关于随机森林的一些理解
目录
- 随机森林简介
- 优缺点
-
- 优点
- 缺点
- sklearn中随机森林参数
- 简单实现
- 小节
随机森林简介
随机森林是一种只关注决策树的集成学习方法,由Leo Breiman和 Adele Cutler提出,它将bagging和随机选择特征结合起来,在树的集成产生之后,对分类问题使用投票的方法来产生预测结果,对回归问题使用算数平均的方法来生成结果。
优缺点
优点
- 由于弱学习器之间没有关联,可以并行进行训练,训练速度快
- 由于随机选择特征,可以避免大数据中的维度灾难
- 由于bagging和随机选择特征模型泛化能力强
- 训练后,可以给出特征重要性
- 相对boosting方法,弱学习器之间存在关联,模型更为简单
缺点
- 相对于决策树不好解释
- 可能需要费功夫使得模型符合数据
sklearn中随机森林参数
https://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/6160412.html
简单实现
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV,cross_val_score,train_test_split
from sklearn import metrics
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
df = pd.read_csv('D:/data/HR_comma_sep.csv',index_col=None)
print(df.shape)
#读入员工离职数据
# (14999, 10)
df.head()
df['left'].value_counts()
df.dtypes
# satisfaction_level float64
# last_evaluation float64
# number_project int64
# average_montly_hours int64
# time_spend_company int64
# Work_accident int64
# left int64
# promotion_last_5years int64
# sales object 分类变量
# salary object 分类变量
# dtype: object
#查看是否存在缺失值
df.isnull().sum()
# satisfaction_level 0
# last_evaluation 0
# number_project 0
# average_montly_hours 0
# time_spend_company 0
# Work_accident 0
# left 0
# promotion_last_5years 0
# sales 0
# salary 0
# dtype: int64
#将string类型转化为类别变量
df.sales = df.sales.astype('category').cat.codes
df.salary = df.salary.astype('category').cat.codes
# 产生x,y 即特征值与目标值
target_name = 'left'
X = df.drop('left',axis=1)
y = df['left']
##将数据分为训练集和测试集
#注意参数stratify=y 就是按照y中的比例分配
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.3,random_state=123,stratify=y)
rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10,oob_score = True,random_state=123)
rf.fit(X_train,y_train)
rf_roc_auc = metrics.roc_auc_score(y_test,rf.predict(X_test))
print('随机森林 AUC = %.2f'% rf_roc_auc)
print('随机森林 OOB = %.2f'% rf.oob_score) # out_of_bag
print(metrics.classification_report(y_test,rf.predict(X_test)))
# 随机森林 AUC = 0.98
# 随机森林 OOB = 1.00
# precision recall f1-score support
# 0 0.99 1.00 0.99 3429
# 1 0.99 0.96 0.98 1071
# micro avg 0.99 0.99 0.99 4500
# macro avg 0.99 0.98 0.98 4500
# weighted avg 0.99 0.99 0.99 4500
#获取特征重要性
importances = rf.feature_importances_
#获取特征名称
feat_name = df.drop('left',axis=1).columns
#排序
indices = np.argsort(importances)[::-1]
#绘图
plt.figure(figsize=(12,6))
plt.title('Feature importance by decision tree')
plt.bar(range(len(indices)),importances[indices],color='lightblue',align='center')
plt.step(range(len(indices)),np.cumsum(importances[indices]),where='mid',label='cumulative')
plt.xticks(range(len(indices)),feat_name[indices],rotation='vertical',fontsize=14)
plt.xlim([-1,len(indices)])
plt.show()
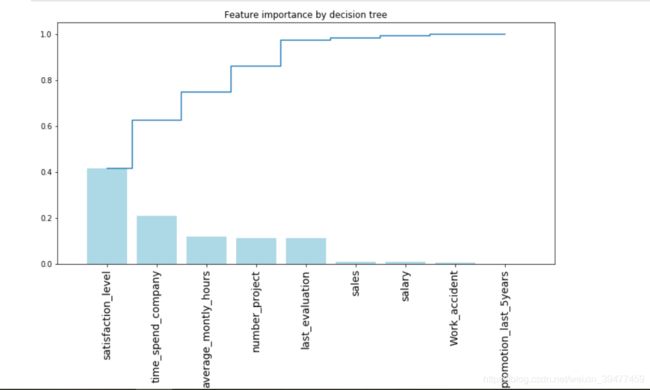
更多关于特征重要性见http://blog.datadive.net/selecting-good-features-part-iii-random-forests/
小节
由于上面模型效果已经很好了,这里就不再进行调参了。如果需要进行调参的话,有如下参数可以进行调参
n_estimators # 弱学习器个数
max_features #划分时考虑的最大特征数
max_depth # 树深
min_samples_split # 内部节点再划分所需最小样本数[2]
min_samples_leaf # 叶子节点最少样本数min_samples_leaf
[1] https://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/6160412.html
[2] http://blog.datadive.net/selecting-good-features-part-iii-random-forests/