JAVA —— ElasticSearch ①
文章目录
-
- 1-文章内容
- 2-初识ElasticSearch
-
- 2.1-基于数据库查询的问题
- 2.2-倒排索引
- 2.3-ES存储和查询的原理
- 2.4-ES概念详解
- 2.5 ElasticSearch和Mysql的区别
- 3-安装ElasticSearch
-
- 3.1-ES安装
- 3.2-ES辅助工具安装
- 4-ElasticSearch核心概念
-
- 1 索引(index)
- 2 类型(type)
- 3 映射(mapping)
- 4 文档(document)
- 5 倒排索引
- 对比MySQL
- 5-脚本操作ES
-
- 5.1-RESTful风格介绍
- 5.2-操作索引
- 5.3-ES数据类型
- 5.4-操作映射
-
- 5.4.1 添加
- 5.4.2 查看
- 5.4.3 索引+ 映射一起创建
- 5.5-操作文档
-
- 5.5.1添加/更新文档
- 5.5.2查看文档(简单查看)
- 5.5.3删除
- 6-分词器
-
- 6.1分词器-介绍
- 6.2-ik分词器安装
- 6.3-ik分词器使用
- 6.4使用IK分词器-查询文档
- 7-ElasticSearch JavaAPI
-
- 7.1-SpringBoot整合ES
- 7.2-创建索引
- 7.3-查询、删除、判断索引
- 7.4-添加文档
- 7.5-修改、查询、删除文档
- 1 ElasticSearch 安装
-
- 1.1 ElasticSearch安装
- 1.2 访问elasticsearch
- 2 Elasticsearch辅助插件安装
-
- 2.1 Postman安装
- 2.2 Kibana安装
- 2.3 head安装
-
- 2.3.1 Node安装
- 2.3.2 grunt安装
- 2.3.3 head安装
- IK分词器安装
-
-
- 1、环境准备
- 2、安装IK分词器
- 3、使用IK分词器
-
1-文章内容
- 初识 ElasticSearch
- 安装 ElasticSearch
- ElasticSearch 核心概念
- 操作 ElasticSearch
- ElasticSearch JavaAPI
2-初识ElasticSearch
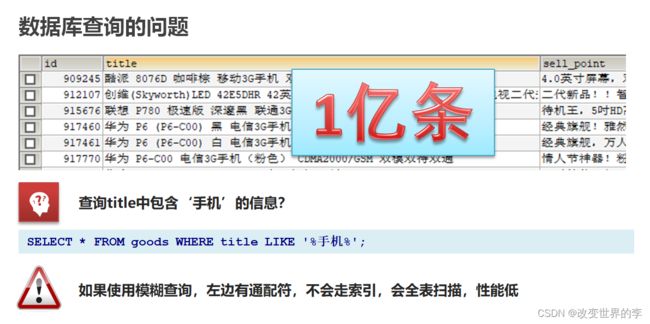
2.1-基于数据库查询的问题
Es通过倒排索引解决这些问题
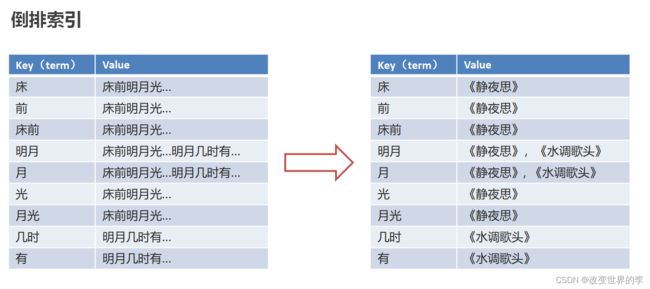
2.2-倒排索引
倒排索引:将文档进行分词,形成词条和id的对应关系即为反向索引。
以唐诗为例,所处包含“前”的诗句
正向索引:由《静夜思》–>窗前明月光—>“前”字
反向索引:“前”字–>窗前明月光–>《静夜思》
反向索引的实现就是对诗句进行分词,分成单个的词,由词推据,即为反向索引
“床前明月光”–> 分词
将一段文本按照一定的规则,拆分为不同的词条(term)
2.3-ES存储和查询的原理
index(索引):相当于mysql的库
映射:相当于mysql 的表结构
document(文档):相当于mysql的表中的数据
数据库查询存在的问题:
-
性能低:使用模糊查询,左边有通配符,不会走索引,会全表扫描,性能低
-
功能弱:对于如下的数据如果以”华为手机“作为条件,查询不出来数据
ES查询解决方法
使用倒排索引,对title 进行分词
-
使用“手机”作为关键字查询
生成的倒排索引中,词条会排序,形成一颗树形结构,提升词条的查询速度
-
使用“华为手机”作为关键字查询
华为:1,3
手机:1,2,3
2.4-ES概念详解
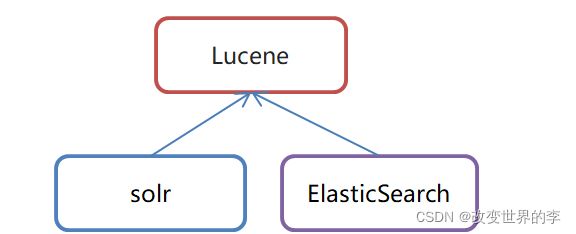
Lucene:是一套用于全文检索和搜寻的开源程式库,由Apache软件基金会支持和提供
•ElasticSearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器
•是一个分布式、高扩展、高实时的搜索与数据分析引擎
•基于RESTful web接口
•Elasticsearch是用Java语言开发的,并作为Apache许可条款下的开放源码发布,是一种流行的企业级搜索引擎
•官网:https://www.elastic.co/
应用场景
•搜索:海量数据的查询
•日志数据分析:ELK
•实时数据分析
2.5 ElasticSearch和Mysql的区别
•MySQL有事务性,而ElasticSearch没有事务性,所以你删了的数据是无法恢复的。
•ElasticSearch没有物理外键这个特性,,如果你的数据强一致性要求比较高,还是建议慎用
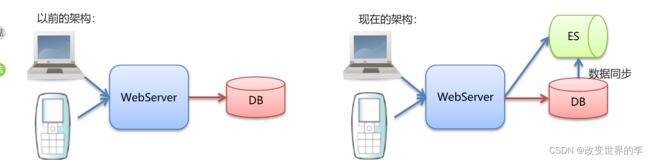
ElasticSearch和MySql分工不同,MySQL负责存储数据,ElasticSearch负责搜索数据。
3-安装ElasticSearch
3.1-ES安装
参见ElasticSearch-ES安装
查看elastic是否启动
ps -ef|grep elastic
3.2-ES辅助工具安装
参见ElasticSearch-ES安装
后台启动
nohup ../bin/kibana &
4-ElasticSearch核心概念
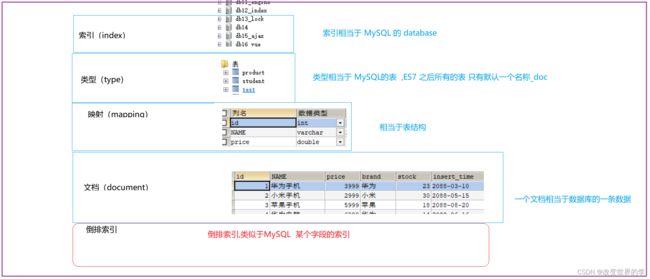
1 索引(index)
ElasticSearch存储数据的地方,可以理解成关系型数据库中的数据库概念。
2 类型(type)
一种type就像一类表。如用户表、角色表等。在Elasticsearch7.X默认type为_doc
\- ES 5.x中一个index可以有多种type。
\- ES 6.x中一个index只能有一种type。
\- ES 7.x以后,将逐步移除type这个概念,现在的操作已经不再使用,默认_doc
3 映射(mapping)
mapping定义了每个字段的类型、字段所使用的分词器等。相当于关系型数据库中的表结构。
4 文档(document)
Elasticsearch中的最小数据单元,常以json格式显示。一个document相当于关系型数据库中的一行数据。
5 倒排索引
一个倒排索引由文档中所有不重复词的列表构成,对于其中每个词,对应一个包含它的文档id列表。
对比MySQL
5-脚本操作ES
5.1-RESTful风格介绍
1.REST(Representational State Transfer),表述性状态转移,是一组架构约束条件和原则。满足这些约束条件和原则的应用程序或设计就是RESTful。就是一种定义接口的规范。
2.基于HTTP。
