NioEventLoop源码分析
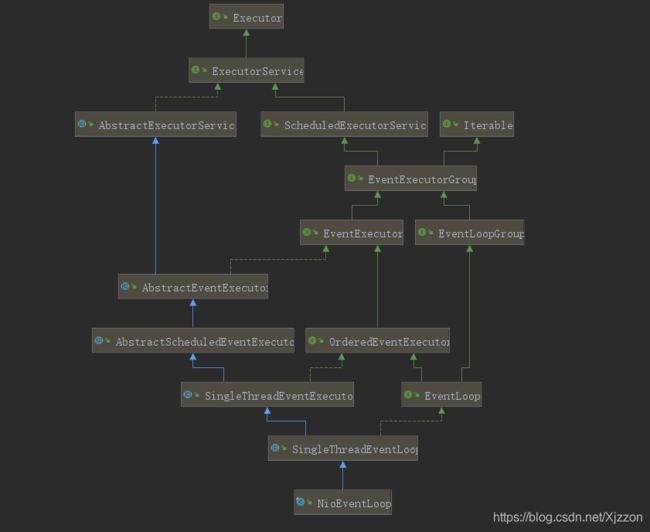
一、NioEventLoop的继承类图
- ScheduledExecutorService接口表示是一个定时任务接口,EventLoop可以接受定时任务。
- EventLoop接口: 一旦Channel注册了,就处理该Channel对应的所有I/O操作。
- SingleThreadEventExecutor表示这是一个单个线程的线程池。
- EventLoop是一个单例的线程池,里面含有一个死循环的线程不断地做着三件事情:监听端口,处理端口事件,处理队列事件。每个Eventloop都可以绑定多个Channel,而每个Channel始终只能由一个EventLoop来处理。
二、 源码
利用NioEventLoop执行一个任务,eventLoop.execute(task);
public void execute(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
// 判断当前线程是否是EventLoop线程
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
// 加入任务队列
addTask(task);
if (!inEventLoop) {
// 不是的话 启动eventLoop线程
startThread();
if (isShutdown()) {
boolean reject = false;
try {
if (removeTask(task)) {
reject = true;
}
} catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {
// The task queue does not support removal so the best thing we can do is to just move on and
// hope we will be able to pick-up the task before its completely terminated.
// In worst case we will log on termination.
}
if (reject) {
reject();
}
}
}
if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) {
// 唤醒selector
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}
看一下doStartThread方法
private void doStartThread() {
assert thread == null;
// 往executor提交一个任务,就是开始运行eventLoop了
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (interrupted) {
thread.interrupt();
}
boolean success = false;
updateLastExecutionTime();
try {
// 执行NioEventLoop的run方法,是一个循环
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run();
success = true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Unexpected exception from an event executor: ", t);
} finally {
for (;;) {
int oldState = state;
if (oldState >= ST_SHUTTING_DOWN || STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this, oldState, ST_SHUTTING_DOWN)) {
break;
}
}
// Check if confirmShutdown() was called at the end of the loop.
if (success && gracefulShutdownStartTime == 0) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Buggy " + EventExecutor.class.getSimpleName() + " implementation; " +
SingleThreadEventExecutor.class.getSimpleName() + ".confirmShutdown() must " +
"be called before run() implementation terminates.");
}
}
try {
// Run all remaining tasks and shutdown hooks.
for (;;) {
if (confirmShutdown()) {
break;
}
}
} finally {
try {
cleanup();
} finally {
FastThreadLocal.removeAll();
STATE_UPDATER.set(SingleThreadEventExecutor.this, ST_TERMINATED);
threadLock.release();
if (!taskQueue.isEmpty()) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("An event executor terminated with " +
"non-empty task queue (" + taskQueue.size() + ')');
}
}
terminationFuture.setSuccess(null);
}
}
}
}
});
}
EventLoop的run方法
protected void run() {
int selectCnt = 0;
for (;;) {
try {
int strategy;
try {
strategy = selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks());
switch (strategy) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT:
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
long curDeadlineNanos = nextScheduledTaskDeadlineNanos();
if (curDeadlineNanos == -1L) {
curDeadlineNanos = NONE; // nothing on the calendar
}
nextWakeupNanos.set(curDeadlineNanos);
try {
if (!hasTasks()) {
// 从通道中select事件,如果没有的话就阻塞一定时间
// curDeadlineNanos和下次定时任务执行时间有关
strategy = select(curDeadlineNanos);
}
} finally {
nextWakeupNanos.lazySet(AWAKE);
}
// fall through
default:
}
} catch (IOException e) {
rebuildSelector0();
selectCnt = 0;
handleLoopException(e);
continue;
}
// select的计数器,代表select的次数,非空循环时会清0
// 空循环时会累加。
selectCnt++;
cancelledKeys = 0;
needsToSelectAgain = false;
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;
boolean ranTasks;
if (ioRatio == 100) {
// ioRation为100,意味着不控制io比例
try {
if (strategy > 0) {
processSelectedKeys();
}
} finally {
// Ensure we always run tasks.
ranTasks = runAllTasks();
}
} else if (strategy > 0) {
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
//根据ioRatio计算定时任务应该要执行的时间
// ioRatio指的是io任务执行时间占全部时间的百分比
// 由此可以算出定时任务应该执行的时间
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
ranTasks = runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
} else {
// strategy意味着没有select到事件,执行最少数量的task
ranTasks = runAllTasks(0); // This will run the minimum number of tasks
}
if (ranTasks || strategy > 0) {
// ranTasks或者strategy > 0意味着本次循环不是空循环
if (selectCnt > MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS && logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row for Selector {}.",
selectCnt - 1, selector);
}
// 本次循环不是空循环就把selectCnt置为0
selectCnt = 0;
} else if (unexpectedSelectorWakeup(selectCnt)) { // Unexpected wakeup (unusual case)
// 空循环次数超出了阈值,已经重启生产了selector,也将selectCnt设置为 // 0
selectCnt = 0;
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
// Harmless exception - log anyway
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + " raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?",
selector, e);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
// Always handle shutdown even if the loop processing threw an exception.
try {
if (isShuttingDown()) {
closeAll();
if (confirmShutdown()) {
return;
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
}
}
三、总结
NioEventLoop就是不断地执行run方法,做三个事情:第一个是select事件,第二个是处理select出来的事件,第三个是处理队列里的任务。