VINS-Mono代码阅读笔记(十三):posegraph中四自由度位姿优化
本篇笔记紧接着VINS-Mono代码阅读笔记(十二):将关键帧加入位姿图当中,来学习pose_graph当中的紧耦合优化部分。
在重定位完成之后,进行位姿图优化是为了将已经产生的所有位姿统一到一个全局一致的配置当中。如论文中展示的下图所示,参考帧处于世界坐标系下,当相机运动的时候![]() 会相对于参考帧发生变化。而由于重力向量始终不会发生变化,所以从重力方向得到的水平面也不会发生变化,进而该水平面对应的
会相对于参考帧发生变化。而由于重力向量始终不会发生变化,所以从重力方向得到的水平面也不会发生变化,进而该水平面对应的![]() 两个向量也不会发生变换。所以,系统中需要计算并且优化的向量只有
两个向量也不会发生变换。所以,系统中需要计算并且优化的向量只有![]() (也就是位置和旋转),这就是4自由度优化的由来。
(也就是位置和旋转),这就是4自由度优化的由来。
1.加入关键帧到位姿图当中
通过代码可以发现,当滑动窗口完成一次边缘化(滑出最旧的帧或者滑动窗口中倒数第二帧)后,在后边的pubKeyframe函数中会将the second latest frame关键帧的位姿信息作为topic发出来。pose_graph节点中接收到这个topic后,构造出对应的关键帧并加入位姿图当中。
1)相关代码
vins-estimator中发送关键帧位姿的代码如下:
void pubKeyframe(const Estimator &estimator)
{
// pub camera pose, 2D-3D points of keyframe
//estimator.marginalization_flag == 0,表示MARGIN_OLD,边缘化删除了最旧的关键帧
//estimator.solver_flag == Estimator::SolverFlag::NON_LINEAR表示视觉和惯导初始化成功
if (estimator.solver_flag == Estimator::SolverFlag::NON_LINEAR && estimator.marginalization_flag == 0)
{
int i = WINDOW_SIZE - 2;
//Vector3d P = estimator.Ps[i] + estimator.Rs[i] * estimator.tic[0];
Vector3d P = estimator.Ps[i];
Quaterniond R = Quaterniond(estimator.Rs[i]);
nav_msgs::Odometry odometry;
odometry.header = estimator.Headers[WINDOW_SIZE - 2];
odometry.header.frame_id = "world";
odometry.pose.pose.position.x = P.x();
odometry.pose.pose.position.y = P.y();
odometry.pose.pose.position.z = P.z();
odometry.pose.pose.orientation.x = R.x();
odometry.pose.pose.orientation.y = R.y();
odometry.pose.pose.orientation.z = R.z();
odometry.pose.pose.orientation.w = R.w();
//printf("time: %f t: %f %f %f r: %f %f %f %f\n", odometry.header.stamp.toSec(), P.x(), P.y(), P.z(), R.w(), R.x(), R.y(), R.z());
pub_keyframe_pose.publish(odometry);而在pose-graph中将该关键帧加入位姿图的代码如下:
/**
* process线程入口函数
*/
void process()
{
.......
