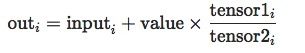PyTorch学习笔记-1.PyTorch基础概念
1.PyTorch基础概念
1.1.PyTorch简介与安装
1.1.1.PyTorch简介
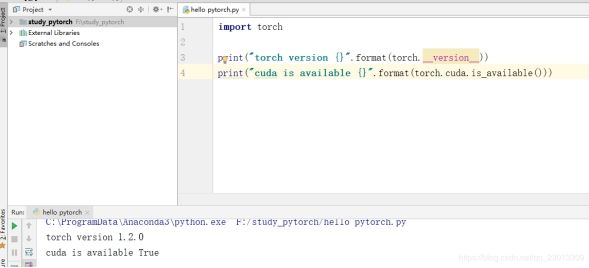
2017年1月,FAIR(Facebook AI Research)发布PyTorch
PyTorch 是在Torch基础上用python语言重新打造的一款深度学习框架
Torch是采用Lua语言为接口的机器学习框架,但因Lua语言较为小众,导致Torch知名度不高
PyTorch 发展
• 2017年1月正式发布PyTorch
• 2018年4月更新0.4.0版,支持W indows系统,caffe2正式并入PyTorch
• 2018年11月更新1.0稳定版,已GitHub 增长第二快的开源项目
• 2019年5月更新1.1.0版,支持TensorBoard,增强可视化功能
• 2019年8月更新1.2.0版,更新torchvision,torchaudio 和torchtext,增加更多功能
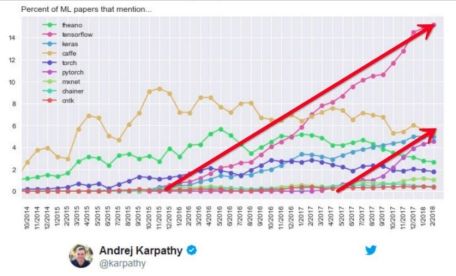
2014年1 0月至 2018年0 2月arXiv论文中深度学习框架提及次数统计,PyTorch的增长速度与TensorFlow一致
2019年3月各深度学习框架在GitHub上的Start,Forks,Watchers和Contributors数量对比
PyTorch优点
• 上手快:掌握Numpy和基本深度学习概念即可上手
• 代码简洁灵活:用nn.module封装使网络搭建更方便;基于动态图机制,更灵活
• Debug方便:调试PyTorch就像调试Python代码一样简单
• 文档规范:https://pytorch.org/docs/可查各版本文档
• 资源多:arXiv中的新算法大多有PyTorch实现
• 开发者多:GitHub上贡献者(Contributors)已超过1100+
• 背靠大树:FaceBook维护开发
• ......
适合人群
• 深度学习初学者:模型算法实现容易,加深深度学习概念认识
• 机器学习爱好者:数十行代码便可实现人脸识别,目标检测,图像生成等有趣实验
• 算法研究员:最新arXiv论文算法快速复现
1.1.2.Anaconda安装
Anaconda是为方便使用python而建立的一个软件包,其包含常用的250多个工具包,多版本python解释器和强大的虚拟环境管理工具,所以Anaconda得名python全家桶
Anaconda可以使安装、运行和升级环境变得更简单,因此推荐安装使用
下载地址:https://www.anaconda.com/download/
双击下载好的安装包
选Just Me和All Users都可以
安装路径可以是默认路径,可以修改路径,只要能配置好环境即可。且路径中不要出现中文字符。
在这一步最好勾选第一个选项配置环境,也可以后续自己配置环境
验证安装成功,打开cmd,输入conda,回车
1.1.3.Pycharm安装
PyCharm 是一款功能强大的 Python 编辑器,而且可以跨平台,在macos和windows下面都可以用,这点比较好。是python现在最好用的编辑器。
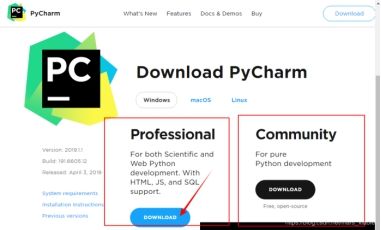
PyCharm官网下载:https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/download/#section=windows
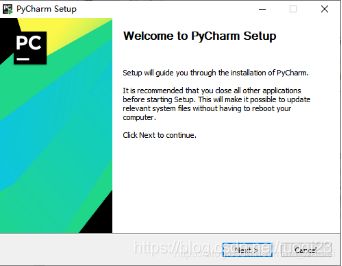
双击exe,进入“欢迎安装”界面,直接下一步
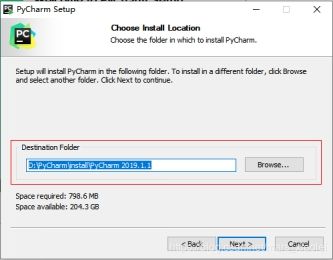
2、进入“选择安装路径”界面,我一般不喜欢安装在系统盘,而是直接安装在软件下载文件夹中 ,选择好路径以后,下一步
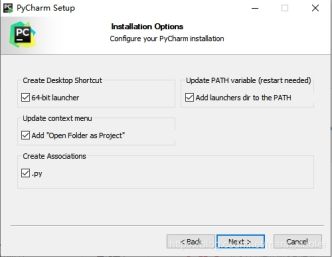
3、 进入“安装选项”界面,按自己需求选择,全选,下一步
一直下一步,直到安装完成。
1.1.4.PyTorch安装
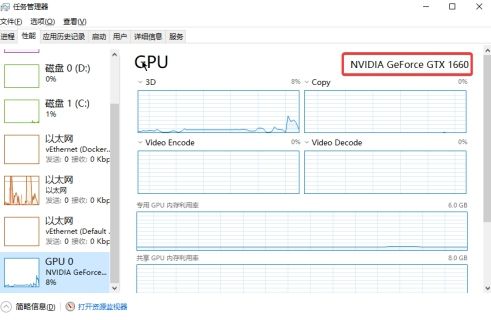
显卡配置(无 Nvidia 显卡的略过)
打开任务管理器,在GPU那里看到 NVIDIA 显卡即可。说明你的硬件驱动,已安装。
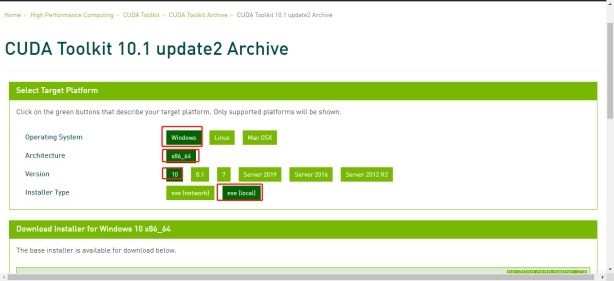
下载Cuda
官网:https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-10.1-download-archive-update2
在https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-toolkit-release-notes/index.html 这里可以查询到我们应该下载哪个版本
下载CuDNN
官网 https://developer.nvidia.com/rdp/cudnn-download
安装Cuda
1.与安装其他的软件类似
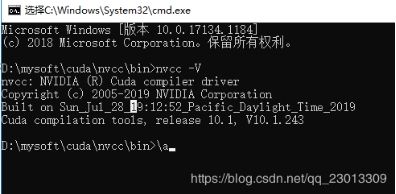
2.安装结束后将 ~/nvcc/bin(因为版本的不同可能在不同的地方) 目录添加到环境变量
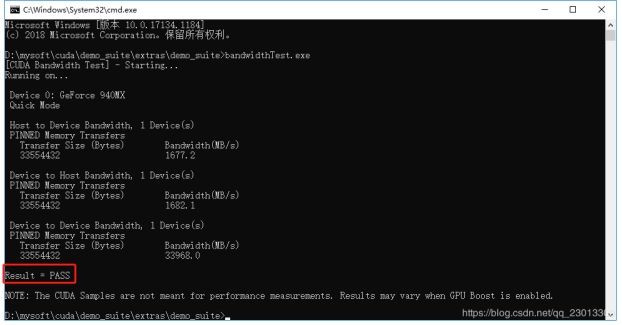
3.在命令行下输入 nvcc -V, 出现下列信息说明Cuda安装成功
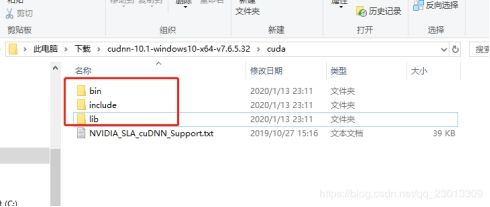
4.将CuDNN压缩包解压后,下面的三个文件夹复制到Cuda的安装目录下
5.然后执行Demo, 如果Demo中显示PASS则说明安装成功
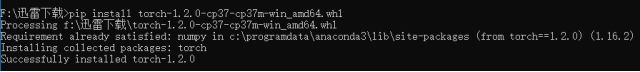
安装Pytorch
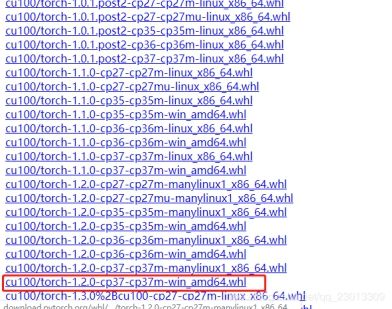
官网 https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html 选择合适的版本
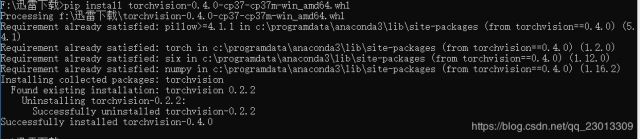
torch/torchvision 都需要安装
验证Pytorch
1.2.Tensor(张量)
1.2.1.张量概念
