Flink:把状态State全都扒光,远走他乡(一):State初始
State:
State是指流计算过程中计算节点的中间计算结果或元数据属性,比如 在aggregation过程中要在state中记录中间聚合结果,比如 Apache Kafka 作为数据源时候,我们也要记录已经读取记录的offset,这些State数据在计算过程中会进行持久化(插入或更新)。所以Apache Flink中的State就是与时间相关的,Apache Flink任务的内部数据(计算数据和元数据属性)的快照。

State分类:Keyed State和Operator State
Keyed State
Keyed State是一种基于key的,它永远和key绑定,key和key之间的state没有关系,不会相互影响
Operator State
Operator State是一种基于Operate的,每个操作有状态的,每个操作之间不会相互影响。举例来说,Flink中的Kafka Connector,就使用了operator state。它会在每个connector实例中,保存该实例中消费topic的所有(partition, offset)映射。
Raw State和Managed State
- Raw即原始状态:由用户自行管理状态具体的数据结构,框架在做checkpoint的时候,使用byte[]来读写状态内容,对其内部数据结构一无所知。
- Managed State:即托管状态,托管状态是由Flink框架管理的状态,如ValueState, ListState, MapState等。
Keyed State ---- Managed State
- ValueState:这将保留一个可以更新和检索的值(如上所述,作用域为输入元素的键,因此该操作看到的每个键可能会有一个值)。该值可以使用设置update(T)和使用检索 T value()。
实例:
package flinkscala.State.Keyed_State
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.RichFlatMapFunction
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.{
ValueState, ValueStateDescriptor}
import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.TypeInformation
import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector
object valueStateTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setParallelism(1)
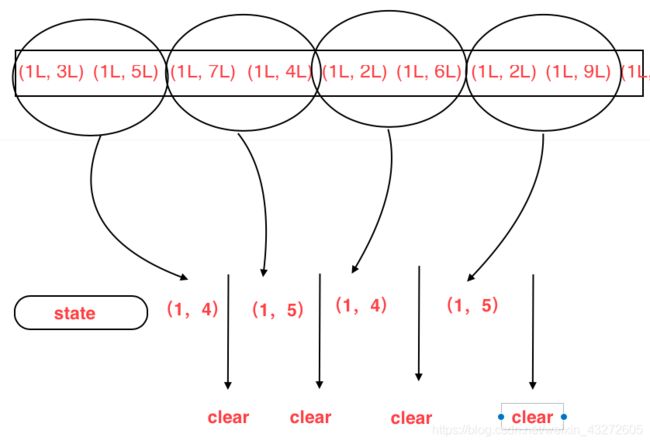
env.fromCollection(List(
(1L, 3L),
(1L, 5L),
(1L, 7L),
(1L, 4L),
(1L, 2L),
(1L, 6L),
(1L, 2L),
(1L, 9L),
(1L, 2L),
(1L, 3L)
)).keyBy(_._1)
.flatMap(new CountWindowAverage())
.print()
env.execute("average Test")
}
}
class CountWindowAverage extends RichFlatMapFunction[(Long,Long),(Long,Long)]{
//定义一个ValueState,保存着(元素的个数,元素的和)
private var sum: ValueState[(Long,Long)] = _
override def flatMap(value: (Long, Long), out: Collector[(Long, Long)]): Unit = {
//先访问ValueState,取出ValueState中的和
//当然,如果是空的话,也就是初次使用的话,就初始化为0,0
var tmpCurrentSum = sum.value()
val surrentSum = if(tmpCurrentSum !=null){
tmpCurrentSum
}else {
(0L,0L)}
/*
* 元素个数+1,元素和+当前进来的元素
*
*/
val newSum = (surrentSum._1+1,surrentSum._2+value._2)
//更新状态State
sum.update(newSum)
//如果达到了两个元素,就计算一次平均值
if(newSum._1>=2){
out.collect((value._1,newSum._2/newSum._1))
sum.clear()//清空状态
}
}
override def open(parameters: Configuration): Unit ={
sum = getRuntimeContext
.getState(
new ValueStateDescriptor[(Long, Long)]("average",createTypeInformation[(Long,Long)])
)
}
}
ListState:这保留了元素列表。您可以追加元素并检索Iterable 所有当前存储的元素。使用add(T)或添加元素addAll(List),可以使用检索Iterable Iterable get()。您还可以使用以下方法覆盖现有列表update(List)
ReducingState:这将保留一个值,该值代表添加到状态的所有值的集合。介面与相似,ListState但使用新增的元素 add(T)会使用指定的简化为汇总ReduceFunction。
AggregatingState
FoldingState
MapState
我们可以通过getRunTimeContext的getstate方法来获取state,一个state与一个句柄StateDescriptor绑定着,不同的状态保存不同的值,这种情况可能需要多种状态,通过StateDescriptor来获取对应的状态。
State Time-To-Live (TTL)
对于状态,我们有时候可以设置它的年龄,或者说过期,即到达一定时间就自动清除,或者做相关操作,有点儿像Redis里面的过期。
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.StateTtlConfig
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ValueStateDescriptor
import org.apache.flink.api.common.time.Time
val ttlConfig = StateTtlConfig
//这个是用来配置生存的过期时间
.newBuilder(Time.seconds(1))
//配置什么时候对状态TTL进行刷新:OnCreateAndWrite-仅在创建和写访问时,OnReadAndWrite-有读取访问时
.setUpdateType(StateTtlConfig.UpdateType.OnCreateAndWrite)
//配置状态可见性用于配置是否清除尚未过期的默认值(
.setStateVisibility(StateTtlConfig.StateVisibility.NeverReturnExpired)
