【TF2.0】From_Residual_Networks_v2a
将Coursera 上吴恩达的教程《Convolutional Neural Networks》第2周的练习2代码转成TF2.0
import tensorflow as tf
from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow
from tensorflow.keras.utils import plot_model
from kt_utils import *
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image
def identity_block(X, f, filters, stage, block):
"""
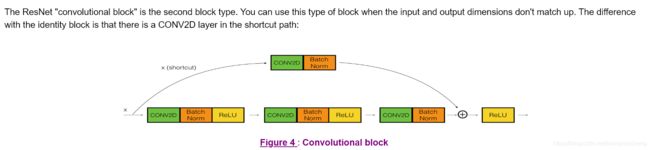
Implementation of the identity block as defined in Figure 4
Arguments:
X -- input tensor of shape (m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev)
f -- integer, specifying the shape of the middle CONV's window for the main path
filters -- python list of integers, defining the number of filters in the CONV layers of the main path
stage -- integer, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network
block -- string/character, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network
Returns:
X -- output of the identity block, tensor of shape (n_H, n_W, n_C)
"""
# defining name basis
conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
# Retrieve Filters
F1, F2, F3 = filters
# Save the input value. You'll need this later to add back to the main path.
X_shortcut = X
# First component of main path
X = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters = F1, kernel_size = (1, 1), strides = (1,1), padding = 'valid', name = conv_name_base + '2a', kernel_initializer = tf.keras.initializers.glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2a')(X)
X = tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu')(X)
# Second component of main path (≈3 lines)
X = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters = F2, kernel_size = (f, f), strides = (1,1), padding = 'same', name = conv_name_base + '2b', kernel_initializer = tf.keras.initializers.glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2b')(X)
X = tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu')(X)
# Third component of main path (≈2 lines)
X = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters = F3, kernel_size = (1, 1), strides = (1,1), padding = 'valid', name = conv_name_base + '2c', kernel_initializer = tf.keras.initializers.glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2c')(X)
# Final step: Add shortcut value to main path, and pass it through a RELU activation (≈2 lines)
X = tf.keras.layers.Add()([X_shortcut, X])
X = tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu')(X)
return Xnp.random.seed(1)
X = np.random.randn(3, 4, 4, 6).astype(np.float32)
A = identity_block(X, f = 2, filters = [2, 4, 6], stage = 1, block = 'a')
out = A.numpy()
print(type(out))
print(out.shape)
print(A[1][1][0])def convolutional_block(X, f, filters, stage, block, s = 2):
"""
Implementation of the convolutional block as defined in Figure 4
Arguments:
X -- input tensor of shape (m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev)
f -- integer, specifying the shape of the middle CONV's window for the main path
filters -- python list of integers, defining the number of filters in the CONV layers of the main path
stage -- integer, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network
block -- string/character, used to name the layers, depending on their position in the network
s -- Integer, specifying the stride to be used
Returns:
X -- output of the convolutional block, tensor of shape (n_H, n_W, n_C)
"""
# defining name basis
conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
# Retrieve Filters
F1, F2, F3 = filters
# Save the input value
X_shortcut = X
##### MAIN PATH #####
# First component of main path
X = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(F1, (1, 1), strides = (s,s), name = conv_name_base + '2a', kernel_initializer = tf.keras.initializers.glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2a')(X)
X = tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu')(X)
# Second component of main path (≈3 lines)
X = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(F2, (f, f), strides = (1,1), name = conv_name_base + '2b', padding = 'same', kernel_initializer = tf.keras.initializers.glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2b')(X)
X = tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu')(X)
# Third component of main path (≈2 lines)
X = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(F3, (1, 1), strides = (1,1), name = conv_name_base + '2c', padding = 'valid', kernel_initializer = tf.keras.initializers.glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '2c')(X)
##### SHORTCUT PATH #### (≈2 lines)
X_shortcut = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(F3, (1, 1), strides = (s,s), name = conv_name_base + '1', padding = 'valid', kernel_initializer = tf.keras.initializers.glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X_shortcut)
X_shortcut = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = bn_name_base + '1')(X_shortcut)
# Final step: Add shortcut value to main path, and pass it through a RELU activation (≈2 lines)
X = tf.keras.layers.Add()([X,X_shortcut])
X = tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu')(X)
return XX = np.random.randn(3, 4, 4, 6).astype(np.float32)
A = convolutional_block(X, f = 2, filters = [2, 4, 6], stage = 1, block = 'a')
out = A
print("out = " + str(out[1][1][0]))def ResNet50(input_shape = (64, 64, 3), classes = 6):
"""
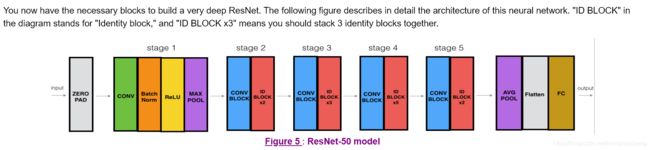
Implementation of the popular ResNet50 the following architecture:
CONV2D -> BATCHNORM -> RELU -> MAXPOOL -> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*2 -> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*3
-> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*5 -> CONVBLOCK -> IDBLOCK*2 -> AVGPOOL -> TOPLAYER
Arguments:
input_shape -- shape of the images of the dataset
classes -- integer, number of classes
Returns:
model -- a Model() instance in Keras
"""
# Define the input as a tensor with shape input_shape
X_input = tf.keras.layers.Input(input_shape)
# Zero-Padding
X = tf.keras.layers.ZeroPadding2D((3, 3))(X_input)
# Stage 1
X = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, (7, 7), strides = (2, 2), name = 'conv1', kernel_initializer = tf.keras.initializers.glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(axis = 3, name = 'bn_conv1')(X)
X = tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu')(X)
X = tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(X)
# Stage 2
X = convolutional_block(X, f = 3, filters = [64, 64, 256], stage = 2, block='a', s = 1)
X = identity_block(X, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='b')
X = identity_block(X, 3, [64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='c')
### START CODE HERE ###
# Stage 3 (≈4 lines)
X = convolutional_block(X, f = 3, filters = [128, 128, 512], stage = 3, block='a', s = 2)
X = identity_block(X, f = 3, filters = [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='b')
X = identity_block(X, f = 3, filters = [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='c')
X = identity_block(X, f = 3, filters = [128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='d')
# Stage 4 (≈6 lines)
X = convolutional_block(X, f = 3, filters = [256, 256, 1024], stage = 4, block='a', s = 2)
X = identity_block(X, f = 3, filters = [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='b')
X = identity_block(X, f = 3, filters = [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='c')
X = identity_block(X, f = 3, filters = [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='d')
X = identity_block(X, f = 3, filters = [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='e')
X = identity_block(X, f = 3, filters = [256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='f')
# Stage 5 (≈3 lines)
X = convolutional_block(X, f = 3, filters = [512, 512, 2048], stage = 5, block='a', s = 2)
X = identity_block(X, f = 3, filters = [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='b')
X = identity_block(X, f = 3, filters = [512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='c')
# AVGPOOL (≈1 line). Use "X = AveragePooling2D(...)(X)"
X = tf.keras.layers.AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(1, 1), padding="valid")(X)
### END CODE HERE ###
# output layer
X = tf.keras.layers.Flatten()(X)
X = tf.keras.layers.Dense(classes, activation='softmax', name='fc' + str(classes), kernel_initializer = tf.keras.initializers.glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
# Create model
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs = X_input, outputs = X, name='ResNet50')
return modelmodel = ResNet50(input_shape = (64, 64, 3), classes = 6)
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])# 辅助函数
import h5py
def load_dataset():
train_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/train_signs.h5', "r")
train_set_x_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_x"][:]) # your train set features
train_set_y_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_y"][:]) # your train set labels
test_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/test_signs.h5', "r")
test_set_x_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_x"][:]) # your test set features
test_set_y_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_y"][:]) # your test set labels
classes = np.array(test_dataset["list_classes"][:]) # the list of classes
train_set_y_orig = train_set_y_orig.reshape((1, train_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
test_set_y_orig = test_set_y_orig.reshape((1, test_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
return train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes
def convert_to_one_hot(Y, C):
Y = np.eye(C)[Y.reshape(-1)].T
return Y# 导入训练数据
X_train_orig, Y_train_orig, X_test_orig, Y_test_orig, classes = load_dataset()
# Normalize image vectors
X_train = X_train_orig/255.
X_test = X_test_orig/255.
# Convert training and test labels to one hot matrices
Y_train = convert_to_one_hot(Y_train_orig, 6).T
Y_test = convert_to_one_hot(Y_test_orig, 6).T
print ("number of training examples = " + str(X_train.shape[0]))
print ("number of test examples = " + str(X_test.shape[0]))
print ("X_train shape: " + str(X_train.shape))
print ("Y_train shape: " + str(Y_train.shape))
print ("X_test shape: " + str(X_test.shape))
print ("Y_test shape: " + str(Y_test.shape))# 开始训练模型
model.fit(X_train, Y_train, epochs = 2, batch_size = 32)#导入预训练好的模型:
# load the pretrain model:
model = tf.keras.models.load_model('ResNet50.h5') # 用模型进行预测
import scipy
img_path = 'images/my_image.jpg'
img = tf.keras.preprocessing.image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(64, 64))
x = image.img_to_array(img)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)
x = x/255.0
print('Input image shape:', x.shape)
my_image = scipy.misc.imread(img_path)
imshow(my_image)
print("class prediction vector [p(0), p(1), p(2), p(3), p(4), p(5)] = ")
print(model.predict(x))model.summary()
plot_model(model, to_file='model.png')