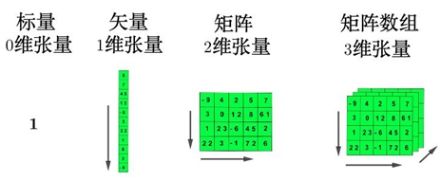
张量是一个多维数组,它是标量、向量、矩阵的高维拓展
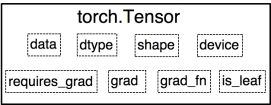
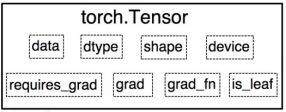
Variable是torch.autograd中的数据类型,主要用于封装Tensor,进行自动求导,其中包含的五个属性:
data:被包装的Tensor
grad:data的梯度
grad_fn:创建Tensor的Function,是自动求导的关键
requires_grad:指示是否需要梯度
is_leaf:指示是否是叶子结点(张量)
PyTorch0.4.0版开始,Variable并入Tensor
dtype:张量的数据类型,如torch.FloatTensor, torch.cuda.FloatTensor
shape:张量的形状,如(64, 3, 224, 224)
device:张量所在设备,GPU/CPU,是加速的关
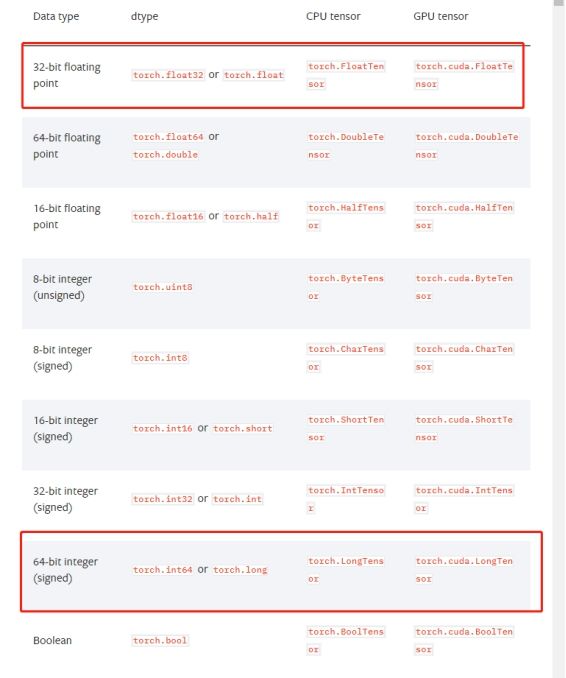
PyTorch的数据类型总共有9种,常用的是float32和int64
1.2.2.直接创建张量
1.torch.tensor():功能:从data创建tensor
• data: 数据, 可以是list, numpy
• dtype : 数据类型,默认与data的一致
• device : 所在设备, cuda/cpu
• requires_grad:是否需要梯度
• pin_memory:是否存于锁页内存,通常设置为false
torch.tensor(
data,
dtype=None,
device=None,
requires_grad=False,
pin_memory=False)
代码实现:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import torch
import numpy as np
# 通过torch.tensor创建张量
arr = np.ones((3, 3))
print("ndarray的数据类型:", arr.dtype)
t = torch.tensor(arr, device='cuda')
# t = torch.tensor(arr)
print(t)
| ndarray的数据类型: float64 tensor([[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64) |
2.torch.from_numpy(ndarray)
功能:从numpy创建tensor
注意事项:从torch.from_numpy创建的tensor于原ndarray共享内存,当修
改其中一个的数据,另外一个也将会被改动
代码实现:
# 通过torch.from_numpy创建张量
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
t = torch.from_numpy(arr)
arr[0, 0] = 0
print("numpy array: ", arr)
print("tensor : ", t)
t[0, 0] = -1
print("numpy array: ", arr)
print("tensor : ", t)
| numpy array: [[0 2 3] [4 5 6]] tensor : tensor([[0, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], dtype=torch.int32)
修改tensor numpy array: [[-1 2 3] [ 4 5 6]] tensor : tensor([[-1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6]], dtype=torch.int32) |
1.2.3.依据数值创建张量
1 torch.zeros()
功能:依size创建全0张量
• size: 张量的形状, 如(3, 3)、(3, 224,224)
• out : 输出的张量
• layout : 内存中布局形式, 有strided,sparse_coo等
• device : 所在设备, gpu/cpu
• requires_grad:是否需要梯度
torch.zeros(*size,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
代码实现:
# 通过torch.zeros创建张量
out_t = torch.tensor([1])
t = torch.zeros((3, 3), out=out_t)
print(t, '\n', out_t)
print(id(t), id(out_t), id(t) == id(out_t))
| tensor([[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]]) tensor([[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]]) 1672654932392 1672654932392 True |
2 torch.zeros_like()
功能:依input形状创建全0张量
• intput: 创建与input同形状的全0张量
• dtype : 数据类型
• layout : 内存中布局形式
torch.zeros_like(input,
dtype=None,
layout=None,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
3 torch.ones()
4 torch.ones_like()
功能:依input形状创建全1张量
• size: 张量的形状, 如(3, 3)、 (3, 224,224)
• dtype : 数据类型
• layout : 内存中布局形式
• device : 所在设备, gpu/cpu
• requires_grad:是否需要梯度
torch.ones(*size,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False
torch.ones_like(input,
dtype=None,
