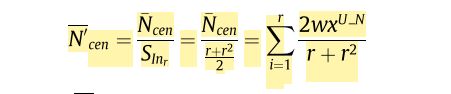【Information Sciences】PMT-Net: Progressive Multi-Task Network for one-shot Person Re-Identification
文章目录
- 背景知识
- 内容概要
-
- 摘要:
- 取得的成果
- 相关工作
- 数据集
- baseline
- backbone
- BIbtex
- 方法提要
-
- 方法特点
- 方法框架
- 实验结果
- 方法详解
- 参考文献
背景知识
内容概要
针对的问题 or 出发点: 人工标注成本大。 还是为了解决小样本问题。
提出了渐进的多任务网络 (PMT-net): 用one-shot初始化模型,然后迭代优化(秉承EUG一脉)
- 首先,行人的属性识别作为辅助任务。 (参照了APR那篇文章,也是EUG同作者的文章)
- 基于学到的特征,根据特征空间中的距离估计身份标签。
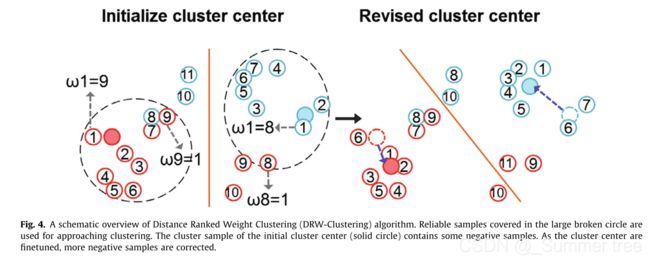
- 此外,为了提高对未标记样本的标签估计的准确性,设计了一种半监督聚类方法——距离加权聚类(Distance Ranked Weight clustering, DRW-Clustering)。 聚类方法根据距离排序的索引顺序对部分未标记样本进行加权,从而能够快速有效地找到真实的聚类中心。
实验结果表明,所提出的方法在one-shot person reid 中达到了与现有方法相当或更好的性能。
摘要:
PMT-Net initial- izes a model using only one labeled sample for each identity, and it iteratively optimizes the model by sampling the most reliable pseudo labels dynamically from unlabeled sam- ples. Firstly, pedestrian attributes recognition is incorporated as an auxiliary task to learn discriminative features. Then, based on the discriminative features, the identity label for unlabeled samples is estimated by the distance between the labeled samples and unlabeled samples in feature space. In addition, to enhance the accuracy of label estimation for the unlabeled samples, a semi-supervised clustering method, named Distance Ranked Weight Clustering (DRW-Clustering) is designed. The clustering method weights partial unlabeled samples by the indexed ordinal of distance sorting, so that it can find the real cluster center quickly and effectively.
取得的成果
the proposed method achieves performance competitive or better than that of the state-of-the-art for one-shot person Re-ID.
相关工作
- Person RE-ID method
- Multi-task learning
- Progressive algorithms
- Semi-supervised clustering
数据集
- Market1501
- DukeMTMC-reID
baseline
Y. Wu, Y. Lin, X. Dong, Y. Yan, W. Bian, Y. Yang, Progressive learning for person re-identification with one example, IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 28 (6) (2019) 2872–2881
backbone
ResNet-50
BIbtex
@article{ZHANG2021133,
title = {PMT-Net: Progressive Multi-Task Network for one-shot Person Re-Identification},
journal = {Information Sciences},
volume = {568},
pages = {133-146},
year = {2021},
issn = {0020-0255},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2021.03.048},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020025521002930},
author = {Yulin Zhang and Bo Ma and Yuqing Feng and Meng Li},
keywords = {One-shot person re-identification, Semi-supervised clustering, Multi-task learning, Progressive learning}, }
方法提要
方法特点
- 结合了属性识别,做多任务训练。
- 提出了Distance Ranked Weight Clustering (DRW-Clustering),提高了标签估计的正确率。
方法框架
实验结果
方法详解
-
损失由属性损失和身份损失组成,加入alpha和belta 平衡贡献。
![]()
- DRW-Clustering:将入选的伪标签样本根据距离排序设置权重,用于重新计算类别中心,最终的标签估计根据新的类中心来进行计算。还增加了防止类中心移动过快的机制。
- 采用了和EUG、plpr一样的渐进采样策略。
小样本学习与智能前沿(下方↓)后台回复“PMT-Net”,即可获得论文电子资源 及更多相关论文导读。
![]()
参考文献
[1] C. Gao, Y. Chen, J.-G. Yu, N. Sang, Pose-guided spatiotemporal alignment for video-based person re-identification, Information Sciences 527 (2020)
176–190.