.build
val stateDescriptor = new ValueStateDescriptor[String]("text state", classOf[String])
stateDescriptor.enableTimeToLive(ttlConfig)
清理过期状态
val ttlConfig = StateTtlConfig
.newBuilder(Time.seconds(1))
.disableCleanupInBackground//防止清理掉后台状态
.build
Managed Operator State
前面说了,操作状态是基于操作算子的,然后又是托管的,即用Flink已经有的ValueState等等
要使用托管操作状态,有状态功能可以实现更通用的CheckpointedFunction 接口,也可以实现ListCheckpointed< T extends Serializable>接口。
CheckpointedFunction
每当必须执行检查点时,都会调用snapshotState()。
每次初始化用户定义函数时,都会调用对应的initializeState()
void snapshotState(FunctionSnapshotContext context) throws Exception;
void initializeState(FunctionInitializationContext context) throws Exception;
无论是在首次初始化函数时,还是在实际从以前的检查点恢复函数时。
因此,initializeState()不仅是初始化不同类型状态的地方,而且也是包含状态恢复逻辑的地方。
当前,支持列表样式的托管操作符状态。该状态应为彼此独立List的可序列化对象,
- Even-split redistribution:每个operator返回一个状态元素列表。整个状态在逻辑上是所有列表的串联。在还原/重新分发时,列表被均匀地划分为尽可能多的子列表,因为有并行operator。每个运算符都得到一个子列表,该子列表可以为空,也可以包含一个或多个元素。例如,如果并行度为1时,operator的检查点状态包含元素element1和element2,则当并行度增加到2时,element1可能会在operator实例0中结束,而element2将转到operator实例1。
- Union redistribution:每个operator都返回状态元素列表。从逻辑上讲,整个状态是所有列表的串联。在还原/重新分发时,每个operator都会获得状态元素的完整列表。
Even-split redistribution演示
package flinkscala.State.Operatior_State
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.{
ListState, ListStateDescriptor}
import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.{
TypeHint, TypeInformation}
import org.apache.flink.runtime.state.{
FunctionInitializationContext, FunctionSnapshotContext}
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.checkpoint.CheckpointedFunction
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.sink.SinkFunction
import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer
object opratorTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
}
}
class BufferingSink(threshold: Int = 0) extends SinkFunction[(String,Int)] with CheckpointedFunction{
private var checkpointedState: ListState[(String,Int)] = _
private val bufferedElements = ListBuffer[(String,Int)]()
override def invoke(value: (_root_.scala.Predef.String, Int), context: _root_.org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.sink.SinkFunction.Context[_]): Unit = {
bufferedElements += value
if(bufferedElements.size == threshold){
for(element <- bufferedElements){
//这里面将它发送到Sink
}
//发完之后就清空
bufferedElements.clear()
}
}
override def snapshotState(context: FunctionSnapshotContext): Unit = {
checkpointedState.clear()
for (element <- bufferedElements) {
checkpointedState.add(element)
}
}
override def initializeState(context: FunctionInitializationContext): Unit = {
val descriptor = new ListStateDescriptor[(String,Int)](
"buffered-elements",
TypeInformation.of(new TypeHint[(String,Int)] {
})
)
checkpointedState = context.getOperatorStateStore.getListState(descriptor)
if(context.isRestored){
for(element <- checkpointedState.get()){
bufferedElements += element
}
}
}
}
ListCheckpointed
该ListCheckpointed接口是的一个更有限的变体CheckpointedFunction,它仅支持列表样式状态,并在还原时使用偶数拆分的重新分配方案。它还需要实现两种方法:
List<T> snapshotState(long checkpointId, long timestamp) throws Exception;
void restoreState(List<T> state) throws Exception;
在snapshotState()操作员上应将对象列表返回给检查点,并且 restoreState在恢复时必须处理此类列表。如果状态不是重新分区,可以随时返回Collections.singletonList(MY_STATE)的snapshotState()。