layout=None,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
5 torch.full()
6 torch.full_like()
功能:依input形状创建全0张量
• size: 张量的形状, 如(3, 3)
• fill_value : 张量的值
torch.full(size,
fill_value,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
代码实现:
# 通过torch.full创建全1张量
t = torch.full((3, 3), 6)
print(t)
| tensor([[6., 6., 6.], [6., 6., 6.], [6., 6., 6.]]) |
7 torch.arange()
功能:创建等差的1维张量
注意事项:数值区间为[start, end)
• start: 数列起始值
• end : 数列“结束值”
• step: 数列公差,默认为1
torch.arange(start=0,
end,
step=1,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
代码实现:
# 通过torch.arange创建等差数列张量
t = torch.arange(2, 10, 2)
print(t)
| tensor([2, 4, 6, 8]) |
8 torch.linspace()
功能:创建均分的1维张量
注意事项:数值区间为[start, end]
• start: 数列起始值
• end : 数列结束值
• steps: 数列长度
torch.linspace(start,
end,
steps=100,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
代码实现:
# 通过torch.linspace创建均分数列张量
# t = torch.linspace(2, 10, 5)
t = torch.linspace(2, 10, 6)
print(t)
| tensor([ 2.0000, 3.6000, 5.2000, 6.8000, 8.4000, 10.0000]) |
9 torch.logspace()
功能:创建对数均分的1维张量
注意事项:长度为steps, 底为base
• start: 数列起始值
• end : 数列结束值
• steps: 数列长度
• base : 对数函数的底,默认为10
torch.logspace(start,
end,
steps=100,
base=10.0,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
10 torch.eye()
功能:创建单位对角矩阵( 2维张量)
注意事项:默认为方阵
• n: 矩阵行数
• m : 矩阵列数
torch.eye(n,
m=None,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
1.2.4.依概率分布创建张量
1 torch.normal()
功能:生成正态分布(高斯分布)
• mean : 均值
• std : 标准差
四种模式:
mean为标量, std为标量
mean为标量, std为张量
mean为张量, std为标量
mean为张量, std为张量
torch.normal(mean,
std,
out=None)
代码实现:
# 通过torch.normal创建正态分布张量
# mean:张量 std: 张量
mean = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
std = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
t_normal = torch.normal(mean, std)
print("mean:{}\nstd:{}".format(mean, std))
print(t_normal)
# mean:标量 std: 标量
t_normal = torch.normal(0., 1., size=(4,))
print(t_normal)
# mean:张量 std: 标量
mean = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
std = 1
t_normal = torch.normal(mean, std)
print("mean:{}\nstd:{}".format(mean, std))
print(t_normal)
| mean:tensor([1., 2., 3., 4.]) std:tensor([1., 2., 3., 4.]) tensor([1.6614, 2.5338, 3.1850, 6.4853]) tensor([-0.4519, -0.1661, -1.5228, 0.3817]) mean:tensor([1., 2., 3., 4.]) std:1 tensor([-0.0276, 1.4369, 2.1077, 3.9417]) |
2 torch.randn()
3 torch.randn_like()
功能:生成标准正态分布
• size : 张量的形状
torch.randn(*size,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
4 torch.rand()
5 torch.rand_like()
功能:在区间[0, 1)上,生成均匀分布
torch.rand(*size,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
6 torch.randint()
7 torch.randint_like()
功能:区间[low, high)生成整数均匀分布
• size : 张量的形状
torch.randint(low=0,
high,
size,
out=None,
dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
8 torch.randperm()
功能:生成从0到n-1的随机排列
• n : 张量的长度
torch.randperm(n,
out=None,
dtype=torch.int64,
layout=torch.strided,
