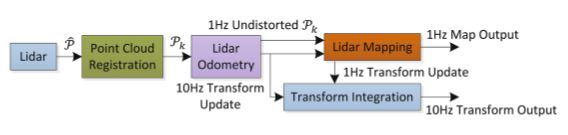
LOAM学习-代码解析(六)地图构建 laserMapping
目录
前言
主函数
1.初始化
2.程序入口
3.转换世界坐标系
4.数据处理
4.1将Lidar坐标系点(0,10,0)转到世界坐标系
4.2立方体cube的中心点在世界坐标系下的原点位置
4.3调整边缘位置向中心移动
4.4在取到的子立方体的125个邻域内寻找配准点
4.5对配准的点云进行滤波处理
4.6点云配准
4.7点云封装
4.8下采样
4.9全部点云转换到世界坐标系
结语
前言
前一篇文章LOAM学习-代码解析(五)地图构建 laserMapping,对laserMapping的预处理部分进行了解析,本文将对laserMapping的主函数部分进行解析。
LOAM代码(带中文注释)的地址:https://github.com/cuitaixiang/LOAM_NOTED
LOAM代码(带中文注释)的百度网盘链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1tVSNBxNQrxKJyd5c9mWFWw 提取码: wwxr
LOAM论文的百度网盘链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/10ahqg8O3G2-xOt9QZ1GuEQ 提取码: hnri
LOAM流程:
主函数
1.初始化
主函数的开始是程序的一些设置。
值得注意的是,为了下采样滤波,VoxeGrid滤波器(体素栅格滤波器)。
//主函数
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
//发布器
ros::init(argc, argv, "laserMapping");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
//订阅信息
ros::Subscriber subLaserCloudCornerLast = nh.subscribe
("/laser_cloud_corner_last", 2, laserCloudCornerLastHandler);
ros::Subscriber subLaserCloudSurfLast = nh.subscribe
("/laser_cloud_surf_last", 2, laserCloudSurfLastHandler);
ros::Subscriber subLaserOdometry = nh.subscribe
("/laser_odom_to_init", 5, laserOdometryHandler);
ros::Subscriber subLaserCloudFullRes = nh.subscribe
("/velodyne_cloud_3", 2, laserCloudFullResHandler);
ros::Subscriber subImu = nh.subscribe ("/imu/data", 50, imuHandler);
//发布信息
ros::Publisher pubLaserCloudSurround = nh.advertise
("/laser_cloud_surround", 1);
ros::Publisher pubLaserCloudFullRes = nh.advertise
("/velodyne_cloud_registered", 2);
ros::Publisher pubOdomAftMapped = nh.advertise ("/aft_mapped_to_init", 5);
//ros里程计信息
nav_msgs::Odometry odomAftMapped;
odomAftMapped.header.frame_id = "/camera_init";
odomAftMapped.child_frame_id = "/aft_mapped";
//ros坐标系信息
tf::TransformBroadcaster tfBroadcaster;
tf::StampedTransform aftMappedTrans;
aftMappedTrans.frame_id_ = "/camera_init";
aftMappedTrans.child_frame_id_ = "/aft_mapped";
//vector初始化
std::vector pointSearchInd;
std::vector pointSearchSqDis;
//点初始化
PointType pointOri, pointSel, pointProj, coeff;
//旋转矩阵
cv::Mat matA0(5, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matB0(5, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(-1));
cv::Mat matX0(3, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
//旋转矩阵
cv::Mat matA1(3, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matD1(1, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matV1(3, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
//旋转矩阵
bool isDegenerate = false;
cv::Mat matP(6, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
//创建VoxelGrid滤波器(体素栅格滤波器)
pcl::VoxelGrid downSizeFilterCorner;
//设置体素大小
downSizeFilterCorner.setLeafSize(0.2, 0.2, 0.2);
pcl::VoxelGrid downSizeFilterSurf;
downSizeFilterSurf.setLeafSize(0.4, 0.4, 0.4);
pcl::VoxelGrid downSizeFilterMap;
downSizeFilterMap.setLeafSize(0.6, 0.6, 0.6);
//指针初始化
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudNum; i++) {
laserCloudCornerArray[i].reset(new pcl::PointCloud());
laserCloudSurfArray[i].reset(new pcl::PointCloud());
laserCloudCornerArray2[i].reset(new pcl::PointCloud());
laserCloudSurfArray2[i].reset(new pcl::PointCloud());
} 2.程序入口
在LOAM学习-代码解析(四)特征点运动估计 laserOdometry中,介绍过进入程序的条件。这里回顾一下
- ros::ok函数。若ros不OK,程序就退出了。最常见的就按下ctrl+c或者在程序遇到ros::shutdown(),就会把ros::ok置为false;
- ros::spinOnce函数是用于接收器的,必须要有spinOnce或者spin,ros才会检测是不是接收到信息。spinOnce就是检测一次,spin()就是一直检测。
这里的if判断和laserOdometry的判断条件是相同的,即确保同时受到同一个点云的特征点以及IMU信息才进入。
