探究UIScrollView及其子类布局和适配的影响因素
前言
很久之前写过两篇文章, 都是关于适配布局的, 分别是iOS6与iOS7屏幕适配 edgesForExtendedLayout和影响屏幕适配的因素及tableview的ContentSize不正确的问题。当然也欢迎大家先看下这两篇文章预热一下, 因为这篇文章其实是对上面这两篇的不足补充和勘正。
今天重新总结一下关于UIScrollView及其子类的布局的问题及影响因素, 只是本文是以TableView为例的, 请大家注意。
UIScrollView布局的影响因素
博主一共发现了9个UIScrollView布局的影响因素。 我把它们归为两个类型, 一类通过影响当前ViewController的View的frame从而影响布局的; 另一类是通过影响scrollView的contentInset从而影响布局的。接下来的每一个因素都会对ScrollView的布局产生影响。
第一类: navigationBar.translucent, vc.edgesForExtendedLayout, vc.extendedLayoutIncludesOpaqueBars。
第二类: scrollView.contentInset, vc.automaticallyAdjustsScrollViewInsets, navigationBar/statusBar的隐藏, NavigationBar/TabBar的有无, TabBar隐藏的方式, 第一个addSubview的是不是当前的scrollView。
iOS11之后, API对于UIScrollView和其子类又做了一些调整, 所以第二类影响因素又分为iOS10及之前版本的影响因素和iOS11及之后版本的影响因素。
而且从iOS11开始, 除了之前的影响因素还多了两个别的因素:
contentInsetAdjustmentBehavior和 additionalSafeAreaInsets。
一个默认条件下的例子
这里我用
UITabBarViewController->UINavigationController->UIViewController->UITableView的结构来进行举例。
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// self.navigationController.navigationBar.translucent = NO;
// self.extendedLayoutIncludesOpaqueBars = YES;
// self.edgesForExtendedLayout = UIRectEdgeNone;
// self.navigationController.navigationBar.hidden = YES;
// self.automaticallyAdjustsScrollViewInsets = NO;
// [self createAnyView];
[self createTableView];
if (@available(iOS 11.0, *)) {
// _tableView.contentInsetAdjustmentBehavior = UIScrollViewContentInsetAdjustmentNever;
// self.additionalSafeAreaInsets = UIEdgeInsetsMake(80.0f, 0.0f, 30.0f, 0.0f);
}
}
- (void)viewWillAppear:(BOOL)animated {
[super viewWillAppear:animated];
[self printRelatedParameters];
}
- (void)viewDidAppear:(BOOL)animated {
[super viewDidAppear:animated];
[self printRelatedParameters];
}
- (void)createTableView {
self.tableView = [[UITableView alloc]initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, kWidth, kHeight) style:UITableViewStylePlain];
_tableView.backgroundColor = [UIColor lightGrayColor];
_tableView.delegate = self;
_tableView.dataSource = self;
[self.view addSubview:_tableView];
[_tableView registerClass:[UITableViewCell class] forCellReuseIdentifier:@"cell"];
UILabel *header = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, kWidth, 64)];
header.text = @"This is header";
header.textAlignment = NSTextAlignmentCenter;
header.backgroundColor = [UIColor cyanColor];
_tableView.tableHeaderView = header;
UILabel *footer = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, kWidth, 49)];
footer.text = @"This is footer";
footer.textAlignment = NSTextAlignmentCenter;
footer.backgroundColor = [UIColor purpleColor];
_tableView.tableFooterView = footer;
}
#pragma mark - UITableViewDelegate/UITableViewDataSource
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView {
return 1;
}
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section {
return 30;
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:@"cell" forIndexPath:indexPath];
cell.textLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"The Num of %ld", indexPath.row];
return cell;
}
- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
return 40;
}
- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
[self printRelatedParameters];
}
- (void)printRelatedParameters {
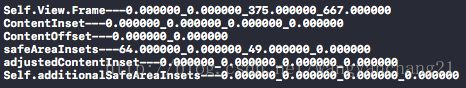
NSLog(@"ContentInset---%f_%f_%f_%f", _tableView.contentInset.top, _tableView.contentInset.left, _tableView.contentInset.bottom, _tableView.contentInset.right);