3.使用XML格式定义或JSON格式定义。
4.每一个URI代表1种资源。
5.客户端使用GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 4个表示操作方式的动词对服务端资源进行操作:
GET:用来获取资源
POST:用来新建资源(也可以用于更新资源)
PUT:用来更新资源
DELETE:用来删除资源
5.2-操作索引
使用Kibana执行命令:http://192.168.52.128:5601/app/kibana#/dev_tools/console?_g=()
# 创建索引
PUT person
# 查看索引
GET person
# 删除索引(同时会删除其所有数据,相当于mysql的drop database)
DELETE person
# 查询所有索引
GET _cat/indices
#清除所有索引
delete /_all
delete /c* (通配符删除c 开头的索引)
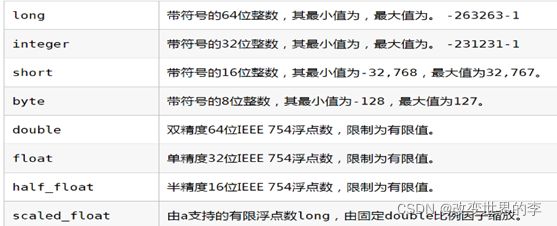
5.3-ES数据类型
- 简单数据类型
-
字符串
text:会分词,不支持聚合 keyword:不会分词,将全部内容作为一个词条,支持聚合 -
数值:long.inteter,double等
-
布尔:boolean
-
二进制:binary
-
范围类型
integer_range, float_range, long_range, double_range, date_range -
日期:date
- 复杂数据类型
-
数组:[ ] Nested:
nested(for arrays of JSON objects 数组类型的JSON对象) -
对象:{ } Object: object(for single JSON objects 单个JSON对象)
注意: 字段类型没有修改功能
5.4-操作映射
5.4.1 添加
#添加映射(相当于添加表字段)
PUT /person/_mapping
{
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"text"
},
"age":{
"type":"integer"
}
}
}
#添加映射_指定分词器(相当于添加表字段)
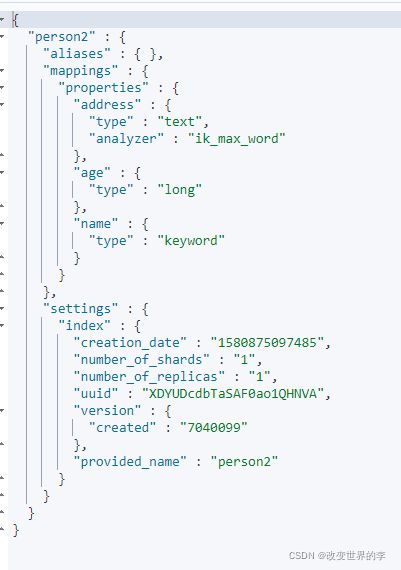
PUT person2
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "keyword" // keyword 类型 不会分词,不建立倒排索引
},
"address": {
"type": "text", // text 类型 会分词, 但不能进行聚合查询(类似SQL group by/sum函数)
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
5.4.2 查看
#仅查看映射(查看表结构)
GET person/_mapping
#仅查看索引,会自动显示表结构(查看表结构)
GET person
5.4.3 索引+ 映射一起创建
#创建索引并添加映射(相当于建立数据库时,(因为只有一张表type=_doc)同时制定表字段)
PUT /person1
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
5.5-操作文档
5.5.1添加/更新文档
# 指定id
POST /person2/_doc/1
{
"name":"张三",
"age":18,
"address":"北京海淀区"
}
#添加文档,不指定id 随机生成id
POST /person1/_doc/
{
"name":"张三",
"age":18,
"address":"北京"
}
5.5.2查看文档(简单查看)
# 根据id 查看
GET /person1/_doc/1
# 查看所有(无条件查询)
GET /person1/_search
5.5.3删除
#删除指定id文档
DELETE /person1/_doc/1
6-分词器
6.1分词器-介绍
•IKAnalyzer是一个开源的,基于java语言开发的轻量级的中文分词工具包
•是一个基于Maven构建的项目
•具有60万字/秒的高速处理能力
•支持用户词典扩展定义
•下载地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/archive/v7.4.0.zip
6.2-ik分词器安装
参见 ik分词器安装
执行如下命令时如果出现 打包失败(501码)将maven镜像换成阿里云的
mvn package
/opt/apache-maven-3.1.1/conf/setting.xml
<mirror>
<id>alimavenid>
<name>aliyun mavenname>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/url>
<mirrorOf>centralmirrorOf>
mirror>
6.3-ik分词器使用
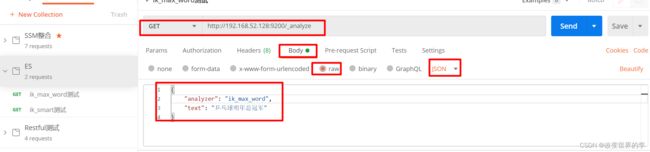
IK分词器有两种分词模式:ik_max_word和ik_smart模式。可以使用Postman测试
1、ik_max_word
#方式一ik_max_word
#会将文本做最细粒度的拆分,比如会将“乒乓球明年总冠军”拆分为“乒乓球、乒乓、球、明年、总冠军、冠军。
GET /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "乒乓球明年总冠军"
}
ik_max_word分词器执行如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "乒乓球",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "乒乓",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "球",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "明年",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "总冠军",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "冠军",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 5