newCornerPointsSharp、newCornerPointsLessSharp、newSurfPointsFlat、newSurfPointsLessFlat、newLaserCloudFullRes、newImuTrans这几个标识位在各自的Handler回调函数里出现,如果有消息来了就会把这些标识位置为True。同时,在回调函数里会由消息收到的时间,所以还需要判断是同一时刻收到的消息,两者时间差小于0.005s即可。
进入if函数后,会把上述标识位置为False。
//程序入口
int frameCount = stackFrameNum - 1; //0
int mapFrameCount = mapFrameNum - 1; //4
ros::Rate rate(100); //循环频率100Hz
bool status = ros::ok(); //ros::ok函数,按下ctrl+c或者在程序遇到ros::shutdown(),就会把ros::ok置为false
while (status) {
ros::spinOnce();//接收器,spinOnce就是检测一次
//同步作用,确保同时收到同一个点云的特征点以及IMU信息才进入
if (newLaserCloudCornerLast && newLaserCloudSurfLast && newLaserCloudFullRes && newLaserOdometry &&
fabs(timeLaserCloudCornerLast - timeLaserOdometry) < 0.005 &&
fabs(timeLaserCloudSurfLast - timeLaserOdometry) < 0.005 &&
fabs(timeLaserCloudFullRes - timeLaserOdometry) < 0.005) {
newLaserCloudCornerLast = false;
newLaserCloudSurfLast = false;
newLaserCloudFullRes = false;
newLaserOdometry = false;3.转换世界坐标系
在点云数据进行处理之前,需要获取旋转矩阵,根据旋转矩阵,将最新接收到的特征点(边沿点和平面点)转换到世界坐标系下。
pointAssociateToMap函数在LOAM学习-代码解析(五)地图构建 laserMapping里已经介绍过了,根据调整计算后的转移矩阵,将点注册到全局世界坐标系下。
执行完折后,获得laserCloudCornerStack2数据。
//控制跳帧数,>=这里实际并没有跳帧,只取>或者增大stackFrameNum才能实现相应的跳帧处理
if (frameCount >= stackFrameNum) {
//获取世界坐标系转换矩阵
transformAssociateToMap();
//将最新接收到的平面点和边沿点进行旋转平移转换到世界坐标系下(这里和后面的逆转换应无必要)
int laserCloudCornerLastNum = laserCloudCornerLast->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudCornerLastNum; i++) {
pointAssociateToMap(&laserCloudCornerLast->points[i], &pointSel);
laserCloudCornerStack2->push_back(pointSel);
}
int laserCloudSurfLastNum = laserCloudSurfLast->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudSurfLastNum; i++) {
pointAssociateToMap(&laserCloudSurfLast->points[i], &pointSel);
laserCloudSurfStack2->push_back(pointSel);
}
}4.数据处理
4.1将Lidar坐标系点(0,10,0)转到世界坐标系
将Lidar坐标系上的(0,10,0)转换到世界坐标系下的坐标
if (frameCount >= stackFrameNum) {
frameCount = 0;
PointType pointOnYAxis;
pointOnYAxis.x = 0.0;
pointOnYAxis.y = 10.0;
pointOnYAxis.z = 0.0;
//获取y方向上10米高位置的点在世界坐标系下的坐标
pointAssociateToMap(&pointOnYAxis, &pointOnYAxis);
4.2立方体cube的中心点在世界坐标系下的原点位置
由于数组下标只能为正数,而地图可能建立在原点前后,英雌每一个维度都需要偏移一个子立方体参数(laserCloudCenWidth、Height、Depth)。
调整之后取值范围:3 < centerCubeI < 18, 3 < centerCubeJ < 8, 3 < centerCubeK < 18。
//立方体中点在世界坐标系下的(原点)位置
//过半取一(以50米进行四舍五入的效果),由于数组下标只能为正数,而地图可能建立在原点前后,因此
//每一维偏移一个laserCloudCenWidth(该值会动态调整,以使得数组利用最大化,初始值为该维数组长度1/2)的量
int centerCubeI = int((transformTobeMapped[3] + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenWidth;
int centerCubeJ = int((transformTobeMapped[4] + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenHeight;
int centerCubeK = int((transformTobeMapped[5] + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenDepth;
//由于计算机求余是向零取整,为了不使(-50.0,50.0)求余后都向零偏移,当被求余数为负数时求余结果统一向左偏移一个单位,也即减一
if (transformTobeMapped[3] + 25.0 < 0) centerCubeI--;
if (transformTobeMapped[4] + 25.0 < 0) centerCubeJ--;
if (transformTobeMapped[5] + 25.0 < 0) centerCubeK--;
//调整之后取值范围:3 < centerCubeI < 18, 3 < centerCubeJ < 8, 3 < centerCubeK < 184.3调整边缘位置向中心移动
如果处于下边界,表明地图向负方向延伸的可能性比较大,则循环移位,将数组中心点向上边界调整一个单位。
//如果处于下边界,表明地图向负方向延伸的可能性比较大,则循环移位,将数组中心点向上边界调整一个单位
while (centerCubeI < 3) {
for (int j = 0; j < laserCloudHeight; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < laserCloudDepth; k++) {//实现一次循环移位效果
int i = laserCloudWidth - 1;
//指针赋值,保存最后一个指针位置
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr laserCloudCubeCornerPointer =
laserCloudCornerArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k];//that's [i + 21 * j + 231 * k]