NSLog(@"ContentOffset---%f_%f", _tableView.contentOffset.x, _tableView.contentOffset.y);
NSLog(@"Self.View.Frame---%f_%f_%f_%f", self.view.frame.origin.x, self.view.frame.origin.y, self.view.frame.size.width, self.view.frame.size.height);
if (@available(iOS 11.0, *)) {
NSLog(@"safeAreaInsets---%f_%f_%f_%f", _tableView.safeAreaInsets.top, _tableView.safeAreaInsets.left, _tableView.safeAreaInsets.bottom, _tableView.safeAreaInsets.right);
NSLog(@"adjustedContentInset---%f_%f_%f_%f", _tableView.adjustedContentInset.top, _tableView.adjustedContentInset.left, _tableView.adjustedContentInset.bottom, _tableView.adjustedContentInset.right);
NSLog(@"Self.additionalSafeAreaInsets---%f_%f_%f_%f", self.additionalSafeAreaInsets.top, self.additionalSafeAreaInsets.left, self.additionalSafeAreaInsets.bottom, self.additionalSafeAreaInsets.right);
}
NSLog(@"\n\n");
}
效果是这样的:

第一类影响因素
navigationBar.translucent
@property(nonatomic,assign,getter=isTranslucent) BOOL translucent NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(3_0) UI_APPEARANCE_SELECTOR; // Default is NO on iOS 6 and earlier. Always YES if barStyle is set to UIBarStyleBlackTranslucent
导航栏透明状态影响布局, iOS6及之前默认为不透明, 之后就默认为透明的了. 这也是为什么 iOS6和 iOS7在添加视图时, frame 不一致需要适配的区别之处.
这个属性影响的是当前VC.View.frame, 在默认的布局下, translucent为YES, 即导航栏为半透明, 此时self.View.Frame的值为0.000000_0.000000_375.000000_667.000000.
self.navigationController.navigationBar.translucent = NO;当我们把此属性改为NO后, self.View.Frame的值为0.000000_64.000000_375.000000_603.000000.

默认属性下, 向上滑动tableView, 浅蓝色的header是可以透过NavigationBar的, 修改translucent属性为NO后, 正是因为VC的view布局不在navigationBar底下了, 所以这是看不到浅蓝色的header的。
edgesForExtendedLayout
@property(nonatomic,assign) BOOL extendedLayoutIncludesOpaqueBars NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(7_0); // Defaults to NO, but bars are translucent by default on 7_0.
This property is applied only to view controllers that are embedded in a container such as UINavigationController. The window’s root view controller does not react to this property. The default value of this property is UIRectEdgeAll.
这个枚举如下:
typedef NS_OPTIONS(NSUInteger, UIRectEdge) {
UIRectEdgeNone = 0,
UIRectEdgeTop = 1 << 0,
UIRectEdgeLeft = 1 << 1,
UIRectEdgeBottom = 1 << 2,
UIRectEdgeRight = 1 << 3,
UIRectEdgeAll = UIRectEdgeTop | UIRectEdgeLeft | UIRectEdgeBottom | UIRectEdgeRight
} NS_ENUM_AVAILABLE_IOS(7_0);我这里的控制器是既有TabBar又有NavigationBar的, 所以, 在默认值UIRectEdgeAll下, 当前控制器就做了上面和下面的延展布局。Self.View.Frame的值为0.000000_0.000000_375.000000_667.000000。
self.edgesForExtendedLayout = UIRectEdgeNone;当我将此属性改变为UIRectEdgeNone时, 上面和下面的延展全部会禁止。Self.View.Frame的值为0.000000_64.000000_375.000000_554.000000, 这说明view从导航栏开始布局, 而且高度为 667-64-49。

这里footer显示不全的原因就是VC的View的高度比tableView的高度小。
extendedLayoutIncludesOpaqueBars
@property(nonatomic,assign) BOOL extendedLayoutIncludesOpaqueBars NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(7_0); // Defaults to NO, but bars are translucent by default on 7_0.
A Boolean value indicating whether or not the extended layout includes opaque bars.
The default value of this property is NO.
这个属性是指是否在不透明导航栏情况下延展布局。
首先要为默认条件添加一行代码:
self.navigationController.navigationBar.translucent = NO;在导航栏不透明, extendedLayoutIncludesOpaqueBars又为默认值NO的情况下, 当然这个效果就是我们所说的第一条中的图片。self.View.Frame的值为0.000000_64.000000_375.000000_603.000000.