}
]
}
2、ik_smart
#方式二ik_smart
#会做最粗粒度的拆分,比如会将“乒乓球明年总冠军”拆分为乒乓球、明年、总冠军。
GET /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"text": "乒乓球明年总冠军"
}
ik_smart分词器执行如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "乒乓球",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "明年",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "总冠军",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 2
}
]
}
由此可见:使用ik_smart可以将文本"text": "乒乓球明年总冠军"分成了【乒乓球】【明年】【总冠军】
这样看的话,这样的分词效果更智能一些,达到了要求。
6.4使用IK分词器-查询文档
-
词条查询:term
词条查询不会分析查询条件,只有当词条和查询字符串完全匹配时才匹配搜索
-
全文查询:match
全文查询会分析查询条件,先将查询条件进行分词,然后查询,求并集
1.创建索引,添加映射,并指定分词器为ik分词器
#如果有删除
delete person2
#添加映射_指定分词器(相当于添加表字段)
PUT person2
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "keyword" // keyword 类型 不会分词
},
"address": {
"type": "text", // text 类型 会分词, 但不能进行聚合查询(类似SQL group by/sum函数)
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
2.添加文档
# 添加几条数据备用
# 指定id
POST /person2/_doc/1
{
"name":"张三",
"age":18,
"address":"北京海淀区"
}
POST /person2/_doc/2
{
"name":"李四",
"age":18,
"address":"北京朝阳区"
}
POST /person2/_doc/3
{
"name":"王五",
"age":18,
"address":"北京昌平区"
}
3.查询映射
GET person2
4.查看分词效果
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "北京海淀"
}
5.词条查询:term,不会将查询条件拆分
查询person2中匹配到"北京"两字的词条
GET /person2/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"address": {
"value": "北京"
}
}
}
}
6.全文查询:match
全文查询会分析查询条件,先将查询条件进行分词,然后查询,求并集
GET /person2/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address":"北京昌平"
}
}
}
7-ElasticSearch JavaAPI
7.1-SpringBoot整合ES
①搭建SpringBoot工程
②引入ElasticSearch相关坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.clientgroupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-clientartifactId>
<version>7.4.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.clientgroupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-clientartifactId>
<version>7.4.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearchgroupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearchartifactId>
<version>7.4.0version>
dependency>
完整依赖如下:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starterartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintagegroupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engineartifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.clientgroupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-clientartifactId>
<version>7.4.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.clientgroupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-clientartifactId>
<version>7.4.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearchgroupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearchartifactId>
<version>7.4.0version>
dependency>
dependencies>
③测试
- 编写配置类ElasticSearchConfig
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="elasticsearch")
public class ElasticSearchConfig {
private String host;
