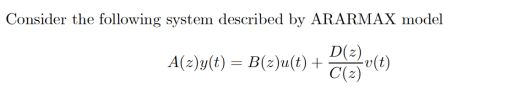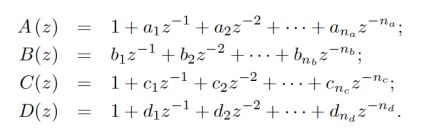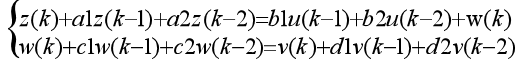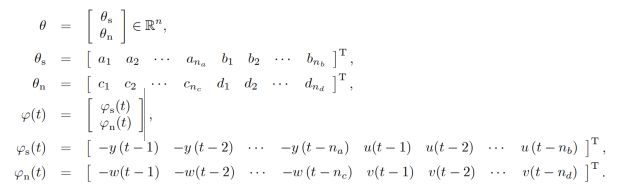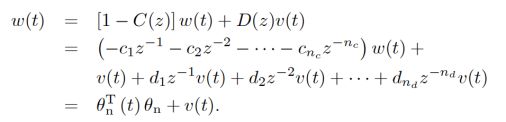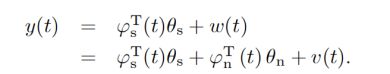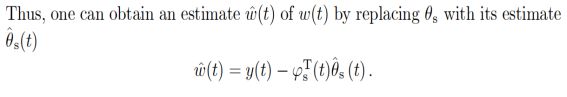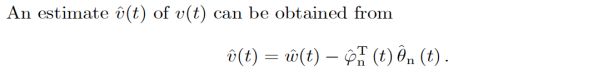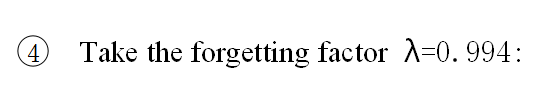系统辨识 广义最小二乘递推算法 matlab仿真实验
广义最小二乘递推 matlab实现
- A. The selected model
- B. Identification algorithm used
- C.Matlab code
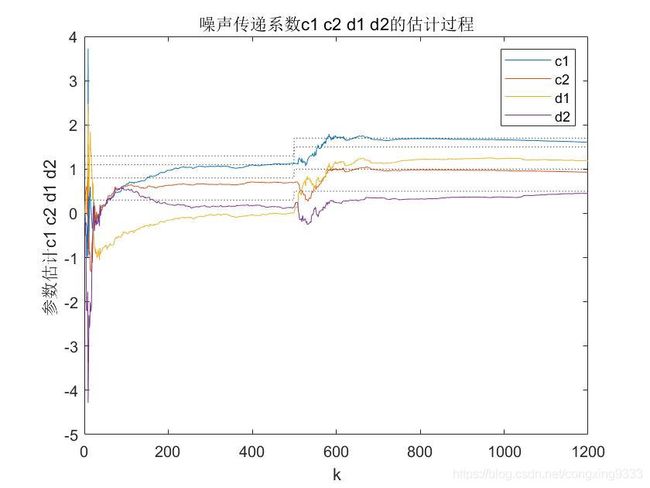
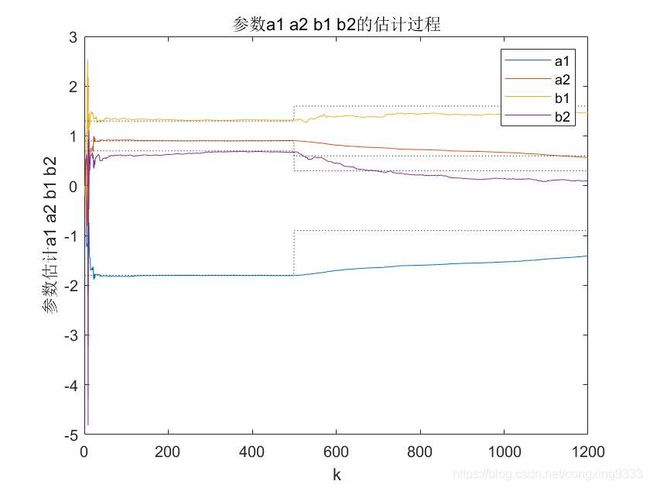
- D.The simulation image
- E. Make a table to compare the estimation of parameters with the truth value
- F. Conclusion
A. The selected model
In this experiment, the specific model is
Where, the truth value of each parameter is:
a1=-1.8;a2=0.9; b1=1.3;b2=0.7;c1=1.3;c2=0.8;d1=1.1;d2=0.3。
In the experiment, the parameters are updated once to verify the stability and reliability of the model,after update(when time >=update_time, and we can set update_time):
a1=-0.9;a2=0.6; b1=1.6;b2=0.3;c1=1.7;c2=1.0;d1=1.5;d2=0.5。
B. Identification algorithm used
Recursive generalized extended least squares algorithm,the derivation is as follows:
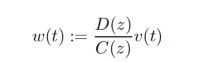
