深度学习实战15(进阶版)-让机器进行阅读理解+你可以变成出题者提问
大家好,我是微学AI,今天给大家带来一个机器阅读理解的项目,利用ERNIE的预训练模型进行微调训练,添加自己的数据集进行训练,训练好就可以利用功能进行阅读式信息抽取啦,也可以问机器一些简单的问题进行抽取。今天采用的paddle深度学习框架,它和pytorch很像,可以快速迁移。
1、数据集
基于语义的阅读理解是检索问答系统中的重要部分,最常见的数据集是单篇章、抽取式阅读理解数据集。关于阅读理解的数据集采用Dureader数据集,它是关注阅读理解模型鲁棒性的中文数据集,在实际业务中,根据需求添加部分业务需求数据集。
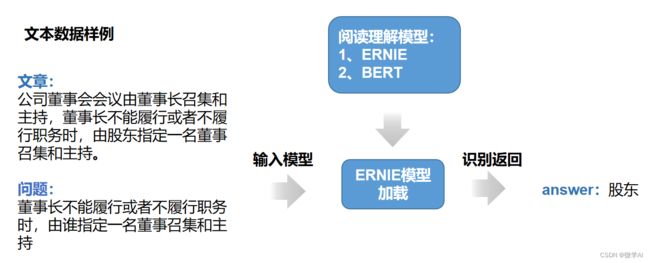
数据样例:
问题 : 陈明董事长被调整为什么职务
篇章 : 大会决定将**人工智能副会长职务调整为陈明董事长兼任,经公司党委研究后向党委报批。
参考答案 : [‘**人工智能副会长’]
数据格式样例:
{
"context": "大会决定将**人工智能副会长职务调整为陈明董事长兼任,经公司党委研究后向党委报批。",
"qas": [
{
"question": "陈明董事长被调整为什么职务",
"id": "0a25cb4bc1ab6f474c699884e04601e4",
"answers": [
{
"text": "**人工智能副会长职务",
"answer_start": 6
}
]
}
]
}我们在实际应用过程中,需要评估模型的鲁棒性,让模型可以预测更多不可控的数据,随着当前数据集的扩大、模型的优化、算力的提升,模型可在大量测试集上取得较好的性能,在实际应用中,这些模型所表现出的鲁棒性还未达到预期效果。于是我们要更进一步优化与微调模型,随着模型研发越来越深,模型优化会越来越好的。
DuReader数据集采用SQuAD数据格式,InputFeature使用滑动窗口的方法生成,即一个example可能对应多个InputFeature。对于过长的文章,采用滑动窗口将文章分成多段,分别与问题组合。再用对应的tokenizer转化为模型可接受的feature。滑动窗口生成InputFeature的过程如下图:
本文采用paddle.io.BatchSampler和paddlenlp.data中提供的方法把数据组成batch。Batchify过程是把数据集中的数据排到多个列中,在划分成多个大小为 batch_size 的集合。然后使用paddle.io.DataLoader接口多线程异步加载数据。
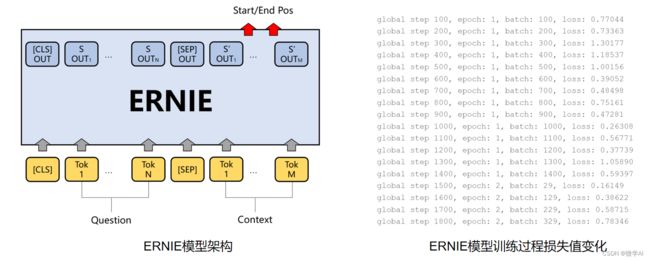
DuReader阅读理解任务的本质是答案抽取任务。根据输入的问题和文章,从预训练模型的sequence_output中预测答案在文章中的起始位置和结束位置。模型训练过程采用梯度下载更新权重参数。
代码训练部分:
import paddle
from paddlenlp.data import Stack, Dict, Pad
import paddlenlp
from paddlenlp.datasets import load_dataset
from utils import prepare_train_features, prepare_validation_features
from functools import partial
train_ds, dev_ds, test_ds = load_dataset('dureader_robust', splits=('train', 'dev', 'test'))
for idx in range(2):
print(train_ds[idx]['question'])
print(train_ds[idx]['context'])
print(train_ds[idx]['answers'])
print(train_ds[idx]['answer_starts'])
print()
# 设置模型名称
MODEL_NAME = 'ernie-1.0'
tokenizer = paddlenlp.transformers.ErnieTokenizer.from_pretrained(MODEL_NAME)
max_seq_length = 512
doc_stride = 128
train_trans_func = partial(prepare_train_features,
max_seq_length=max_seq_length,
doc_stride=doc_stride,
tokenizer=tokenizer)
train_ds.map(train_trans_func, batched=True, num_workers=4)
dev_trans_func = partial(prepare_validation_features,
max_seq_length=max_seq_length,
doc_stride=doc_stride,
tokenizer=tokenizer)
dev_ds.map(dev_trans_func, batched=True, num_workers=4)
test_ds.map(dev_trans_func, batched=True, num_workers=4)
for idx in range(2):
print(train_ds[idx]['input_ids'])
print(train_ds[idx]['token_type_ids'])
print(train_ds[idx]['overflow_to_sample'])
print(train_ds[idx]['offset_mapping'])
print(train_ds[idx]['start_positions'])
print(train_ds[idx]['end_positions'])
batch_size = 12
# 定义BatchSampler
train_batch_sampler = paddle.io.DistributedBatchSampler(
train_ds, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
dev_batch_sampler = paddle.io.BatchSampler(
dev_ds, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
test_batch_sampler = paddle.io.BatchSampler(
test_ds, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
# 定义batchify_fn
train_batchify_fn = lambda samples, fn=Dict({
"input_ids": Pad(axis=0, pad_val=tokenizer.pad_token_id),
"token_type_ids": Pad(axis=0, pad_val=tokenizer.pad_token_type_id),