device=None,
requires_grad=False)
9 torch.bernoulli()
功能:以input为概率,生成伯努力分布(0-1分布,两点分布)
• input : 概率值
torch.bernoulli(input,
*,
generator=None,
out=None)
1.3.张量操作与线性回归
1.3.1.张量的操作:拼接、切分、索引和变换
1.张量拼接与切分
1.1 torch.cat()
功能:将张量按维度dim进行拼接
• tensors: 张量序列
• dim : 要拼接的维度
torch.cat(tensors,
dim=0,
out=None)
代码实现:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import torch
torch.manual_seed(1)
# torch.cat
t = torch.ones((2, 3))
t_0 = torch.cat([t, t], dim=0)
t_1 = torch.cat([t, t, t], dim=1)
print("t_0:{} shape:{}\nt_1:{} shape:{}".format(t_0, t_0.shape, t_1, t_1.shape))
| t_0:tensor([[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]]) shape:torch.Size([4, 3]) t_1:tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]]) shape:torch.Size([2, 9]) |
1.2 torch.stack()
功能:在新创建的维度dim上进行拼接
• tensors:张量序列
• dim :要拼接的维度
torch.stack(tensors,
dim=0,
out=None)
代码实现:
# torch.stack
t = torch.ones((2, 3))
t_stack = torch.stack([t, t, t], dim=0)
print("\nt_stack:{} shape:{}".format(t_stack, t_stack.shape))
| t_stack:tensor([[[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]],
[[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]],
[[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]]]) shape:torch.Size([3, 2, 3]) |
1.3 torch.chunk()
功能:将张量按维度dim进行平均切分
返回值:张量列表
注意事项:若不能整除,最后一份张量小于其他张量
• input: 要切分的张量
• chunks : 要切分的份数
• dim : 要切分的维度
torch.chunk(input,
chunks,
dim=0)
代码实现:
# torch.chunk
a = torch.ones((2, 7)) # 7
list_of_tensors = torch.chunk(a, dim=1, chunks=3) # 3
for idx, t in enumerate(list_of_tensors):
print("第{}个张量:{}, shape is {}".format(idx+1, t, t.shape))
| 第1个张量:tensor([[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]]), shape is torch.Size([2, 3]) 第2个张量:tensor([[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]]), shape is torch.Size([2, 3]) 第3个张量:tensor([[1.], [1.]]), shape is torch.Size([2, 1]) |
1.4 torch.split()
功能:将张量按维度dim进行切分
返回值:张量列表
• tensor: 要切分的张量
• split_size_or_sections : 为int时,表示每一份的长度;为list时,按list 元素切分
• dim : 要切分的维度
torch.split(tensor,
split_size_or_sections,
dim=0)
代码实现:
# torch.split
t = torch.ones((2, 5))
list_of_tensors = torch.split(t, [2, 1, 2], dim=1) # 2
for idx, t in enumerate(list_of_tensors):
print("第{}个张量:{}, shape is {}".format(idx+1, t, t.shape))
| 第1个张量:tensor([[1., 1.], [1., 1.]]), shape is torch.Size([2, 2]) 第2个张量:tensor([[1.], [1.]]), shape is torch.Size([2, 1]) 第3个张量:tensor([[1., 1.], [1., 1.]]), shape is torch.Size([2, 2]) |
2.张量索引
2.1 torch.index_select()
功能:在维度dim上,按index索引数据
返回值:依index索引数据拼接的张量
• input: 要索引的张量
• dim: 要索引的维度
• index : 要索引数据的序号
torch.index_select(input,
dim,
index,
out=None)
代码实现:
# torch.index_select
t = torch.randint(0, 9, size=(3, 3))
idx = torch.tensor([0, 2], dtype=torch.long) # float
t_select = torch.index_select(t, dim=0, index=idx)
print("t:\n{}\nt_select:\n{}".format(t, t_select))