private int port;
public String getHost() {
return host;
}
public void setHost(String host) {
this.host = host;
}
public int getPort() {
return port;
}
public void setPort(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient client(){
return new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
new HttpHost(host,port,"http")
));
}
}
-
配置es信息: src\main\resources\application.yml
elasticsearch: host: 192.168.52.128 port: 9200 -
ElasticsearchDay01ApplicationTests
注意:使用@Autowired注入RestHighLevelClient 如果报红线,则是因为配置类所在的包和测试类所在的包,包名不一致造成的
@SpringBootTest
class ElasticsearchDay01ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
RestHighLevelClient client;
/**
* 测试
*/
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(client);
}
}
7.2-创建索引
1.添加索引
/**
* 添加索引
*/
@Test
public void addIndex() throws IOException {
//1.使用client获取操作索引的对象
IndicesClient indicesClient = client.indices();
//2.具体操作,获取返回值
CreateIndexRequest createRequest = new CreateIndexRequest("xxx");
CreateIndexResponse response = indicesClient.create(createRequest,
RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//3.根据返回值判断结果
System.out.println(response.isAcknowledged());
}
2.添加索引,并添加映射
/**
* 添加索引,并添加映射
*/
@Test
public void addIndexAndMapping() throws IOException {
//1.使用client获取操作索引对象
IndicesClient indices = client.indices();
//2.具体操作获取返回值
//2.具体操作,获取返回值
CreateIndexRequest createIndexRequest = new CreateIndexRequest("xxx");
//2.1 设置mappings
String mapping = "{\n" +
" \"properties\" : {\n" +
" \"address\" : {\n" +
" \"type\" : \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\" : \"ik_max_word\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"age\" : {\n" +
" \"type\" : \"long\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"name\" : {\n" +
" \"type\" : \"keyword\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }";
createIndexRequest.mapping(mapping,XContentType.JSON);
CreateIndexResponse createIndexResponse = indices.create(createIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//3.根据返回值判断结果
System.out.println(createIndexResponse.isAcknowledged());
}
7.3-查询、删除、判断索引
- 查询索引
/**
* 查询索引
*/
@Test
public void queryIndex() throws IOException {
IndicesClient indices = client.indices();
GetIndexRequest getRequest=new GetIndexRequest("xxx");
GetIndexResponse response = indices.get(getRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
Map<String, MappingMetaData> mappings = response.getMappings();
//iter 提示foreach
for (String key : mappings.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key+"==="+mappings.get(key).getSourceAsMap());
}
}
- 删除索引
/**
* 删除索引
*/
@Test
public void deleteIndex() throws IOException {
IndicesClient indices = client.indices();
DeleteIndexRequest deleteRequest=new DeleteIndexRequest("xxx");
AcknowledgedResponse delete = indices.delete(deleteRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(delete.isAcknowledged());
