深蓝-视觉slam-第五讲学习笔记
引言:之前我们学习过,一个SLAM系统分为前端和后端,前端称为视觉里程计。视觉里程计根据相邻两图像的信息来估计粗略的相机运动,给后端提供一个比较好的初值。
视觉里程计的算法分为两大类:特征点法和直接法。
特征点法估计相机的运动是长久以来视觉里程计的主流方向。具有稳定,对光照,动态物体不敏感的优势。本讲将从 特征点入手,学习如何提取,匹配图像特征点,然后通过两帧图像的信息来估计相机的运动和场景结构,从而实现一个两帧间的视觉里程计。
第五讲 特征点VO
1.特征点提取与匹配
2.2D-2D 对极几何
3.3D-2D PnP
4. 3D-3D ICP
5. 三角化与深度估计
6.实践
1.特征点提取与匹配
视觉里程计的核心:如何根据图像估计相机运动


高效:提点和匹配点在几个毫秒之内解决。
评分:评分越高越像角点,只留高分角点。
提角点的算法:FAST角点只有位置,ORB角点既有位置,又有朝向。其他的还有评分和大小信息。
描述子:用来判断两幅图像中的某个点是否为同一个点。(ORB采用二进制描述子)
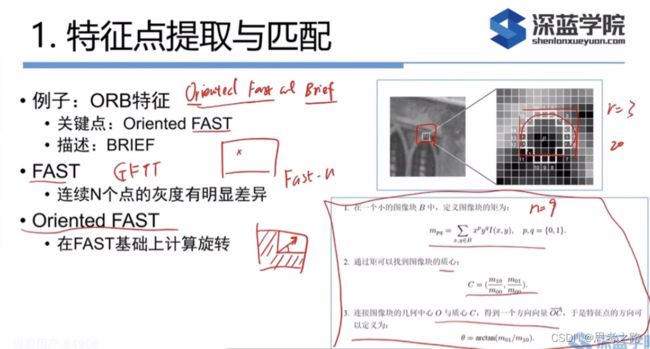
ORB(Oritend fast and brief):旋转之后的关键点(Oritend fast)+描述子(brief)。
以下是提取关键点的过程:

FAST:是一种提取角点的方式(提角点的速度快),即给一个图像,图像中的任意一个像素,判断这个像素是不是一个关键点。
FAST的具体做法:给出图像中任意一个像素点,这个点周围半径为3的圈上的连续的N(人为定义)个点的亮度都比这个点亮或暗(亮或暗的阈值比如是20),则这个点是个特征点。提取出来后容易扎堆,在小块区域内进行过滤,找最好的点,次要的点不需要了。
Orited Fast : 因为它既有位置又有朝向的原因,提取到该角点后,然后找到该点周围图像的重心所在的地方。其中,图像中越亮的地方越重,方向指的是从质心(就是指以图像块灰度值作为权重的中心) 指向重心的方向,这个向量的角度就是这个特征点的方向,通过灰质心法找到计算描述子旋转的角度。

描述子:在特征点周围取128对随即的点对,对每个点对进行一次像素大小的比较,这样可以得到128位0或1的串。
两幅图像中可以通过描述子的相似程度判断是不是同一点。
ORB的描述:如果使用二进制进行描述,由于相机发生了旋转,两幅图中对应的像素周围的描述子没有发生旋转,这个差别会比较大,而ORB描述是说,我们在通过Orited FAST提出角点时,计算出了旋转角度,通过角度,将需要匹配的第二幅图像中的相应点对也旋转该角度——旋转不变性
平移不变性——相机发生平移,描述子不会发生太大的变化,只是发生了一个平移的位置。
尺度不变性质——ORB没有,SIFT(三者都有),就是通过金字塔将原始图像每往上一层,就对图像进行一定倍率的缩放,我们就得到不同分辨率的图像,从而实现尺度不变性。
提取ORB特征分为两个步骤:
(1)FAST角点的提取:找出图中的角点。相较于FAST,ORB计算了特征点的主方向,为之后的、描述子增加了旋转不变性质。
(2)BRIEF描述子:对前一步提取出的特征点周围的区域进行描述。ORB对BRIEF进行了改进,主要指在BRIEF中使用了先前计算的方向信息。