//创建关键帧
KeyFrame* keyframe = new KeyFrame(pose_msg->header.stamp.toSec(), frame_index,
T, R,
image,point_3d, point_2d_uv, point_2d_normal, point_id, sequence);
m_process.lock();
start_flag = 1;
//位姿图中加入关键帧,flag_detect_loop设置为1
posegraph.addKeyFrame(keyframe, 1);2)位姿图中的顶点和边
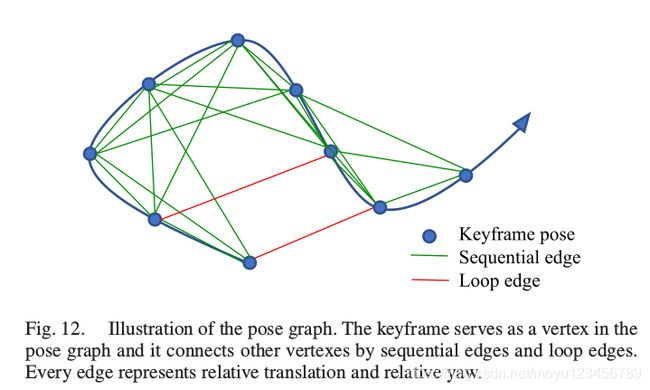
每一个关键帧在位姿图中作为一个顶点存在,它和其他关键帧以序列变和闭环边两种类型的边进行连接,如下图所示:
序列边(Sequential Edge):
一个关键帧将与其前边的多个关键帧建立序列边(如上图所示)。一个序列边表示两个关键帧之间的相对变换,这个可以直接从VIO中得出。假设关键帧![]() 和其前边的一个关键帧
和其前边的一个关键帧![]() ,两个关键帧构成的序列边只包含相对位置
,两个关键帧构成的序列边只包含相对位置![]() 和偏航角
和偏航角![]() ,则这两个值表达如下:
,则这两个值表达如下:
![]()
![]()
闭环边(Loop-Closure Edge):
如果一个关键帧有闭环连接,那么它在位姿图中和闭环帧之间的连接为闭环边。相似的,闭环边只包括一个4自由度的相对位姿变换,定义和上边的序列变相同。闭环边的值,是通过重定位得到的。
2.四自由度的位姿图优化
我们定义关键帧![]() 和
和![]() 之间的边的最小化残差如下:
之间的边的最小化残差如下:
这里的![]() 和
和![]() 两个值,是从单目VIO中估计得到的roll和pitch的角度,是固定的。
两个值,是从单目VIO中估计得到的roll和pitch的角度,是固定的。
序列边和闭环边的所有图通过最小化下面的损失函数来进行优化:
这里![]() 是所有序列变的集合,
是所有序列变的集合,![]() 是所有闭环边的集合。尽管紧耦合的重定位已经帮助消除了错误的闭环,在这里增加另一个Huber核函数
是所有闭环边的集合。尽管紧耦合的重定位已经帮助消除了错误的闭环,在这里增加另一个Huber核函数![]() 以进一步减少任何可能的错误闭环的影响。
以进一步减少任何可能的错误闭环的影响。
优化部分在pose_graph节点构造posegraph对象的时候,在构造函数当中新启了一个线程来完成。PoseGraph的构造函数代码如下:
/**
* PoseGraph构造函数
*/
PoseGraph::PoseGraph()
{
posegraph_visualization = new CameraPoseVisualization(1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0);
posegraph_visualization->setScale(0.1);
posegraph_visualization->setLineWidth(0.01);
//创建位姿优化线程
t_optimization = std::thread(&PoseGraph::optimize4DoF, this);
earliest_loop_index = -1;
t_drift = Eigen::Vector3d(0, 0, 0);
yaw_drift = 0;
r_drift = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity();
w_t_vio = Eigen::Vector3d(0, 0, 0);
w_r_vio = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity();
global_index = 0;
sequence_cnt = 0;
sequence_loop.push_back(0);
base_sequence = 1;
}位姿优化的线程入口函数为optimize4DoF,optimize4DoF代码如下:
/**
* 位姿图中的优化,这里是4个自由度的位姿优化
*/
void PoseGraph::optimize4DoF()
{
while(true)
{
int cur_index = -1;
int first_looped_index = -1;
m_optimize_buf.lock();
//从优化队列当中获取最新的一个关键帧的index
while(!optimize_buf.empty())
{
cur_index = optimize_buf.front();
//earliest_loop_index当中存放的是数据库中第一个和滑动窗口中关键帧形成闭环的关键帧的index
first_looped_index = earliest_loop_index;
optimize_buf.pop();
}
m_optimize_buf.unlock();
//optimize_buf中取出来的cur_index都是闭环帧的index
if (cur_index != -1)
{
printf("optimize pose graph \n");
TicToc tmp_t;
m_keyframelist.lock();
KeyFrame* cur_kf = getKeyFrame(cur_index);
//max_length为要优化的变量最大个数
int max_length = cur_index + 1;
// w^t_i w^q_i
double t_array[max_length][3];//平移数组,其中存放每个关键帧的平移向量
Quaterniond q_array[max_length];//旋转数组,其中存放每个关键帧的旋转四元数
double euler_array[max_length][3];
double sequence_array[max_length];
ceres::Problem problem;