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr laserCloudCubeSurfPointer =
laserCloudSurfArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k];
//循环移位,I维度上依次后移
for (; i >= 1; i--) {
laserCloudCornerArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k] =
laserCloudCornerArray[i - 1 + laserCloudWidth*j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k];
laserCloudSurfArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k] =
laserCloudSurfArray[i - 1 + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k];
}
//将开始点赋值为最后一个点
laserCloudCornerArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k] =
laserCloudCubeCornerPointer;
laserCloudSurfArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k] =
laserCloudCubeSurfPointer;
laserCloudCubeCornerPointer->clear();
laserCloudCubeSurfPointer->clear();
}
}
centerCubeI++;
laserCloudCenWidth++;
} 如果处于上边界,表明地图向正方向延伸的可能性比较大,则循环移位,将数组中心点向下边界调整一个单位。
//如果处于上边界,表明地图向正方向延伸的可能性比较大,则循环移位,将数组中心点向下边界调整一个单位
while (centerCubeI >= laserCloudWidth - 3) {//18
for (int j = 0; j < laserCloudHeight; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < laserCloudDepth; k++) {
int i = 0;
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr laserCloudCubeCornerPointer =
laserCloudCornerArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k];
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr laserCloudCubeSurfPointer =
laserCloudSurfArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k];
//I维度上依次前移
for (; i < laserCloudWidth - 1; i++) {
laserCloudCornerArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k] =
laserCloudCornerArray[i + 1 + laserCloudWidth*j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k];
laserCloudSurfArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k] =
laserCloudSurfArray[i + 1 + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k];
}
laserCloudCornerArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k] =
laserCloudCubeCornerPointer;
laserCloudSurfArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k] =
laserCloudCubeSurfPointer;
laserCloudCubeCornerPointer->clear();
laserCloudCubeSurfPointer->clear();
}
}
centerCubeI--;
laserCloudCenWidth--;
} 上面是对I维度进行调整,J和K维度的调整同理。
4.4在取到的子立方体的125个邻域内寻找配准点
在每一维附近5个cube(前2个,后2个,中间1个)里进行查找(前后250米范围内,总共500米范围),三个维度总共125个cube。
- 将每个子立方体cube对应的点坐标,换算成实际比例,在世界坐标系下的坐标
- 判断是否在lidar视线范围的标志
- 将在lidar视线范围的点存入数组,匹配用数组laserCloudValidInd,显示用数组laserCloudSurroundInd
这一步骤本质上就是减少计算量,只对取到的点云在其125个邻域内进行处理。
//寻找配准点
int laserCloudValidNum = 0;
int laserCloudSurroundNum = 0;
//在每一维附近5个cube(前2个,后2个,中间1个)里进行查找(前后250米范围内,总共500米范围),三个维度总共125个cube
//在这125个cube里面进一步筛选在视域范围内的cube
for (int i = centerCubeI - 2; i <= centerCubeI + 2; i++) {
for (int j = centerCubeJ - 2; j <= centerCubeJ + 2; j++) {
for (int k = centerCubeK - 2; k <= centerCubeK + 2; k++) {
if (i >= 0 && i < laserCloudWidth &&
j >= 0 && j < laserCloudHeight &&
k >= 0 && k < laserCloudDepth) {//如果索引合法
//换算成实际比例,在世界坐标系下的坐标
float centerX = 50.0 * (i - laserCloudCenWidth);
float centerY = 50.0 * (j - laserCloudCenHeight);
float centerZ = 50.0 * (k - laserCloudCenDepth);
bool isInLaserFOV = false;//判断是否在lidar视线范围的标志(Field of View)
for (int ii = -1; ii <= 1; ii += 2) {
for (int jj = -1; jj <= 1; jj += 2) {
for (int kk = -1; kk <= 1; kk += 2) {
//上下左右八个顶点坐标
float cornerX = centerX + 25.0 * ii;
float cornerY = centerY + 25.0 * jj;
float cornerZ = centerZ + 25.0 * kk;
//原点到顶点距离的平方和