暴力匹配:对两幅图像都进行特征点的提取,然后用第一幅图像中的特征点的描述子于第二幅图中的每个特征点的描述子进行比较,把不一样的位数加起来就是汉明距离,距离接近0,说明这个匹配好的同一点。
暴力匹配缺点:计算量大。
快速最近邻:当相机运动不大时,用第一幅图中的某个特征点与第二幅图中的某个区域的内的特征点,不用根第二幅图像中的每个特征点进行比较,节省计算量。纹理相同的时候,匹配不太好。
在未筛选的匹配中带有大量的误匹配,经过筛选后,匹配数量减少了许多,但大多数匹配都是正确的,筛选的依据是:汉明距离小于座小距离的两倍
2.对极几何:
2.1 作用:通过匹配好的p1,p2点,求相机的运动R,t;

O1,O2,P组成极平面 , O1,O2是基线 基线与象平面的交点(e1,e2)称为极点 极平面与象平面的交线称为极线
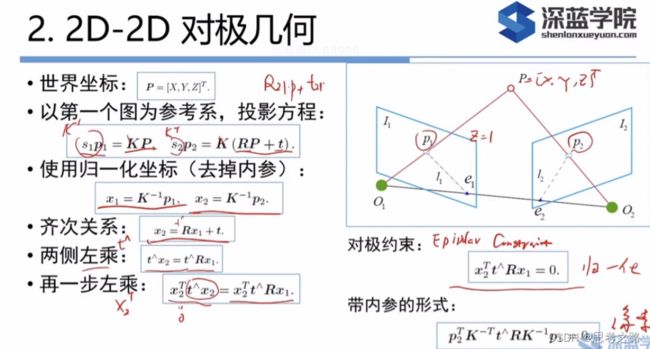

E = t^R, E是3x3的矩阵,有6个自由度,由于尺度不定性,共有五个自由度;
E当成普通矩阵的话,有9个元素,去调Scale(尺度)后,还有8个自由度;

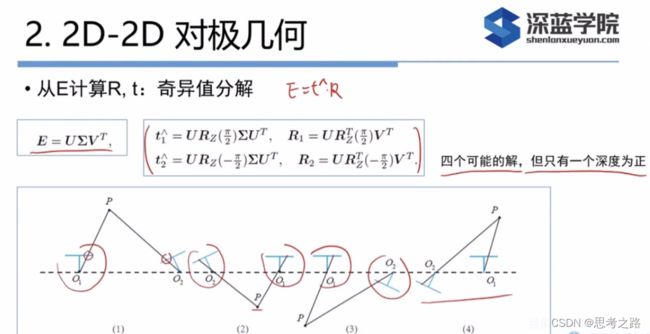
如果根据线性方程求解出来的E,不满足E的内在性质——它的奇异值不一定是 σ \sigma σ, σ \sigma σ,0的形式。这是我们需要把 ∑ \sum ∑矩阵调整成上面的那种形式,通常的做法是,对8点法求的的E进行SVD分解,得到奇异值矩阵 ∑ \sum ∑ = diag( σ 1 \sigma_1 σ1, σ 2 \sigma_2 σ2, σ 3 \sigma_3 σ3),设 σ 1 \sigma_1 σ1>= σ 2 \sigma_2 σ2>= σ 3 \sigma_3 σ3,取
∑ \sum ∑ = U d i a g ( σ 1 + σ 2 2 , σ 1 + σ 2 2 , 0 ) V T Udiag(\frac{\sigma_1+ \sigma_2}{2},\frac{\sigma_1+ \sigma_2}{2},0) V^T Udiag(2σ1+σ2,2σ1+σ2,0)VT,这相当于把求出来的矩阵投影到E所在的流形上。更简单的做法就是将奇异值矩阵取为diag(1,1,0),因为E具有尺度等价性。

