【MyBatis】mybatis执行流程与缓存机制分析
1. 编程式使用mybatis
首先,我们直观地看一下怎样编程式(非配置式)使用mybatis作为ORM框架实现数据库的基本操作。
private static void testId() throws IOException {
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
// 获取代理 -> MapperProxy
StudentDao studentDao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
Student student = new Student();
student.setStudentName("AutoIncrementId");
student.setStudentNumber("2014216003");
// sqlSession.insert("insertEntry", student);
studentDao.insertEntry(student);
System.out.println(student.getId());// 3
// commit & close
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
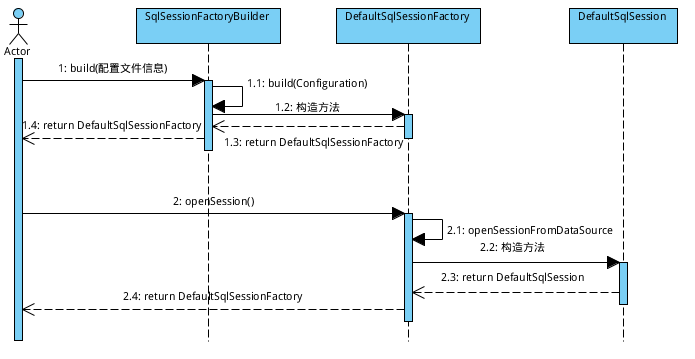
可以清晰地看到一共分为三个步骤:第一步,使用mybatis配置文件创建SqlSessionFactory,并打开一个sqlSession;第二步,获取代理MapperProxy类;第三步,执行数据库基本操作。
2. 第一步,获取sqlSession
图片来源: 深入浅出Mybatis系列(十)---SQL执行流程分析(源码篇)
3. 第二步,获取代理MapperProxy
3.0
sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao. class );
sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao. class );
3.1 DefaultSqlSession
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type)
configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
3.2 Configuration
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession)
mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);3.3 MapperRegistry
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession)
mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); 3.4 MapperProxyFactory
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession)
(T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);3.5 Proxy
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
图片来源: 深入浅出Mybatis系列(十)---SQL执行流程分析(源码篇)
4. 第三步,执行数据库操作
4.1 MapperProxy
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable
mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);4.2 MapperMethod
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args)
sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param)4.3 DefaultSqlSession
public int insert(String statement, Object parameter) update(statement, parameter);public int update(String statement, Object parameter)
executor .update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter));
4.4 CachingExcutor
public int
update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject)
throws
SQLException
delegate .update(ms, parameterObject);
4.5 BaseExcutor
delegate .update(ms, parameterObject);
4.5 BaseExcutor
public int
update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter)
throws
SQLException
doUpdate(ms, parameter);
doUpdate(ms, parameter);
4.6 SimpleExcutor
public int
doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter)
handler.update(stmt);
4.7 PreparedStatementHandler
handler.update(stmt);
4.7 PreparedStatementHandler
public int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
ps.execute();
int rows = ps.getUpdateCount();
Object parameterObject = boundSql.getParameterObject();
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator();
keyGenerator.processAfter(executor, mappedStatement, ps, parameterObject);
return rows;
}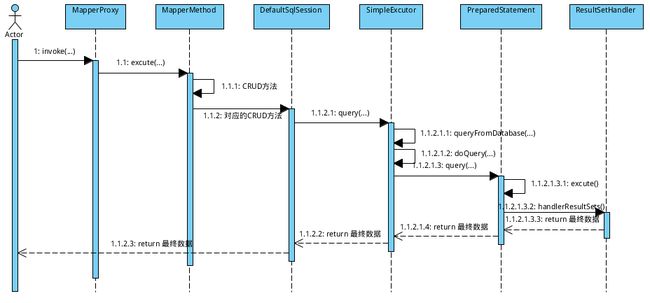
图片来源: 深入浅出Mybatis系列(十)---SQL执行流程分析(源码篇)
5. MyBatis缓存机制分析
private static void testCache() throws IOException {
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config2.xml");
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
long id = 1L;
Student student = new Student();
student.setStudentName("Ethan");
student.setStudentNumber("2014216001");
sqlSession.insert("insertEntry", student);
System.out.println(student.getId());// null
// query from db
// 加入一级缓存和二级transactional缓存,由于sqlsession未commit,所以二级transactional缓存的代理未真正缓存
student = sqlSession.selectOne("selectByKey", id);
System.out.println(student.getId());
System.out.println(student.getStudentName());
// local cache hit
// 由于二级缓存未真正缓存,只能从一级缓存那里命中
student = sqlSession.selectOne("selectByKey", id);
System.out.println(student.getId());
System.out.println(student.getStudentName());
// commit
sqlSession.commit();
// sqlsession在commit之后,transactional缓存的代理才真正缓存起来,二级缓存命中
student = sqlSession.selectOne("selectByKey", id);
System.out.println(student.getId());
System.out.println(student.getStudentName());
// update 会clear未commit的transactional缓存中的内容,同时设置标志位clearOnCommit为true,会clear掉local cache
student.setStudentName("Hunt");
int update = sqlSession.update("updateByKey", student);
System.out.println("update: " + update);
// select again
// 在二级缓存中找到了缓存,但是由于clearOnCommit标志位为true,所以返回null
student = sqlSession.selectOne("selectByKey", id);
System.out.println(student.getId());
System.out.println(student.getStudentName());
// commit & close
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
6. References
深入浅出Mybatis系列(十)---SQL执行流程分析(源码篇)
MyBatis 缓存
MyBatis 缓存机制深度解剖 / 自定义二级缓存
mybatis的缓存机制(一级缓存二级缓存和刷新缓存)和mybatis整合ehcache