当我们将此属性改为YES:
self.extendedLayoutIncludesOpaqueBars = YES;此时self.View.Frame的值为0.000000_0.000000_375.000000_667.000000.

第二类影响因素(iOS10及之前版本)
scrollView.contentInset
@property(nonatomic) UIEdgeInsets contentInset; // default UIEdgeInsetsZero. add additional scroll area around content
The distance that the content view is inset from the enclosing scroll view.
Use this property to add to the scrolling area around the content. The unit of size is points. The default value is UIEdgeInsetsZero.
关于ScrollView的这个属性, 初始值为0, 所有对contentInset值的自动调整都是在viewWillAppear和viewDidAppear 之间进行调整的。默认条件下, viewWillAppear中打印ContentInset—0.000000_0.000000_0.000000_0.000000, viewDidAppear中打印ContentInset—64.000000_0.000000_49.000000_0.000000。
!!!特别注意!!!
正常情况下想要设置contentInset的值需要在viewDidLoad中进行. 需要注意的是, 设置contentInset值并不是覆盖了原值, 而是与原值进行了各项相加的处理。
比如, 我在创建tableView的时候, 添加一行代码:
_tableView.contentInset = UIEdgeInsetsMake(-64, 0, 0, 0);默认值top应该是64的, 设置新值后并没有覆盖, 而应该是-64+64=0;
这时, 打印的结果为: viewWillAppear中打印ContentInset—-64.000000_0.000000_0.000000_0.000000, viewDidAppear中打印ContentInset–ContentInset—0.000000_0.000000_49.000000_0.000000。

automaticallyAdjustsScrollViewInsets
@property(nonatomic,assign) BOOL automaticallyAdjustsScrollViewInsets API_DEPRECATED(“Use UIScrollView’s contentInsetAdjustmentBehavior instead”, ios(7.0,11.0),tvos(7.0,11.0)); // Defaults to YES
A Boolean value that indicates whether the view controller should automatically adjust its scroll view insets.
The default value of this property is YES, which lets container view controllers know that they should adjust the scroll view insets of this view controller’s view to account for screen areas consumed by a status bar, search bar, navigation bar, toolbar, or tab bar. Set this property to NO if your view controller implementation manages its own scroll view inset adjustments.
这个属性为当前控制器是否要自动调整contentInset, 默认为YES。
而且这个属性在iOS7.0开始启用, iOS11开始废弃, 被UIScrollView的 contentInsetAdjustmentBehavior属性所替代(它的具体介绍请看下文)。
默认条件下, viewWillAppear中打印ContentInset—0.000000_0.000000_0.000000_0.000000, viewDidAppear中打印ContentInset—64.000000_0.000000_49.000000_0.000000。
当修改其值为NO后,
self.automaticallyAdjustsScrollViewInsets = NO;修改后控制器不会根据系统的默认情况自动调整contentInset了, 所以在viewWillAppear中打印ContentInset—0.000000_0.000000_0.000000_0.000000, viewDidAppear中打印ContentInset—0.000000_0.000000_0.000000_0.000000。

NavigationBar/TabBar 的有无
就如上面说过的, NavigationBar和TabBar的存在才是以上那些影响因素的前提。如果没有它们这些属性是无效果的, 只有它们的存在才能通过这些属性影响ScrollView的布局。没有导航栏和TabBar的情况是这样的:
NavigationBar/StatusBar 的隐藏
默认情况下NavigationBar和StatusBar都是不隐藏的, 当我们设置NavigationBar的hide为YES后, 会有什么显示效果?

NavigationBar和StatusBar都隐藏后显示效果呢?