[2] L. An, X. Chen, S. Yang, B. Bhanu, Sparse representation matching for person re-identification, Information Sciences 355 (2016) 74–89.
[3] S. Basu, A. Banerjee, R.J. Mooney, Semi-supervised clustering by seeding, 2002, pp. 27–34…
[4] G. Bender, P.-J. Kindermans, B. Zoph, V. Vasudevan, Q. Le, Understanding and simplifying one-shot architecture search, in: International Conference on
Machine Learning, 2018, pp. 549–558.
[5] Y. Bengio, J. Louradour, R. Collobert, J. Weston, Curriculum learning, 2009, pp. 41–48.
[6] F. Chen, N. Wang, J. Tang, D. Liang, A negative transfer approach to person re-identification via domain augmentation, Information Sciences 549, 1–12…
[7] D. Cheng, Y. Gong, X. Chang, W. Shi, A. Hauptmann, N. Zheng, Deep feature learning via structured graph laplacian embedding for person reidentification, Pattern Recognition 82 (2018) 94–104.
[8] H. Fan, L. Zheng, C. Yan, Y. Yang, Unsupervised person re-identification: clustering and fine-tuning, ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing,
Communications, and Applications (TOMM) 14 (4) (2018) 83.
[9] D. Figueira, L. Bazzani, H.Q. Minh, M. Cristani, A. Bernardino, V. Murino, Semi-supervised multi-feature learning for person re-identification (2013)
111–116…
[10] K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, J. Sun, Deep residual learning for image recognition, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition, 2016, pp. 770–778.
[11] S. Ioffe, C. Szegedy, Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift, 2015, arXiv preprint
arXiv:1502.03167…
[12] A.K. Jain, Data clustering: 50 years beyond k-means 31 (8) (2010) 651–666.
[13] L. Jiang, D. Meng, S. Yu, Z. Lan, S. Shan, A.G. Hauptmann, Self-paced learning with diversity (2014) 2078–2086…
[14] M.M. Kalayeh, E. Basaran, M. Gökmen, M.E. Kamasak, M. Shah, Human semantic parsing for person re-identification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018, pp. 1062–1071.
[15] A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, G.E. Hinton, Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks, in: Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems, 2012, pp. 1097–1105…
[16] M.P. Kumar, B. Packer, D. Koller, Self-paced learning for latent variable models, 2010, pp. 1189–1197.
[17] Y.J. Lee, K. Grauman, Learning the easy things first: Self-paced visual category discovery, 2011, pp. 1721–1728.
[18] H. Li, J. Xu, J. Zhu, D. Tao, Z. Yu, Top distance regularized projection and dictionary learning for person re-identification, Information Sciences (2019).
[19] H. Li, J. Xu, J. Zhu, D. Tao, Z. Yu, Top distance regularized projection and dictionary learning for person re-identification, Information Sciences 502
(2019) 472–491.
[20] J. Li, A.J. Ma, P.C. Yuen, Semi-supervised region metric learning for person re-identification, International Journal of Computer Vision 126 (8) (2018)
855–874.
[21] Y. Lin, L. Zheng, Z. Zheng, Y. Wu, Z. Hu, C. Yan, Y. Yang, Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity learning, Pattern Recognition
(2019).
[22] X. Liu, W. Liu, T. Mei, H. Ma, Provid: Progressive and multimodal vehicle reidentification for large-scale urban surveillance, IEEE Transactions on
Multimedia 20 (3) (2017) 645–658.
[23] Z. Liu, D. Wang, H. Lu, Stepwise metric promotion for unsupervised video person re-identification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference
on Computer Vision, 2017, pp. 2429–2438.
[24] Z. Lu, T.K. Leen, Semi-supervised learning with penalized probabilistic clustering, in: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2005, pp.
849–856…
[25] X. Ma, X. Zhu, S. Gong, X. Xie, J. Hu, K.-M. Lam, Y. Zhong, Person re-identification by unsupervised video matching, Pattern Recognition 65 (2017) 197–
210.
[26] E. Ristani, F. Solera, R. Zou, R. Cucchiara, C. Tomasi, Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking, in: European
Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2016, pp. 17–35.
