2021年大数据Hadoop(十二):HDFS的API操作
目录
HDFS的API操作
HDFS的JAVA API操作
配置Windows下Hadoop环境
导入Maven依赖
使用文件系统方式访问数据
1、涉及的主要类
2、获取FileSystem方式
3、遍历HDFS中所有文件
4、HDFS上创建文件夹
5、下载文件-方式1
6、下载文件-方式2
7、上传文件
8、小文件合并
9、hdfs访问权限控制
HDFS的API操作
HDFS的JAVA API操作
HDFS在生产应用中主要是客户端的开发,其核心步骤是从HDFS提供的api中构造一个HDFS的访问客户端对象,然后通过该客户端对象操作(增删改查)HDFS上的文件。
配置Windows下Hadoop环境
在windows上做HDFS客户端应用开发,需要设置Hadoop环境,而且要求是windows平台编译的Hadoop,不然会报以下的错误:
缺少winutils.exe
Could not locate executable null \bin\winutils.exe in the hadoop binaries
缺少hadoop.dll
Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform… using builtin-Java classes where applicable
搭建步骤:
第一步:将已经编译好的Windows版本Hadoop解压到到一个没有中文没有空格的路径下面
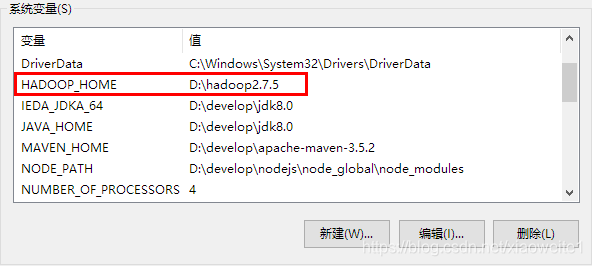
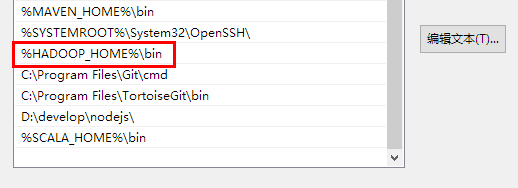
第二步:在windows上面配置hadoop的环境变量: HADOOP_HOME,并将%HADOOP_HOME%\bin添加到path中
第三步:把hadoop2.7.5文件夹中bin目录下的hadoop.dll文件放到系统盘: C:\Windows\System32 目录
第四步:关闭windows重启
导入Maven依赖
org.apache.hadoop
hadoop-common
2.7.5
org.apache.hadoop
hadoop-client
2.7.5
org.apache.hadoop
hadoop-hdfs
2.7.5
org.apache.hadoop
hadoop-mapreduce-client-core
2.7.5
junit
junit
4.12
使用文件系统方式访问数据
1、涉及的主要类
在java中操作HDFS,主要涉及以下Class:
Configuration:该类的对象封转了客户端或者服务器的配置;
FileSystem:该类的对象是一个文件系统对象,可以用该对象的一些方法来对文件进行操作,通过FileSystem的静态方法get获得该对象。
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);get方法从conf中的一个参数 fs.defaultFS的配置值判断具体是什么类型的文件系统。如果我们的代码中没有指定fs.defaultFS,并且工程classpath下也没有给定相应的配置,conf中的默认值就来自于hadoop的jar包中的core-default.xml,默认值为: file:///,则获取的将不是一个DistributedFileSystem的实例,而是一个本地文件系统的客户端对象。
2、获取FileSystem方式
第一种方式
@Test
public void getFileSystem1() throws IOException {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
//指定我们使用的文件系统类型:
configuration.set("fs.defaultFS", "hdfs://node1:8020/");
//获取指定的文件系统
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(configuration);
System.out.println(fileSystem.toString());
}第二种方式
@Test
public void getFileSystem2() throws Exception{
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(new URI("hdfs://node1:8020"), new Configuration());
System.out.println("fileSystem:"+fileSystem);
}3、遍历HDFS中所有文件
@Test
public void listMyFiles()throws Exception{
//获取fileSystem类
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(new URI("hdfs://node1:8020"), new Configuration());
//获取RemoteIterator 得到所有的文件或者文件夹,第一个参数指定遍历的路径,第二个参数表示是否要递归遍历
RemoteIterator locatedFileStatusRemoteIterator = fileSystem.listFiles(new Path("/"), true);
while (locatedFileStatusRemoteIterator.hasNext()){
LocatedFileStatus next = locatedFileStatusRemoteIterator.next();
System.out.println(next.getPath().toString());
}
fileSystem.close();
} 4、HDFS上创建文件夹
@Test
public void mkdirs() throws Exception{
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(new URI("hdfs://node01:8020"), new Configuration());
boolean mkdirs = fileSystem.mkdirs(new Path("/hello/mydir/test"));
fileSystem.close();
}5、下载文件-方式1
@Test
public void getFileToLocal()throws Exception{
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(new URI("hdfs://node01:8020"), new Configuration());
FSDataInputStream inputStream = fileSystem.open(new Path("/timer.txt"));
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File("e:\\timer.txt"));
IOUtils.copy(inputStream,outputStream );
IOUtils.closeQuietly(inputStream);