如图, 我们看到的, NavigationBar隐藏后, 在默认自动调整contentInset的情况下, 其top的值为20。所以, 想要做透明导航栏又不隐藏状态栏的需求的, 需要注意下这里。 当然使用上面的设置scrollView.contentInset的方法可以解决此问题。
TabBar 隐藏的方式
一般的App在每个Tab首页的VC才会展示出TabBar, 而在第二层页面开始就要隐藏TabBar了。但是TabBar不同的隐藏方式, 会产生某些影响, 从而影响scrollView.contentInset。
关于TabBar的隐藏方式有兴趣的可以了解我的另一篇文章iOS各种 bar 隐藏的方法。
比如说我们使用的是系统的TabBar, 通过hidesBottomBarWhenPushed方法进行隐藏TabBar和tabBar.hidden 两种方式来对比。
- (BOOL) hidesBottomBarWhenPushed {
return YES;
}此方法下, viewWillAppear中打印ContentInset—0.000000_0.000000_0.000000_0.000000, viewDidAppear中打印ContentInset—64.000000_0.000000_0.000000_0.000000。
- (void)viewWillAppear:(BOOL)animated {
[super viewWillAppear:animated];
[self.tabBarController.tabBar setHidden:YES];
}
- (void)viewDidAppear:(BOOL)animated {
[super viewDidAppear:animated];
[self.tabBarController.tabBar setHidden:YES];
}此方法下, viewWillAppear中打印ContentInset—0.000000_0.000000_0.000000_0.000000, viewDidAppear中打印ContentInset—64.000000_0.000000_49.000000_0.000000。
两种方法的区别在于, 执行tabBar隐藏的时机不同, hidesBottomBarWhenPushed方法在viewDidLoad之前执行, 而tabBar.hidden 是在viewWillAppear中执行的。正是因为此, 造成ScrollView.contentInset的不同, 因为hidesBottomBarWhenPushed方法在布局配置前就隐藏了tabBar了, 所以不会有内嵌的影响了。