2.2 对于单目SLAM的初始化,刚开始相机是没有变化的,只有当相机发生了一定的平移之后才能估计出相机的运动(对极几何问题),在这个过程中算t和R的过程就是单目的初始化。
初始化的过程中的要点:
(1)根据匹配点,算E,然后计算t和R,如果相机只有旋转而没有平移,t = 0, 那么E = t^R = 0, 就没办法去分解E,没办法计算R和t。
(2)单目初始化的时候一定要发生一定程度的平移。
(3)当E乘以任意一非零常数k,还是满足对极几何约束的的,这就导致E进行分解的时候t乘了一个常数k,也就是平移部分可以乘以任意非零常数,说明t只代表了相机运动的方向信息,而不会告诉我们具体动了多少,这就是单目的尺度问题。尺度问题告诉我们,长时间的单目的轨迹缩小任意一非零的倍数,地图也缩小相同的倍数,投影到相机上的像素位置和之前是一模一样的,这就说明,按没有缩小的和缩小后的,他们在相机中的投影是一模一样的,这说明单目相机是无法估计相机的轨迹和地图尺度的,因为看到的都是投影之后的像素,这就导致单目存在尺度不定性问题.
(4)单目尺度不定性本质是因为我们没办法在计算分解E的时候去计算尺度信息的,但在实际的过程中,我们会做归一化处理,在初始化过程中,令t的长度为1,然后通过通过这些匹配的点把三维空间点算出来。t扩大也是满足我的观测的。后面的点就可以通过3D到2D的投影关系找到。
(5)单目的工作方式:单目一开始会有一个初始化的过程,相机运动的过程中有段时间是在初始化,初始化好后,就会按照初始化选择的尺度去计算后面的运动轨迹,后面的是可以通过3D到2D的去计算相机的运动,但后面的尺度是跟着初始化 的轨迹的。
实际的过程中,不是我们初始化定好尺度为1,后面的运动都是尺度为1的,由于误差的存在,相机的运动会变得越来越小或越来越大(单目的尺度漂移问题,本质上是因为看到的是投影信息),累积误差。
2.3 特征点的匹配可能存在误匹配怎么解决?
(1)通过重投影关系,把误匹配的点去掉。
(2)通过RANSAC,把误匹配的点去掉。
RANSAC:假设已经有了200对匹配,在这200对匹配点中随意选择8对,用这8对点通过Essental(本质矩阵)算出t和R,然后通过Rt看这200个匹配中,有多少个是符合这个R,t的。


单应矩阵描述的是通常处于共同平面上的一些点在两张图像之间的变换关系。图像I1,I2上有一对匹配好的特征点p1,p2,这个特征点落在P平面上。平面满足方程: n T P + d = 0 n^T P+ d = 0 nTP+d=0, 处理后 − n T P d = 1 -\frac{n^TP}{d} = 1 −dnTP=1, p 2 ≃ K ( R P + t ) p_2 \simeq K(RP +t) p2≃K(RP+t), 将 − n T P d = 1 -\frac{n^TP}{d} = 1 −dnTP=1带入p2中可得到: p 2 ≃ K ( R − t n T d ) K − 1 p 1 p_2 \simeq K(R -\frac{tn^T}{d} )K^{-1}p_1 p2≃K(R−dtnT)K−1p1, 于是有 p 2 ≃ H p 1 p_2 \simeq Hp_1 p2≃Hp1, H的定义与旋转,平移,平面的参数有关。

3.PnP



线性方法是:先求相机位姿,再求空间点位置。而非线性优化是把相机位置姿和三维点看成优化变量。我们可以利用重投影误差对PNP或ICP给出的结果进行优化。
这一类把相机和三维点放在一起进行最小化的问题称为 Bundle Adjustment
我们先学习两个视图下的基本形式,后面学大规模的BA问题。
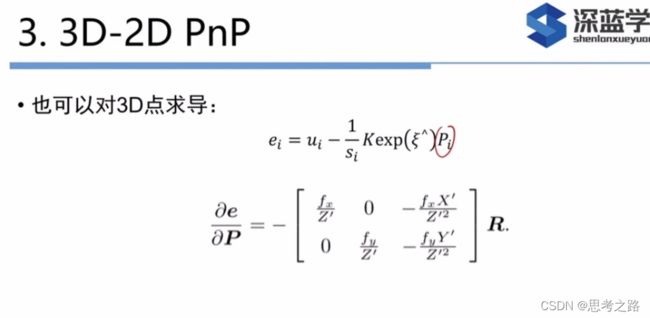
n个三维空间点P及其投影p,计算R,t,它的李群是T,空间点坐标与投影的像素坐标之间的关系如下:
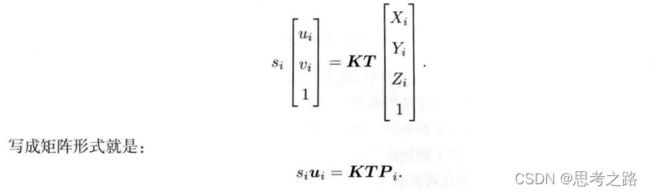
由于相机的位姿和观测点的噪声,该等式存在一个误差。因此,我们把误差求和,构建最小二乘问题,然后寻找最好的相机位姿,使它最小化:

重投影误差:将3D点的投影位置与观测位置作差。使用齐次坐标时,误差是3维的。由于最后一维为1,所以此维的误差一直为0,因此,我们更多的时使用非齐次坐标,误差就有两维。
如下图所式:p1,p2是同一个空间点P的投影,但是不知道相机的位姿。在初始值中,P的投影p2与实际的p2之间有一定的距离。与是我们需要调整相机的位姿,使得这个距离变小。不过,由于调整需要考虑很多点,最后的效果就是整体误差的减小,而每个点的误差通常不会精确为0。

使用李代数可以构建无约束的优化问题,然后通过GN,LM等方法优化算法进行求解。
在使用这两个优化算法前,我们需要知道误差项对于优化变量的导数,也就是线性化:

J T J^T JT的形式:e是像素坐标误差(2维), x是相机位姿(6维), J T J^T JT是一个2x6的矩阵。
在定义了中间变量后,我们对T左乘扰动量 δ ξ \delta \xi δξ,然后考虑e关于扰动量的导数,利用链是法则:如下:


这个J描述了:重投影误差关于相机位姿李代数的一阶变化关系。符号表示误差是观测-预测的定义。
除了优化位姿,我们还优化特征点的空间位置,如下:

4,3D-3D ICP
求解方法:线性代数方法(SVD), 非线性优化方法(BA)
SVD方法:




非线性优化方法:
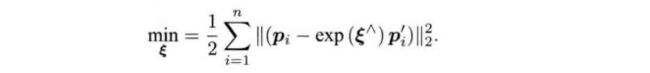 每个误差项关于位姿的导数,使用李代数扰动模型:
每个误差项关于位姿的导数,使用李代数扰动模型:
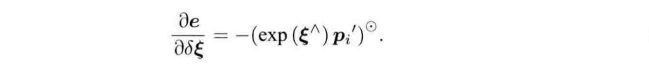
在非线性优化过程中,需要不断的迭代,才能找到极小值。
在某些场合,一个像素的深度数据可能有,可能测不到,所以可以混合使用PnP和ICP优化;对深度已知的特征点,建模他们的3D-3D的误差,对于深度未知的特征点,建立3D-2D的重投影误差。可以将所有的误差放在同一个问题中考虑。

5.三角化与深度估计
用对极几何估计了相机的运动,得到运动后,我们需要用相机的运动来估计特征点的空间位置,在单目SLAM中,无法获取像素的距离信息,我们需要通过三角化的方式估计地图点的深度。

三角化:通过对不同位置对同一路标点进行观察,从观察的位置来推断路标点的距离。
理论上,上述的两直线会交与一点,由于噪声的影响,这两条直线无法相交,此时,需要用最小二乘法求解。
上图中x1,x2是归一化坐标点,已知R,t求两个特征点的深度s1,s2。
上图中先求s1,s2都可。得到s1,s2信息后,由于噪声和R,t是估计的原因,等是不一定精确的等与0,所以常见的做法是最小二乘法,而不是直接求解。

6,实例
6.1 <1>OpenCV的ORB特征
代码:
#include 代码中用到了opencv中的一些特征点提取,检测,匹配的通用接口,此文章中有详细的解释:https://editor.csdn.net/md/?articleId=124145732
运行结果:
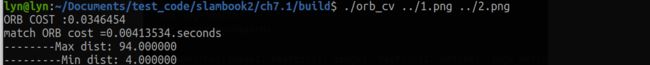
从运行结果可以看出,ORB提取花了32毫秒,匹配大约花费4毫秒,可见大部分计算时间花在了特征点提取上了。


