shufflenet v2网络详解
ShuffleNet V2: Practical Guidelines for Efficient CNN Architecture Design
这里写目录标题
- ShuffleNet V2: Practical Guidelines for Efficient CNN Architecture Design
- 引言
- 网络设计准则
- 网络结构
文章链接 https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.11164
本文通过实验得到4条网络准则来提高cnn网络的效果
1、输入通道数与输出通道数保持相等可以最小化内存访问成本(memory access cost,MAC)。
2、分组卷积中使用过多的分组数会增加内存访问成本
3、 网络结构太复杂(分支和基本单元过多)会降低网络的并行程度
4、 Element-wise 的操作消耗也不可忽略(包括ReLU,Tensor的相加,偏置的相加等等操作)
引言
目前一些有效的卷积神经网络是靠分组卷积(gw)和分离卷积(dw),而且网络的复杂度一般都是靠 浮点运算操作的数量 (即 FLOPs)就是网络中的乘法和加法操作的数量,但是,本文发现,flops和计算速度不是成正比的。因为有内存的访问成本(mac)还有一个就是网络的并行化程度,在相同的 FLOPs 下,网络并行化程度更高的网络速度更快。
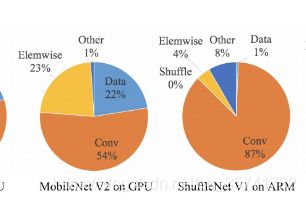
而且在不同的计算平台对不同的操作计算也是不同的,如图在gpu上有54%的计算量在conv,而在arm上87%在conv,(即有些操作对GPU结构友好但是对ARM结构并不友好,反之亦然)
所以我们也应该针对自己的开发平台来开发模型。
本文实验硬件条件: GPU 为一块 GeForce GTX 1080Ti; ARM 结构为 高通骁龙 810 芯片。
网络设计准则
1、尽量保持输入通道数和输出通道数相同才能使mac最低,速度最快。
2、在分组卷积中不能一味的增加分组来提高准确率,太多的分组会导致mac增加,降低运行速度。
3、结构太复杂,会影响网络运行速度
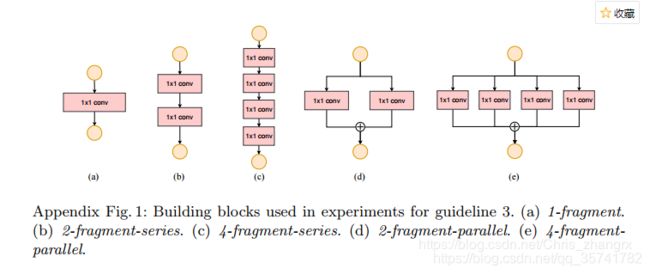
以上是在实验中使用的基本网络结构,分别将它们重复10次,然后进行实验。实验结果如下:
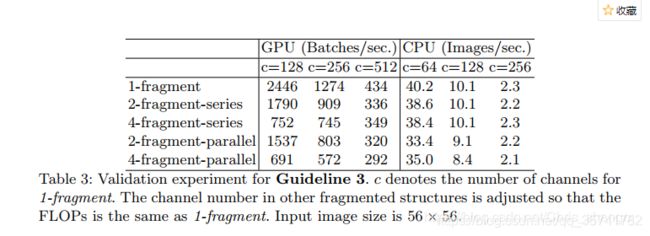
看的出,卷积串联太多会影响速度,且并行比串联速度要快一些。
4、Element-wise 的操作消耗也不可忽略(Element-wise包括ReLU,Tensor的相加,偏置的相加等等操作)
所以应该尽量减少Element-wise 的操作
网络结构
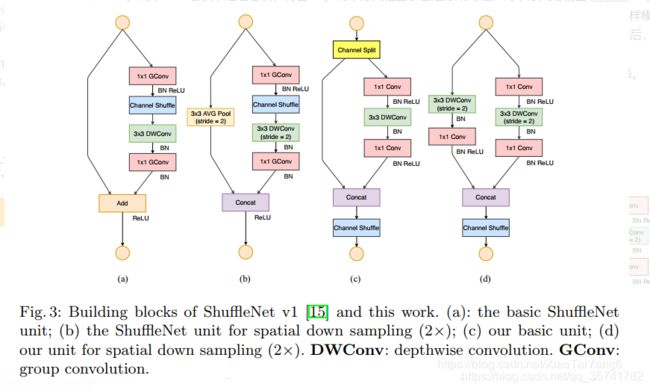
a and b:shufflenet v1的基本单元块
c and d:shufflenet v2的基本单元块
shufflenet v1缺点:
depthwise convolution 和 瓶颈结构增加了 MAC,用了太多的 group,跨层连接中的 element-wise Add 操作也是可以优化的点。所以在 shuffleNet V2 中增加了几种新特性。
所谓的 channel split 其实就是将通道数一分为2,化成两分支来代替原先的分组卷积结构(G2),并且每个分支中的卷积层都是保持输入输出通道数相同(G1),其中一个分支不采取任何操作减少基本单元数(G3),最后使用了 concat 代替原来的 elementy-wise add,并且后面不加 ReLU 直接(G4),再加入channle shuffle 来增加通道之间的信息交流。 对于下采样层,在这一层中对通道数进行翻倍。 在网络结构的最后,即平均值池化层前加入一层 1x1 的卷积层来进一步的混合特征。这段话出自
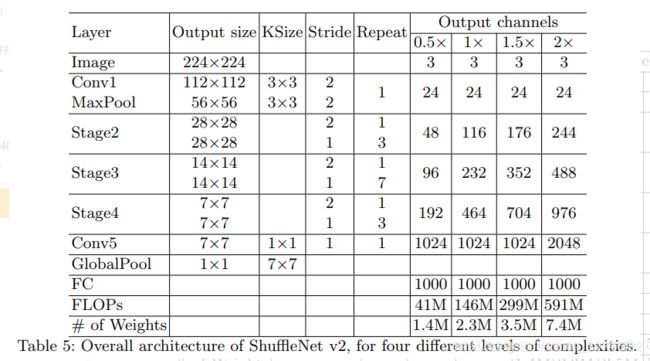
代码:pytorch官网实现的
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
__all__ = [
'ShuffleNetV2', 'shufflenet_v2_x0_5', 'shufflenet_v2_x1_0',
'shufflenet_v2_x1_5', 'shufflenet_v2_x2_0'
]
model_urls = {
'shufflenetv2_x0.5': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/shufflenetv2_x0.5-f707e7126e.pth',
'shufflenetv2_x1.0': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/shufflenetv2_x1-5666bf0f80.pth',
'shufflenetv2_x1.5': None,
'shufflenetv2_x2.0': None,
}
def channel_shuffle(x, groups):
batchsize, num_channels, height, width = x.data.size()
channels_per_group = num_channels // groups
# reshape
x = x.view(batchsize, groups,
channels_per_group, height, width)
x = torch.transpose(x, 1, 2).contiguous()
# flatten
x = x.view(batchsize, -1, height, width)
return x
class InvertedResidual(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, stride):
super(InvertedResidual, self).__init__()
if not (1 <= stride <= 3):
raise ValueError('illegal stride value')
self.stride = stride
branch_features = oup // 2
assert (self.stride != 1) or (inp == branch_features << 1)
if self.stride > 1:
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
self.depthwise_conv(inp, inp, kernel_size=3, stride=self.stride, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(inp),
nn.Conv2d(inp, branch_features, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(branch_features),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp if (self.stride > 1) else branch_features,
branch_features, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(branch_features),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
self.depthwise_conv(branch_features, branch_features, kernel_size=3, stride=self.stride, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(branch_features),
nn.Conv2d(branch_features, branch_features, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(branch_features),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
@staticmethod
def depthwise_conv(i, o, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False):
return nn.Conv2d(i, o, kernel_size, stride, padding, bias=bias, groups=i)