float squaredSide1 = (transformTobeMapped[3] - cornerX)
* (transformTobeMapped[3] - cornerX)
+ (transformTobeMapped[4] - cornerY)
* (transformTobeMapped[4] - cornerY)
+ (transformTobeMapped[5] - cornerZ)
* (transformTobeMapped[5] - cornerZ);
//pointOnYAxis到顶点距离的平方和
float squaredSide2 = (pointOnYAxis.x - cornerX) * (pointOnYAxis.x - cornerX)
+ (pointOnYAxis.y - cornerY) * (pointOnYAxis.y - cornerY)
+ (pointOnYAxis.z - cornerZ) * (pointOnYAxis.z - cornerZ);
float check1 = 100.0 + squaredSide1 - squaredSide2
- 10.0 * sqrt(3.0) * sqrt(squaredSide1);
float check2 = 100.0 + squaredSide1 - squaredSide2
+ 10.0 * sqrt(3.0) * sqrt(squaredSide1);
//视角在60°范围内
if (check1 < 0 && check2 > 0) {//if |100 + squaredSide1 - squaredSide2| < 10.0 * sqrt(3.0) * sqrt(squaredSide1)
isInLaserFOV = true;
}
}
}
}
//记住视域范围内的cube索引,匹配用
if (isInLaserFOV) {
laserCloudValidInd[laserCloudValidNum] = i + laserCloudWidth * j
+ laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k;
laserCloudValidNum++;
}
//记住附近所有cube的索引,显示用
laserCloudSurroundInd[laserCloudSurroundNum] = i + laserCloudWidth * j
+ laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k;
laserCloudSurroundNum++;
}
}
}
}4.5对配准的点云进行滤波处理
论文作者在此处将特征点转一会local坐标系,注释里写着“为了下采样滤波操作不越界”,滤波器使用的VoxelGrid滤波器(体素栅格滤波器)。
VoxelGrid滤波器使用体素化网格方法实现下采样,即减少点的数量,减少点云数据,并同时保持点云的形状特征,在提高配准、曲面重建、形状识别等算法速度中非常实用。PCL实现的VoxelGrid类通过输入的点云数据创建一个三维体素栅格(可把体素栅格想象为微小的空间三维立方体的集合),然后在每个体素(即,三维立方体)内,用体素中所有点的重心来近似显示体素中其他点,这样该体素就内所有点就用一个重心点最终表示,对于所有体素处理后得到过滤后的点云。这种方法比用体素中心来逼近的方法更慢,但它对于采样点对应曲面的表示更为准确。通过使用这种方法可以保留原始点云的形状等边界信息。
//点云滤波处理
laserCloudCornerFromMap->clear();
laserCloudSurfFromMap->clear();
//构建特征点地图,查找匹配使用
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudValidNum; i++) {
*laserCloudCornerFromMap += *laserCloudCornerArray[laserCloudValidInd[i]];
*laserCloudSurfFromMap += *laserCloudSurfArray[laserCloudValidInd[i]];
}
int laserCloudCornerFromMapNum = laserCloudCornerFromMap->points.size();
int laserCloudSurfFromMapNum = laserCloudSurfFromMap->points.size();
//先从世界坐标系转为Lidar坐标系
int laserCloudCornerStackNum2 = laserCloudCornerStack2->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudCornerStackNum2; i++) {
pointAssociateTobeMapped(&laserCloudCornerStack2->points[i], &laserCloudCornerStack2->points[i]);
}
int laserCloudSurfStackNum2 = laserCloudSurfStack2->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudSurfStackNum2; i++) {
pointAssociateTobeMapped(&laserCloudSurfStack2->points[i], &laserCloudSurfStack2->points[i]);
}
//滤波处理,降采样
laserCloudCornerStack->clear();
downSizeFilterCorner.setInputCloud(laserCloudCornerStack2);//设置滤波对象
downSizeFilterCorner.filter(*laserCloudCornerStack);//执行滤波处理
int laserCloudCornerStackNum = laserCloudCornerStack->points.size();//获取滤波后体素点尺寸
laserCloudSurfStack->clear();
downSizeFilterSurf.setInputCloud(laserCloudSurfStack2);
downSizeFilterSurf.filter(*laserCloudSurfStack);
int laserCloudSurfStackNum = laserCloudSurfStack->points.size();
laserCloudCornerStack2->clear();
laserCloudSurfStack2->clear();4.6点云配准
在LOAM学习-代码解析(四)特征点运动估计 laserOdometry中,已经详细介绍了点云配准的基本流程。
在获得点云特征点后,构建kd树寻找临近的五个点,对点云协方差矩阵的特征值分解。如果五个点都在一条直线上,则协方差矩阵的最大特征值大于第二大特征值三倍以上,那么这个特征值相关的特征向量就表示所在直线的方向;如果五个点都在一个平面上,则协方差矩阵的最小特征值足够得小(这一个在代码里没有发现-_-),那么这个特征值相关的特征向量就表示所处平面的法线方向。
//点云配准
if (laserCloudCornerFromMapNum > 10 && laserCloudSurfFromMapNum > 100) {
kdtreeCornerFromMap->setInputCloud(laserCloudCornerFromMap);//构建kd-tree
kdtreeSurfFromMap->setInputCloud(laserCloudSurfFromMap);
for (int iterCount = 0; iterCount < 10; iterCount++) {//最多迭代10次
