力扣算法篇:队列与栈
队列与栈篇
- 队列
-
- 设计循环队列
- 队列与广搜
- 岛屿数量(BFS)
- 打开转盘锁
- 完全平方数
- 栈
-
- 有效的括号
- 每日温度
- 逆波兰表达式求值
- 栈与深搜
- 岛屿数量(DFS)
- 克隆图
- 目标和
- 二叉树的中序遍历
- 小结
-
- 用栈实现队列
- 用队列实现栈
- 字符串解码
- 图像渲染
- 01矩阵
- 钥匙和房间
队列
queue<int> q;
//入队
q.push();
//出队
q.pop();
//队首元素
q.front();
//队尾元素
q.back();
//长度
q.size();
//判空
q.empty();
设计循环队列
class MyCircularQueue {
private:
vector<int> data;
int head;
int tail;
int size;
public:
MyCircularQueue(int k) {
data.resize(k);
head = -1;
tail = -1;
size = k;
}
bool enQueue(int value) {
//入队
//判断是否满了
if(isFull()){
//满了
return false;
}
//判断是否为空
if(isEmpty()){
head = 0;
}
//移动尾指针 入队修改尾指针
tail = (tail+1)%size;
//赋值
data[tail] = value;
return true;
}
bool deQueue() {
//出队
//判断是否为空
if(isEmpty()){
return false;
}
//最后一个元素 出完即为空
if(head == tail){
head = -1;
tail = -1;
return true;
}
//否则 修改头指针 出队修改头指针
head = (head + 1) % size;
return true;
}
int Front() {
//返回队首元素
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return data[head];
}
int Rear() {
//返回队尾元素
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return data[tail];
}
bool isEmpty() {
return head == -1;
}
bool isFull() {
//满的判断条件
return ((tail+1)%size) == head;
}
};
队列与广搜
广度优先搜索(BFS)的一个常见应用是找出从根结点到目标结点的最短路径。第一次找到目标结点时,已处于最短路径中。
模板:
一、
/**
* Return the length of the shortest path between root and target node.
*/
int BFS(Node root, Node target) {
//存储待处理的结点
Queue<Node> queue;
//从根结点到当前结点需要的步数
int step = 0;
// 初始化 将根结点加入队列中
add root to queue;
// BFS 广搜
while (queue is not empty) {
step = step + 1;
// 处理已经在队列中的同一层结点
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
//处理头结点
Node cur = the first node in queue;
//如果是目标结点直接返回
return step if cur is target;
//否则 将他的“儿子结点”均加入队列中
for (Node next : the neighbors of cur) {
add next to queue;
}
//删除处理过的第一个结点 此时头结点更新了
remove the first node from queue;
}
}
//从根结点到目标结点没有路径
return -1;
}
二、当需要确定一个结点不会被访问两次时,需要使用哈希集解决这个问题
/**
* Return the length of the shortest path between root and target node.