}
- 索引是否存在
/**
* 索引是否存在
*/
@Test
public void existIndex() throws IOException {
IndicesClient indices = client.indices();
GetIndexRequest getIndexRequest=new GetIndexRequest("xxx");
boolean exists = indices.exists(getIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(exists);
}
7.4-添加文档
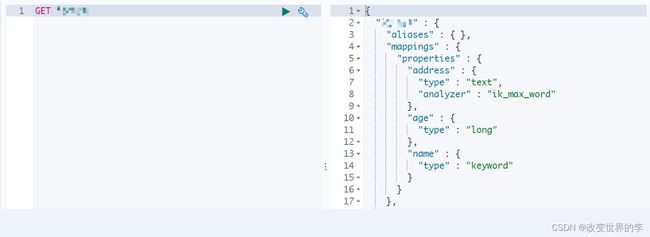
1.添加文档,使用map作为数据
/**
* 添加文档,使用map作为数据
*/
@Test
public void addDoc() throws IOException {
//数据对象,map
Map data = new HashMap();
data.put("address", "北京昌平");
data.put("name", "大胖");
data.put("age", 20);
//1.获取操作文档的对象
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("xxx").id("1").source(data);
//添加数据,获取结果
IndexResponse response = client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//打印响应结果
System.out.println(response.getId());
}
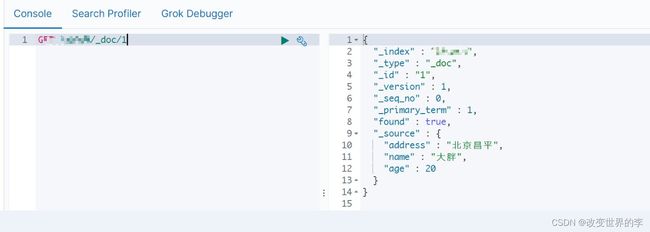
2.添加文档,使用对象作为数据
/**
* 添加文档,使用对象作为数据
*/
@Test
public void addDoc2() throws IOException {
//数据对象,javaObject
Person p = new Person();
p.setId("2");
p.setName("小胖2222");
p.setAge(30);
p.setAddress("陕西西安");
//将对象转为json
String data = JSON.toJSONString(p);
//1.获取操作文档的对象
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("xxx").id(p.getId()).source(data,
XContentType.JSON);
//添加数据,获取结果
IndexResponse response = client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//打印响应结果
System.out.println(response.getId());
}
注意!!!对象转化为JSON需要导入JSON的依赖坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>fastjsonartifactId>
<version>1.2.4version>
dependency>
7.5-修改、查询、删除文档
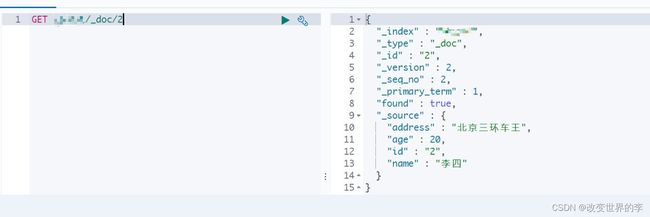
1.修改文档:添加文档时,如果id存在则修改,id不存在则添加
/**
* 修改文档:添加文档时,如果id存在则修改,id不存在则添加
*/
@Test
public void UpdateDoc() throws IOException {
Person person=new Person();
person.setId("2");
person.setName("李四");
person.setAge(20);
person.setAddress("北京三环车王");
String data = JSON.toJSONString(person);
IndexRequest request=new IndexRequest("xxx").id(person.getId()).source(data,XContentType.JSON);
IndexResponse response = client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.getId());
}
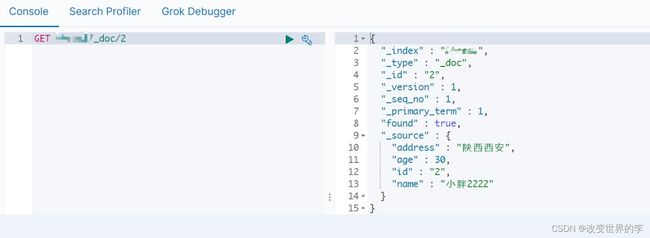
2.根据id查询文档
/**
* 根据id查询文档
*/
@Test
public void getDoc() throws IOException {
//设置查询的索引、文档
GetRequest indexRequest=new GetRequest("xxx","2");
GetResponse response = client.get(indexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.getSourceAsString());
}
3.根据id删除文档
/**
* 根据id删除文档
*/
@Test
public void delDoc() throws IOException {
//设置要删除的索引、文档
DeleteRequest deleteRequest=new DeleteRequest("xxx","1");
DeleteResponse response = client.delete(deleteRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.getId());
}
1 ElasticSearch 安装
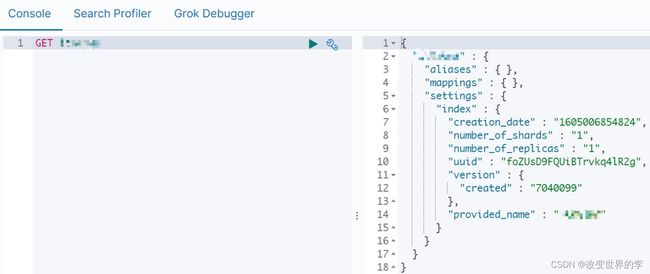
1.1 ElasticSearch安装
1、上传ElasticSearch安装包
alt+p # 打开sftp窗口
# 上传es安装包
put e:/software/elasticsearch-7.4.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
2、执行解压操作 ,如下图