C.Matlab code
%广义最小二乘的递推算法
%z(k)-1.8*z(k-1)+0.9*z(k-2)=1.3*M(k-1)+0.7*M(k-2)+w(k)
%w(k)+1.3*w(k-1)+0.8*w(k-2)=v(k)+1.1*v(k-1)+0.3*v(k-2)
%参数更新后:
%z(k)-0.9*z(k-1)+0.6*z(k-2)=1.6*M(k-1)+0.3*M(k-2)+w(k)
%w(k)+1.7*w(k-1)+1.0*w(k-2)=v(k)+1.5*v(k-1)+0.5*v(k-2)
%========================================
clear all
close all
clc
%===========系统参数真值==============
a=[-1.8 0.9]';
b=[1.3 0.7]';
c=[1.3 0.8]';
d=[1.1 0.3]';
na=length(a);nb=length(b);nc=length(c);nd=length(d); %%na,nb,nc,nd 为输出输入系数矩阵 A,B,C,D 的阶数
a1=[-0.9 0.6]'; %系统参数更新后的真值
b1=[1.6 0.3]';
c1=[1.7 1.0]';
d1=[1.5 0.5]';
%========================================
time=1200; %仿真总时间长度
update_time=500;%更新参数的时间节点
uk=zeros(nb,1);yk=zeros(na,1); %输入输出初始化
u=randn(time,1); %输入信号,采用方差为1的白噪声序列
xi=sqrt(0.1)*randn(time,1); %干扰信号,采用方差为0.1的白噪声序列
vk=sqrt(0.1)*randn(nd,1);wk=zeros(nc,1); %w输入输出初始化
vk_estimate=zeros(nd,1);wk_estimate=zeros(nc,1); %w输入输出估计初始化
%========================================
thetae_1=zeros(na+nb+nc+nd,1); %参数初值
P=10^6*eye(na+nb+nc+nd); %修正系数初值
lambda=1; %遗忘因子范围[0.9 1],遗忘因子=1时,即为标准递推最小二乘
for k=1:time
if k>=update_time %更新参数
theta_1(:,k)=[a1;b1]; %系统参数真值
theta_2(:,k)=[c1;d1]; %系统参数真值
else
theta_1(:,k)=[a;b]; %系统参数真值
theta_2(:,k)=[c;d]; %系统参数真值
end