| t: tensor([[4, 5, 0], [5, 7, 1], [2, 5, 8]]) t_select: tensor([[4, 5, 0], [2, 5, 8]]) |
2.2 torch.masked_select()
功能:按mask中的True进行索引
返回值:一维张量
• input: 要索引的张量
• mask: 与input同形状的布尔类型张量
torch.masked_select(input,
mask,
out=None)
代码实现:
# torch.masked_select
t = torch.randint(0, 9, size=(3, 3))
mask = t.le(5) # ge is mean greater than or equal/ gt: greater than le lt
t_select = torch.masked_select(t, mask)
print("t:\n{}\nmask:\n{}\nt_select:\n{} ".format(t, mask, t_select))
| t: tensor([[4, 5, 0], [5, 7, 1], [2, 5, 8]]) mask: tensor([[ True, True, True], [ True, False, True], [ True, True, False]]) t_select: tensor([4, 5, 0, 5, 1, 2, 5]) |
3.张量变换
3.1 torch.reshape()
功能:变换张量形状
注意事项:当张量在内存中是连续时,新张量与input共享数据内存
• input: 要变换的张量
• shape: 新张量的形状
torch.reshape(input,
shape)
代码实现:
# torch.reshape
t = torch.randperm(8)
t_reshape = torch.reshape(t, (-1, 2, 2)) # -1
print("t:{}\nt_reshape:\n{}".format(t, t_reshape))
t[0] = 1024
print("t:{}\nt_reshape:\n{}".format(t, t_reshape))
print("t.data 内存地址:{}".format(id(t.data)))
print("t_reshape.data 内存地址:{}".format(id(t_reshape.data)))
| t:tensor([5, 4, 2, 6, 7, 3, 1, 0]) t_reshape: tensor([[[5, 4], [2, 6]],
[[7, 3], [1, 0]]]) t:tensor([1024, 4, 2, 6, 7, 3, 1, 0]) t_reshape: tensor([[[1024, 4], [ 2, 6]],
[[ 7, 3], [ 1, 0]]]) t.data 内存地址:1809503205640 t_reshape.data 内存地址:1809503205640 |
3.2 torch.transpose()
功能:交换张量的两个维度
• input: 要变换的张量
• dim0: 要交换的维度
• dim1: 要交换的维度
torch.transpose(input,
dim0,
dim1)
代码实现:
# torch.transpose
t = torch.rand((2, 3, 4))
t_transpose = torch.transpose(t, dim0=1, dim1=2) # c*h*w h*w*c
print("t shape:{}\nt_transpose shape: {}".format(t.shape, t_transpose.shape))
| t shape:torch.Size([2, 3, 4]) t_transpose shape: torch.Size([2, 4, 3]) |
3.3 torch.t()
功能: 2维张量转置,对矩阵而言,等价于torch.transpose(input, 0, 1)
torch.t(input)
3.4 torch.squeeze()
功能: 压缩长度为1的维度(轴)
• dim: 若为None,移除所有长度为1的轴;若指定维度,当且仅当该轴长度为1 时,可以被移除;
torch.squeeze(input,
dim=None,
out=None)
代码实现:
# torch.squeeze
t = torch.rand((1, 2, 3, 1))
t_sq = torch.squeeze(t)
t_0 = torch.squeeze(t, dim=0)
t_1 = torch.squeeze(t, dim=1)
print(t.shape)
print(t_sq.shape)
print(t_0.shape)
print(t_1.shape)
| torch.Size([1, 2, 3, 1]) torch.Size([2, 3]) torch.Size([2, 3, 1]) torch.Size([1, 2, 3, 1]) |
3.5 torch.unsqueeze()
功能:依据dim扩展维度
• dim: 扩展的维度
torch.usqueeze(input,
dim,
out=None)
1.3.2.张量数学运算
1.加减乘除
torch.add()
torch.addcdiv()
torch.addcmul()
torch.sub()
torch.div()
torch.mul()
torch.add()
功能:逐元素计算 input+alpha×other
• input: 第一个张量
• alpha: 乘项因子
• other: 第二个张量
torch.add(input,
alpha=1,
other,
out=None)
torch.addcdiv()
torch.addcmul()
![]()
torch.addcmul(input,
value=1,
tensor1,
tensor2,
out=None)
代码实现:
# torch.add
t_0 = torch.randn((3, 3))
t_1 = torch.ones_like(t_0)
t_add = torch.add(t_0, 10, t_1)
print("t_0:\n{}\nt_1:\n{}\nt_add_10:\n{}".format(t_0, t_1, t_add))