# 将elasticsearch-7.4.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz解压到opt文件夹下. -C 大写
tar -zxvf elasticsearch-7.4.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz -C /opt
3、创建普通用户
因为安全问题,Elasticsearch 不允许root用户直接运行,所以要创建新用户,在root用户中创建新用户,执行如下命令:
useradd itXXX # 新增itXXX用户
passwd itXXX # 为itXXX用户设置密码
5、为新用户授权,如下图
chown -R itXXX:itXXX /opt/elasticsearch-7.4.0 #文件夹所有者
将 /opt/elasticsearch-7.4.0文件夹授权给itXXX用户,由上图可见,文件夹权限赋给了itXXX
6、修改elasticsearch.yml文件
vim /opt/elasticsearch-7.4.0/config/elasticsearch.yml
# ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration =========================
cluster.name: my-application
node.name: node-1
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
cluster.name:配置elasticsearch的集群名称,默认是elasticsearch。建议修改成一个有意义的名称
node.name:节点名,elasticsearch会默认随机指定一个名字,建议指定一个有意义的名称,方便管理
network.host:设置为0.0.0.0允许外网访问
http.port:Elasticsearch的http访问端口
cluster.initial_master_nodes:初始化新的集群时需要此配置来选举master
7、修改配置文件
新创建的itXXX用户最大可创建文件数太小,最大虚拟内存太小,切换到root用户,编辑下列配置文件, 添加类似如下内容
# 切换到root用户
su root
#1. ===最大可创建文件数太小=======
vim /etc/security/limits.conf
# 在文件末尾中增加下面内容
itXXX soft nofile 65536
itXXX hard nofile 65536
# =====
vim /etc/security/limits.d/20-nproc.conf
# 在文件末尾中增加下面内容
itXXX soft nofile 65536
itXXX hard nofile 65536
* hard nproc 4096
# 注:* 代表Linux所有用户名称
#2. ===最大虚拟内存太小=======
vim /etc/sysctl.conf
# 在文件中增加下面内容
vm.max_map_count=655360
# 重新加载,输入下面命令:
sysctl -p
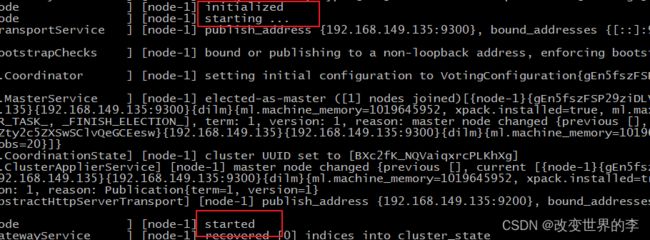
8、启动elasticsearch
su itXXX # 切换到itXXX用户启动
cd /opt/elasticsearch-7.4.0/bin
./elasticsearch #启动
通过上图可以看到elasticsearch已经成功启动
1.2 访问elasticsearch
1、在访问elasticsearch前,请确保防火墙是关闭的,执行命令:
#暂时关闭防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld
# 或者
#永久设置防火墙状态
systemctl enable firewalld.service #打开防火墙永久性生效,重启后不会复原
systemctl disable firewalld.service #关闭防火墙,永久性生效,重启后不会复原
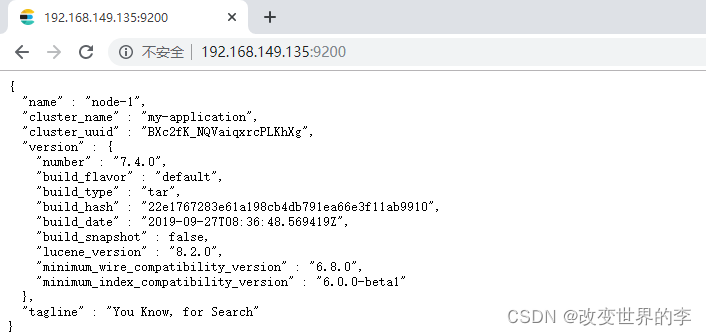
浏览器输入http://192.168.149.135:9200/,如下图
此时elasticsearch已成功启动:
重点几个关注下即可:
number" : "7.4.0" 表示elasticsearch版本
lucene_version" : "8.2.0" 表示lucene版本
name : 默认启动的时候指定了 ES 实例名称
cluster_name : 默认名为 elasticsearch
2 Elasticsearch辅助插件安装
2.1 Postman安装
1、什么是Postman
Postman是一个http模拟请求的工具。
官网介绍:“Modern software is built on APIs,Postman helps you develop APIs faster”
看得出来,它是一个专门测试 API 的工具,Postman 提供功能强大的 Web API 和 HTTP 请求的调试,它能够发送任何类型的HTTP 请求 (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE…),并且能附带任何数量的参数和 Headers。不仅如此,它还提供测试数据和环境配置数据的导入导出。
进入官网www.getpostman.com,下载
2.2 Kibana安装
1、什么是Kibana
Kibana是一个针对Elasticsearch的开源分析及可视化平台,用来搜索、查看交互存储在Elasticsearch索引中的数据。使用Kibana,可以通过各种图表进行高级数据分析及展示。
Kibana让海量数据更容易理解。它操作简单,基于浏览器的用户界面可以快速创建仪表板(dashboard)实时显示Elasticsearch查询动态。
2、上传kibana
CRT中克隆一个窗口,上传Kibana
put E:\software\kibana-7.4.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
2、解压kibana
tar -xzf kibana-7.4.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz -C /opt
解压到当前目录(/opt)下
3、修改kibana配置
vim /opt/kibana-7.4.0-linux-x86_64/config/kibana.yml
server.port: 5601
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
