL or key[A[i]]Fibonacci-Heap-Link(H,y,x)
remove y from the root list of H
make y a child of x
degree[x] := degree[x] + 1
mark[y] := FALSE5、减小关键字的值
首先,判断节点的关键字值是否小于要替换的值;
若不小于它,则将该值赋给节点的关键字值;进而对该堆进行调整使该堆满足斐波那契堆的性质。
Fibonacci-Heap-Decrease-Key(H,x,k)
if k > key[x]
then error "new key is greater than current key"
key[x] := k
y := p[x]
if y <> NIL and key[x]CUT(H,x,y)
Remove x from the child list of y, decrementing degree[y]
Add x to the root list of H
p[x]:= NIL
mark[x]:= FALSE
CASCADING-CUT(H,y)
z:= p[y]
if z <> NIL
then if mark[y] = FALSE
then mark[y]:= TRUE
else CUT(H, y, z)
CASCADING-CUT(H, z)
6、删除节点
Fibonacci-Heap-Delete(H,x)
Fibonacci-Heap-Decrease-Key(H,x,-infinity)
Fibonacci-Heap-Extract-Min(H)
完整程序
1、函数定义
#ifndef FIBONACCI_H_INCLUDE
#define FIBONACCI_H_INCLUDE
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
typedef struct FibonacciHeapNode *FibHeapNode;
typedef struct FibonacciHeapNode
{
int key;//节点值
int degree;//节点度数
FibHeapNode child;//孩子节点
FibHeapNode parent;//父节点
FibHeapNode left;//左兄弟
FibHeapNode right;//右兄弟
bool mark;
}FibNode;
typedef struct FibonacciHeap *FibHeap;
typedef struct FibonacciHeap
{
FibHeapNode min;//最小节点
int numNode;//节点数
int maxNumofDegree;//最大度数
}FiboHeap;
void FibHeap_Consolidate(FibHeap heap);
/*创建并返回一个空的FibonacciHeap*/
FibHeap Make_FibHeap()
{
FibHeap heap=NULL;
heap=(FibHeap)malloc(sizeof(FiboHeap));
if(NULL==heap)
{
printf("malloc heap is failed.\n");
exit(1);
}
memset(heap,0,sizeof(FiboHeap));
return heap;
}
/*初始化节点*/
FibHeapNode intial_Node()
{
FibHeapNode x=NULL;
x=(FibHeapNode)malloc(sizeof(FibNode));
if(NULL==x)
{
printf("malloc the node of x is failed.\n");
exit(1);
}
memset(x,0,sizeof(FibNode));
x->left=x->right=x;
return x;
}
/*将节点x插入到节点y之前*/
void FibHeapNode_Add(FibHeapNode x,FibHeapNode y)
{
x->left=y->left;
x->right=y;
y->left->right=x;
y->left=x;
}
/*插入一个节点*/
void FibHeap_Insert(FibHeap heap,FibHeapNode x)
{
if(NULL==heap->min)
{
heap->min=x;
}
else
{
FibHeapNode_Add(x,heap->min);
if(x->keymin->key)
heap->min=x;
}
heap->numNode=heap->numNode+1;
}
/*寻找最小节点*/
FibHeapNode FibHeap_Minimum(FibHeap heap)
{
return heap->min;
}
/*合并两个斐波那契堆*/
FibHeap FibHeap_Union(FibHeap H1,FibHeap H2)
{
FibHeap H=Make_FibHeap();
FibHeapNode Next1,Next2;
H->min=H1->min;
Next1=H1->min->right;
Next2=H2->min->right;
//concatenate the root list of H2 with the root list of H;
H->min->right=Next2;
Next2->left=H->min;
H2->min->right=Next1;
Next1->left=H2->min;
//choose the new minimum for the heap;
if((NULL==H1->min)||(H2->min!=NULL && H2->min->keymin->key))
H->min=H2->min;
H->numNode=H1->numNode+H2->numNode;
// Complete the union by setting the H1 and H2 heap to emptiness
// then destroying it
H2->min=NULL;
H2->numNode=0;
free(H2);
H1->min=NULL;
H1->numNode=0;
free(H1);
return H;
}
/*抽取最小节点*/
FibHeapNode FibHeap_ExtractMin(FibHeap *heap)
{
FibHeapNode Result;
//FibHeapNode MinRoot=heap->min;
FibHeap ChildHeap = NULL;
// Remove minimum node and set MinRoot to next node
if ((Result = FibHeap_Minimum(*heap)) == NULL)
return NULL;
(*heap)->min = Result->right;
Result->right->left = Result->left;
Result->left->right = Result->right;
Result->left = Result->right = NULL;
(*heap)->numNode --;
if (Result->mark)
{
Result->mark = false;
}
Result->degree = 0;
// Attach child list of Minimum node to the root list of the heap
// If there is no child list, then do no work
if (Result->child == NULL)
{
if ((*heap)->min == Result)
(*heap)->min = NULL;
}
// If MinRoot==Result then there was only one root tree, so the root list is
// the child list of that node (NULL if this is the last node in the list)
else if ((*heap)->min == Result)
(*heap)->min = Result->child;
// If MinRoot is different, then the child list is pushed into a new temporary
// heap, which is then merged by Union() onto the root list of this heap.
else
{
ChildHeap = Make_FibHeap();
ChildHeap->min = Result->child;
}
// Complete the disassociation of the Result node from the heap
if (Result->child != NULL)
Result->child->parent = NULL;
Result->child = Result->parent = NULL;
// If there was a child list, then we now merge it with rest of the root list
if (ChildHeap)
*heap=FibHeap_Union(ChildHeap,*heap);
// Consolidate heap to find new minimum and do reorganize work
if ((*heap)->min != NULL)
FibHeap_Consolidate(*heap);
// Return the minimum node, which is now disassociated with the heap
// It has Left, Right, Parent, Child, Mark and Degree cleared.
