JavaScript数据结构与算法 - 二叉堆和堆排序
1. 二叉堆
- 二叉堆是一种特殊的二叉树,是一棵完全二叉树
- 结构特性: 树的每一层都有左侧和右侧子节点(除了最后一层的叶节点),并且最后一层的叶节点尽可能都是左侧子节点
- 二叉堆分最小堆和最大堆
- 二叉堆能高效、快速地找出最大值和最小值,常被应用于优先队列
- 也常被用于堆排序算法
二叉堆是二叉树,但不一定是二叉搜索树(BST)。
- 在二叉堆中,每个子节点都要大于等于父节点(最小堆)或小于等于父节点(最大堆)
- 在二叉搜索树中,左侧子节点总是比父节点小,右侧子节点也总是更大
2. 最小堆
2.1 创建最小堆类
function defaultCompare(a, b) {
if (a === b) {
return Compare.EQUALS;
}
return a < b ? Compare.LESS_THAN : Compare.BIGGER_THAN;
}
class MinHeap {
constructor(compareFn = defaultCompare) {
// 比较存储在数据结构中的值
this.compareFn = compareFn;
// 使用数组存储数据
this.heap = [];
}
}
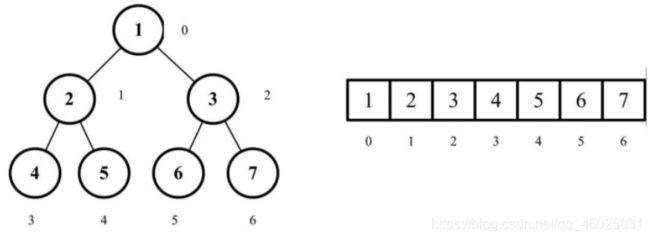
2.2 二叉树的数组表示
二叉树的两种表示方式:
访问使用普通数组的二叉树节点,可以通过操作index
对于给定位置index的节点:
- 它的左侧子节点的位置:2 * index + 1(如果位置可用)
- 它的右侧子节点的位置:2 * index + 2(如果位置可用)
- 它的父节点的位置:index / 2(如果位置可用)
getLeftIndex(index) {
return 2 * index + 1;
}
getRightIndex(index) {
return 2 * index + 2;
}
getParentIndex(index) {
if (index === 0) {
return undefined;
}
return Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
}
常用方法:
- insert(value):向堆中插入一个新的值。如果插入成功,返回true,否则返回false
- extract():移除最小值(最小堆)或最大值(最大堆),并返回这个值
- findMinimum():返回最小值(最小堆)或最大值(最大堆),不会移除这个值
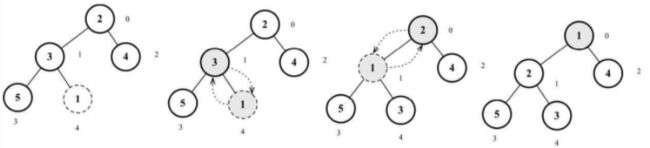
2.3 向堆中插入值
指将值插入堆的底部叶节点(数组的最后一个位置),再将这个值和它的父节点进行交换,直到父节点小于这个插入的值,称为上移操作。
insert(value) {
if (value != null) {
// 将值插入堆的底部叶节点
this.heap.push(value);
// 上移操作
this.siftUp(this.heap.length - 1);
return true;
}
return false;
}
- 上移操作
siftUp(index) {
// siftUp方法接收插入值的位置作为参数,获取其父节点位置
let parent = this.getParentIndex(index);
while (
index > 0 &&
this.compareFn(this.heap[parent], this.heap[index]) > Compare.BIGGER_THAN
) {
// 如果插入的值小于它的父节点
// 将这个元素和父节点交换
swap(this.heap, parent, index);
index = parent;
// 重复交换过程直到堆的根节点也经过了交换节点和父节点位置的操作
parent = this.getParentIndex(index);
}
}
- 交换函数
function swap(array, a, b) {
const temp = array[a];
array[a] = array[b];
array[b] = temp;
}
使用ES6语法写:
const swap = (array, a, b) => [array[a], array[b]] = [array[b], array[a]];
演示结果如下图:
const heap = new MinHeap();
heap.insert(2);
heap.insert(3);
heap.insert(4);
heap.insert(5);
heap.insert(1);
2.4 从堆中找到最小值或最大值
- 最小堆中,最小值总是位于数组的第一个位置
- 最大堆中,数组的第一个元素保存了最大值,可以使用相同代码
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
findMinimum() {
// 如果堆不为空,返回数组的第一个值
return this.isEmpty() ? undefined : this.heap[0];
}