ceres::Solver::Options options;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::SPARSE_NORMAL_CHOLESKY;
//options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true;
//options.max_solver_time_in_seconds = SOLVER_TIME * 3;
options.max_num_iterations = 5;
ceres::Solver::Summary summary;
ceres::LossFunction *loss_function;
loss_function = new ceres::HuberLoss(0.1);
//loss_function = new ceres::CauchyLoss(1.0);
//AngleLocalParameterization类的主要作用是指定yaw角优化变量的迭代更新,重载了括号运算
ceres::LocalParameterization* angle_local_parameterization =
AngleLocalParameterization::Create();
list::iterator it;
int i = 0;
//遍历关键帧列表
for (it = keyframelist.begin(); it != keyframelist.end(); it++)
{
//first_looped_index为第一次闭环帧的index,需要优化的关键帧为从第一次闭环帧到当前帧间的所有关键帧
if ((*it)->index < first_looped_index)
continue;
(*it)->local_index = i;
Quaterniond tmp_q;
Matrix3d tmp_r;
Vector3d tmp_t;
//获取关键帧it的位姿
(*it)->getVioPose(tmp_t, tmp_r);
tmp_q = tmp_r;
t_array[i][0] = tmp_t(0);
t_array[i][1] = tmp_t(1);
t_array[i][2] = tmp_t(2);
q_array[i] = tmp_q;
//将矩阵转换为向量
Vector3d euler_angle = Utility::R2ypr(tmp_q.toRotationMatrix());
euler_array[i][0] = euler_angle.x();
euler_array[i][1] = euler_angle.y();
euler_array[i][2] = euler_angle.z();
sequence_array[i] = (*it)->sequence;
//将关键帧列表中所有index>=first_looped_index的关键帧的位姿加入到参数块当中
problem.AddParameterBlock(euler_array[i], 1, angle_local_parameterization);
problem.AddParameterBlock(t_array[i], 3);
//设置约束:如果该帧是最早的闭环帧的情况下,则固定它的位姿
if ((*it)->index == first_looped_index || (*it)->sequence == 0)
{
problem.SetParameterBlockConstant(euler_array[i]);
problem.SetParameterBlockConstant(t_array[i]);
}
//add edge 这里添加的是序列边,是指通过VIO计算的两帧之间的相对位姿,每帧分别与其前边最多四帧构成序列边
/**
* 顺序边的测量方程:p̂_{ij}^{i} = {R̂_i^w}^{-1} (p̂_j^w - p̂_i^w)
* \hat{ψ}_ij = \hat{ψ}_j − \hat{ψ̂}_i
* 两个关键帧之间的相对位姿,由两个关键帧之间的VIO位姿估计变换得到
* |------------------------------------|
* | |----------------------------|
* | | |-------------------|
* | | | |---------|
* |帧1| |帧2| |帧3| |帧4| |帧5|
*/
for (int j = 1; j < 5; j++)
{
if (i - j >= 0 && sequence_array[i] == sequence_array[i-j])
{
Vector3d euler_conncected = Utility::R2ypr(q_array[i-j].toRotationMatrix());
//p̂_j^w - p̂_i^w 计算平移量的偏差
Vector3d relative_t(t_array[i][0] - t_array[i-j][0], t_array[i][1] - t_array[i-j][1], t_array[i][2] - t_array[i-j][2]);
//p̂_{ij}^{i} = {R̂_i^w}^{-1} (p̂_j^w - p̂_i^w)
//p̂ ij= (R̂ iw ) (p̂ jw − p̂ iw )
relative_t = q_array[i-j].inverse() * relative_t;
//ψ̂ _ij = ψ̂ _j − ψ̂ _i
double relative_yaw = euler_array[i][0] - euler_array[i-j][0];
ceres::CostFunction* cost_function = FourDOFError::Create( relative_t.x(), relative_t.y(), relative_t.z(),
relative_yaw, euler_conncected.y(), euler_conncected.z());
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, NULL, euler_array[i-j],