*/
int BFS(Node root, Node target) {
//存储待处理的结点
Queue<Node> queue;
//哈希集 保证不重复
Set<Node> used;
//从根结点到当前结点需要的步数
int step = 0;
// 初始化 将根结点加入队列中
add root to queue;
add root to used;
// BFS
while (queue is not empty) {
step = step + 1;
// 处理已经在队列中的同一层结点
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
//处理头结点
Node cur = the first node in queue;
//如果是目标结点直接返回
return step if cur is target;
//否则 将他的“儿子结点”加入队列中
for (Node next : the neighbors of cur) {
//下一个结点不在哈希集中 即不重复
if (next is not in used) {
add next to queue;
add next to used;
}
}
remove the first node from queue;
}
}
//从根结点到目标结点没有路径
return -1;
}
有两种情况你不需要使用哈希集:
1.你完全确定没有循环,例如,在树遍历中;
2.你确实希望多次将结点添加到队列中。
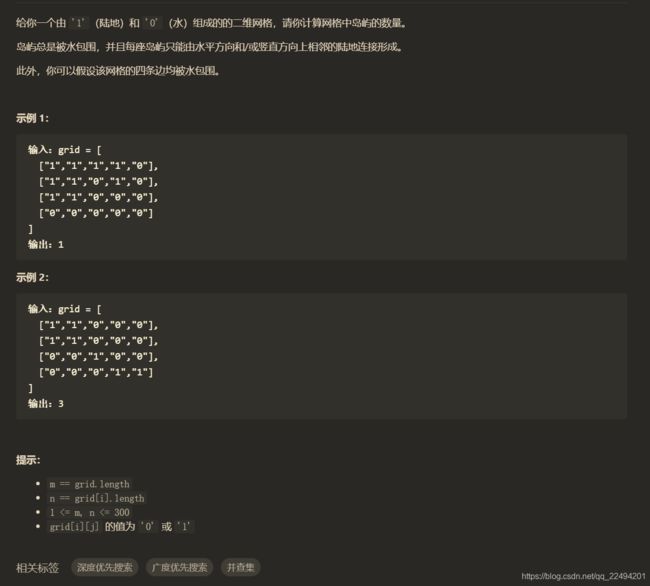
岛屿数量(BFS)
class Solution {
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
//需要保证一个结点不被多次加入队列 除了使用哈希集 可以使用一个数组来记录是否被搜过
//m行n列
int m = grid.size();
if(m == 0){
return 0;
}
int n = grid[0].size();
//队列
queue<pair<int,int>> que;
//岛屿个数
int ans = 0;
//BFS 遍历二维数组
for(int i = 0;i<m;i++){
for(int j = 0;j<n;j++){
//如果字符为1 岛屿数++
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
ans++;
//并将其置为0
grid[i][j]='0';
//加入队列
que.push({
i,j});
//队列不为空
while(!que.empty()){
//当前结点
auto current = que.front();
//出列
que.pop();
//将当前结点周围的1都置为0
int row = current.first;
int col = current.second;
//上
if(row-1>=0 && grid[row-1][col] == '1'){
//加入队列
que.push({
row-1,col});
grid[row-1][col] = '0';
}
//下
if(row+1<m && grid[row+1][col] == '1'){
//加入队列
que.push({
row+1,col});
grid[row+1][col] = '0';
}
//左
if(col-1>=0 && grid[row][col-1] == '1'){
//加入队列
que.push({
row,col-1});
grid[row][col-1] = '0';
}
//右
if(col+1 < n && grid[row][col+1] == '1'){
//加入队列
que.push({
row,col+1});
grid[row][col+1] = '0';
}
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
打开转盘锁
class Solution {
public:
int openLock(vector<string>& deadends, string target) {
//先判断死亡数字中是否包含初始状态0000
