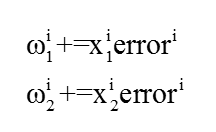参考资料
chapter2
Training Ma
chine Learning Algorithms for Classifcation
引言
在上一节,我们学习了梯度下降算法,现在我们来了解一下梯度下降算法的一个类型——随机梯度下降,每一次更新只考虑一个样本的数据误差,所以速度很快,能进行在线的参数更新... ...
原理
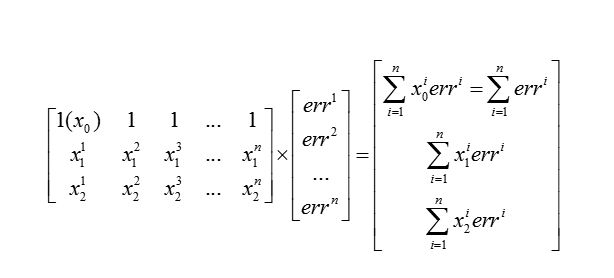
基本原理与批量梯度下降算法相同,不同的是更新权值的方法
这是上一章节的权值更新方法
在随机梯度下降中,我们一次考虑一个样本的误差,再逐个加和,一旦到达最小,就可以停下来,所以可以大大加快模拟的速度,同时每一次迭代开始的时候,我们都打乱一遍训练集,为了减小样本之间造成的参数更新抵消问题
Python实现
我们在上一节AdalineGD类的基础上稍加改动就得到了AdalineSGD类
主要的改动有:
- 增加了一个洗牌(shuffle)方法,用于在每一次迭代开始的时候打乱训练集
- 增加了一个权值更新(._update_weights)方法, 用于更新每一个样本的误差
ok
上代码吧, 有什么问题都在注释里说明了
__author__ = 'Administrator'
#! /usr/bin/python
# -*- coding:utf8 -*-
import numpy as np
from numpy.random import seed
class AdalineSGD(object):
"""
ADAlineSGD Linear Neuron classifier.
Parameters(参数)
------------
eta : float
Learning rate (between 0.0 and 1.0) 学习效率
n_iter : int
Passes over the training dataset(数据集).
Attributes(属性)
-----------
w_ : 1d-array
Weights after fitting.
errors_ : list
Number of misclassifications in every epoch(时间起点).
shuffle: bool (default :True) 洗牌
每次训练开始的时候将训练集重新打乱
如果为真,阻止循环
用随机数来 打乱数据集 并且初始化权值
"""
def __init__(self, eta=0.01, n_iter=10,shuffle = True,
random_state = None):
self.eta = eta
self.n_iter = n_iter
self.w_initialiezed = False
self.shuffle = shuffle
if random_state:
seed(random_state)
def _shuffle(self, X, y):
"""shuffle training data"""
r = np.random.permutation(len(y))
#random.permutation(array/number)
#接受array的时候返回的是 array 的打乱的排列 ,
# 接受 数字的时候 返回一个 range(number) 的打乱的排列
# 所谓‘排列’可以理解成一个有数组序号组成的数组
#X[r] 就是 X 按照 r 的排列重排的数组(只重排第一个索引(重排行)),
# 同时 X[r] 返回一个copy 的对象
#X 本身并没有改变
#random.shuffle(array)不返回对象,重排array,改变array本身
return X[r], y[r]
def _initialize_weights(self, m):
"""Initialize weights to zeros"""
self.w_ = np.zeros(1+m)
#初始化之后把属性 w_initialiezd 设为 True
self.w_initialiezed = True
def fit(self, X, y):
'''
Fit training data.
Parameters
----------
X : {array-like}, shape = [n_samples, n_features] X的形式是列表的列表
Training vectors, where n_samples is the number of samples
and n_features is the number of features.
y : array-like, shape = [n_samples]
Target values.
Returns
-------
self : object
'''
self._initialize_weights(X.shape[1])
#将 权值属性self.w_初始化 (100,1)的0数组
#X.shape = (100,2)
self.cost_ =[]
#self.cost_损失函数 cost_function
for i in range(self.n_iter):
#开始默认 shuffle为真
if self.shuffle:
X, y = self._shuffle(X,y)
cost = []
for xi,target in zip(X,y):
cost.append(self._update_weights(xi,target))
avg_cost = sum(cost)/len(y)
#avg_cost = np.array(cost).mean()
#也可用这种方法求平均数
self.cost_.append(avg_cost)
return self
def partial_fit(self, X, y):
"""Fit training data without reinitializing the weights"""
if not self.w_initialiezed:
self._initialize_weights(X.shape[1])
if y.ravel().shape[0] > 1:
for xi, target in zip(X, y):
self._update_weights(xi,target)
else:
self._update_weights(X, y)
return self
def _update_weights(self, xi, target):
"""Apply Adaline learning rule to update the weights"""
output = self.net_input(xi)
error = (target - output)
#每次error都是一个float
#xi对应一个样本 (2,1)
#wi 的 update = eta* xi[i]*error
self.w_[1:] += self.eta * xi.dot(error)
self.w_[0] += self.eta * error
cost = 0.5 * error ** 2
return cost
def net_input(self, X):
"""Calculate net input"""
#np.dot(A,B)表示矩阵乘法 ,X(100,2) self.w_[1:](2,1)
#注意 这里每一组 向量x = [x1,x2] 不是 [x1,,,,,,x100]!!!