| t_0: tensor([[ 0.6614, 0.2669, 0.0617], [ 0.6213, -0.4519, -0.1661], [-1.5228, 0.3817, -1.0276]]) t_1: tensor([[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]]) t_add_10: tensor([[10.6614, 10.2669, 10.0617], [10.6213, 9.5481, 9.8339], [ 8.4772, 10.3817, 8.9724]]) |
2.对数,指数,幂函数
torch.log(input, out=None)
torch.log10(input, out=None)
torch.log2(input, out=None)
torch.exp(input, out=None)
torch.pow()
3.三角函数
torch.abs(input, out=None)
torch.acos(input, out=None)
torch.cosh(input, out=None)
torch.cos(input, out=None)
torch.asin(input, out=None)
torch.atan(input, out=None)
torch.atan2(input, other, out=None)
1.3.3.线性回归
线性回归是分析一个变量与另外一(多)个变量之间关系的方法
因变量: y
自变量: x
关系:线性 y = wx + b
分析:求解w, b
求解步骤:
1. 确定模型 y = wx + b
2. 选择损失函数 MSE: 
3. 求解梯度并更新w,b w = w – LR * w.grad b = b – LR * w.grad
代码实现:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
torch.manual_seed(10)
lr = 0.05 # 学习率
# 创建训练数据
x = torch.rand(20, 1) * 10 # x data (tensor), shape=(20, 1)
y = 2*x + (5 + torch.randn(20, 1)) # y data (tensor), shape=(20, 1)
# 构建线性回归参数
w = torch.randn((1), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros((1), requires_grad=True)
for iteration in range(1000):
# 前向传播
wx = torch.mul(w, x)
y_pred = torch.add(wx, b)
# 计算 MSE loss
loss = (0.5 * (y - y_pred) ** 2).mean()
# 反向传播
loss.backward()
# 更新参数
b.data.sub_(lr * b.grad)
w.data.sub_(lr * w.grad)
# 清零张量的梯度
w.grad.zero_()
b.grad.zero_()
# 绘图
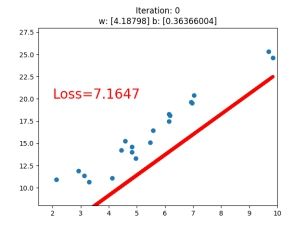
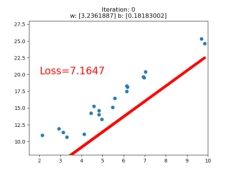
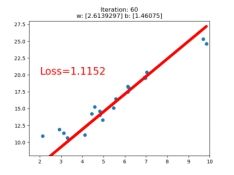
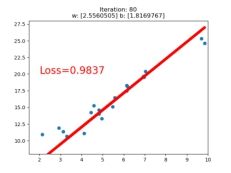
if iteration % 20 == 0:
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), y_pred.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
plt.text(2, 20, 'Loss=%.4f' % loss.data.numpy(), fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.xlim(1.5, 10)
plt.ylim(8, 28)
plt.title("Iteration: {}\nw: {} b: {}".format(iteration, w.data.numpy(), b.data.numpy()))
plt.pause(0.5)
if loss.data.numpy() < 1:
break
1.4.计算图与动态图机制
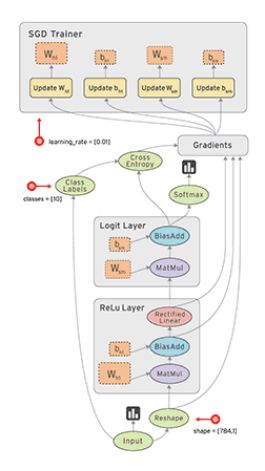
1.4.1.计算图
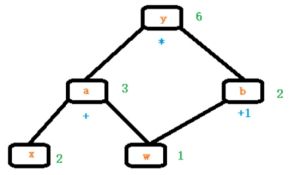
计算图是用来描述运算的有向无环图
计算图有两个主要元素: 结点( Node)和边( Edge)
结点表示数据,如向量,矩阵,张量
边表示运算,如加减乘除卷积等
用计算图表示: y = (x+ w) * (w+1)
a = x + w b = w + 1 y = a * b
计算图与梯度求导:计算y对w的导数
![]()
![]()
![]()
=![]()
叶子结点:用户创建的结点称为叶子结点,如X 与 W
is_leaf: 指示张量是否为叶子结点
grad_fn: 记录创建该张量时所用的方法(函数)
y.grad_fn =
a.grad_fn =
b.grad_fn =
代码实现:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import torch
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)
x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)
a = torch.add(w, x)
# a.retain_grad() # 保存a的梯度
b = torch.add(w, 1)
y = torch.mul(a, b)
y.backward()
print(w.grad)
# 查看叶子结点
print("is_leaf:\n", w.is_leaf, x.is_leaf, a.is_leaf, b.is_leaf, y.is_leaf)
# 查看梯度
print("gradient:\n", w.grad, x.grad, a.grad, b.grad, y.grad)
# 查看 grad_fn
print("grad_fn:\n", w.grad_fn, x.grad_fn, a.grad_fn, b.grad_fn, y.grad_fn)