vector<string>::iterator iter = find(deadends.begin(),deadends.end(),"0000");
if(iter != deadends.end()){
//存在 直接返回
return -1;
}
//不存在
//最小旋转次数
int result = 0;
//对存储待处理结点
queue<string> q;
//使用一个哈希表存储dead node和访问过的结点
unordered_set<string> visited;
//用数组初始化哈希表
visited.insert(deadends.begin(),deadends.end());
//将初始结点0000加入队列
q.push("0000");
//队列不为空
while(!q.empty()){
int s = q.size();
//处理同层结点
for(int i = 0;i<s;i++){
//当前结点
string current = q.front();
//将其弹出
q.pop();
//开始处理该结点
if(current == target){
return result;
}
//将8叉树的下一层结点加入队列和哈希表
for(int j = 0;j<4;j++){
for(int k = -1;k<2;k = k+2){
//计算可能出现的情况
string temp = current;
//8种temp 字符-/+字符 = 数字 为了考虑0-1的情况 加一个10保证为正数
temp[j] = char((current[j]-'0'+k+10)%10+'0');
//判断该结点是否为死亡结点或者是曾经访问过的结点
if(visited.count(temp)<=0){
//不存在 加入队列和哈希表
q.push(temp);
visited.insert(temp);
}
}
}
}
//处理完同层结点 步数++
result++;
}
//出了循环 说明无路可达
return -1;
}
};
完全平方数

题解:每一个结点都是由上一个结点的值加上当前平方数结点值 与目标数n匹配时,返回层数即可
class Solution {
public:
int numSquares(int n) {
//先将需要用的完全平方数储存起来
vector<int> squares;
for(int i = 1;i<=sqrt(n);i++){
if(i*i<n){
squares.push_back(i*i);
}else if(i*i == n){
//该数就是完全平方数 返回1即可
return 1;
}else{
break;
}
}
//m叉树
int m = squares.size();
//所需要完全平方数的个数
int num_square = 0;
//队列
queue<int> q;
//记录访问过的结点值
unordered_set<int> hash;
//将0结点加入队列
q.push(0);
//处理队列
while(!q.empty()){
//处理当层结点
int s = q.size();
for(int i = 0;i<s;i++){
//当前结点
int current = q.front();
//将其弹出
q.pop();
//开始处理该结点
if(current == n){
return num_square;
}
//将m叉树的下一层结点加入队列
for(int i = 0;i<m;i++){
int temp = squares[i]+current;
if(hash.count(temp)<=0){
q.push(temp);
hash.insert(temp);
}
}
}
//处理完同层结点
num_square++;
}
return num_square;
}
};
栈
stack<int> st;
st.push();
st.pop();
//栈顶元素
st.top();
//判断是否为空
st.empty();
//长度
st.size();
有效的括号

题解:遇到左括号将右括号入栈 遇到右括号判断栈是否为空 为空不匹配 不为空判断当前元素是否与栈顶元素相同 字符串全部遍历完毕时 若栈为空 则匹配 否则 不匹配
class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
//将当前输入字符与栈顶元素匹配
//定义栈
stack<char> st;
