import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
加载数据
iris = pd.read_csv('E:/练习/Iris.csv')
iris.head()
|
id |
SepalLengthCm |
SepalWidthCm |
PetalLengthCm |
PetalWidthCm |
Species |
| 0 |
1 |
5.1 |
3.5 |
1.4 |
0.2 |
0 |
| 1 |
2 |
4.9 |
3.0 |
1.4 |
0.2 |
0 |
| 2 |
3 |
4.7 |
3.2 |
1.3 |
0.2 |
0 |
| 3 |
4 |
4.6 |
3.1 |
1.5 |
0.2 |
0 |
| 4 |
5 |
5.0 |
3.6 |
1.4 |
0.2 |
0 |
打印数据内存使用情况
iris.info()
RangeIndex: 150 entries, 0 to 149
Data columns (total 6 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 id 150 non-null int64
1 SepalLengthCm 150 non-null float64
2 SepalWidthCm 150 non-null float64
3 PetalLengthCm 150 non-null float64
4 PetalWidthCm 150 non-null float64
5 Species 150 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(4), int64(2)
memory usage: 7.2 KB
iris.drop('id',axis=1,inplace=True)
iris.info()
RangeIndex: 150 entries, 0 to 149
Data columns (total 5 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 SepalLengthCm 150 non-null float64
1 SepalWidthCm 150 non-null float64
2 PetalLengthCm 150 non-null float64
3 PetalWidthCm 150 non-null float64
4 Species 150 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(4), int64(1)
memory usage: 6.0 KB
fig = iris[iris.Species==0].plot(kind='scatter',x='SepalLengthCm',y='SepalWidthCm',color='orange', label='Setosa')
iris[iris.Species==1].plot(kind='scatter',x='SepalLengthCm',y='SepalWidthCm',color='blue', label='versicolor',ax=fig)
iris[iris.Species==2].plot(kind='scatter',x='SepalLengthCm',y='SepalWidthCm',color='green', label='virginica', ax=fig)
fig.set_xlabel("Sepal Length")
fig.set_ylabel("Sepal Width")
fig.set_title("Sepal Length VS Width")
fig=plt.gcf()
fig.set_size_inches(10,6)
plt.show()

上图显示了萼片长度和宽度之间的关系。现在我们将检查花瓣长度和宽度之间的关系。
fig = iris[iris.Species==0].plot.scatter(x='PetalLengthCm',y='PetalWidthCm',color='orange', label='Setosa')
iris[iris.Species==1].plot.scatter(x='PetalLengthCm',y='PetalWidthCm',color='blue', label='versicolor',ax=fig)
iris[iris.Species==2].plot.scatter(x='PetalLengthCm',y='PetalWidthCm',color='green', label='virginica', ax=fig)
fig.set_xlabel("Petal Length")
fig.set_ylabel("Petal Width")
fig.set_title(" Petal Length VS Width")
fig=plt.gcf()
fig.set_size_inches(10,6)
plt.show()
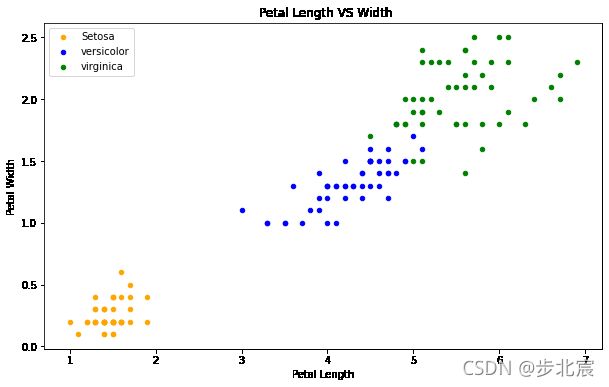
正如我们所看到的,与萼片特征相比,花瓣特征给出了更好的簇划分。这表明花瓣有助于更好、更准确地预测萼片。我们稍后再检查。
长度和宽度是如何分布的
iris.hist(edgecolor='black', linewidth=1.2)
fig=plt.gcf()
fig.set_size_inches(12,6)
plt.show()

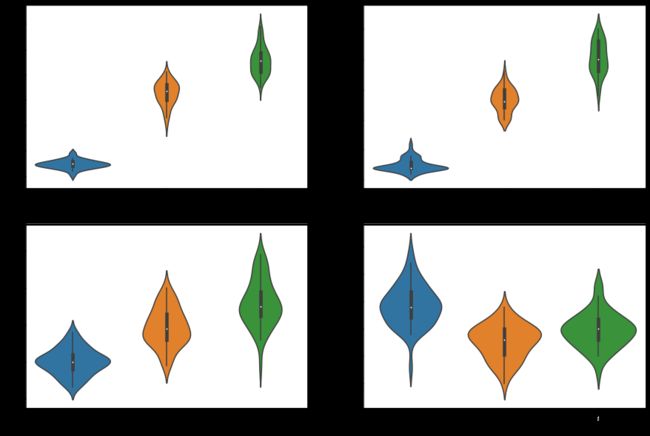
长度和宽度如何随物种而变化
seaborn.vinlinplot–绘制小提琴图
小提琴图是 箱型图 和核密度图的结合
展示了数据随种类的长度和密度。越窄的部分说明数据密度较低,越宽的部分说明数据密度高
plt.figure(figsize=(15,10))
plt.subplot(2,2,1)
sns.violinplot(x='Species',y='PetalLengthCm',data=iris)
plt.subplot(2,2,2)
sns.violinplot(x='Species',y='PetalWidthCm',data=iris)