虽与本主题无关, 但还是推荐大家使用hidesBottomBarWhenPushed`方法。
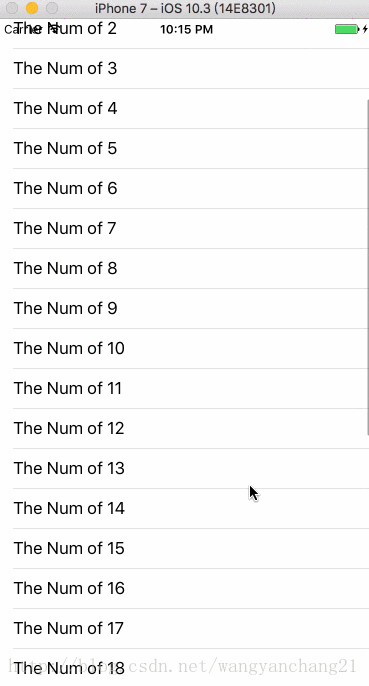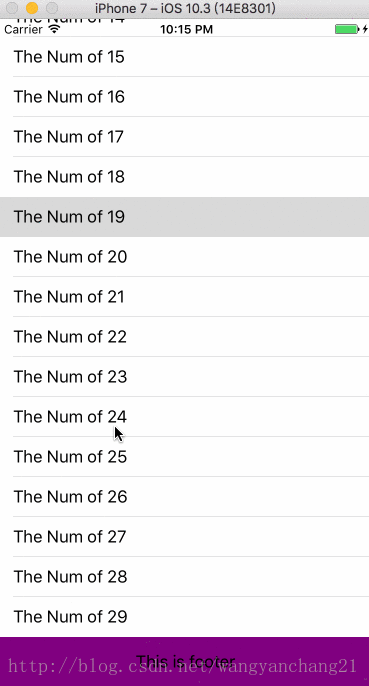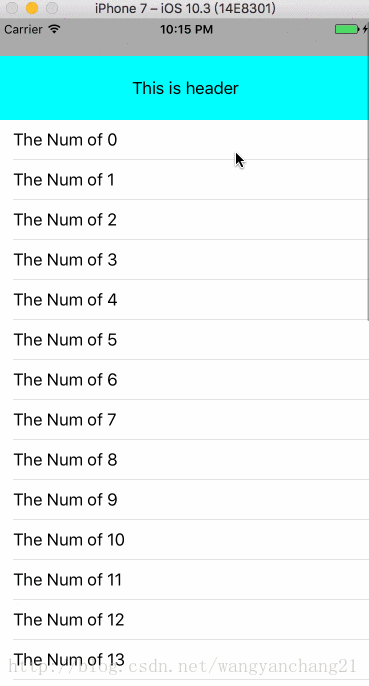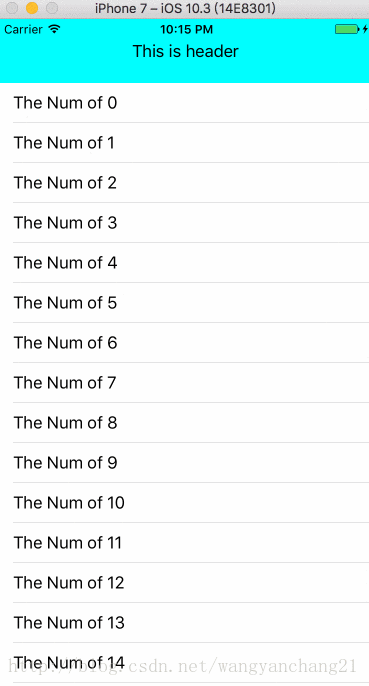
第一个addSubview的是不是当前的scrollView
当前控制器中, self.view上第一个addSubview的如果是ScrollView, 则以上的所有因素才可以影响其布局。如果不是第一个添加的, 则以上所有的属性影响失效。
当我们在viewDidLoad中第一个添加一个任何的View
- (void)createAnyView {
UIView *firstView = [[UIView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, 100, 200)];
firstView.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
[self.view addSubview:firstView];
}代码添加的效果如下:
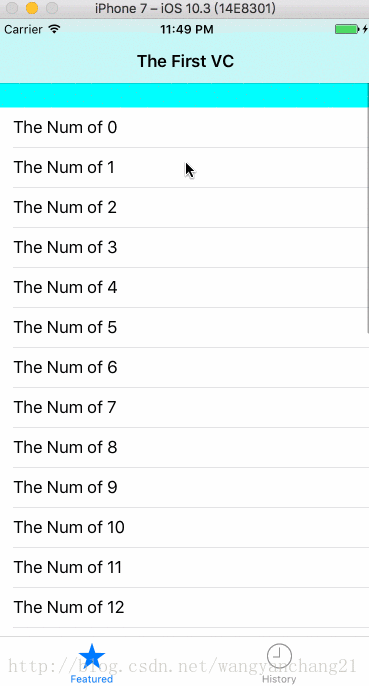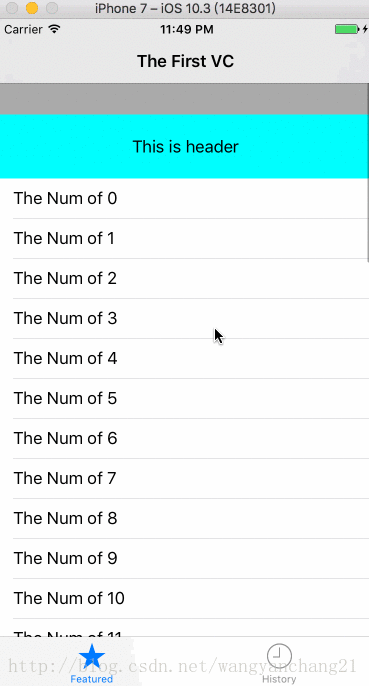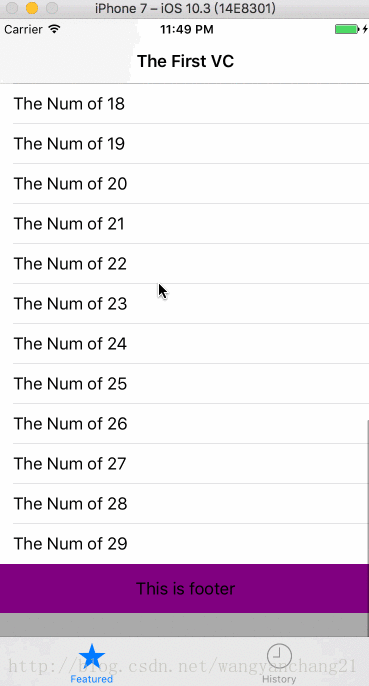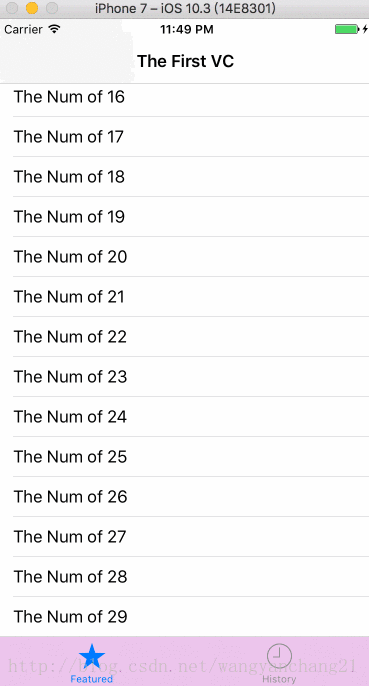
而且还有一个布局方面的问题, 在默认情况下只要是第一个添加的ScrollView, 无论ScrollView.frame为多少, 它的contentInset是会一直存在的。
_tableView.frame = CGRectMake(0, 100, kWidth, kHeight - 200);效果如下:

第二类影响因素(iOS11及之后版本)