laserCloudOri->clear();
coeffSel->clear();
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudCornerStackNum; i++) {
pointOri = laserCloudCornerStack->points[i];
//转换回世界坐标系
pointAssociateToMap(&pointOri, &pointSel);
kdtreeCornerFromMap->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 5, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);//寻找最近距离五个点
if (pointSearchSqDis[4] < 1.0) {//5个点中最大距离不超过1才处理
//将五个最近点的坐标加和求平均
float cx = 0;
float cy = 0;
float cz = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
cx += laserCloudCornerFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x;
cy += laserCloudCornerFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y;
cz += laserCloudCornerFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z;
}
cx /= 5;
cy /= 5;
cz /= 5;
//求均方差
float a11 = 0;
float a12 = 0;
float a13 = 0;
float a22 = 0;
float a23 = 0;
float a33 = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
float ax = laserCloudCornerFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x - cx;
float ay = laserCloudCornerFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y - cy;
float az = laserCloudCornerFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z - cz;
a11 += ax * ax;
a12 += ax * ay;
a13 += ax * az;
a22 += ay * ay;
a23 += ay * az;
a33 += az * az;
}
a11 /= 5;
a12 /= 5;
a13 /= 5;
a22 /= 5;
a23 /= 5;
a33 /= 5;
//构建矩阵
matA1.at(0, 0) = a11;
matA1.at(0, 1) = a12;
matA1.at(0, 2) = a13;
matA1.at(1, 0) = a12;
matA1.at(1, 1) = a22;
matA1.at(1, 2) = a23;
matA1.at(2, 0) = a13;
matA1.at(2, 1) = a23;
matA1.at(2, 2) = a33;
//特征值分解
cv::eigen(matA1, matD1, matV1);
if (matD1.at(0, 0) > 3 * matD1.at(0, 1)) {//如果最大的特征值大于第二大的特征值三倍以上
float x0 = pointSel.x;
float y0 = pointSel.y;
float z0 = pointSel.z;
float x1 = cx + 0.1 * matV1.at(0, 0);
float y1 = cy + 0.1 * matV1.at(0, 1);
float z1 = cz + 0.1 * matV1.at(0, 2);
float x2 = cx - 0.1 * matV1.at(0, 0);
float y2 = cy - 0.1 * matV1.at(0, 1);
float z2 = cz - 0.1 * matV1.at(0, 2);
float a012 = sqrt(((x0 - x1)*(y0 - y2) - (x0 - x2)*(y0 - y1))
* ((x0 - x1)*(y0 - y2) - (x0 - x2)*(y0 - y1))
+ ((x0 - x1)*(z0 - z2) - (x0 - x2)*(z0 - z1))
* ((x0 - x1)*(z0 - z2) - (x0 - x2)*(z0 - z1))
+ ((y0 - y1)*(z0 - z2) - (y0 - y2)*(z0 - z1))
* ((y0 - y1)*(z0 - z2) - (y0 - y2)*(z0 - z1)));
float l12 = sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2)*(y1 - y2) + (z1 - z2)*(z1 - z2));
float la = ((y1 - y2)*((x0 - x1)*(y0 - y2) - (x0 - x2)*(y0 - y1))
+ (z1 - z2)*((x0 - x1)*(z0 - z2) - (x0 - x2)*(z0 - z1))) / a012 / l12;
float lb = -((x1 - x2)*((x0 - x1)*(y0 - y2) - (x0 - x2)*(y0 - y1))
- (z1 - z2)*((y0 - y1)*(z0 - z2) - (y0 - y2)*(z0 - z1))) / a012 / l12;
float lc = -((x1 - x2)*((x0 - x1)*(z0 - z2) - (x0 - x2)*(z0 - z1))
+ (y1 - y2)*((y0 - y1)*(z0 - z2) - (y0 - y2)*(z0 - z1))) / a012 / l12;
float ld2 = a012 / l12;
//unused
pointProj = pointSel;
pointProj.x -= la * ld2;
pointProj.y -= lb * ld2;
pointProj.z -= lc * ld2;
//权重系数计算
float s = 1 - 0.9 * fabs(ld2);
coeff.x = s * la;
coeff.y = s * lb;
coeff.z = s * lc;
coeff.intensity = s * ld2;
if (s > 0.1) {//距离足够小才使用
laserCloudOri->push_back(pointOri);
coeffSel->push_back(coeff);
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudSurfStackNum; i++) {
pointOri = laserCloudSurfStack->points[i];
pointAssociateToMap(&pointOri, &pointSel);
kdtreeSurfFromMap->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 5, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);
if (pointSearchSqDis[4] < 1.0) {
