猴子摘香蕉问题-人工智能模拟
题目:
利用一阶谓词逻辑求解猴子摘香蕉问题:房内有一个猴子,一个箱子,天花板上挂了一串香蕉,其位置如图1所示,猴子为了拿到香蕉,它必须把箱子搬到香蕉下面,然后再爬到箱子上。请定义必要的谓词,列出问题的初始化状态(即下图所示状态),目标状态(猴子拿到了香蕉,站在箱子上,箱子位于位置b)。(附加:从初始状态到目标状态的谓词演算过程。)

1.定义描述环境状态的谓词。
AT(x,w):x在w处,个体域:x?{monkey},w?{a,b,c,box};
HOLD(x,t):x手中拿着t,个体域:t?{box,banana};
EMPTY(x):x手中是空的;
ON(t,y):t在y处,个体域:y?{b,c,ceiling};
CLEAR(y):y上是空的;
BOX(u):u是箱子,个体域:u?{box};
BANANA(v):v是香蕉,个体域:v?{banana};
2.使用谓词、连结词、量词来表示环境状态。
问题的初始状态可表示为:So:AT(monkey,a)?EMPTY(monkey)?ON(box,c)?ON(banana,ceiling)?CLEAR(b)?BOX(box)?
BANANA(banana)
要达到的目标状态为:Sg:
AT(monkey,box)?HOLD(monkey,banana)?ON(box,b)?CLEAR(ceiling)?CLEAR©?
BOX(box)?BANANA(banana)
3.从初始状态到目标状态的转化, 猴子需要完成一系列操作, 定义操作类谓词表示其动作。
WALK(m,n):猴子从m走到n处,个体域:m,n?{a,b,c};
CARRY(s,r):猴子在r处拿到s,个体域:r?{c,ceiling},s?{box,banana};
CLIMB(u,b):猴子在b处爬上u;
这3个操作也可分别用条件和动作来表示。条件直接用谓词公式表示,是为完成相应操作所必须具备的条件;当条件中的事实使其均为真时,则可激活操作规则,于是可执行该规则中的动作部分。动作通过前后状态的变化表示,即通过从动作前删除或增加谓词公式来描述动作后的状态。
WALK(m,n):猴子从m走到n处
条件:AT(monkey,m)
动作:

CARRY(s,r):猴子在r处拿到s
条件:AT(monkey,r)?EMPTY(monkey)?ON(s,r)?BOX(box)?BANANA(banana)
动作:

CLIMB(u,b):猴子在b处爬上u
条件:AT(monkey,b)?HOLD(monkey,u)?CLEAR(b)?BOX(box)?BANANA(banana)
动作:
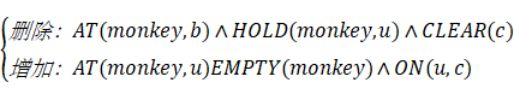
4.按照行动计划, 一步步进行状态替换, 直至目标状态
AT(monkey,a)?EMPTY(monkey)?ON(box,c)?ON(banana,ceiling)?CLEAR(b)?BOX(box)?
BANANA(banana)
AT(monkey,c)?EMPTY(monkey)?ON(box,c)?ON(banana,ceiling)?CLEAR(b)?BOX(box)?
BANANA(banana)
AT(monkey,c)?HOLD(monkey,box)?ON(banana,ceiling)?CLEAR(b)?CLEAR©?BOX(box)?
BANANA(banana)
AT(monkey,b)?HOLD(monkey,box)?ON(banana,ceiling)?CLEAR(b)?CLEAR©?BOX(box)?
BANANA(banana)
AT(monkey,box)?EMPTY(monkey)?ON(box,b)?ON(banana,ceiling)?CLEAR©?BOX(box)?
BANANA(banana)
AT(monkey,box)?HOLD(monkey,banana)?ON(box,b)?CLEAR(ceiling)?CLEAR©?BOX(box)?
BANANA(banana)(目标得解)
猴子行动的规则序列是:WALK(a,c)→CARRY(c,box)→WALK(c,b)→CLIMB(box,b)→
CARRY(banana,ceiling)
代码:
#include