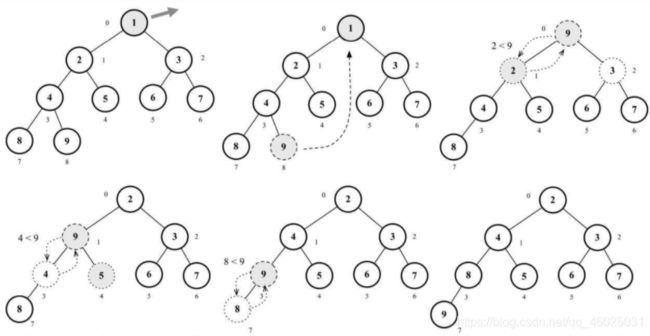
2.5 导出堆中的最小值或最大值
移除最小值(最小堆)或最大值(最大堆)表示移除数组中的第一个元素(堆的根节点)。
在移除后,需要将堆的最后一个元素移动至根部并执行siftDown函数,表示将交换元素直到堆的结构正常。
extract() {
// 堆为空,返回undefined
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
// 只有一个值,直接移除
if (this.size() === 1) {
return this.heap.shift();
}
// 不止一个值,需要将第一个移除
const removedValue = this.heap.shift();
// 存储到一个临时变量中以便执行完下移操作后返回它
this.siftDown(0);
return removedValue;
}
- 下移操作(堆化)
siftDown(index) {
let element = index;
// 获取左侧子节点的值
const left = this.getLeftIndex(index);
// 获取右侧子节点的值
const right = this.getRightIndex(index);
const size = this.size();
if (
left < size &&
this.compareFn(this.heap[element], this.heap[left]) > Compare.BIGGER_THAN
) {
// 如果元素比左侧子节点小且index合法
// 交换元素和它的左侧子节点
element = left;
}
if (
right < size &&
this.compareFn(this.heap[element], this.heap[right]) > Compare.BIGGER_THAN
) {
// 如果元素小于它的右侧子节点且index合法
// 交换元素和它的右侧子节点
element = right;
}
if (index !== element) {
// 找到最小子节点后,要检验它的值是否和element相同
// 如果不相同,就将它和最小的element交换
swap(this.heap, index, element);
// 重复这个过程
this.siftDown(element);
}
}
heap = new MinHeap();
for (let i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
heap.insert(i);
}
console.log(heap.extract()); // 1
3. 最大堆
创建最大堆类
MaxHeap类的算法和MinHeap类的算法一模一样。不同之处在于要把所有>(大于)的比较换成<(小于)的比较。
class MaxHeap extends MinHeap {
constructor(compareFn = defaultCompare) {
super(compareFn);
// 要将比较反转,不将a和b进行比较,而是将b和a进行比较
this.compareFn = reverseCompare(compareFn);
}
}
function reverseCompare(compareFn) {
return (a, b) => compareFn(a, b);
}
可以使用测试最小堆的代码来测试最大堆。不同点是最大的值会是堆的根节点,而不是最小的值。
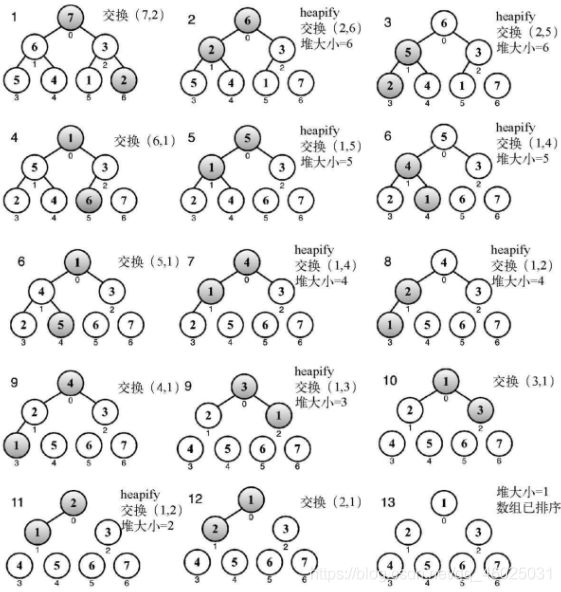
4. 堆排序算法
步骤:
- 用数组创建一个最大堆用作源数据
- 在创建最大堆后,最大的值会被存储在堆的第一个位置。要将它替换为堆的最后一个值,将堆的大小减1
- 将堆的根节点下移并重复步骤2直到堆的大小为1
用最大堆得到一个升序排列的数组(从最小到最大)。如果想要这个数组按降序排列,可以用最小堆代替。
堆排序算法:
function heapSort(array, compareFn = defaultCompare) {
let heapSize = array.length;
buildMaxHeap(array, compareFn); // 步骤1
while (heapSize > 1) {
swap(array, 0, --heapSize); // 步骤2
heapify(array, 0, heapSize, compareFn); // 步骤3
}
return array;
}
构建最大堆:
function buildMaxHeap(array, compareFn) {
for (let i = Math.floor(array.length / 2); i >= 0; i -= 1) {
heapify(array, i, array.length, compareFn);
}
return array;
}
最大堆函数会重新组织数组的顺序。
归功于要进行的所有比较,只需要对后半部分数组执行heapify(下移)函数(前半部分会被自动排好序,所以不需要对已经知道排好序的部分执行函数)。