| tensor([5.]) is_leaf: True True False False False gradient: tensor([5.]) tensor([2.]) None None None grad_fn: None None |
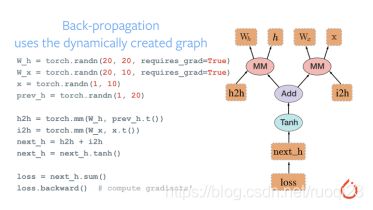
1.4.2.动态图
动态图vs 静态图
动态图 Dynamic Graph:运算与搭建同时进行,灵活,易调节 ---PyTorch
静态图:先搭建图,后运算,高效,不灵活 ---tensorflow(2.0版本之前)
1.5.自动求导与逻辑回归
1.5.1.自动求导
autograd—自动求导系统
torch.autograd.backward
功能:自动求取梯度
• tensors: 用于求导的张量,如 loss
• retain_graph : 保存计算图
• create_graph : 创建导数计算图,用于高阶求导
• grad_tensors:多梯度权重
torch.autograd.backward(tensors,
grad_tensors=None,
retain_graph=None,
create_graph=False)
代码实现:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import torch
torch.manual_seed(10)
#retain_graph
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)
x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)
a = torch.add(w, x)
b = torch.add(w, 1)
y = torch.mul(a, b)
y.backward(retain_graph=True) #如果不保存,后面再次反向求导会报错
print(w.grad)
y.backward()
| tensor([5.]) |
# grad_tensors
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)
x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)
a = torch.add(w, x) # retain_grad()
b = torch.add(w, 1)
y0 = torch.mul(a, b) # y0 = (x+w) * (w+1)
y1 = torch.add(a, b) # y1 = (x+w) + (w+1) dy1/dw = 2
loss = torch.cat([y0, y1], dim=0) # [y0, y1]
grad_tensors = torch.tensor([1., 2.]) # 为y0和y1的梯度设置权重
loss.backward(gradient=grad_tensors) # gradient 传入 torch.autograd.backward()中的grad_tensors
print(w.grad)
| tensor([9.]) |
torch.autograd.grad
功能:求取梯度
• outputs: 用于求导的张量,如 loss
• inputs : 需要梯度的张量
• create_graph : 创建导数计算图,用于高阶求导
• retain_graph : 保存计算图
• grad_outputs:多梯度权重
torch.autograd.grad(outputs,
inputs,
grad_outputs=None,
retain_graph=None,
create_graph=False)
代码实现:
# autograd.gard
x = torch.tensor([3.], requires_grad=True)
y = torch.pow(x, 2) # y = x**2
grad_1 = torch.autograd.grad(y, x, create_graph=True) # grad_1 = dy/dx = 2x = 2 * 3 = 6
print(grad_1)
grad_2 = torch.autograd.grad(grad_1[0], x) # grad_2 = d(dy/dx)/dx = d(2x)/dx = 2
print(grad_2)
| (tensor([6.], grad_fn= (tensor([2.]),) |
autograd注意事项:
1. 梯度不自动清零
代码示例:
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)
x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)
for i in range(4):
a = torch.add(w, x)
b = torch.add(w, 1)
y = torch.mul(a, b)
y.backward()
print(w.grad)
w.grad.zero_()
| tensor([5.]) tensor([5.]) tensor([5.]) tensor([5.]) |
2. 依赖于叶子结点的结点, requires_grad默认为True
代码示例:
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)
x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)
a = torch.add(w, x)
b = torch.add(w, 1)
y = torch.mul(a, b)
print(a.requires_grad, b.requires_grad, y.requires_grad)
| True True True |
3. 叶子结点不可执行in-place
代码示例:
# in-place操作
a = torch.ones((1, ))
print(id(a), a)
a = a + torch.ones((1, ))
print(id(a), a)
a += torch.ones((1, ))
print(id(a), a)