plt.subplot(2,2,3)
sns.violinplot(x='Species',y='SepalLengthCm',data=iris)
plt.subplot(2,2,4)
sns.violinplot(x='Species',y='SepalWidthCm',data=iris)
分类算法
sklearn.linear_model —逻辑回归算法
sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split --将数据集随机分成训练集合测试集
sklearn.neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier --K临近算法
sklearn.svm --支持向量机算法
sklearn.metrics.accuracy——score --检查模型的准确性
sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeClassifier --决策树算法
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
pandas.DataFrame.shape–返回DataFrame数据形状
iris.shape
(150, 5)
现在,当我们训练任何算法时,特征的数量及其相关性起着重要的作用。如果存在特征且许多特征高度相关,则训练具有所有特征的算法将降低精度。因此,应仔细选择特征。该数据集的功能较少,但我们仍将看到相关性。
pandas.DataFrame.corr–计算相关系数
seaborn.heatmap --热力图
plt.figure(figsize=(7,4))
sns.heatmap(iris.corr(),annot=True,cmap='cubehelix_r')
plt.show()

观察
萼片宽度和长度不相关,花瓣宽度和长度高度相关
我们将使用所有功能来训练算法并检查其准确性。然后我们将使用1个花瓣特征和1个萼片特征来检查算法的准确性,因为我们只使用2个不相关的特征。因此,我们可以在数据集中有一个方差,这可能有助于提高准确性。我们稍后再查。
训练算法步骤
1.将数据集拆分为培训和测试数据集。测试数据集通常比训练数据集小,因为它有助于更好地训练模型。
2.根据问题(分类或回归)选择算法。
3.然后将训练数据集传递给算法进行训练。我们使用.fit()方法
4.然后将测试数据传递给经过训练的算法,以预测结果。我们使用.predict()方法。
5.比较预测结果和真实值,给出算法准确性。
将数据拆分为训练和测试数据集
test_size = 0.3测试集数据占比30%
train, test = train_test_split(iris, test_size = 0.3)
print(train.shape)
print(test.shape)
(105, 5)
(45, 5)
获取训练集X的特征: [‘SepalLengthCm’,‘SepalWidthCm’,‘PetalLengthCm’,‘PetalWidthCm’]
训练集Y的实际分布
测试集X的特征
测试集Y的实际分布
train_X = train[['SepalLengthCm','SepalWidthCm','PetalLengthCm','PetalWidthCm']]
train_y=train.Species
test_X= test[['SepalLengthCm','SepalWidthCm','PetalLengthCm','PetalWidthCm']]
test_y =test.Species
检查训练集和测试集
train_X.head(2)
|
SepalLengthCm |
SepalWidthCm |
PetalLengthCm |
PetalWidthCm |
| 72 |
6.3 |
2.5 |
4.9 |
1.5 |
| 39 |
5.1 |
3.4 |
1.5 |
0.2 |
test_X.head(2)
|
SepalLengthCm |
SepalWidthCm |
PetalLengthCm |
PetalWidthCm |
| 143 |
6.8 |
3.2 |
5.9 |
2.3 |
| 40 |
5.0 |
3.5 |
1.3 |
0.3 |
训练集中分类的输出值(原始列表中标注的分类)
train_y.head()
72 1
39 0
21 0
109 2
106 2
Name: Species, dtype: int64
SVM支持向量机
sklearn.svm.SVC --SVC算法
sklearn.svm.SVC.fit–对于训练集使用fit方法训练算法
sklearn.svm.SVC.predict-- 传入测试集,使用predict方法给出预测值
sklearn.metrics.accuracy_score --预测值与实际值对比,给出算法准确度
model = svm.SVC()
model.fit(train_X,train_y)
prediction=model.predict(test_X)
print('The accuracy of the SVM is:',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y))
The accuracy of the SVM is: 0.9777777777777777
支持向量机具有很好的精度。我们将继续检查不同型号的精度。现在我们将按照上面相同的步骤来训练各种机器学习算法。
逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(train_X,train_y)
prediction=model.predict(test_X)
print('The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y))
The accuracy of the Logistic Regression is 0.9777777777777777
D:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\linear_model\_logistic.py:763: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge (status=1):