//遍历字符串
for(int i = 0;i<s.length();i++){
//遇到左括号 将右括号入栈
if(s[i] == '('){
st.push(')');
}else if(s[i] == '['){
st.push(']');
}else if(s[i] == '{'){
st.push('}');
}else{
//遇到右括号 判断栈是否为空
if(st.empty()){
//为空 不匹配 返回false
return false;
}else{
//不为空 查看栈顶元素是否与当前字符相等
if(st.top()==s[i]){
//相等 匹配 将其出栈
st.pop();
}else{
//不等 不匹配 返回false
return false;
}
}
}
}
//遍历结束 判断栈中是否还有元素
if(st.empty()){
//为空 匹配
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
每日温度
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> dailyTemperatures(vector<int>& T) {
//列表长度
int n = T.size();
//如果列表长度为1
if(n == 1){
//返回[0]
return {
0};
}
//结果列表
vector<int> result(n);
//栈
stack<int> st;
//遍历数组
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
//如果栈不为空并且当前元素大于T[栈顶元素]
while(!st.empty() && T[i]>T[st.top()]){
//将栈顶元素出栈 且更新result数组
result[st.top()] = i-st.top();
st.pop();
}
//否则 入栈
st.push(i);
}
return result;
}
};
逆波兰表达式求值
class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
//逆波兰表达式
//定义栈
stack<int> st;
//两个运算数字
int a,b;
int result = 0;
for(string token:tokens){
if(token == "+"){
//取出栈中两个数字进行运算
a = st.top();
st.pop();
b = st.top();
st.pop();
result = a+b;
//将运算结果压入栈中
st.push(result);
}else if(token == "-"){
//取出栈中两个数字进行运算
a = st.top();
st.pop();
b = st.top();
st.pop();
result = b-a;
//将运算结果压入栈中
st.push(result);
}else if(token == "*"){
//取出栈中两个数字进行运算
a = st.top();
st.pop();
b = st.top();
st.pop();
result = a*b;
//将运算结果压入栈中
st.push(result);
}else if(token == "/"){
//取出栈中两个数字进行运算
a = st.top();
st.pop();
b = st.top();
st.pop();
result = b/a;
//将运算结果压入栈中
st.push(result);
}else{
//是数字
int n = atoi(token.c_str());
//压入栈
st.push(n);
}
}
//返回运算结果
return st.top();
}
};
栈与深搜
从根结点出发,沿一条路径到达最深结点之后,回溯,尝试令一条路径。
与BFS不同,DFS更早访问的结点可能不是更靠近根结点的结点。因此,在DFS 中找到的第一条路径可能不是最短路径。
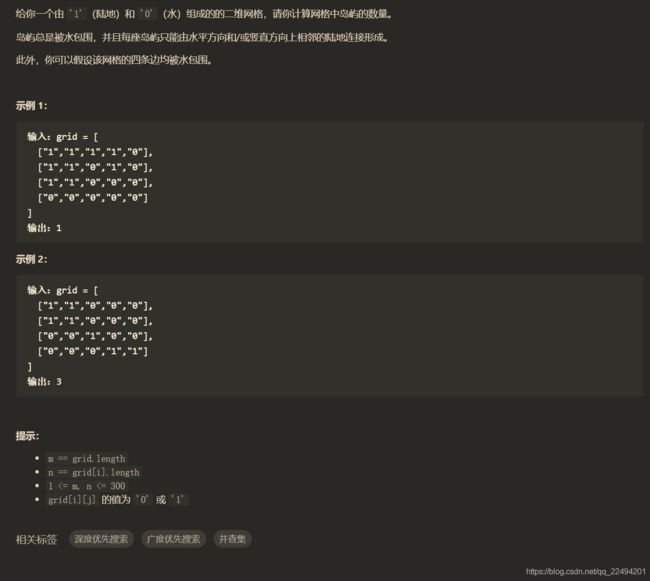
岛屿数量(DFS)
class Solution {
public:
//dfs
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid,int i,int j){