server.name: "kibana-XXX"
elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://127.0.0.1:9200"]
elasticsearch.requestTimeout: 99999
server.port:http访问端口
server.host:ip地址,0.0.0.0表示可远程访问
server.name:kibana服务名
elasticsearch.hosts:elasticsearch地址
elasticsearch.requestTimeout:请求elasticsearch超时时间,默认为30000,此处可根据情况设置
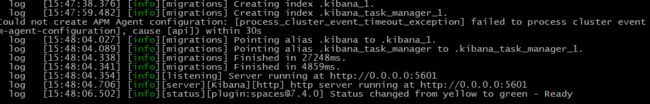
4、启动kibana
由于kibana不建议使用root用户启动,如果用root启动,需要加–allow-root参数
# 切换到kibana的bin目录
cd /opt/kibana-7.4.0-linux-x86_64/bin
# 启动
./kibana --allow-root
启动成功。
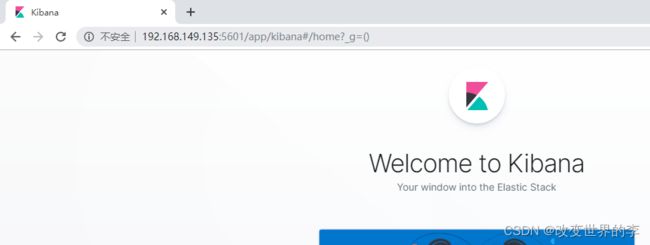
5、访问kibana
1.浏览器输入http://192.168.149.135:5601/,如下图:
http://192.168.149.135:5601/
看到这个界面,说明Kibanan已成功安装。
Discover:可视化查询分析器
Visualize:统计分析图表
Dashboard:自定义主面板(添加图表)
Timelion:Timelion是一个kibana时间序列展示组件(暂时不用)
Dev Tools:Console控制台(同CURL/POSTER,操作ES代码工具,代码提示,很方便)
Management:管理索引库(index)、已保存的搜索和可视化结果(save objects)、设置 kibana 服务器属性。
2.3 head安装
Tips:
课后扩展内容
head简介
ead插件是ES的一个可视化管理插件,用来监视ES的状态,并通过head客户端和ES服务进行交互,比如创建映射、创建索引等。
在登陆和访问head插件地址和ElasticSearch前需要事先在服务器上安装和配置好ElasticSearch以及head插件。安装完后,默认head插件的web端口为9100,ElasticSearch服务的端口为9200,使用浏览器访问head地址,如http://IP地址:9100/,推荐使用Chrome浏览器,head插件对Chrome浏览器兼容更佳。进入head页面后将ElasticSearch连接输入框中填写正确的ElasticSearch服务地址,就可以监控ElasticSearch运行信息
2.3.1 Node安装
- 什么是Node
简单的说 Node.js 就是运行在服务端的 JavaScript。Node.js 是一个基于 Chrome V8 引擎的 JavaScript 运行环境。Node.js 使用了一个事件驱动、非阻塞式 I/O 的模型,使其轻量又高效。Node.js 的包管理器 npm,是全球最大的开源库生态系统。
- 下载Node
上一节已经安装好了Elasticsearch,接下来来安装head插件,由于elasticsearch-head插件是由nodejs语言编写,所以安装elasticsearch-head前需要先安装nodejs。
首先,执行以下命令安装nodejs和grunt
打开虚拟机,执行wget命令下载Node,如下图:
wget https://nodejs.org/dist/v10.15.2/node-v10.15.2-linux-x64.tar.xz
3)解压Node包
tar xvf node-v10.15.2-linux-x64.tar.xz
4)设置软连接
解压文件的 bin 目录底下包含了 node、npm 等命令,可以使用 ln 命令来设置软连接:
ln -s bin/npm /usr/local/bin/
ln -s bin/node /usr/local/bin/
在/etc/profile中配置好path环境变量
vi ~/.bash_profile
export NODE_HOME=/opt/nodejs/node-v10.15.2-linux-x64
export PATH=$PATH:$NODE_HOME/bin
保存退出,使文件生效
source ~/.bash_profile
查看node安装版本,执行 node -v 验证安装如下图:
![]()
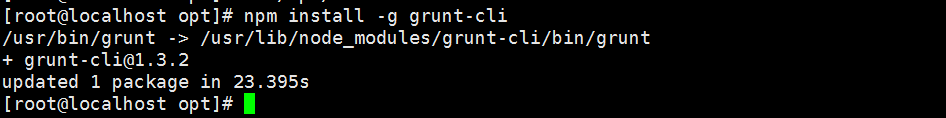
2.3.2 grunt安装
安装grunt(运行在Node.js上面的任务管理器(task runner)),为了获得Grunt的更多产品特性,需要全局安装Grunt’s 命令行接口(CLI),使用npm进行安装,如下:
npm install -g grunt-cli
查看grunt版本
输出grunt版本信息,表示安装成功。
2.3.3 head安装
- 执行命令安装git
git yum install git -y
- 切换到/opt目录下,执行下面的克隆命令
git clone git://github.com/mobz/elasticsearch-head.git
- 进入到elasticsearch-head目录
cd elasticsearch-head
- 运行
在运行之前需要修改下elasticsearch.yml,因为ES默认不开启跨域访问,需要添加以下配置:
#开启cors跨域访问支持,默认为false
http.cors.enabled: true
#跨域访问允许的域名地址,(允许所有域名)以上使用正则
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
然后开始执行运行命令:
npm run start
- 访问head
浏览器输入ip:port:9100,如下图
看到这个界面说明head插件成功安装并且成功连接Elasticsearch。
IK分词器安装
1、环境准备
Elasticsearch 要使用 ik,就要先构建 ik 的 jar包,这里要用到 maven 包管理工具,而 maven 需要java 环境,而 Elasticsearch 内置了jdk, 所以可以将JAVA_HOME设置为Elasticsearch 内置的jdk
1)设置JAVA_HOME
vim /etc/profile
# 在profile文件末尾添加
#java environment