STOP: TOTAL NO. of ITERATIONS REACHED LIMIT.
Increase the number of iterations (max_iter) or scale the data as shown in:
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/preprocessing.html
Please also refer to the documentation for alternative solver options:
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/linear_model.html#logistic-regression
n_iter_i = _check_optimize_result(
决策树(Decision Tree)
model=DecisionTreeClassifier()
model.fit(train_X,train_y)
prediction=model.predict(test_X)
print('The accuracy of the Decision Tree is',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y))
The accuracy of the Decision Tree is 0.9777777777777777
K均值聚类(Kmeans)
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
model = KMeans(n_clusters=3)
model.fit(train_X,train_y)
prediction=model.predict(test_X)
print('The accuracy of the KMeans is',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y))
x0 = (train_X,train_y)[prediction == 0]
x1 = (train_X,train_y)[prediction == 1]
x2 = (train_X,train_y)[prediction == 2]
plt.scatter(x0[:, 0], x0[:, 1], c = "red", marker='o', label='label0')
plt.scatter(x1[:, 0], x1[:, 1], c = "green", marker='*', label='label1')
plt.scatter(x2[:, 0], x2[:, 1], c = "blue", marker='+', label='label2')
plt.xlabel('petal length')
plt.ylabel('petal width')
plt.legend(loc=2)
plt.show()
The accuracy of the KMeans is 0.3111111111111111
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
in
4 print('The accuracy of the KMeans is',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y))
5
----> 6 x0 = (train_X,train_y)[prediction == 0]
7 x1 = (train_X,train_y)[prediction == 1]
8 x2 = (train_X,train_y)[prediction == 2]
TypeError: only integer scalar arrays can be converted to a scalar index
K邻近算法(K-Nearest Neighbours)
n_neighbors=3:检查邻近3个点判断属于哪个分类
model=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)
model.fit(train_X,train_y)
prediction=model.predict(test_X)
print('The accuracy of the KNN is',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y))
The accuracy of the KNN is 0.9777777777777777
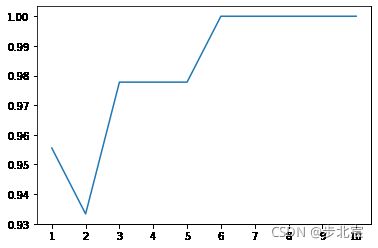
当n_neighbors值不同时,检查KNN算法的准确度变化,少数服从多数
a_index=list(range(1,11))
a=pd.Series()
x=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
for i in list(range(1,11)):
model=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=i)
model.fit(train_X,train_y)
prediction=model.predict(test_X)
a=a.append(pd.Series(metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y)))
plt.plot(a_index, a)
plt.xticks(x)
:2: DeprecationWarning: The default dtype for empty Series will be 'object' instead of 'float64' in a future version. Specify a dtype explicitly to silence this warning.