#所以得到的 net_input 是(100,1)的矩阵 表示100个样本的net_input
return (np.dot(X, self.w_[1:])+self.w_[0])
def activation(self,X):
"""Compute linear activation"""
return self.net_input(X)
def predict(self, X):
"""return class label after unit step"""
return np.where(self.net_input(X) >= 0.0, 1, -1)
一样用鸢尾花 Iris 的数据集来验证一下
__author__ = 'Administrator'
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf8 -*-
from GDR import AdalineSGD
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from PDC import plot_decision_regions
filename = 'Iris.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(filename,header=None)
y = df.iloc[0:100, 4].values # .values将dataframe中的值存进一个list中
y = np.where(y=='Iris-setosa',-1,1) #如果是 Iris-setosa y=-1否则就是1 (二元分类)
X = df.iloc[0:100,[0,2]].values
X_std = np.copy(X)
X_std[:,0] = (X[:,0]-X[:,0].mean())/ X[:,0].std() #.std() 标准差
X_std[:,1] = (X[:,1]-X[:,1].mean())/ X[:,1].std() #.std() 标准差
ada = AdalineSGD(n_iter=15, eta=0.01,random_state=1)
ada.fit(X_std, y)
plot_decision_regions(X_std, y, classifier=ada)
plt.title('Adaline - Stochastic Gradient Descent')
plt.xlabel('sepal length [standardized]')
plt.ylabel('petal length [standardized]')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.savefig('Adaline- Stochastic Gradient Descent.png')
plt.show()
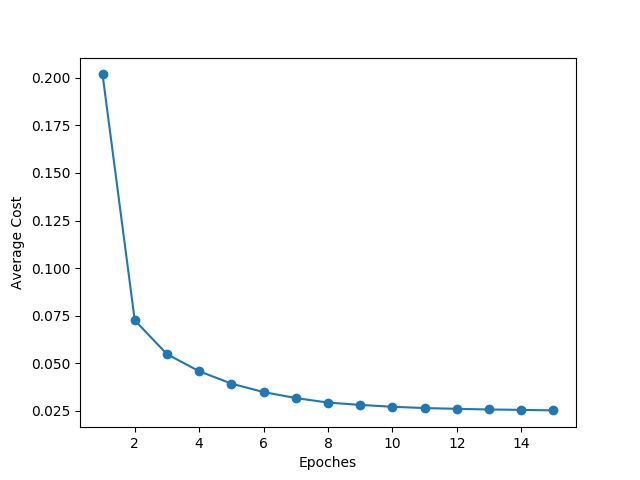
plt.plot(range(1,len(ada.cost_)+1), ada.cost_, marker='o')
plt.xlabel('Epoches')
plt.ylabel('Average Cost')
plt.savefig('Average Cost - Epoches.png')
plt.show()
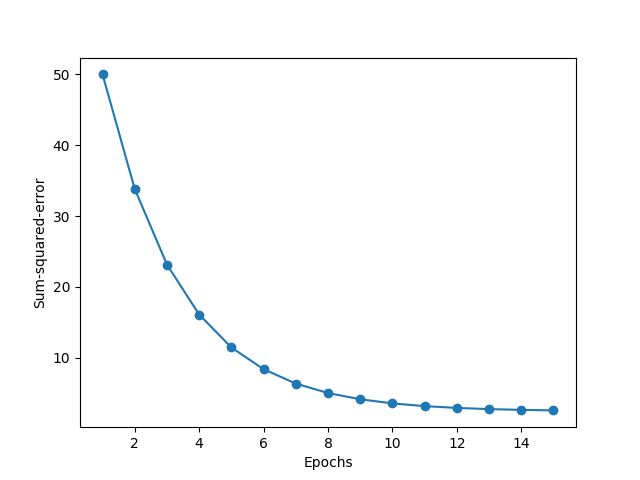
比较一下达到最优的速率
SGD
BGD
很明显 SGD 的收敛速率要快一点
OK!