if(i<0 || i>=grid.size() || j<0 || j>=grid[0].size() || grid[i][j] == '0'){
return;
}
//否则 置零
grid[i][j] = '0';
//上
dfs(grid,i-1,j);
//下
dfs(grid,i+1,j);
//左
dfs(grid,i,j-1);
//右
dfs(grid,i,j+1);
}
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
//深搜
//m行n列
int m = grid.size();
if(m == 0){
return 0;
}
int n = grid[0].size();
//岛屿个数
int ans = 0;
//遍历格子
for(int i = 0;i<m;i++){
for(int j = 0;j<n;j++){
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
ans++;
//将该1以及四周的1全部置为0
dfs(grid,i,j);
}
}
}
//返回岛屿个数
return ans;
}
};
克隆图
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector neighbors;
Node() {
val = 0;
neighbors = vector();
}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
neighbors = vector();
}
Node(int _val, vector _neighbors) {
val = _val;
neighbors = _neighbors;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
private:
unordered_map<Node*,Node*> hash;
public:
Node* cloneGraph(Node* node) {
//判断所给结点是否为空
if(node == nullptr){
return node;
}
//不为空 判断该结点是否被创建过
if(hash.count(node)>0){
//存在 返回克隆结点
return hash[node];
}
//不存在 创建新结点copy该结点
Node* newNode = new Node(node->val);
//将该结点加入哈希表中
hash.insert(make_pair(node,newNode));
//创建该结点的邻居结点
for(Node* neighbor:node->neighbors){
newNode->neighbors.push_back(cloneGraph(neighbor));
}
return newNode;
}
};
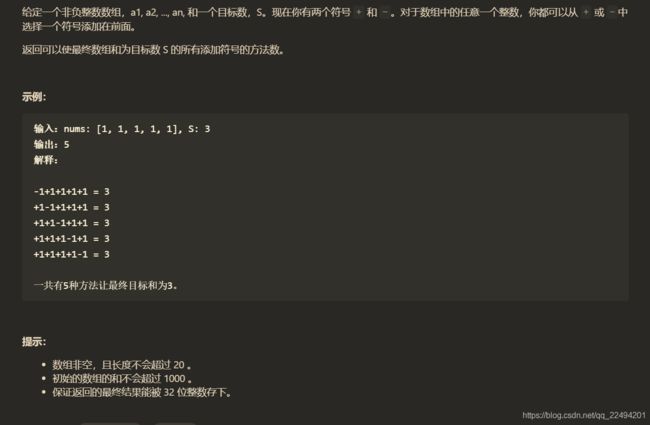
目标和
题解:
class Solution {
public:
//深搜
int count=0;
//cur 当前和 i数组下标索引 target 目标值
void dfs(vector<int>& nums,int cur,int i,int target){
//如果i等于数组长度了 截止
if(i == nums.size()){
//判断和是否为目标值
if(cur == target){
count++;
return;
}
}else{
//搜起 加或者减下一个数
dfs(nums,cur+nums[i],i+1,target);
dfs(nums,cur-nums[i],i+1,target);
}
}
int findTargetSumWays(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
//目标和 深搜
dfs(nums,0,0,target);
return count;
}
};
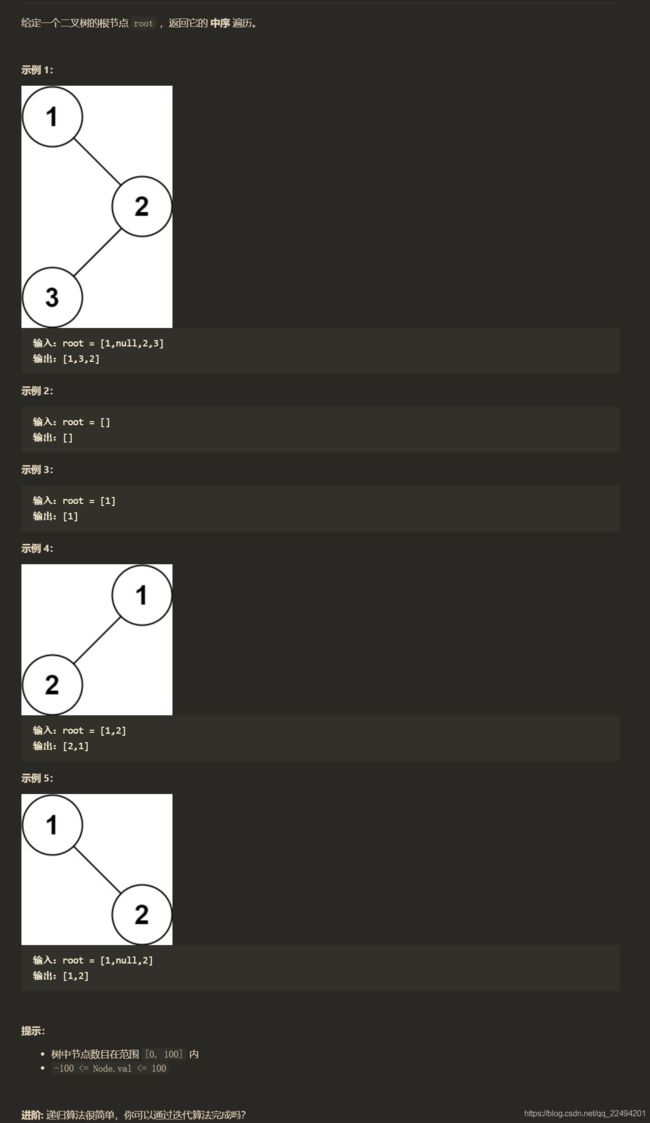
二叉树的中序遍历
使用显式栈的模板:
/*
* Return true if there is a path from cur to target.