//heap->numNode--;
free(ChildHeap);
return Result;
}
/*The node y is removed from the root list and becomes a subtree of node x.*/
void FibHeapNode_Link(FibHeap heap,FibHeapNode y,FibHeapNode x)
{
//Remove node y from the root list of heap;
if(NULL!=y->right)
y->right->left=y->left;
if(NULL!=y->left)
y->left->right=y->right;
// Make node y a singleton circular list with a parent of x;
y->left=y->right=y;
y->parent=x;
//If node x has no children, then list y is its new child list;
if(NULL==x->child)
x->child=y;
// Otherwise, node y must be added to node x's child list;
else
{
FibHeapNode_Add(y,x->child);
x->child=y;
}
x->degree++;
y->mark=false;
}
void SWAP(FibHeapNode *x,FibHeapNode *y)
{
FibHeapNode temp;
temp=*x;
*x=*y;
*y=temp;
}
/*Consolidate the same degree of the root node*/
void FibHeap_Consolidate(FibHeap heap)
{
int i,d,Dn;
FibHeapNode x,y,w;
heap->maxNumofDegree=(int)(log(heap->numNode*1.0)/log(2.0))+1;
Dn=heap->maxNumofDegree;
FibHeapNode *A;
A=(FibHeapNode*)malloc(sizeof(FibNode)*Dn);
//A=new FibHeapNode*[Dn];
// Initialize the consolidation detection array
//memset(A,0,sizeof(FibNode)*Dn);
for(i=0;imin->left->right=NULL;
heap->min->left=NULL;
w=heap->min;
do
{
x=w;
d=x->degree;
w=w->right;
while(NULL!=A[d])
{
y=A[d];//another node with the same degree as x
if(x->key>y->key)
SWAP(&x,&y);//exchange the pointer
if(w==y)
w=y->right;
FibHeapNode_Link(heap,y,x);
A[d]=NULL;
d++;
}
A[d]=x;
}while(NULL!=w);
// Now we rebuild the root list, find the new minimum,
// set all root list nodes' parent pointers to NULL and
// count the number of subtrees.
heap->min=NULL;
for(i=0;imin)
heap->min=A[i];
else
{
//FibHeapNode_Add(A[i],heap->min);
heap->min->right=A[i];
A[i]->left=heap->min;
if((A[i]->key)min->key)
heap->min=A[i];
}
}
}
free(A);
}
/*切断节点x与父节点y的链接,并使x成为根节点*/
void FibHeap_Cut(FibHeap heap,FibHeapNode x,FibHeapNode y)
{
//remove x from the child list of y,decrementing y.degree
y->degree--;
if(x->right==x)
y->child=NULL;
else
{
if(y->child==x)
y->child=x->right;
x->left->right=x->right;
x->right->left=x->left;
}
//add x to thr root list of heap
FibHeapNode_Add(x,heap->min);
x->parent=NULL;
x->mark=false;
}
/*级联剪切*/
void FibHeap_CascadingCut(FibHeap heap,FibHeapNode y)
{
FibHeapNode z=NULL;
z=y->parent;
if(NULL!=z)
{
if(false==y->mark)
y->mark=true;
else
{
FibHeap_Cut(heap,y,z);
FibHeap_CascadingCut(heap,z);
}
}
}
/*减小关键字的值*/
void FibHeap_DecreaseKey(FibHeap *heap,FibHeapNode x,int k)
{
FibHeapNode y=NULL;
if(k>x->key)
{
printf("new key is greater than current key.");
return;
}
x->key=k;
y=x->parent;
if(NULL!=y && x->keykey)
{
FibHeap_Cut(*heap,x,y);
FibHeap_CascadingCut(*heap,y);
}
if(x->key<(*heap)->min->key)
(*heap)->min=x;
}
/*删除节点*/
void FibHeapNode_Delete(FibHeap *heap,FibHeapNode x)
{
FibHeap_DecreaseKey(heap,x,INT_MIN);
FibHeap_ExtractMin(heap);
if((*heap)->min->left==NULL||(*heap)->min->right==NULL)
{
(*heap)->min->left=(*heap)->min->right=(*heap)->min;
}
}
//输出打印堆
void FibNodePrint(FibHeapNode x)
{
FibHeapNode p = NULL;
if (NULL == x)
{
return ;
}
p = x;
do {
printf(" (");
printf("%d", p->key);
if (p->child != NULL) {
FibNodePrint(p->child);
}
printf(") ");
p = p->left;
}while (x != p);
}
void FibHeapPrint(FibHeap heap)
{
printf("The numNode = %d\n", heap->numNode);
FibNodePrint(heap->min);
printf("\n");
}
#endif // FIBONACCI_H_INCLUDE 2、测试程序
#include
#include
#include"Fibonacci_Heap.h"
int main()
{
int n,i,key;
FibHeapNode x;
FibHeap heap;
heap=Make_FibHeap();
printf("Enter the numbers of node:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("\n");
for(i=0;ikey=key;
FibHeap_Insert(heap,x);
}
FibHeapPrint(heap);
x=FibHeap_ExtractMin(&heap);
FibHeapPrint(heap);
int k;
printf("Enter the number you want to decrease:");
scanf("%d",&k);
FibHeap_DecreaseKey(&heap,heap->min,k);
FibHeapPrint(heap);
/* int del;
printf("Enter the key you want to delete:");
scanf("%d",&del);
x=intial_Node();
x->key=del;*/
FibHeapNode_Delete(&heap,heap->min->child);
printf("After delete the node,the heap are:\n");
FibHeapPrint(heap);
return 0;
}