PCL-3D特征描述子
3D特征描述子
- 什么是3D特征描述子?
- 特征描述子 Feature Descriptor
- 是每个特征点独特的身份认证
- 同一空间点在不同视角的特征点具有高度相似的描述子
- 不同特征点的描述子差异性尽量大
- 通常描述子是一个具有固定长度的向量
描述子可以分为以下几种类型:基于不变性的描述子、基于直方图的描述子、二进制描述子
PCL主要实现了:
- NARF特征点描述子
- PFH(FPFH)点特征直方图描述子
- RoPs 特征
- VFH视点特征直方图描述子
- GASD全局对齐的空间分布描述子
- 基于惯性矩和偏心率的描述子
PFH点特征直方图描述子
表面法线和曲率估计是某个点周围的几何特征的基本表示方法。虽然计算起来比较容易,但是能够提供的信息并不多。因为他们只是用很少的几个参数值近似地表示一个点的k邻域几何特征。大部分场景下都会有很多相同或相似的特征值,故而只采用点特征就会少了很多全局的特征信息。
我们可以通过点特征直方图(Point Feature Histograms, PFH)来采集详细的特征信息。
基础理论
-
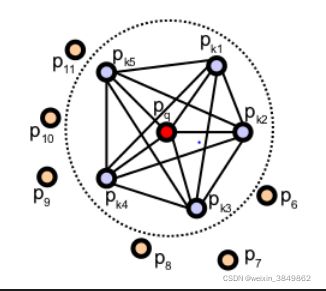
我们首先确定一个k的数值(或者半径),对范围内的目标点p以及目标点的k临近点,做两两组合。我们需要通过一种手段来描述这些点对之间的法线 n ⃗ \vec n n和位置的相对信息。
-
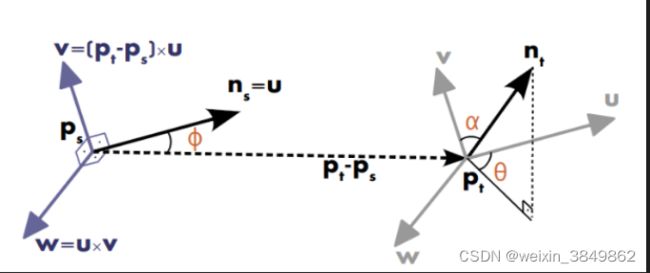
首先设定两个k临近范围内的点, p s p_s ps和 p t p_t pt,以及它们对应的法线 n ⃗ s \vec n_s ns和 n ⃗ t \vec n_t nt. 我们先看下面的图以 p s p_s ps作为初始坐标点
这里d表示 P t , P s P_t,P_s Pt,Ps之间的欧式距离,即 d = ∣ ∣ P t − P s ∣ ∣ 2 d=||P_t-P_s||^2 d=∣∣Pt−Ps∣∣2,通过计算每一个点对的 < α , ϕ , θ , d > <\alpha,\phi,\theta,d> <α,ϕ,θ,d>,就可以把两个点之间法向量的12(2x旋转自由度x平移自由度)个参数变成4个。
以下代码为每个点估算PFH四元组,可以使用以下代码:
#include
/** \brief 计算点对的PFH特征的4个特征元素值,包含3个角度值和一个两点间的距离值
* \param[in] p1 the first XYZ point 第一个点的xyz坐标
* \param[in] n1 the first surface normal 第一个点所在区域的表面法向量
* \param[in] p2 the second XYZ point 第二个点的xyz坐标
* \param[in] n2 the second surface normal 第二个点所在区域的表面法向量
* \param[out] f1 第一个角度特征值 Θ (angle between the projection of nq_idx and u)
* \param[out] f2 第二个角度特征值 α (angle between nq_idx and v)
* \param[out] f3 第三个角度特征值 Φ (angle between np_idx and |p_idx - q_idx|)
* \param[out] f4 两点间的欧式距离 d (p_idx - q_idx)
*/
computePairFeatures (const Eigen::Vector4f &p1, const Eigen::Vector4f &n1,
const Eigen::Vector4f &p2, const Eigen::Vector4f &n2,
float &f1, float &f2, float &f3, float &f4);
下面是PFH直方图的统计方式
- 将<α,ϕ,θ,d>中的每个特征值范围划分为b个子区间(默认为5,这个数值可以自行计算并设置),则4个特征共有 b 4 b^4 b4个子区间。我们设b=5,那么子空间的数量就是625个子空间,但是往往d不计入其中,因此仅125个子空间。
- 现在我们的直方图就是625维度(125维度,如果是三个特征向量),看看对应的特征值(如[1,1,1,1])落入那个子空间中,最后统计k临近范围内所有点对,落入的不同子空间的数量,就可以变成直方图了。
- 由于<α,ϕ,θ>三个特征都是法线之间的角度信息,则它们的值很可能会归为同一个空间(范围内)。
注意:在一些情况下,第四个特征d通常跟设备捕获2.5D深度数据是相关的,临近点的距离d是从视点开始递增的,在不同视角下,这些值的变化意义不大,所以在扫描局部点密度影响特征时,省略距离d效果会更好。
默认PFH的实现,对每个特征都使用5个子区间进行分类,这里不包括距离d。这样就组成了一个125个浮点数元素的特征向量(53),保存在数据类型pcl::PFHSignature125中。
/** \brief Estimate the PFH (Point Feature Histograms) individual signatures of the three angular (f1, f2, f3)
* features for a given point based on its spatial neighborhood of 3D points with normals
* \param[in] cloud the dataset containing the XYZ Cartesian coordinates of the two points
* \param[in] normals the dataset containing the surface normals at each point in \a cloud
* \param[in] indices the k-neighborhood point indices in the dataset