//构建五个最近点的坐标矩阵
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
matA0.at(j, 0) = laserCloudSurfFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x;
matA0.at(j, 1) = laserCloudSurfFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y;
matA0.at(j, 2) = laserCloudSurfFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z;
}
//求解matA0*matX0=matB0
cv::solve(matA0, matB0, matX0, cv::DECOMP_QR);
float pa = matX0.at(0, 0);
float pb = matX0.at(1, 0);
float pc = matX0.at(2, 0);
float pd = 1;
float ps = sqrt(pa * pa + pb * pb + pc * pc);
pa /= ps;
pb /= ps;
pc /= ps;
pd /= ps;
bool planeValid = true;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (fabs(pa * laserCloudSurfFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x +
pb * laserCloudSurfFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y +
pc * laserCloudSurfFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z + pd) > 0.2) {
planeValid = false;
break;
}
}
if (planeValid) {
float pd2 = pa * pointSel.x + pb * pointSel.y + pc * pointSel.z + pd;
//unused
pointProj = pointSel;
pointProj.x -= pa * pd2;
pointProj.y -= pb * pd2;
pointProj.z -= pc * pd2;
float s = 1 - 0.9 * fabs(pd2) / sqrt(sqrt(pointSel.x * pointSel.x
+ pointSel.y * pointSel.y + pointSel.z * pointSel.z));
coeff.x = s * pa;
coeff.y = s * pb;
coeff.z = s * pc;
coeff.intensity = s * pd2;
if (s > 0.1) {
laserCloudOri->push_back(pointOri);
coeffSel->push_back(coeff);
}
}
}
}
float srx = sin(transformTobeMapped[0]);
float crx = cos(transformTobeMapped[0]);
float sry = sin(transformTobeMapped[1]);
float cry = cos(transformTobeMapped[1]);
float srz = sin(transformTobeMapped[2]);
float crz = cos(transformTobeMapped[2]);
int laserCloudSelNum = laserCloudOri->points.size();
if (laserCloudSelNum < 50) {//如果特征点太少
continue;
}
cv::Mat matA(laserCloudSelNum, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAt(6, laserCloudSelNum, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAtA(6, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matB(laserCloudSelNum, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAtB(6, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matX(6, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudSelNum; i++) {
pointOri = laserCloudOri->points[i];
coeff = coeffSel->points[i];
float arx = (crx*sry*srz*pointOri.x + crx*crz*sry*pointOri.y - srx*sry*pointOri.z) * coeff.x
+ (-srx*srz*pointOri.x - crz*srx*pointOri.y - crx*pointOri.z) * coeff.y
+ (crx*cry*srz*pointOri.x + crx*cry*crz*pointOri.y - cry*srx*pointOri.z) * coeff.z;
float ary = ((cry*srx*srz - crz*sry)*pointOri.x
+ (sry*srz + cry*crz*srx)*pointOri.y + crx*cry*pointOri.z) * coeff.x
+ ((-cry*crz - srx*sry*srz)*pointOri.x
+ (cry*srz - crz*srx*sry)*pointOri.y - crx*sry*pointOri.z) * coeff.z;
float arz = ((crz*srx*sry - cry*srz)*pointOri.x + (-cry*crz-srx*sry*srz)*pointOri.y)*coeff.x
+ (crx*crz*pointOri.x - crx*srz*pointOri.y) * coeff.y
+ ((sry*srz + cry*crz*srx)*pointOri.x + (crz*sry-cry*srx*srz)*pointOri.y)*coeff.z;
matA.at(i, 0) = arx;
matA.at(i, 1) = ary;
matA.at(i, 2) = arz;
matA.at(i, 3) = coeff.x;
matA.at(i, 4) = coeff.y;
matA.at(i, 5) = coeff.z;
matB.at(i, 0) = -coeff.intensity;
}
cv::transpose(matA, matAt);
matAtA = matAt * matA;
matAtB = matAt * matB;
cv::solve(matAtA, matAtB, matX, cv::DECOMP_QR);
//退化场景判断与处理
if (iterCount == 0) {
cv::Mat matE(1, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matV(6, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matV2(6, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::eigen(matAtA, matE, matV);