运行过程中出现的问题:Ptr matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create(“BruteForce-Hamming”);中参数不能随意写入。
<2>手写ORB特征
![]()
程序编译过程中出现上述错误,通过在CMakeLists.txt中添加:set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS “-std=c++14 -mfma”)解决。
手写ORB查看:https://editor.csdn.net/md?not_checkout=1&spm=1000.2115.3001.5352&articleId=124157706
6.2 对极约束求解相机运动
实例代码:
#include 形式,匹配点的pt是整数的,实际的归一化坐标是float型
vector<Point2f> points1;
vector<Point2f> points2;
for(int i = 0; i < (int)matches.size(); i++) {
points1.push_back(keypoint1[matches[i].queryIdx].pt);
points2.push_back(keypoint2[matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
}
Point2d prinfcipal_point(325.1, 249.7); //相机的光心;
double focal_length = 521; //相机焦距
//计算基础矩阵
Mat essential_matrix;
essential_matrix = findEssentialMat(points1, points2, focal_length, prinfcipal_point);
cout << "essential matrix = " << essential_matrix << endl;
//本质矩阵
Mat fundamental ;
fundamental = findFundamentalMat(points1, points2, CV_FM_8POINT);
cout << "fundamental matrix " << fundamental << endl;
//单应矩阵
Mat homography_matrix;
homography_matrix = findHomography(points1, points2, RANSAC, 3);
cout << "homography matrix =" << homography_matrix << endl;
//从本质矩阵恢复旋转和平移
recoverPose(fundamental, points1, points2, R, t, focal_length, prinfcipal_point);
cout << "R is" << R << endl;
cout << "t is" << t.t() << endl;
}
//像素坐标系转相机归一化坐标系
Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat & K)
{
return Point2d(p.x - K.at<double>(0,2)/K.at<double>(0,0), p.y - K.at<double>(1,2)/K.at<double>(1,1));
}
#include 的形式
vector<Point2f> points1;
vector<Point2f> points2;
for(int i = 0; i < (int)matches.size(); i++) {
points1.push_back(keypoint1[matches[i].queryIdx].pt);
points2.push_back(keypoint2[matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
}
//计算本质矩阵
Point2d principal_point(325.1, 249.7); //相机主点, TUM dataset标定值
int focal_length = 521; //相机焦距, TUM dataset标定值
Mat essential_matrix;
essential_matrix = findEssentialMat(points1, points2, focal_length, principal_point);
//本质矩阵中恢复出旋转和平移
recoverPose(essential_matrix, points1, points2, R, t, focal_length, principal_point);
}
void triangulation(const std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoint1, const std::vector<KeyPoint>&keypoint2, const std::vector<DMatch> matches, Mat &R, Mat &t, vector<Point3d> &points)
{
Mat T1 = (Mat_<float>(3, 4) <<
1, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0);
Mat T2 = (Mat_<float>(3, 4) <<
R.at<double>(0, 0), R.at<double>(0, 1), R.at<double>(0, 2), t.at<double>(0, 0),
R.at<double>(1, 0), R.at<double>(1, 1), R.at<double>(1, 2), t.at<double>(1, 0),
R.at<double>(2, 0), R.at<double>(2, 1), R.at<double>(2, 2), t.at<double>(2, 0)
);
Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3,3) <<520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1);
vector<Point2f> pts1, pts2;
for(DMatch m:matches) {
pts1.push_back(pixel2cam(keypoint1[m.queryIdx].pt, K));
pts2.push_back(pixel2cam(keypoint2[m.trainIdx].pt, K));
}
Mat pts_4d;
cv::triangulatePoints(T1, T2, pts1, pts2, pts_4d);
//cout << "pts_4d" << pts_4d << endl;
//转换成非其次坐标
for(int i = 0; i<pts_4d.cols; i++)
{
Mat x = pts_4d.col(i);
x/= x.at<float>(3, 0); //归一化
Point3d p(x.at<float>(0,0), x.at<float>(1, 0),x.at<float>(2, 0));
points.push_back(p);
}
}
Point2f pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K)
{
return Point2f((p.x - K.at<double>(0, 2)) / K.at<double>(0, 0), (p.y - K.at<double>(1,2))/ K.at<double>(1, 1));
}
运行结果:

函数recoverPose(essential_matrix, points1, points2, R, t, focal_length, principal_point);通过看参数就很明确了,不于以解释;
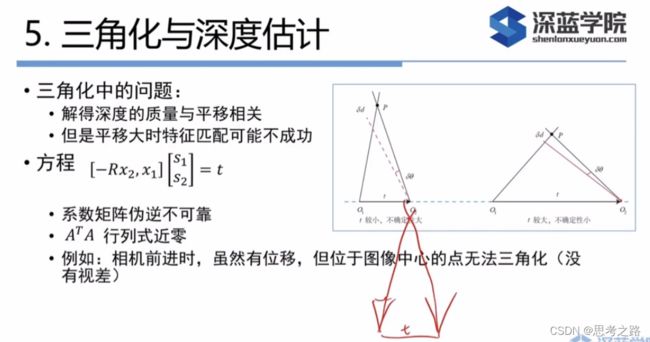
三角测量是由平移得到的,纯旋转是无法使用三角测量。在平移存在的情况下,引出一个三角测量的矛盾
三角测量矛盾:当平移很小时,像素上的不确定性会导致较大的深度不确定性。平移大时,在同样的相机分辨率下,三角测量更精确。
解决三角测量矛盾方法:1,提高特征点的提取精度,即提高图像分辨率,但会导致图像增大,增加成本;2,增大位移,这会使得特针点的提取和匹配变得困难。
三角化的矛盾(视差):增大平移,可能导致匹配失效;平移太小,则三角化精度不够;
延迟三角化:单目图像没有深度,需要等特征点被追踪几帧后产生足够的视角,在用三角化来确定新增点的深度值。
6.4 求解PnP
使用OpenCV的EPnP求解PnP问题,然后通过非线性优化再次求解。PnP需要3D点,为避免初始化的麻烦,使用RGB-D相机中的深度图(1.png)作为特征点的3D位置。
在例程中,得到匹配好的特征点后,我们在第一个图的深度图中寻找它门的深度,并求出空间位置。以此3D空间位置再以第二幅图的像素位置,调用EPnP球技和iePnP问题。
OpenCV使用PnP估计R,t代码:
#include 运行结果:

由结果可看到有3D信息时,R几乎和2D-2D中的是一样的,t相差多,是由于引入新的深度信息(采集到的深度图本身就有一定的误差),所以3D点不准确。在大规模的BA中,我们会把所有的位姿和空间点同时优化。
6.5,手写位姿估计(使用非线性优化),手写一个GN的PnP;
实现代码:
#include 运行结果:

6.6,用g2o来求解
6.6.1 使用g2o进行BA优化

在这个图有化模型中:
- 节点:第二个相机的位姿点T ;
- 边:每个3D点在第二个相机中的投影,以观测方程来描述;
z j = h ( T , P j ) z_j = h(T,P_j) zj=h(T,Pj)
由于第一个相机的位姿为0,所以不考虑第一个相机的位姿,现在我们根据一组3D点和第二个图像中的2D的投影,来估计第二个相机的运动。在更多的场合中,我们考虑更多相机的运动。
6.6.2 实现代码:
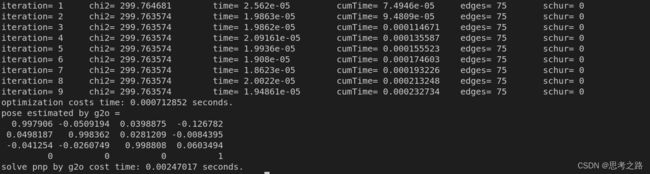
#include 运行结果:
6.7求解ICP
6.7.1 SVD方法:
使用两幅图的RGB-D图像,通过特征点匹配获取两组3D点,最后用ICP计算位姿变换。
实现代码:
#include detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" );
// Ptr descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" );
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming");
//-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置
detector->detect(img_1, keypoints_1);
detector->detect(img_2, keypoints_2);
//-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子
descriptor->compute(img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);
descriptor->compute(img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);
//-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离
vector<DMatch> match;
// BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING );
matcher->match(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match);
//-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选
double min_dist = 10000, max_dist = 0;
//找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离
for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {
double dist = match[i].distance;
if (dist < min_dist) min_dist = dist;
if (dist > max_dist) max_dist = dist;
}
printf("-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist);
printf("-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist);
//当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限.
for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {
if (match[i].distance <= max(2 * min_dist, 30.0)) {
matches.push_back(match[i]);
}
}
}
Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K) {
return Point2d(
(p.x - K.at<double>(0, 2)) / K.at<double>(0, 0),
(p.y - K.at<double>(1, 2)) / K.at<double>(1, 1)
);
}
void pose_estimation_3d3d(const vector<Point3f> &pts1,
const vector<Point3f> &pts2,
Mat &R, Mat &t) {
Point3f p1, p2; // center of mass
int N = pts1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
p1 += pts1[i];
p2 += pts2[i];
}
p1 = Point3f(Vec3f(p1) / N);
p2 = Point3f(Vec3f(p2) / N);
vector<Point3f> q1(N), q2(N); // remove the center
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
q1[i] = pts1[i] - p1;
q2[i] = pts2[i] - p2;
}
// compute q1*q2^T
Eigen::Matrix3d W = Eigen::Matrix3d::Zero();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
W += Eigen::Vector3d(q1[i].x, q1[i].y, q1[i].z) * Eigen::Vector3d(q2[i].x, q2[i].y, q2[i].z).transpose();
}
cout << "W=" << W << endl;
// SVD on W
Eigen::JacobiSVD<Eigen::Matrix3d> svd(W, Eigen::ComputeFullU | Eigen::ComputeFullV);
Eigen::Matrix3d U = svd.matrixU();
Eigen::Matrix3d V = svd.matrixV();
cout << "U=" << U << endl;
cout << "V=" << V << endl;
Eigen::Matrix3d R_ = U * (V.transpose());
if (R_.determinant() < 0) {
R_ = -R_;
}
Eigen::Vector3d t_ = Eigen::Vector3d(p1.x, p1.y, p1.z) - R_ * Eigen::Vector3d(p2.x, p2.y, p2.z);
// convert to cv::Mat
R = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) <<
R_(0, 0), R_(0, 1), R_(0, 2),
R_(1, 0), R_(1, 1), R_(1, 2),
R_(2, 0), R_(2, 1), R_(2, 2)
);
t = (Mat_<double>(3, 1) << t_(0, 0), t_(1, 0), t_(2, 0));
}
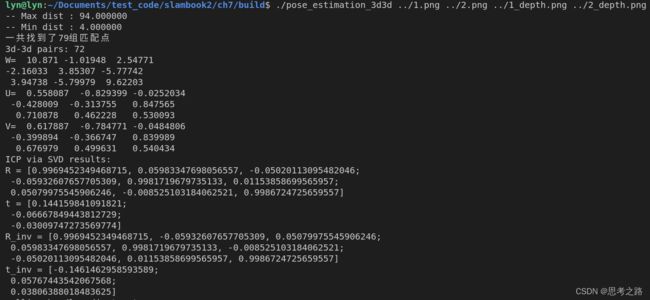
运行结果如下:
6.7.2 非线性优化方法:
其中J矩阵是3x6的矩阵。
#include CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(vo1)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
add_definitions("-DENABLE_SSE")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 -O2 ${SSE_FLAGS} -msse4")
list(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake)
find_package(OpenCV 3 REQUIRED)
find_package(G2O REQUIRED)
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
include_directories(
${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${G2O_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS}
"/usr/include/eigen3/"
)
add_executable(orb_cv orb_cv.cpp)
target_link_libraries(orb_cv ${OpenCV_LIBS})
add_executable(orb_self orb_self.cpp)
target_link_libraries(orb_self ${OpenCV_LIBS})
add_executable(pose_estimation_2d2d pose_estimation_2d2d.cpp)
target_link_libraries(pose_estimation_2d2d ${OpenCV_LIBS})
add_executable(triangulation triangulation.cpp)
target_link_libraries(triangulation ${OpenCV_LIBS})
add_executable(pose_estimation_3d2d pose_estimation_3d2d.cpp)
target_link_libraries(pose_estimation_3d2d
g2o_core g2o_stuff
${OpenCV_LIBS})
add_executable(pose_estimation_3d3d pose_estimation_3d3d.cpp)
target_link_libraries(pose_estimation_3d3d
g2o_core g2o_stuff
${OpenCV_LIBS})
运行结果:

从运行结果可以看出:仅一次迭代后,算法就收敛了,从位姿结果看出和SVD一样,说明SVD已经给出了优化问题的解析解。所以可以认为SVD给出了相机位姿的最优解。