"start_positions": Stack(dtype="int64"),
"end_positions": Stack(dtype="int64")
}): fn(samples)
dev_batchify_fn = lambda samples, fn=Dict({
"input_ids": Pad(axis=0, pad_val=tokenizer.pad_token_id),
"token_type_ids": Pad(axis=0, pad_val=tokenizer.pad_token_type_id)
}): fn(samples)
# 构造DataLoader
train_data_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(
dataset=train_ds,
batch_sampler=train_batch_sampler,
collate_fn=train_batchify_fn,
return_list=True)
dev_data_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(
dataset=dev_ds,
batch_sampler=dev_batch_sampler,
collate_fn=dev_batchify_fn,
return_list=True)
test_data_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(
dataset=test_ds,
batch_sampler=test_batch_sampler,
collate_fn=dev_batchify_fn,
return_list=True)
for step, batch in enumerate(train_data_loader, start=1):
input_ids, segment_ids, start_positions, end_positions = batch
print(input_ids)
break
from paddlenlp.transformers import ErnieForQuestionAnswering
# 模型加载
model = ErnieForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained(MODEL_NAME)
#损失函数设定
class CrossEntropyLossForRobust(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(CrossEntropyLossForRobust, self).__init__()
def forward(self, y, label):
start_logits, end_logits = y # both shape are [batch_size, seq_len]
start_position, end_position = label
start_position = paddle.unsqueeze(start_position, axis=-1)
end_position = paddle.unsqueeze(end_position, axis=-1)
start_loss = paddle.nn.functional.softmax_with_cross_entropy(
logits=start_logits, label=start_position, soft_label=False)
start_loss = paddle.mean(start_loss)
end_loss = paddle.nn.functional.softmax_with_cross_entropy(
logits=end_logits, label=end_position, soft_label=False)
end_loss = paddle.mean(end_loss)
loss = (start_loss + end_loss) / 2
return loss
# 训练过程中的最大学习率
learning_rate = 3e-5
# 训练轮次
epochs = 2
# 学习率预热比例
warmup_proportion = 0.1
# 权重衰减系数,类似模型正则项策略,避免模型过拟合
weight_decay = 0.01
num_training_steps = len(train_data_loader) * epochs
# 学习率衰减策略
lr_scheduler = paddlenlp.transformers.LinearDecayWithWarmup(learning_rate, num_training_steps, warmup_proportion)
decay_params = [
p.name for n, p in model.named_parameters()
if not any(nd in n for nd in ["bias", "norm"])
]
optimizer = paddle.optimizer.AdamW(
learning_rate=lr_scheduler,
parameters=model.parameters(),
weight_decay=weight_decay,
apply_decay_param_fun=lambda x: x in decay_params)
from utils import evaluate
criterion = CrossEntropyLossForRobust()
global_step = 0
for epoch in range(1, epochs + 1):
for step, batch in enumerate(train_data_loader, start=1):
global_step += 1
input_ids, segment_ids, start_positions, end_positions = batch
logits = model(input_ids=input_ids, token_type_ids=segment_ids)
loss = criterion(logits, (start_positions, end_positions))
if global_step % 100 == 0 :
print("global step %d, epoch: %d, batch: %d, loss: %.5f" % (global_step, epoch, step, loss))
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
lr_scheduler.step()
optimizer.clear_grad()
evaluate(model=model, data_loader=dev_data_loader)
更多细节,可私信咨询。