IOUtils.closeQuietly(outputStream);
fileSystem.close();
}
6、下载文件-方式2
@Test
public void downLoadFile() throws URISyntaxException, IOException, InterruptedException {
//1:获取FiletSystem对象
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(new URI("hdfs://node1:8020"), new Configuration());
//2:实现文件下载
fileSystem.copyToLocalFile(new Path("/anaconda-ks.cfg"), new Path("E:\\test"));
//3:释放资源
fileSystem.close();
}7、上传文件
@Test
public void putData() throws Exception{
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(new URI("hdfs://node1:8020"), new Configuration());
fileSystem.copyFromLocalFile(new Path("file:///c:\\install.log"),new Path("/hello/mydir/test"));
fileSystem.close();
}8、小文件合并
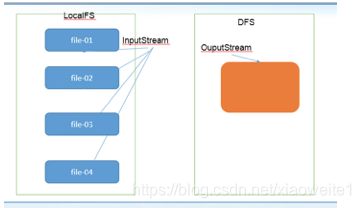
由于 Hadoop 擅长存储大文件,因为大文件的元数据信息比较少,如果 Hadoop 集群当中有大量的小文件,那么每个小文件都需要维护一份元数据信息,会大大的增加集群管理元数据的内存压力,所以在实际工作当中,如果有必要一定要将小文件合并成大文件进行一起处理,可以在上传的时候将小文件合并到一个大文件里面去小文件合并
@Test
public void mergeFile() throws Exception{
//获取分布式文件系统
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(new URI("hdfs://node1:8020"), new Configuration(),"root");
FSDataOutputStream outputStream = fileSystem.create(new Path("/bigfile.txt"));
//获取本地文件系统
LocalFileSystem local = FileSystem.getLocal(new Configuration());
//通过本地文件系统获取文件列表,为一个集合
FileStatus[] fileStatuses = local.listStatus(new Path("file:///E:\\input"));
for (FileStatus fileStatus : fileStatuses) {
FSDataInputStream inputStream = local.open(fileStatus.getPath());
IOUtils.copy(inputStream,outputStream);
IOUtils.closeQuietly(inputStream);
}
IOUtils.closeQuietly(outputStream);
local.close();
fileSystem.close();
}9、hdfs访问权限控制
HDFS权限模型和Linux系统类似。每个文件和目录有一个所有者(owner)和一个组(group)。文件或目录对其所有者、同组的其他用户以及所有其他用户(other)分别有着不同的权限。对文件而言,当读取这个文件时需要有r权限,当写入或者追加到文件时需要有w权限。对目录而言,当列出目录内容时需要具有r权限,当新建或删除子文件或子目录时需要有w权限,当访问目录的子节点时需要有x权限。但hdfs的文件权限需要开启之后才生效,否则在HDFS中设置权限将不具有任何意义!
HDFS的权限设置是通过hdfs-site.xml文件来设置,在搭建Hadoop集群时,将HDFS的权限关闭了,所以对HDFS的任何操作都不会受到影响的。
接下来我们将HDFS的权限开启,测试下HDFS的权限控制。
1.停止hdfs集群,在node1机器上执行以下命令
stop-dfs.sh2.修改node1机器上的hdfs-site.xml当中的配置文件
vim hdfs-site.xml
dfs.permissions.enabled
true
3.修改完成之后配置文件发送到其他机器上面去
scp hdfs-site.xml node2:$PWD
scp hdfs-site.xml node3:$PWD4.重启hdfs集群
start-dfs.sh5.随意上传一些文件到我们hadoop集群当中准备测试使用
cd /export/server/hadoop-2.7.5/etc/hadoop
hadoop fs -mkdir /config
hadoop fs -put *.xml /config
hadoop fs -chmod 600 /config/core-site.xml经过以上操作之后,core-site.xml文件的权限如下:
这个权限是当前所属用户root具有对core-site.xml文件的可读,可写权限。
6.使用代码准备下载文件
@Test
public void getConfig()throws Exception{
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(new URI("hdfs://node01:8020"), new Configuration(),"root");
fileSystem.copyToLocalFile(new Path("/config/core-site.xml"),new Path("file:///c:/core-site.xml"));
fileSystem.close();
}
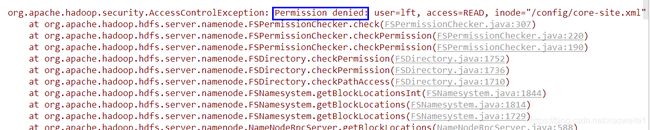
当HDFS的权限开启之后,运行以上代码发现权限拒绝,不允许访问。
这是因为我们在Windows下运行HDFS的客户端,用户名一般不是root,是其他用户,所以对core-site.xml文件没有任何操作权限。
解决方法:
方式1-修改core-site.xml的文件权限
hadoop fs -chmod 777/config/core-site.xml方式2-伪造用户
在这里,我们可以以root用户的身份去访问文件
@Test
public void getConfig()throws Exception{
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(new URI("hdfs://node01:8020"), new Configuration(),"root");
fileSystem.copyToLocalFile(new Path("/config/core-site.xml"),new Path("file:///c:/core-site.xml"));
fileSystem.close();
}执行结果如下
执行成功