*/
//java
boolean DFS(int root, int target) {
Set<Node> visited;
Stack<Node> s;
add root to s;
while (s is not empty) {
Node cur = the top element in s;
return true if cur is target;
for (Node next : the neighbors of cur) {
if (next is not in visited) {
add next to s;
add next to visited;
}
}
remove cur from s;
}
return false;
}
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
//中序遍历 左儿子 根结点 右儿子
//定义栈
stack<TreeNode*> st;
//哈希表
unordered_set<TreeNode*> hash;
//结果数组
vector<int> result;
while(!st.empty() || root!=nullptr){
//不断向左结点深入 直到叶子结点
while(root!=nullptr){
st.push(root);
root = root->left;
}
//叶子结点
TreeNode* top = st.top();
//加入结果数组
result.push_back(top->val);
//出栈
st.pop();
//右儿子结点
root = top->right;
}
return result;
}
};
小结
用栈实现队列
class MyQueue {
//双栈结构
//输入栈
stack<int> in_stack;
//输出栈
stack<int> out_stack;
public:
/** 初始化 */
MyQueue() {
}
/** 加入一个元素到队列 输入栈 */
void push(int x) {
//加入到输入栈
in_stack.push(x);
}
/** 移除队头元素 */
int pop() {
//如果输出栈为空 将输入栈的元素压入输出栈
if(out_stack.empty()){
while(!in_stack.empty()){
//加入输出栈
out_stack.push(in_stack.top());
//队头出栈
in_stack.pop();
}
}
//不为空了 输出栈的队尾元素就是原来的队头元素
int x = out_stack.top();
out_stack.pop();
//将移除的队头元素返回
return x;
}
/** 得到队头元素 */
int peek() {
//如果输出栈为空 将输入栈的元素压入输出栈
if(out_stack.empty()){
while(!in_stack.empty()){
//加入输出栈
out_stack.push(in_stack.top());
//队头出栈
in_stack.pop();
}
}
//不为空了 输出栈的队尾元素就是原来的队头元素
return out_stack.top();
}
/** 判断队列是否为空 */
bool empty() {
//输入栈和输出栈均为空时才为空
return in_stack.empty()&& out_stack.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->peek();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
用队列实现栈
class MyStack {
//双队列 a,b
queue<int> in_queue;
queue<int> out_queue;
public:
/** 初始化 */
MyStack() {
}
/** 压入一个元素进栈 */
void push(int x) {
//加入不为空的队列中
if(!in_queue.empty()){
in_queue.push(x);
}else if(!out_queue.empty()){
out_queue.push(x);
}else{
//两个都为空 加入in队列
in_queue.push(x);
}
}
/** 移除栈顶元素并返回栈顶元素*/
int pop() {
//栈顶元素在队列中为队尾元素 输出队列不为空时将输入队列的值压入队列
//查看不空队列是哪个
if(in_queue.empty()){
int n = out_queue.size();
//n-1次出列
while(--n){
int top = out_queue.front();
in_queue.push(top);
out_queue.pop();
}
//最后一个元素出列
int back = out_queue.front();
out_queue.pop();
return back;
}else if(out_queue.empty()){
int n = in_queue.size();