* \param[in] nr_split the number of subdivisions for each angular feature interval
* \param[out] pfh_histogram the resultant (combinatorial) PFH histogram representing the feature at the query point
*/
void
computePointPFHSignature (const pcl::PointCloud &cloud,
const pcl::PointCloud &normals,
const std::vector &indices, int nr_split,
Eigen::VectorXf &pfh_histogram);
参数说明:
- cloud:包含xyz坐标点信息的数据集
- normals:数据集中点的法向量信息
- indices:指定查询点,数据集中k邻域点的索引
- nr_split:每个角特征的区间数,默认为5
- pfh_histogram(输出):结果PFH直方图,表示查询点处的特征
#include ::Ptr tree (new pcl::KdTreeFLANN ()); -- older call for PCL 1.5-
pfh.setSearchMethod(tree);
// Output datasets
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125>::Ptr pfhs(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PFHSignature125>());
// Use all neighbors in a sphere of radius 5cm
// 使用一个半径为5厘米的球体,作为搜索邻域
// IMPORTANT: the radius used here has to be larger than the radius used to estimate the surface normals!!!
// 重点: 半径必须要比用于估算法向量的邻域半径要大
pfh.setRadiusSearch(0.08);
// Compute the features
pfh.compute(*pfhs);
unsigned long size = pfhs->points.size();
for (int j = 0; j < size; ++j) {
pcl::PFHSignature125 &signature125 = pfhs->points[j];
float* h = signature125.histogram;
printf("%d: %f,%f,%f \n", j, h[1], h[2], h[3]);
}
// visualize normals
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("PCL Viewer");
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.5);
viewer.addPointCloudNormals<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal>(cloud, normals, 1, 0.01, "normals");
while (!viewer.wasStopped()) {
viewer.spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}
FPFH快速点特征直方图描述子
如果点云P中有n个点,则其点特征直方图PFH的理论计算复杂度 O ( n k 2 ) O(nk^2) O(nk2),其中k是点云P中每个点p计算特征向量时,要考虑的邻域数量。对于实时应用或近实时应用,密集点云的点特征直方图PFH的计算,是一个主要的性能瓶颈,故而我们可以将之进行简化,称为快速点特征直方图FPFH(Fast Point Feature Histograms)。这个FPFH将计算复杂度降到了O(nk),但是仍然保留了PFH大部分的识别特性。
FPFH计算过程
- 为查询点求得它和其k邻域内每个点之间的三个特征元素值(不算d),然后统计成一个SimplePFH;
- 分别对k邻域中的每个点确定k邻域,按第一步分别形成自己的SPFH;
- 对邻域中的各个SPFH进行加权统计,得到最终的FPFH公式如下:

FPFH快点特征直方图的影响区域图。 每个查询点(红色)仅连接到其直接的k邻居(由灰色圆圈包围)。 每个直接邻居都连接到其自己的邻居,并将所得直方图与查询点的直方图一起加权以形成FPFH。 较粗的连接两次会被重复计数2次(比较重要的点对)。(这里很难理解,为什么计算复杂度会被降到K,如果重复的点对,会被重复计数,但不需要重新计算到确实有可能) (现在理解了,重复的点对会被重复计数,但不需要被重新计算)
FPFH与PFH的主要区别
- FPFH没有对全互连点的所有邻近点的计算参数进行统计,因此可能漏掉了一些重要的点对,而这些漏掉的对点可能对捕获查询点周围的几何特征有贡献;
- PFH特征模型是对查询点周围的一个精确的邻域半径内,而FPFH还包括半径r范围以外的额外点对(但不超过2r的范围);
- 因为采用权重计算的方式,所以FPFH结合SPFH值,重新捕获邻近重要点对的几何信息;
- 由于FPFH大大地降低了PFH的整体复杂性,因此FPFH经常使用在实时应用中;
- 通过分解三元组,简化了合成的直方图。也就是简单生成d分离特征直方图,对每个特征维度来单独绘制,并把它们连接在一起。(这里我来解释一波吧,比如PFH三个特征对应于125个子空间,也就是5x5x5,这是空间耦合的结果,如[1,1,1]落在1号空间里面,统计结果+1.但在FPFH里面应该5+5+5=15,这种情况下[1,1,1]再三个特征段里面各加一个1,也就是统计结果+3.