matV.copyTo(matV2);
isDegenerate = false;
float eignThre[6] = {100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100};
for (int i = 5; i >= 0; i--) {
if (matE.at(0, i) < eignThre[i]) {
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
matV2.at(i, j) = 0;
}
isDegenerate = true;
} else {
break;
}
}
matP = matV.inv() * matV2;
}
if (isDegenerate) {
cv::Mat matX2(6, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
matX.copyTo(matX2);
matX = matP * matX2;
}
//积累每次的调整量
transformTobeMapped[0] += matX.at(0, 0);
transformTobeMapped[1] += matX.at(1, 0);
transformTobeMapped[2] += matX.at(2, 0);
transformTobeMapped[3] += matX.at(3, 0);
transformTobeMapped[4] += matX.at(4, 0);
transformTobeMapped[5] += matX.at(5, 0);
float deltaR = sqrt(
pow(rad2deg(matX.at(0, 0)), 2) +
pow(rad2deg(matX.at(1, 0)), 2) +
pow(rad2deg(matX.at(2, 0)), 2));
float deltaT = sqrt(
pow(matX.at(3, 0) * 100, 2) +
pow(matX.at(4, 0) * 100, 2) +
pow(matX.at(5, 0) * 100, 2));
//旋转平移量足够小就停止迭代
if (deltaR < 0.05 && deltaT < 0.05) {
break;
}
}
//迭代结束更新相关的转移矩阵
transformUpdate();
}
4.7点云封装
在完成点云配准之后,将当前时刻的特征点(边沿和平面)封装在不同的子立方体cube中。
- 特征点按距离(比例尺缩小)归入相应的立方体cube
//特征点的点云封装
//将corner points按距离(比例尺缩小)归入相应的立方体
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudCornerStackNum; i++) {
//转移到世界坐标系
pointAssociateToMap(&laserCloudCornerStack->points[i], &pointSel);
//按50的比例尺缩小,四舍五入,偏移laserCloudCen*的量,计算索引
int cubeI = int((pointSel.x + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenWidth;
int cubeJ = int((pointSel.y + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenHeight;
int cubeK = int((pointSel.z + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenDepth;
if (pointSel.x + 25.0 < 0) cubeI--;
if (pointSel.y + 25.0 < 0) cubeJ--;
if (pointSel.z + 25.0 < 0) cubeK--;
if (cubeI >= 0 && cubeI < laserCloudWidth &&
cubeJ >= 0 && cubeJ < laserCloudHeight &&
cubeK >= 0 && cubeK < laserCloudDepth) {//只挑选-laserCloudCenWidth * 50.0 < point.x < laserCloudCenWidth * 50.0范围内的点,y和z同理
//按照尺度放进不同的组,每个组的点数量各异
int cubeInd = cubeI + laserCloudWidth * cubeJ + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * cubeK;
laserCloudCornerArray[cubeInd]->push_back(pointSel);
}
}
//将surf points按距离(比例尺缩小)归入相应的立方体
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudSurfStackNum; i++) {
pointAssociateToMap(&laserCloudSurfStack->points[i], &pointSel);
int cubeI = int((pointSel.x + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenWidth;
int cubeJ = int((pointSel.y + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenHeight;
int cubeK = int((pointSel.z + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenDepth;
if (pointSel.x + 25.0 < 0) cubeI--;
if (pointSel.y + 25.0 < 0) cubeJ--;
if (pointSel.z + 25.0 < 0) cubeK--;
if (cubeI >= 0 && cubeI < laserCloudWidth &&
cubeJ >= 0 && cubeJ < laserCloudHeight &&
cubeK >= 0 && cubeK < laserCloudDepth) {
int cubeInd = cubeI + laserCloudWidth * cubeJ + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * cubeK;
laserCloudSurfArray[cubeInd]->push_back(pointSel);
}
}4.8下采样
特征点下采样之后,要进行汇总下采样,每隔五帧发布一次
//特征点下采样
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudValidNum; i++) {
int ind = laserCloudValidInd[i];
laserCloudCornerArray2[ind]->clear();
downSizeFilterCorner.setInputCloud(laserCloudCornerArray[ind]);
downSizeFilterCorner.filter(*laserCloudCornerArray2[ind]);//滤波输出到Array2
laserCloudSurfArray2[ind]->clear();
downSizeFilterSurf.setInputCloud(laserCloudSurfArray[ind]);