iOS11开始, 关于影响UIScrollView的布局的API有了一些调整, 弃用了一些之前版本的属性, 又加入了一些新的属性。比如automaticallyAdjustsScrollViewInsets 在iOS11开始被弃用, 取而代之的是contentInsetAdjustmentBehavior 属性。我们先了解下iOS11 之后新添加的一些概念和属性。
但最大的区别是, iOS11引入一个全新的概念 safeAreaLayoutGuide, 它改变了整个iOS的布局机制, 当然也影响了ScrollView的布局。还有相应的一系列的属性, adjustedContentInset, additionalSafeAreaInsets, contentInsetAdjustmentBehavior, 它们与UIScrollView的布局相关。
默认的示例代码在iOS11中, 的显示结果如下:

safeAreaLayoutGuide 和 safeArea
@property(nonatomic,readonly,strong) UILayoutGuide *safeAreaLayoutGuide API_AVAILABLE( ios(11.0), tvos(11.0));
指可以与自动布局交互的矩形区域。使用布局指南来替换您可能创建的虚拟视图来表示视图间空间或封装在用户界面中。传统上,有一些自动布局技术需要虚拟视图。虚拟视图是一个空视图,它没有任何自己的可视元素,仅用于在视图层次结构中定义一个矩形区域。
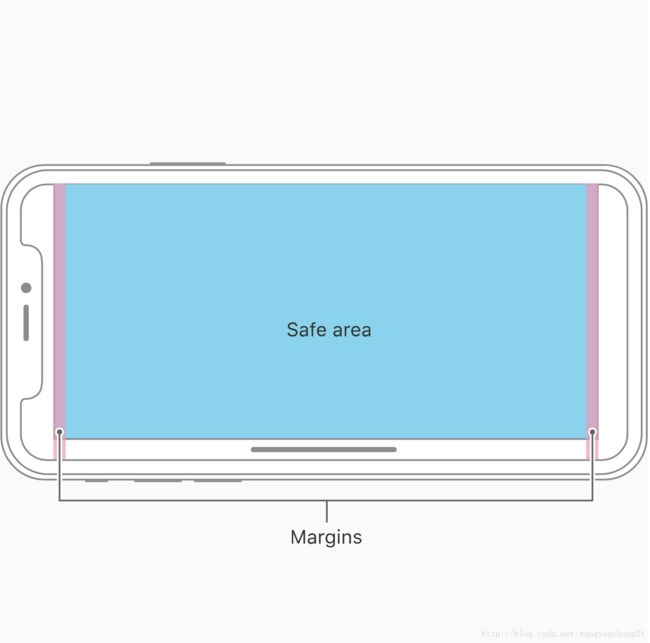
这个属性是UIView的一个只读属性,意味着所有UIView对象都有并且是系统自动定义好的。继承自UILayoutGuide,它有layoutFrame属性意味着它能代表一块区域, 代表的这块区域就是safeArea。它反映了UIView对象避开Navigation bar, tab bar,tool bar以及隐藏视图控制器视图的父View中覆盖的区域, 从而形成的一个安全区域。safeAreaLayoutGuide是一个相对抽象的概念, 但我们可以理解为它的layoutFrame属性, 即一个矩形区域可以称为safeArea。
以iPhone X为例, safeArea区域:

iOS11中 ContentInset 和 safeAreaInsets
其实在iOS11开始, 第二类影响因素(除第一个addSubview的是不是当前的scrollView外)依然会影响到UIScrollView的布局。而且影响的效果也与iOS10及之前一致, 那么区别是什么?
