GeekBand--第一周分享
第一课:开启安卓开发之旅
首先总结的说学习编程需要的是热情,是精神,是态度。只要对这份编程的热爱才能学好。
然后秉着这份热情去学习安卓,可以把搭建一个安卓程序看成是建房子,activity可以看做是一面墙,然后需要设计一些布局(layout),然后一些资源放在res中,举例的说TextView就像是挂在墙面的书法(字),Button就像是墙上的按钮。而且按钮按下需要有反应吧,所以需要交互,需要onClick,首先按钮设置setOnclickListener的监听,然后onClick下写出要执行的操作即可。
并且在ui中可以设置很多种布局,一共有5中布局方式:LinearLayout (线性布局),FrameLayout (框架布局),AbsoluteLayout(绝对布局),RelativeLayout (相对布局),TableLayout (表格布局)。
在一个安卓程序中AndroidMainfest.xml 这个文件非常的重要,就像应用的灵魂,组织应用所有的部件,就像人体的骨骼串通人体的各个部件。
文件内部主要的代码如下
<application
android:allowBackup="true" //是否允许后台允许
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" //应用的图标
android:label="@string/app_name" //应用的名称
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
需要提醒下的是在AS中版本号,版本名是在build.gradle中配置的,而eclipse中是在AndroidMainfest.xml 中配置的
然后调用控件是通过FindviewById方法。注意的是该方法返回的是一个视图,需要强制类型转换成对应的控件类型。
安卓间页面的跳转是通过如下代码实现
Intent intent = new Intent( 现在的页面, 要跳转到页面) //一个意图
例如 Intent intent = new Intent (A.this,B.class);
startActivity(intent) //打开这个意图
第二课:Activity你必须知道的那些事
Handler.postDelayed(Runable r,long delayMillis)也就是在一个线程中,延迟多少时间再去执行run()方法中的行为。
在平常的应用中我们都需要在Activity中传递一些数据,可以调用intent中的putExtra()方法
例如intent.putExtra(“title”,title) //就是放入数据(数据可以是所有类型)
再通过
Intent intent = geIntent(); //取得数据
If(intent != null){
String title = Intent.getStringExtra(“title”);
}
而且Activity中还能传递对象,前提是需要序列化对象
例如 Intent.putExtra(“userInfo”,userinfo) //传递对象
Userinfo userInfo = (UserInfo) intent.getSerializableExtra(“userInfo”) //取得对象
需要注意的是放入数据的key值最好弄成静态的常量,这样代码比较美观
例如intent.putExtra(“TITLE”,title) //就是放入数据
如果要是activity中的互传数据
Intent intent = new Intent (A.this,B.class);
A即原始页面,B即目的页面也就是要跳转到的页面。
在打开意图的时候用 startActivityForResult(intent,requsetCode);
在目的页面setResult(resultcode,intent)
原始页面调用 OnActivityResult()方法,
判断requsercode和resultcode
然后String title = data.getStringExtra(TITLE);即可得到目的页面送回来的数据
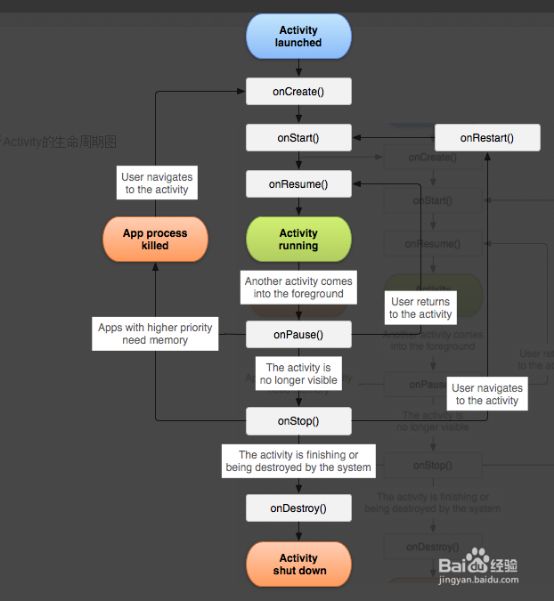
接下来要认识安卓中的生命周期
onCreate() //创建
onStart() //开始
onResume() //展示
onPause() //暂停
onStop() //停止
onDestroy() //销毁
onRestart() //重新启动
下图是生命周期运转的图此图摘至百度经验(安卓Activity生命周期详解) 2016.2.29
http://jingyan.baidu.com/article/455a9950842bc0a166277829.html
第三课进入多姿多彩的控件世界
android:text="@string/hello_world_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content" //适应自身宽度
android:layout_width="match_content" //撑满父控件宽度
android:layout_width="100dp" //自定义宽度
android:gravity="center" //设置文字位置
android:textColor="@color/red" //设置颜色
android:singleLine="true" //显示不下的文字用省略号代替
android:maxLines="2" //设置文字行数
android:background="@color/red" //设置背景
android:layout_height="wrap_content" //高度
/>
Ps:设置文本宽度或高度单位用dp,文本大小的时候用sp
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="number" //设置输入的类型
/>
editText.addTextChangedListener(new TextWatcher() { //editText特有的方法
@Override
public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after) {
}
@Override
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {
}
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {
}
});
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/ii" //资源
android:background="@drawable/tt" //背景
android:scaleType="center" //决定图片显示的样子
/>
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
安卓的控件包括属性有太多了这里就不一一列举了,这么多东西需要自己平时的查阅和积累,让我们一起加油学习吧!