phi=[-yk;uk(1:nb)]; %输出输入矩阵
phi_w=[-wk;vk(1:nd)]; %w输出输入矩阵
phi_w_estimate=[-wk_estimate;vk_estimate(1:nd)];
phiall=[phi;phi_w]
y(k)=phiall'*[theta_1(:,k);theta_2(:,k)]+xi(k); %系统实际输出
phiall_estimate=[phi;phi_w_estimate]
%递推公式
L=P*phiall_estimate/(lambda+phiall_estimate'*P*phiall_estimate);
thetae(:,k)=thetae_1+L*(y(k)-phiall_estimate'*thetae_1);
P=(eye(na+nb+nc+nd)-L*phiall_estimate')*P/lambda;
%更新数据
thetae_1=thetae(:,k);
for i=nb:-1:2
uk(i)=uk(i-1);
end
uk(1)=u(k);
for j=nc:-1:2
wk_estimate(j)=wk_estimate(j-1);
end
wk_estimate(1)=y(k)-phi'*thetae_1(1:na+nb);
for s=nd:-1:2
vk_estimate(j)=vk_estimate(j-1);
end
vk_estimate(1)=y(k)-phiall_estimate'*thetae_1(:);
for j=nc:-1:2
wk(j)=wk(j-1);
end
wk(1)=phi_w'*theta_2(:,k)+xi(k);%w系统实际输出
for s=nd:-1:2
vk(j)=vk(j-1);
end
vk(1)=sqrt(0.1)*randn(1);
for i=na:-1:2
yk(i)=yk(i-1);
end
yk(1)=y(k);
end
%=====================输出结果及作图=========================
disp('参数 a1 a2 b1 b2 的估计结果(更新参数前):')
ab=thetae(1:na+nb,update_time-1)
disp('噪声传递系数 c1 c2 d1 d2 的估计结果(更新参数前):')
cd=thetae(na+nb+1:na+nb+nc+nd,update_time-1)
disp('参数 a1 a2 b1 b2 的估计结果(更新参数后):')
ab_updata=thetae(1:na+nb,time)
disp('噪声传递系数 c1 c2 d1 d2 的估计结果(更新参数后):')
cd_updata=thetae(na+nb+1:na+nb+nc+nd,time)
disp('参数估计的平方误差总和:')