a=pd.Series()
([,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
],
[Text(0, 0, ''),
Text(0, 0, ''),
Text(0, 0, ''),
Text(0, 0, ''),
Text(0, 0, ''),
Text(0, 0, ''),
Text(0, 0, ''),
Text(0, 0, ''),
Text(0, 0, ''),
Text(0, 0, '')])
我们在上述模型中使用了iris的所有特征。现在我们将分别使用花瓣和萼片
创建花瓣和萼片训练数据
花萼:长度和宽度相关性很低
花瓣:长度和宽度相关性很高
petal=iris[['PetalLengthCm','PetalWidthCm','Species']]
sepal=iris[['SepalLengthCm','SepalWidthCm','Species']]
train_p,test_p=train_test_split(petal,test_size=0.3,random_state=0)
train_x_p=train_p[['PetalWidthCm','PetalLengthCm']]
train_y_p=train_p.Species
test_x_p=test_p[['PetalWidthCm','PetalLengthCm']]
test_y_p=test_p.Species
train_s,test_s=train_test_split(sepal,test_size=0.3,random_state=0)
train_x_s=train_s[['SepalWidthCm','SepalLengthCm']]
train_y_s=train_s.Species
test_x_s=test_s[['SepalWidthCm','SepalLengthCm']]
test_y_s=test_s.Species
SVM
model=svm.SVC()
model.fit(train_x_p,train_y_p)
prediction=model.predict(test_x_p)
print('The accuracy of the SVM using Petals is:',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y_p))
model=svm.SVC()
model.fit(train_x_s,train_y_s)
prediction=model.predict(test_x_s)
print('The accuracy of the SVM using Sepal is:',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y_s))
The accuracy of the SVM using Petals is: 0.9777777777777777
The accuracy of the SVM using Sepal is: 0.8
逻辑回归
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(train_x_p,train_y_p)
prediction=model.predict(test_x_p)
print('The accuracy of the Logistic Regression using Petals is:',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y_p))
model.fit(train_x_s,train_y_s)
prediction=model.predict(test_x_s)
print('The accuracy of the Logistic Regression using Sepals is:',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y_s))
The accuracy of the Logistic Regression using Petals is: 0.9777777777777777
The accuracy of the Logistic Regression using Sepals is: 0.8222222222222222
决策树
model=DecisionTreeClassifier()
model.fit(train_x_p,train_y_p)
prediction=model.predict(test_x_p)
print('The accuracy of the Decision Tree using Petals is:',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y_p))
model.fit(train_x_s,train_y_s)
prediction=model.predict(test_x_s)
print('The accuracy of the Decision Tree using Sepals is:',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y_s))
The accuracy of the Decision Tree using Petals is: 0.9555555555555556
The accuracy of the Decision Tree using Sepals is: 0.6444444444444445
K均值聚类
model=KMeans(n_clusters=3)
model.fit(train_x_p,train_y_p)
prediction=model.predict(test_x_p)
print('The accuracy of the KMeans using Petals is:',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y_p))
model.fit(train_x_s,train_y_s)
prediction=model.predict(test_x_s)
print('The accuracy of the KMeans using Sepals is:',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y_s))
The accuracy of the KMeans using Petals is: 0.022222222222222223
The accuracy of the KMeans using Sepals is: 0.7555555555555555
KNN
model=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)
model.fit(train_x_p,train_y_p)
prediction=model.predict(test_x_p)
print('The accuracy of the KNN using Petals is:',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y_p))
model.fit(train_x_s,train_y_s)
prediction=model.predict(test_x_s)
print('The accuracy of the KNN using Sepals is:',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y_s))
The accuracy of the KNN using Petals is: 0.9777777777777777
The accuracy of the KNN using Sepals is: 0.7333333333333333
总结
使用花瓣覆盖萼片来训练数据可以提供更好的准确性。
正如我们在上面的热图中看到的,这是意料之中的,萼片宽度和长度之间的相关性非常低,而花瓣宽度和长度之间的相关性非常高。
结语
因此,我们刚刚实现了一些常见的机器学习算法。由于数据集很小,功能很少,所以我没有介绍一些概念,因为当我们有很多特征时,它们是相关的。