默认pcl实现的的FPFH使用11个统计区间(对每个特征值都将其参数区间分割为11个),分别计算特征直方图,然后合并得到了一个33个元素的特征向量,保存在数据类型pcl::FPFHSignature33中。
代码实现
#include 利用OpenMP提高FPFH的计算速度
对于计算速度要求苛刻的用户,PCL提供了一个FPFH估计的另一实现,它使用多核/多线程规范,利用OpenMP开发模式来提高计算速度。这个类的名称是pcl::FPFHEstimationOMP,并且它的应用程序接口(API)100%兼容单线程pcl::FPFHEstimation,这使它适合作为一个替换元件。在8核系统中,OpenMP的实现可以在6-8倍更快的计算时间内完全同样单核系统上的计算。
VFH视点特征直方图描述子
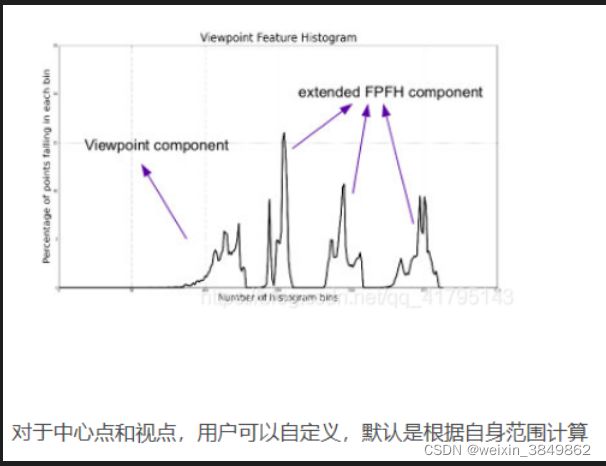
源于FPFH描述子,为了使构造的特征保持缩放不变性的同时,还要区分不同的位姿,因而计算时,需要加入视点信息。VFH时点特征直方图包含两个部分:
- 视点方向的相关分量
- 包含扩展FPFH的描述表面形状的分量
这个理解相对简单一点 - 视点与其他点的关系
- 中心点与其他点的关系
视点与其他点的关系:视点与中心点形成的向量与其他点法向量形成的夹角;即图中alpha ,相对于FPFH就是多了这个角度,其他基本都差不多,当然还多了一个中心点与其他各点的距离
- 对于官方文档中的示意图个人认为是有错误的,表述是视点与中心点的向量,示意图却是视点与其他点的向量。源码中计算使用的是中心点。
- 且官方文档中对于中心点与其他点特征计算表述易造成误解,文档表述为扩展的FPFH,但其实本质就是SPFH,易造成还需要加权计算的误解。
- 以下对官方代码进行注释,并扩展
实现代码 VFH_estimation.cpp
int main()
{
// load point cloud
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
// pcl::io::loadPCDFile("./data/target.pcd", *cloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("./data/bunny.pcd", *cloud);
// estimate normals ------------------------------------------------------------- 计算法向量
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
// Object for normal estimation.
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> normalEstimation;
//normalEstimation.setIndices()
normalEstimation.setInputCloud(cloud);
// For every point, use all neighbors in a radius of 3cm.
normalEstimation.setRadiusSearch(0.03);
// A kd-tree is a data structure that makes searches efficient. More about it later.
// The normal estimation object will use it to find nearest neighbors.
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr kdtree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
normalEstimation.setSearchMethod(kdtree);
// Calculate the normals.
normalEstimation.compute(*normals);
// Create the VFH estimation class, and pass the input dataset+normals to it
pcl::VFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::VFHSignature308> vfh;
vfh.setInputCloud (cloud);
vfh.setInputNormals (normals);
// alternatively, if cloud is of type PointNormal, do vfh.setInputNormals (cloud);
// Create an empty kdtree representation, and pass it to the FPFH estimation object.
// Its content will be filled inside the object, based on the given input dataset (as no other search surface is given).
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ> ());
vfh.setSearchMethod (tree);
// Output datasets
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::VFHSignature308>::Ptr vfhs (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::VFHSignature308> ());
// Compute the features
vfh.compute (*vfhs);
// vfhs->size () should be of size 1*
unsigned long size = vfhs->points.size();
for (int j = 0; j < size; ++j) {
pcl::VFHSignature308 &Signature308 = vfhs->points[j];
float* h = Signature308.histogram;
printf("%d: %f,%f,%f \n", j, h[1], h[2], h[3]);
}
// visualize normals
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("PCL Viewer");
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.5);
viewer.addPointCloudNormals<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal>(cloud, normals, 1, 0.01, "normals");
while (!viewer.wasStopped()) {
viewer.spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}
其中pcl::VFHSignature308中308指,默认视点特征分割为128bin,其他每个特征分割bin数为45,现在视点特征有一个角度,中心点特征有三个角度和一个距离,则一共128+45*4=308