看一段打印结果你就明白了, 默认举例的代码中viewDidAppear中打印结果对比。在iOS10及之前版本中:
![]()
iOS11中:
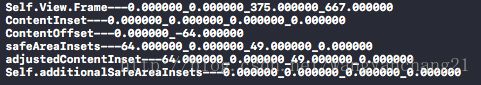
根据上面的打印结果, 可以得出: iOS10及之前版本 中所有第二类影响因素最终都会以系统自动调整UIScrollView的contentInset 属性的值来对其布局产生影响。而iOS11开始所有的自动调整都会通过safeAreaInsets中的值来影响布局。所以我们会看到无论我们如何设置第二类影响因素, UIScrollView的contentInset 默认情况下都会是0.000000_0.000000_0.000000_0.000000。反而, 这些值, 会出现在safeArea中64.000000_0.000000_49.000000_0.000000。
总结一下就是, 在iOS11 中, 第二类影响因素同样会影响UIScrollView的布局, 只是在iOS10 自动调整的值有contentInset 改为了 safeAreaInsets。但有一个因素在iOS11 将不受影响, 就是第一个addSubview的是不是当前的scrollView 这个因素。
contentInsetAdjustmentBehavior
iOS11 开始, Controller的属automaticallyAdjustsScrollViewInsets 被弃用, 新加入了ScrollView的属性 contentInsetAdjustmentBehavior 与其有相同的功能。
@property(nonatomic) UIScrollViewContentInsetAdjustmentBehavior contentInsetAdjustmentBehavior API_AVAILABLE( ios(11.0), tvos(11.0));
typedef NS_ENUM(NSInteger, UIScrollViewContentInsetAdjustmentBehavior) {
UIScrollViewContentInsetAdjustmentAutomatic,
UIScrollViewContentInsetAdjustmentScrollableAxes,
UIScrollViewContentInsetAdjustmentNever,
UIScrollViewContentInsetAdjustmentAlways,
} API_AVAILABLE(ios(11.0),tvos(11.0));
ScrollView的属性 contentInsetAdjustmentBehavior 分为四个枚举, 分别是Automatic, ScrollableAxes, Never, Always。有些疑惑的可能是前面两个枚举, 那我做个解析。
先说ScrollableAxes, 是在可滑动方向上根据安全区域来自动调整contentInset, 不可滑动的方向不会自动调整contentInset。 就像API中描述的 (contentSize.width/height > frame.size.width/height or alwaysBounceHorizontal/Vertical = YES), 可滑动时或者强制设置为横向/纵向可回弹时, 才会自动调整contentInset。