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/elasticsearch-7.4.0/jdk
export PATH=$PATH:${JAVA_HOME}/bin
# 保存退出后,重新加载profile
source /etc/profile
2)下载maven安装包
wget http://mirror.cc.columbia.edu/pub/software/apache/maven/maven-3/3.1.1/binaries/apache-maven-3.1.1-bin.tar.gz
3)解压maven安装包
tar xzf apache-maven-3.1.1-bin.tar.gz
4)设置软连接
ln -s apache-maven-3.1.1 maven
5)设置path
打开文件
vim /etc/profile.d/maven.sh
将下面的内容复制到文件,保存
export MAVEN_HOME=/opt/maven
export PATH=${MAVEN_HOME}/bin:${PATH}
设置好Maven的路径之后,需要运行下面的命令使其生效
source /etc/profile.d/maven.sh
6)验证maven是否安装成功
mvn -v
2、安装IK分词器
1)下载IK
wget https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/archive/v7.4.0.zip
执行如下图:
2)解压IK
由于这里是zip包不是gz包,所以需要使用unzip命令进行解压,如果本机环境没有安装unzip,请执行:
yum install zip
yum install unzip
解压IK
unzip v7.4.0.zip
3)编译jar包
# 切换到 elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.4.0目录
cd elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.4.0/
#打包
mvn package
4) jar包移动
package执行完毕后会在当前目录下生成target/releases目录,将其中的elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.4.0.zip。拷贝到elasticsearch目录下的新建的目录plugins/analysis-ik,并解压
#切换目录
cd /opt/elasticsearch-7.4.0/plugins/
#新建目录
mkdir analysis-ik
cd analysis-ik
#执行拷贝
cp -R /opt/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.4.0/target/releases/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.4.0.zip /opt/elasticsearch-7.4.0/plugins/analysis-ik
#执行解压
unzip /opt/elasticsearch-7.4.0/plugins/analysis-ik/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.4.0.zip
5)拷贝辞典
将elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.4.0目录下的config目录中的所有文件 拷贝到elasticsearch的config目录
cp -R /opt/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.4.0/config/* /opt/elasticsearch-7.4.0/config
记得一定要重启Elasticsearch!!!
3、使用IK分词器
IK分词器有两种分词模式:ik_max_word和ik_smart模式。
1、ik_max_word
会将文本做最细粒度的拆分,比如会将“乒乓球明年总冠军”拆分为“乒乓球、乒乓、球、明年、总冠军、冠军。
#方式一ik_max_word
GET /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "乒乓球明年总冠军"
}
ik_max_word分词器执行如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "乒乓球",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "乒乓",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "球",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "明年",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "总冠军",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "冠军",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 5
}
]
}
2、ik_smart
会做最粗粒度的拆分,比如会将“乒乓球明年总冠军”拆分为乒乓球、明年、总冠军。
#方式二ik_smart
GET /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"text": "乒乓球明年总冠军"
}
ik_smart分词器执行如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "乒乓球",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "明年",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "总冠军",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 2
}
]
}
由此可见 使用ik_smart可以将文本"text": "乒乓球明年总冠军"分成了【乒乓球】【明年】【总冠军】
这样看的话,这样的分词效果达到了的要求。