abcd=[a;b;c;d;a1;b1;c1;d1]-[ab;cd;ab_updata;cd_updata];
erro=abcd'*abcd
i=1:time;
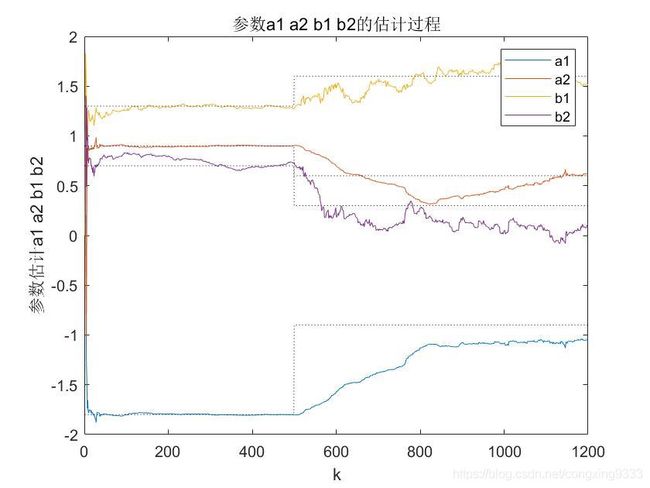
figure('name','参数a,b')
plot(i,thetae(1,:),i,thetae(2,:),i,thetae(3,:),i,thetae(4,:));hold on;plot(i,theta_1(:,:),'k:');
xlabel('k');ylabel(' 参数估计a1 a2 b1 b2 ');
legend('a1','a2','b1','b2');
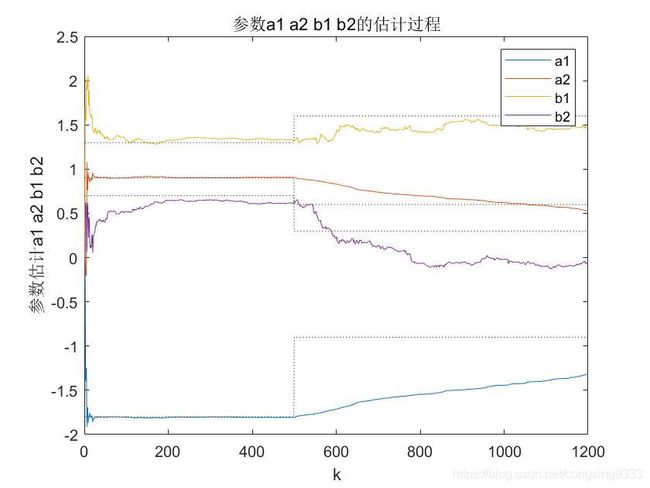
title(' 参数a1 a2 b1 b2的估计过程 ');
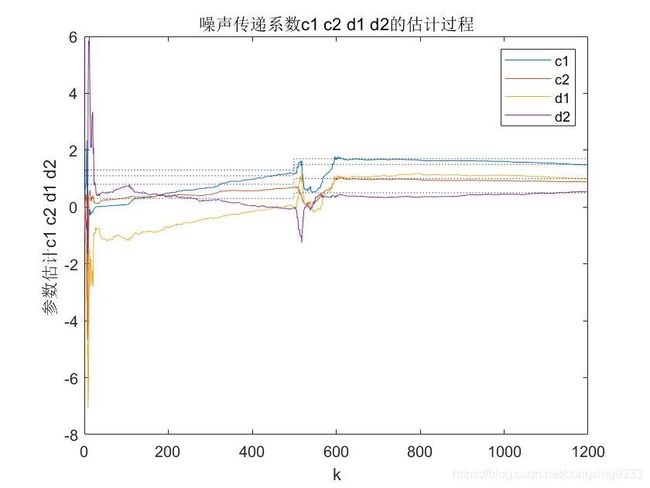
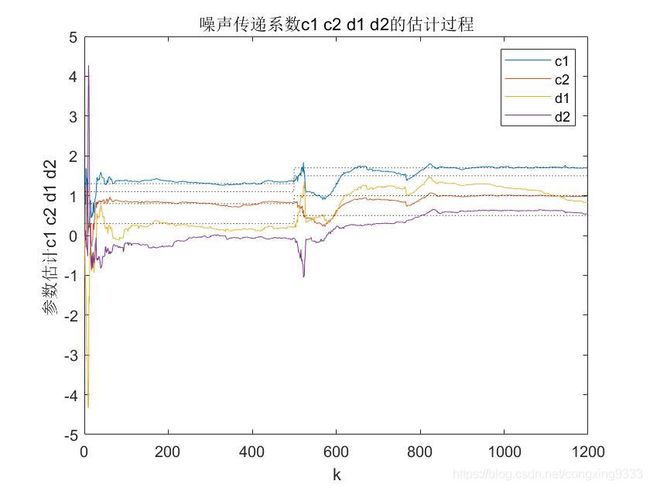
figure('name',' 参数c,d ')
plot(i,thetae(5,:),i,thetae(6,:),i,thetae(7,:),i,thetae(8,:));hold on;hold on;plot(i,theta_2(:,:),'k:');
xlabel('k');ylabel('参数估计c1 c2 d1 d2 ');
legend('c1','c2','d1','d2');
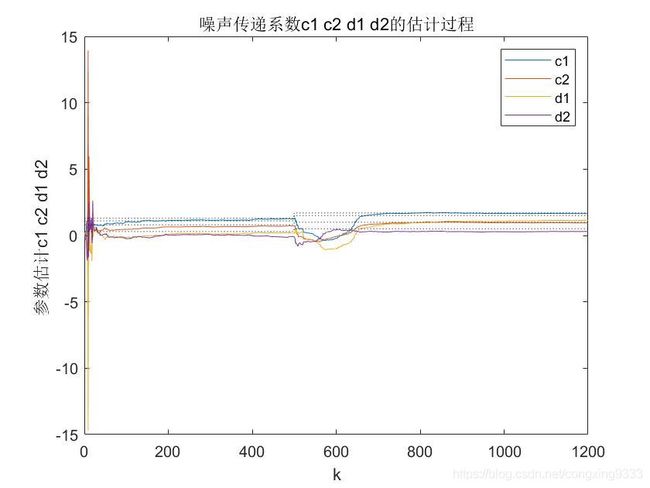
title('噪声传递系数c1 c2 d1 d2的估计过程');
D.The simulation image
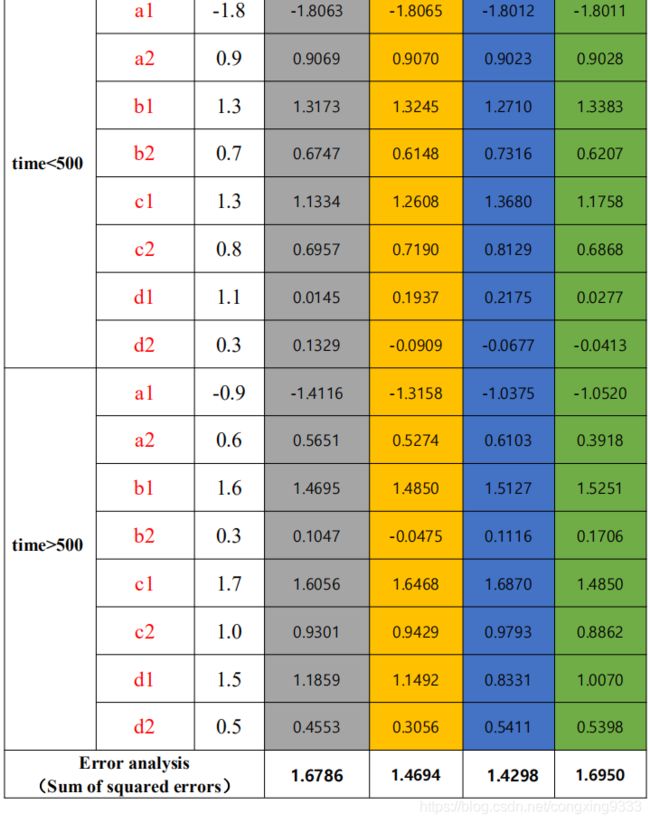
E. Make a table to compare the estimation of parameters with the truth value
F. Conclusion
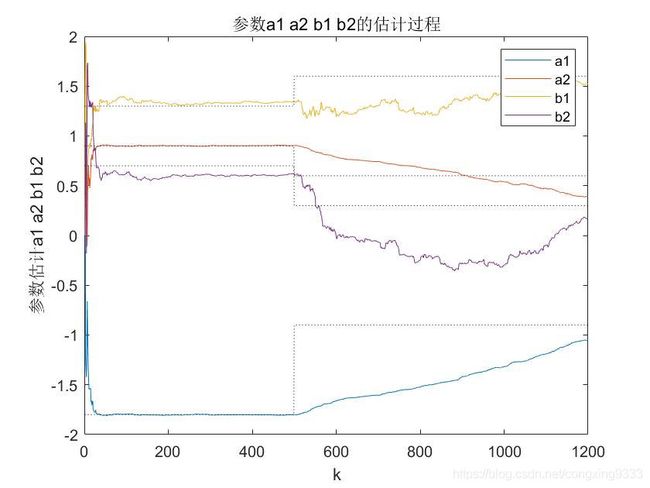
As can be seen from the comparison in the table,the experimental results are close to the real value.Compare the experimental results produced by different forgetting factor,when we take the forgetting factor=0.996,sum of squared errors is minimum,about 1.4298,that means parameter estimation works best.