def forward(self, x):
if self.stride == 1:
x1, x2 = x.chunk(2, dim=1)
out = torch.cat((x1, self.branch2(x2)), dim=1)
else:
out = torch.cat((self.branch1(x), self.branch2(x)), dim=1)
out = channel_shuffle(out, 2)
return out
class ShuffleNetV2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, stages_repeats, stages_out_channels, num_classes=1000):
super(ShuffleNetV2, self).__init__()
if len(stages_repeats) != 3:
raise ValueError('expected stages_repeats as list of 3 positive ints')
if len(stages_out_channels) != 5:
raise ValueError('expected stages_out_channels as list of 5 positive ints')
self._stage_out_channels = stages_out_channels
input_channels = 3
output_channels = self._stage_out_channels[0]
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(input_channels, output_channels, 3, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(output_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
input_channels = output_channels
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
stage_names = ['stage{}'.format(i) for i in [2, 3, 4]]
for name, repeats, output_channels in zip(
stage_names, stages_repeats, self._stage_out_channels[1:]):
seq = [InvertedResidual(input_channels, output_channels, 2)]
for i in range(repeats - 1):
seq.append(InvertedResidual(output_channels, output_channels, 1))
setattr(self, name, nn.Sequential(*seq))
input_channels = output_channels
output_channels = self._stage_out_channels[-1]
self.conv5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(input_channels, output_channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(output_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
self.fc = nn.Linear(output_channels, num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.stage2(x)
x = self.stage3(x)
x = self.stage4(x)
x = self.conv5(x)
x = x.mean([2, 3]) # globalpool
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def _shufflenetv2(arch, pretrained, progress, *args, **kwargs):
model = ShuffleNetV2(*args, **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model_url = model_urls[arch]
if model_url is None:
raise NotImplementedError('pretrained {} is not supported as of now'.format(arch))
else:
state_dict = load_state_dict_from_url(model_url, progress=progress)
model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
return model
def shufflenet_v2_x0_5(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
"""
Constructs a ShuffleNetV2 with 0.5x output channels, as described in
`"ShuffleNet V2: Practical Guidelines for Efficient CNN Architecture Design"
`_.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _shufflenetv2('shufflenetv2_x0.5', pretrained, progress,
[4, 8, 4], [24, 48, 96, 192, 1024], **kwargs)
def shufflenet_v2_x1_0(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
"""
Constructs a ShuffleNetV2 with 1.0x output channels, as described in
`"ShuffleNet V2: Practical Guidelines for Efficient CNN Architecture Design"
`_.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _shufflenetv2('shufflenetv2_x1.0', pretrained, progress,
[4, 8, 4], [24, 116, 232, 464, 1024], **kwargs)
def shufflenet_v2_x1_5(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
"""
Constructs a ShuffleNetV2 with 1.5x output channels, as described in
`"ShuffleNet V2: Practical Guidelines for Efficient CNN Architecture Design"
`_.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _shufflenetv2('shufflenetv2_x1.5', pretrained, progress,
[4, 8, 4], [24, 176, 352, 704, 1024], **kwargs)
def shufflenet_v2_x2_0(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
"""
Constructs a ShuffleNetV2 with 2.0x output channels, as described in
`"ShuffleNet V2: Practical Guidelines for Efficient CNN Architecture Design"
`_.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _shufflenetv2('shufflenetv2_x2.0', pretrained, progress,
[4, 8, 4], [24, 244, 488, 976, 2048], **kwargs)