while(--n){
int top = in_queue.front();
out_queue.push(top);
in_queue.pop();
}
//最后一个元素出列
int back = in_queue.front();
in_queue.pop();
return back;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
/** 得到栈顶元素 */
int top() {
if(!in_queue.empty()){
return in_queue.back();
}else if(!out_queue.empty()){
return out_queue.back();
}else{
//均为空
return -1;
}
}
/** 栈是否为空*/
bool empty() {
//两队列为空时才为空
return in_queue.empty()&&out_queue.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack* obj = new MyStack();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
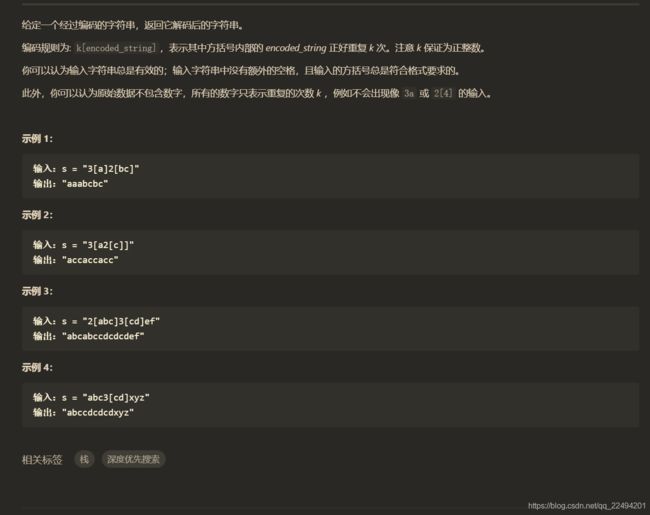
字符串解码
class Solution {
public:
string decodeString(string s) {
//考虑只有一个字符的情况
if(s.length() == 1){
return s;
}
//为了有效地解决嵌套括号 使用3个栈
//数字栈
stack<int> st1;
//括号栈
stack<char> st2;
//字母栈
stack<char> st3;
//结果字符串
string result;
//遍历字符串
for(int i = 0;i<s.length();i++){
//判断是数字还是括号还是字母
if(isdigit(s[i])!=0){
//是数字 数字可能不止1位 例如:100
//如果括号栈为空 那么该数字和前面的数组是一起的
if(st1.empty()){
st1.push(s[i]-'0');
}else{
//不为空且括号栈为空
if(st2.empty()){
//该数字和数字栈中的数字是一起的 取出然后再次压入
int count = st1.top()*10+(s[i]-'0');
// cout<<"count:"<
//出栈
st1.pop();
//再次入栈
st1.push(count);
}else{
//括号栈不为空
if(st1.top() == '#'){
st1.push(s[i]-'0');
}else{
int count = st1.top()*10+(s[i]-'0');
// cout<<"count:"<
//出栈
st1.pop();
//再次入栈
st1.push(count);
}
}
}
}else if(isalpha(s[i]) !=0 ){
//是字母 查看括号栈中是否有括号 没有括号直接加入到结果字符串中
if(st2.empty()){
//为空 不需要重复
result+=s[i];
}else{
//不为空 压入字母栈
st3.push(s[i]);
}
}else{
//是括号
//左括号
if(s[i] == '['){
//压入括号栈 同时为了解决嵌套问题 在字母栈和数字栈压入一个#
st2.push(s[i]);
st1.push('#');
st3.push('#');
}else{
//右括号
//如果括号栈内只有一个括号
if(st2.size() == 1){
//取出字母栈中的字母
string temp;
int n2 = st3.size();
while(--n2){
temp+=st3.top();
st3.pop();
}
//将#出栈
st3.pop();
//字符串反转
reverse(temp.begin(),temp.end());
//重复
//先将数字栈中的#出栈
st1.pop();
int n = st1.top();
//数字出栈
st1.pop();
string temp2;
while(n--){
temp2+=temp;
}
//加入结果字符
result+=temp2;
//将括号栈中的括号出栈
st2.pop();
}else{
//不止一个括号 存在括号的嵌套
//取出字母栈中的字母
string temp;
while(st3.top()!='#'){
temp+=st3.top();
st3.pop();
}
//将#出栈
st3.pop();
//字符串反转
reverse(temp.begin(),temp.end());
//将temp重复
//先将数字栈中的#出栈
st1.pop();
int n = st1.top();
//数字出栈
st1.pop();
string temp2;
while(n--){
temp2+=temp;
}
//将temp再次压入栈中
for(int j = 0;j<temp2.length();j++){