t_array[i-j],
euler_array[i],
t_array[i]);
}
}
//add loop edge
//这里添加的是闭环边,是指检测到闭环的两帧
if((*it)->has_loop)
{
assert((*it)->loop_index >= first_looped_index);
int connected_index = getKeyFrame((*it)->loop_index)->local_index;
Vector3d euler_conncected = Utility::R2ypr(q_array[connected_index].toRotationMatrix());
Vector3d relative_t;
relative_t = (*it)->getLoopRelativeT();
double relative_yaw = (*it)->getLoopRelativeYaw();
ceres::CostFunction* cost_function = FourDOFWeightError::Create( relative_t.x(), relative_t.y(), relative_t.z(),
relative_yaw, euler_conncected.y(), euler_conncected.z());
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, loss_function, euler_array[connected_index],
t_array[connected_index],
euler_array[i],
t_array[i]);
}
if ((*it)->index == cur_index)
break;
i++;
}
m_keyframelist.unlock();
//开始优化
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
//std::cout << summary.BriefReport() << "\n";
//printf("pose optimization time: %f \n", tmp_t.toc());
/*
for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++)
{
printf("optimize i: %d p: %f, %f, %f\n", j, t_array[j][0], t_array[j][1], t_array[j][2] );
}
*/
m_keyframelist.lock();
//优化完成,使用优化后的位姿来更新关键帧列表中index大于等于first_looped_index的所有关键帧的位姿
i = 0;
for (it = keyframelist.begin(); it != keyframelist.end(); it++)
{
if ((*it)->index < first_looped_index)
continue;
Quaterniond tmp_q;
//向量转换为矩阵
tmp_q = Utility::ypr2R(Vector3d(euler_array[i][0], euler_array[i][1], euler_array[i][2]));
Vector3d tmp_t = Vector3d(t_array[i][0], t_array[i][1], t_array[i][2]);
Matrix3d tmp_r = tmp_q.toRotationMatrix();
(*it)-> updatePose(tmp_t, tmp_r);
if ((*it)->index == cur_index)
break;
i++;
}
//根据计算出当前帧的drift,更新全部关键帧位姿
Vector3d cur_t, vio_t;
Matrix3d cur_r, vio_r;
//获取优化后当前帧的位姿cur_t,cur_r
cur_kf->getPose(cur_t, cur_r);
//获取优化前有漂移的当前帧的位姿vio_t,vio_r
cur_kf->getVioPose(vio_t, vio_r);
m_drift.lock();
yaw_drift = Utility::R2ypr(cur_r).x() - Utility::R2ypr(vio_r).x();
r_drift = Utility::ypr2R(Vector3d(yaw_drift, 0, 0));
t_drift = cur_t - r_drift * vio_t;
m_drift.unlock();
//cout << "t_drift " << t_drift.transpose() << endl;
//cout << "r_drift " << Utility::R2ypr(r_drift).transpose() << endl;
//cout << "yaw drift " << yaw_drift << endl;
it++;
//下面代码为把当前关键帧it之后的关键帧的位姿通过求解的偏移量转换到world坐标系下
for (; it != keyframelist.end(); it++)
{
Vector3d P;
Matrix3d R;
(*it)->getVioPose(P, R);
P = r_drift * P + t_drift;
R = r_drift * R;
(*it)->updatePose(P, R);
}
m_keyframelist.unlock();
//优化完后更新path
updatePath();
}
std::chrono::milliseconds dura(2000);
std::this_thread::sleep_for(dura);
}
} 这里除了梳理优化的函数中的代码流程,还需要对比以上的残差公式来看一下序列边和闭环边的残差计算。FourDOFError类中的operator()中是序列边的残差计算代码。
struct FourDOFError
{