再来说Automatic, 默认枚举, 与ScrollableAxes类似, 但它会根据你的布局来判断是否需要自动调整contentInset。在NavigationBar, TabBar, StatusBar 等情况下, 一定会自动调整contentInset, 只有在特殊情况它也不会做自动调整的。 比如, 下图绿色箭头处自动调整了, 但左侧的iphoneX的齐刘海没有自动调整:

这里参考了contentInsetAdjustmentBehavior各个值之间的区别 这篇文章, 具体情况, 里面也有代码举例。
在扯回我们的主题中, 当在示例代码中添加这样的代码
_tableView.contentInsetAdjustmentBehavior = UIScrollViewContentInsetAdjustmentNever;
adjustedContentInset
@property(nonatomic, readonly) UIEdgeInsets adjustedContentInset API_AVAILABLE( ios(11.0), tvos(11.0));
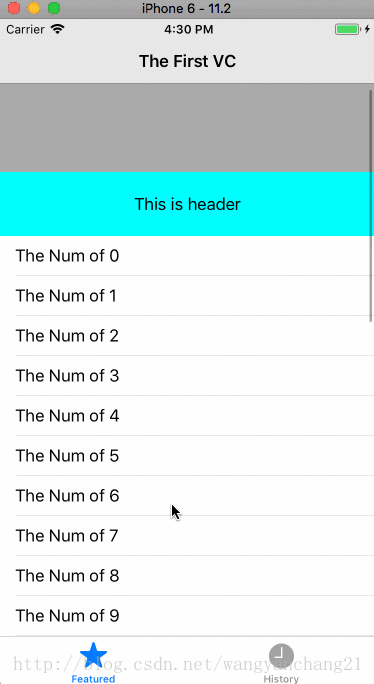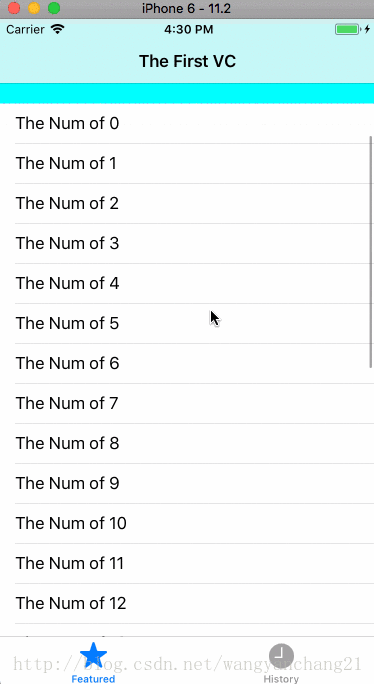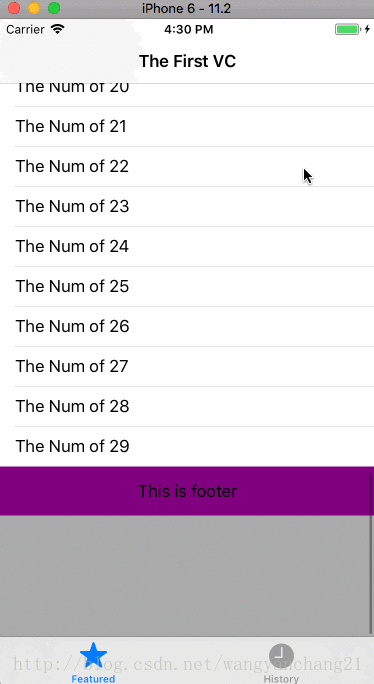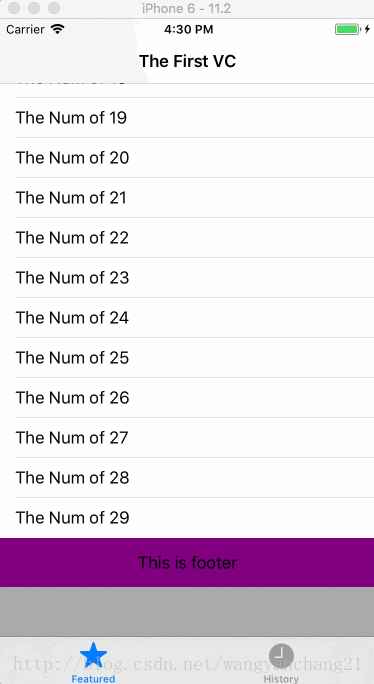
这是UIScrollView的属性, 且为只读属性, 当contentInsetAdjustmentBehavior允许时,他是safeAreaInsets和adjustedContentInset 的和。
如果当我们调整tablevew的contentInset时,
_tableView.contentInset = UIEdgeInsetsMake(100.0f, 0.0f, 50.0f, 0.0f);显示结果如下:
additionalSafeAreaInsets
@property(nonatomic) UIEdgeInsets additionalSafeAreaInsets API_AVAILABLE( ios(11.0), tvos(11.0));
这个属性是UIViewController的属性, UIViewController的子类可以使用这个属性来调整UIViewController的safeAreaInsets。我们可以使用此属性来扩展安全区域,以在界面中包含自定义内容。 例如,绘图应用程序可能会使用此属性来避免在工具选项板下显示内容。
显示结果如下:

打印结果如下:
![]()
此文章仅仅是抛砖引玉, 若有问题或者新的因素的话, 麻烦在我的博客留言, 谢谢。
相关代码下载地址:
Scrollview/TableView布局的影响因素
相关资料:
iOS6与iOS7屏幕适配 edgesForExtendedLayout
影响屏幕适配的因素及tableview的ContentSize不正确的问题
iOS各种 bar 隐藏的方法