| 1380195580808 tensor([1.]) 1380196952968 tensor([2.]) 1380196952968 tensor([3.]) |
w = torch.tensor([1.], requires_grad=True)
x = torch.tensor([2.], requires_grad=True)
a = torch.add(w, x)
b = torch.add(w, 1)
y = torch.mul(a, b)
w.add_(1)
y.backward()
| w.add_(1) RuntimeError: a leaf Variable that requires grad has been used in an in-place operation. |
原因是反向求导时找的是数据的地址,由于正向计算时数据是原始数据,反向求导时如果数据改变,会造成求导结果的变换,所以不允许数据的改变
1.5.2.逻辑回归
逻辑回归是线性的二分类模型
模型表达式:
![]() 称为Sigmoid函数,也称为Logistic函数,图形如下:
称为Sigmoid函数,也称为Logistic函数,图形如下:
线性回归是分析自变量x与因变量y(标量)之间关系的方法:![]()
逻辑回归是分析自变量x与因变量y(概率)之间关系的方法
逻辑回归也称为对数几率回归:
![]()
![]()
代码实现:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
torch.manual_seed(10)
# step 1/5 生成数据
sample_nums = 100
mean_value = 1.7
bias = 1
n_data = torch.ones(sample_nums, 2)
x0 = torch.normal(mean_value * n_data, 1) + bias # 类别0 数据 shape=(100, 2)
y0 = torch.zeros(sample_nums) # 类别0 标签 shape=(100, 1)
x1 = torch.normal(-mean_value * n_data, 1) + bias # 类别1 数据 shape=(100, 2)
y1 = torch.ones(sample_nums) # 类别1 标签 shape=(100, 1)
train_x = torch.cat((x0, x1), 0)
train_y = torch.cat((y0, y1), 0)
# step 2/5 选择模型
class LR(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LR, self).__init__()
self.features = nn.Linear(2, 1)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = self.sigmoid(x)
return x
lr_net = LR() # 实例化逻辑回归模型
# step 3/5 选择损失函数
loss_fn = nn.BCELoss()
# step 4/5 选择优化器
lr = 0.01 # 学习率
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(lr_net.parameters(), lr=lr, momentum=0.9)
# step 5/5 模型训练
for iteration in range(1000):
# 前向传播
y_pred = lr_net(train_x)
# 计算 loss
loss = loss_fn(y_pred.squeeze(), train_y)
# 反向传播
loss.backward()
# 更新参数
optimizer.step()
# 清空梯度
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 绘图
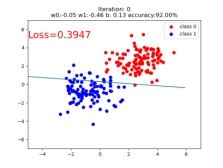
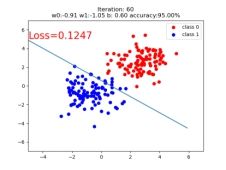
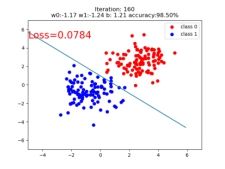
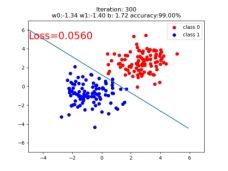
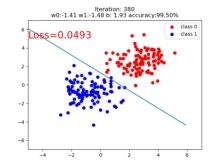
if iteration % 20 == 0:
mask = y_pred.ge(0.5).float().squeeze() # 以0.5为阈值进行分类
correct = (mask == train_y).sum() # 计算正确预测的样本个数
acc = correct.item() / train_y.size(0) # 计算分类准确率
plt.scatter(x0.data.numpy()[:, 0], x0.data.numpy()[:, 1], c='r', label='class 0')
plt.scatter(x1.data.numpy()[:, 0], x1.data.numpy()[:, 1], c='b', label='class 1')
w0, w1 = lr_net.features.weight[0]
w0, w1 = float(w0.item()), float(w1.item())
plot_b = float(lr_net.features.bias[0].item())
plot_x = np.arange(-6, 6, 0.1)
plot_y = (-w0 * plot_x - plot_b) / w1
plt.xlim(-5, 7)
plt.ylim(-7, 7)
plt.plot(plot_x, plot_y)
plt.text(-5, 5, 'Loss=%.4f' % loss.data.numpy(), fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.title("Iteration: {}\nw0:{:.2f} w1:{:.2f} b: {:.2f} accuracy:{:.2%}".format(iteration, w0, w1, plot_b, acc))
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plt.pause(0.5)
if acc > 0.99:
break