st3.push(temp2[j]);
}
//将括号栈中的一个括号出栈
st2.pop();
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
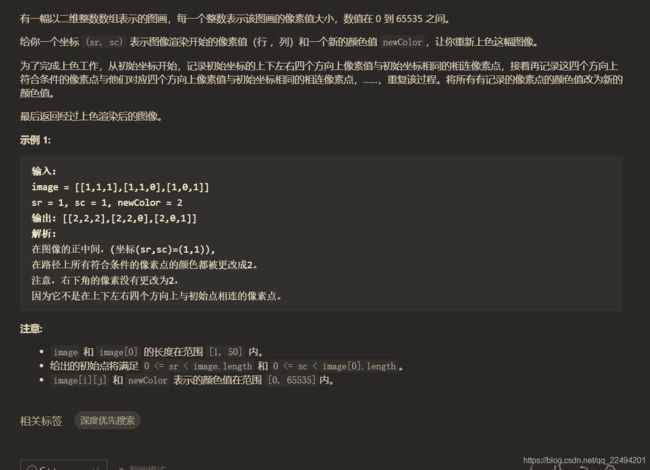
图像渲染
class Solution {
public:
//深搜函数
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& image, int sr, int sc,int num,int newNum){
//该点是否超出界限
if(sr<0 ||sr>=image.size() || sc<0 ||sc>=image[0].size()){
return;
}
//如果该值为num
if(image[sr][sc] == num){
// 更改该值
image[sr][sc] = newNum;
}else{
//不为num
return;
}
//四个方向搜起
dfs(image,sr+1,sc,num,newNum);
dfs(image,sr-1,sc,num,newNum);
dfs(image,sr,sc+1,num,newNum);
dfs(image,sr,sc-1,num,newNum);
}
vector<vector<int>> floodFill(vector<vector<int>>& image, int sr, int sc, int newColor) {
//深搜 图像渲染
//使用一个数组标志是否需要改像素值
//深搜
int num = image[sr][sc];
if(num!=newColor){
dfs(image,sr,sc,num,newColor);
}
return image;
}
};
01矩阵
class Solution {
private:
static constexpr int dirs[4][2] = {
{
-1,0},{
1,0},{
0,-1},{
0,1}};
public:
vector<vector<int>> updateMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
//01矩阵 广搜
//m行n列
int m = matrix.size();
int n = matrix[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> dist(m,vector<int>(n));
vector<vector<int>> seen(m,vector<int>(n));
queue<pair<int,int>> q;
//将所有的0添加进初始队列
for(int i = 0;i<m;i++){
for(int j = 0;j<n;j++){
if(matrix[i][j] == 0){
q.emplace(i,j);
seen[i][j] = 1;
}
}
}
//广搜
while(!q.empty()){
//队头元素
auto [i,j] = q.front();
//弹出
q.pop();
//当前元素的四个方向
for(int d = 0;d<4;d++){
int ni = i+dirs[d][0];
int nj = j+dirs[d][1];
//不越界且未加入队列
if(ni>=0 && ni<m&&nj>=0&&nj<n&&!seen[ni][nj]){
//从i,j到ni,nj,只需一步 加1即可
dist[ni][nj] = dist[i][j]+1;
//加入队列
q.emplace(ni,nj);
//标记已加入队列
seen[ni][nj] = 1;
}
}
}
return dist;
}
};
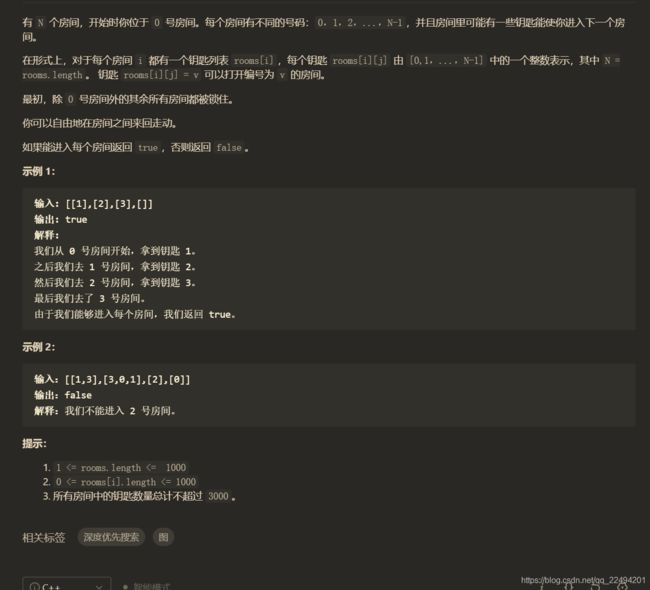
钥匙和房间
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<int> &visited, int room)
{
// 已访问
visited[room] = 1;
// 遍历该房间room号房存在的钥匙
for (int i = 0; i < rooms[room].size(); i++){
int x = rooms[room][i];
// x房间还没去过,就去x房间
if(visited[x] == 0){
dfs(rooms,visited,x);
}
}
}
bool canVisitAllRooms(vector<vector<int>>& rooms) {
//房间个数
int n = rooms.size();
//是否访问过该房间 访问过为1 未访问为0
vector<int> visited(n,0);
//深搜
dfs(rooms,visited,0);
//走过的房间数
int res = 0;
for (int x:visited){
res += x;
}
//走过的房间数=房间数 即可达
return n == res;
}
};