downSizeFilterSurf.filter(*laserCloudSurfArray2[ind]);
//Array与Array2交换,即滤波后自我更新
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr laserCloudTemp = laserCloudCornerArray[ind];
laserCloudCornerArray[ind] = laserCloudCornerArray2[ind];
laserCloudCornerArray2[ind] = laserCloudTemp;
laserCloudTemp = laserCloudSurfArray[ind];
laserCloudSurfArray[ind] = laserCloudSurfArray2[ind];
laserCloudSurfArray2[ind] = laserCloudTemp;
}
mapFrameCount++;
//特征点汇总下采样,每隔五帧publish一次,从第一次开始
if (mapFrameCount >= mapFrameNum) {
mapFrameCount = 0;
laserCloudSurround2->clear();
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudSurroundNum; i++) {
int ind = laserCloudSurroundInd[i];
*laserCloudSurround2 += *laserCloudCornerArray[ind];
*laserCloudSurround2 += *laserCloudSurfArray[ind];
}
laserCloudSurround->clear();
downSizeFilterCorner.setInputCloud(laserCloudSurround2);
downSizeFilterCorner.filter(*laserCloudSurround);
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 laserCloudSurround3;
pcl::toROSMsg(*laserCloudSurround, laserCloudSurround3);
laserCloudSurround3.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeLaserOdometry);
laserCloudSurround3.header.frame_id = "/camera_init";
pubLaserCloudSurround.publish(laserCloudSurround3);
} 4.9全部点云转换到世界坐标系
这里就是最后的操作,将全部点云转换到世界坐标系,并发布出去,同时广播坐标系旋转平移参量。
//将点云中全部点转移到世界坐标系下
int laserCloudFullResNum = laserCloudFullRes->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudFullResNum; i++) {
pointAssociateToMap(&laserCloudFullRes->points[i], &laserCloudFullRes->points[i]);
}
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 laserCloudFullRes3;
pcl::toROSMsg(*laserCloudFullRes, laserCloudFullRes3);
laserCloudFullRes3.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeLaserOdometry);
laserCloudFullRes3.header.frame_id = "/camera_init";
pubLaserCloudFullRes.publish(laserCloudFullRes3);
geometry_msgs::Quaternion geoQuat = tf::createQuaternionMsgFromRollPitchYaw
(transformAftMapped[2], -transformAftMapped[0], -transformAftMapped[1]);
odomAftMapped.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeLaserOdometry);
odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.x = -geoQuat.y;
odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.y = -geoQuat.z;
odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.z = geoQuat.x;
odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.w = geoQuat.w;
odomAftMapped.pose.pose.position.x = transformAftMapped[3];
odomAftMapped.pose.pose.position.y = transformAftMapped[4];
odomAftMapped.pose.pose.position.z = transformAftMapped[5];
//扭转量
odomAftMapped.twist.twist.angular.x = transformBefMapped[0];
odomAftMapped.twist.twist.angular.y = transformBefMapped[1];
odomAftMapped.twist.twist.angular.z = transformBefMapped[2];
odomAftMapped.twist.twist.linear.x = transformBefMapped[3];
odomAftMapped.twist.twist.linear.y = transformBefMapped[4];
odomAftMapped.twist.twist.linear.z = transformBefMapped[5];
pubOdomAftMapped.publish(odomAftMapped);
//广播坐标系旋转平移参量
aftMappedTrans.stamp_ = ros::Time().fromSec(timeLaserOdometry);
aftMappedTrans.setRotation(tf::Quaternion(-geoQuat.y, -geoQuat.z, geoQuat.x, geoQuat.w));
aftMappedTrans.setOrigin(tf::Vector3(transformAftMapped[3],
transformAftMapped[4], transformAftMapped[5]));
tfBroadcaster.sendTransform(aftMappedTrans);
}
}
status = ros::ok();
rate.sleep();
}
return 0;
}
结语
至此,已经把laserMapping.cpp的内容解析完了。上述内容还有几处不太理解的,如果有人能够解答,就请给我留言吧,十分感谢。
如果你看到这里,说明你已经下定决心要学习loam了,学习新知识的过程总是痛苦的,与君共勉吧!