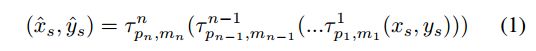关于深度学习模型泛化问题的一些思考
1、假设只有一个source domain的训练数据,那么训练时就会存在一个精度与泛化能力之间平衡的问题
精度是要求在source domain上效果好,而泛化能力是要求模型在未知的target domain上结果好,两者似乎有一定权衡。比如,在做增广的时候,如果为了提高泛化,增加了增广的旋转角度和噪声水平,那么可能会影响模型在source domain上的精度?
2、一般解决模型泛化的方案有2个,transfer learning 以及domain adaptation (CycleGAN - based).
transfer learning 一般是微调一个预训练的网络(部分参数),让其适应target domain。这种方案只需要少量目标域的标注数据。但缺点也是,需要标注数据,而且预训练模型最好是基于大量的数据训练好的,另外这个方案,每遇到一个新的domain, 需要fine tuning一次模型,对于大规模应用部署来说,不太现实。
而domain adaptation的目标是把模型泛化到一个已知目标域(has data but no annotation),一般是在模型训练当中直接集成CycleGAN或其变种,手段要么是提取一些与域无关的特征(source domain和target domain共有的特征),要么是在source domain与target domain之间进行风格迁移。这个方案只能解决known target domain的问题,就是已经有数据。
总结起来,这2个方案都是针对known domain的问题,但是对于一个准确大规模部署的产品来说,可能遇到的数据会是各种差异性非常大的(i.e., different hospitals, scanner vendors, imaging protocols, patient populations, etc.)。那么什么样的模型才能满足这种需求呢?
3、unseen domain的泛化问题
1)采集数据,保证数量和勾画质量,另外还要保证多样性,尽量覆盖不同医院、不同设备、不同影像规范、不同患者群体;有文献表明,the error rate of a deep model for retinal image analysis was 5.5% on images from the same vendor used in training dataset, but decreased to 46.6% on images from another vendor。ref 《Clinically applicable deep learning for diagnosis and referral in retinal disease》 Nature Medicine, vol. 24, no. 9, p. 1342, 2018
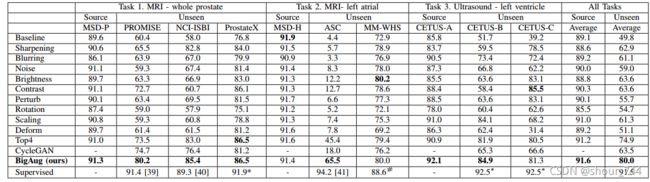
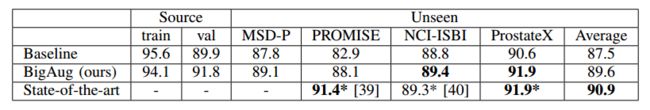
2)数据增广,进一步增加数据多样性,参考《Generalizing Deep Learning for Medical Image Segmentation to Unseen Domains via Deep Stacked Transformation》;
3)模型本身;有没有什么模型结构或者是模块,本身就是比其他结构具有更强的泛化能力呢?在数据量一定的情况下,是否模型越深,参数量越多,模型泛化越强呢?比如三层unet 和四层unet,如果在source domain上结果相当,是否在unseen domain上会有差距呢?
参考文献《Generalizing Deep Learning for Medical Image Segmentation to Unseen Domains via Deep Stacked Transformation》的研究结果:
bigAug, 即对图像进行一系列级联的变化:
主要涉及图像的三个方面(image quality, appearance, and spatial configuration)
image quality的增广 ,包括锐化、模糊、噪声
appearance的增广,包括亮度,对比度,强度干扰
Spatial configuration的增广,包括旋转,缩放,变形