FourDOFError(double t_x, double t_y, double t_z, double relative_yaw, double pitch_i, double roll_i)
:t_x(t_x), t_y(t_y), t_z(t_z), relative_yaw(relative_yaw), pitch_i(pitch_i), roll_i(roll_i){}
template
bool operator()(const T* const yaw_i, const T* ti, const T* yaw_j, const T* tj, T* residuals) const
{
T t_w_ij[3];
t_w_ij[0] = tj[0] - ti[0];
t_w_ij[1] = tj[1] - ti[1];
t_w_ij[2] = tj[2] - ti[2];
// euler to rotation
T w_R_i[9];
YawPitchRollToRotationMatrix(yaw_i[0], T(pitch_i), T(roll_i), w_R_i);
// rotation transpose
T i_R_w[9];
//求出旋转矩阵的转置
RotationMatrixTranspose(w_R_i, i_R_w);
// rotation matrix rotate point
T t_i_ij[3];
RotationMatrixRotatePoint(i_R_w, t_w_ij, t_i_ij);
//计算残差
residuals[0] = (t_i_ij[0] - T(t_x));
residuals[1] = (t_i_ij[1] - T(t_y));
residuals[2] = (t_i_ij[2] - T(t_z));
residuals[3] = NormalizeAngle(yaw_j[0] - yaw_i[0] - T(relative_yaw));
return true;
}
static ceres::CostFunction* Create(const double t_x, const double t_y, const double t_z,
const double relative_yaw, const double pitch_i, const double roll_i)
{
return (new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<
FourDOFError, 4, 1, 3, 1, 3>(
new FourDOFError(t_x, t_y, t_z, relative_yaw, pitch_i, roll_i)));
}
double t_x, t_y, t_z;
double relative_yaw, pitch_i, roll_i;
}; FourDOFWeightError类中的operator()是闭环边的残差计算代码。
struct FourDOFWeightError
{
FourDOFWeightError(double t_x, double t_y, double t_z, double relative_yaw, double pitch_i, double roll_i)
:t_x(t_x), t_y(t_y), t_z(t_z), relative_yaw(relative_yaw), pitch_i(pitch_i), roll_i(roll_i){
weight = 1;
}
template
bool operator()(const T* const yaw_i, const T* ti, const T* yaw_j, const T* tj, T* residuals) const
{
T t_w_ij[3];
t_w_ij[0] = tj[0] - ti[0];
t_w_ij[1] = tj[1] - ti[1];
t_w_ij[2] = tj[2] - ti[2];
// euler to rotation
T w_R_i[9];
YawPitchRollToRotationMatrix(yaw_i[0], T(pitch_i), T(roll_i), w_R_i);
// rotation transpose
T i_R_w[9];
RotationMatrixTranspose(w_R_i, i_R_w);
// rotation matrix rotate point
T t_i_ij[3];
RotationMatrixRotatePoint(i_R_w, t_w_ij, t_i_ij);
//计算残差
residuals[0] = (t_i_ij[0] - T(t_x)) * T(weight);
residuals[1] = (t_i_ij[1] - T(t_y)) * T(weight);
residuals[2] = (t_i_ij[2] - T(t_z)) * T(weight);
residuals[3] = NormalizeAngle((yaw_j[0] - yaw_i[0] - T(relative_yaw))) * T(weight) / T(10.0);
return true;
}
static ceres::CostFunction* Create(const double t_x, const double t_y, const double t_z,
const double relative_yaw, const double pitch_i, const double roll_i)
{
return (new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<
FourDOFWeightError, 4, 1, 3, 1, 3>(
new FourDOFWeightError(t_x, t_y, t_z, relative_yaw, pitch_i, roll_i)));
}
double t_x, t_y, t_z;
double relative_yaw, pitch_i, roll_i;
double weight;
}; VINS-Mono代码阅读笔记(十四):posegraph的存储和加载