[27] E. Ristani, C. Tomasi, Features for multi-target multi-camera tracking and re-identification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition, 2018, pp. 6036–6046.
[28] J. Si, H. Zhang, C.-G. Li, J. Kuen, X. Kong, A.C. Kot, G. Wang, Dual attention matching network for context-aware feature sequence based person reidentification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018, pp. 5363–5372.
[29] Y. Suh, J. Wang, S. Tang, T. Mei, K. Mu Lee, Part-aligned bilinear representations for person re-identification, in: Proceedings of the European Conference
on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2018, pp. 402–419.
[30] J.S. Supancic, D. Ramanan, Self-paced learning for long-term tracking (2013) 2379–2386…
[31] J. Wang, X. Zhu, S. Gong, W. Li, Transferable joint attribute-identity deep learning for unsupervised person re-identification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018, pp. 2275–2284.
[32] L. Wei, S. Zhang, H. Yao, W. Gao, Q. Tian, Glad: Global-local-alignment descriptor for pedestrian retrieval, in: Proceedings of the 25th ACM International
Conference on Multimedia, ACM, 2017, pp. 420–428.
[33] Y. Wen, K. Zhang, Z. Li, Y. Qiao, A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition, in: European Conference on Computer Vision,
Springer, 2016, pp. 499–515.
[34] A. Wu, W.-S. Zheng, X. Guo, J.-H. Lai, Distilled person re-identification: towards a more scalable system, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019, pp. 1187–1196.
[35] Y. Wu, Y. Lin, X. Dong, Y. Yan, W. Bian, Y. Yang, Progressive learning for person re-identification with one example, IEEE Transactions on Image
Processing 28 (6) (2019) 2872–2881.
[36] Y. Wu, Y. Lin, X. Dong, Y. Yan, W. Ouyang, Y. Yang, Exploit the unknown gradually: one-shot video-based person re-identification by stepwise learning,
in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018, pp. 5177–5186.
[37] J. Xu, R. Zhao, F. Zhu, H. Wang, W. Ouyang, Attention-aware compositional network for person re-identification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference
on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018, pp. 2119–2128.
[38] X. Yang, M. Wang, R. Hong, Q. Tian, Y. Rui, Enhancing person re-identification in a self-trained subspace, ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing,
Communications, and Applications (TOMM) 13 (3) (2017) 27.
[39] Y. Yang, L. Wen, S. Lyu, S.Z. Li, Unsupervised learning of multi-level descriptors for person re-identification, in: Thirty-First AAAI Conference on
Artificial Intelligence, 2017.
[40] M. Ye, A.J. Ma, L. Zheng, J. Li, P.C. Yuen, Dynamic label graph matching for unsupervised video re-identification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE International
Conference on Computer Vision, 2017, pp. 5142–5150.
[41] H.-X. Yu, W.-S. Zheng, A. Wu, X. Guo, S. Gong, J.-H. Lai, Unsupervised person re-identification by soft multilabel learning, in: Proceedings of the IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019, pp. 2148–2157.
[42] D. Zhang, D. Meng, J. Han, Co-saliency detection via a self-paced multiple-instance learning framework, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence 39 (5) (2017) 865–878.
[43] Z. Zhang, C. Lan, W. Zeng, Z. Chen, Densely semantically aligned person re-identification (2019) 667–676…
[44] H. Zhao, M. Tian, S. Sun, J. Shao, J. Yan, S. Yi, X. Wang, X. Tang, Spindle net: Person re-identification with human body region guided feature
decomposition and fusion, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017, pp. 1077–1085.
[45] L. Zheng, L. Shen, L. Tian, S. Wang, J. Wang, Q. Tian, Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark, in: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference
on Computer Vision, 2015, pp. 1116–1124.
[46] Z. Zheng, X. Yang, Z. Yu, L. Zheng, Y. Yang, J. Kautz, Joint discriminative and generative learning for person re-identification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019, pp. 2138–2147.
[47] Z. Zheng, L. Zheng, Y. Yang, Pedestrian alignment network for large-scale person re-identification, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video
Technology (2018).
[48] Z. Zhong, L. Zheng, D. Cao, S. Li, Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017, pp. 1318–1327.
[49] S. Zhou, J. Wang, D. Meng, X. Xin, Y. Li, Y. Gong, N. Zheng, Deep self-paced learning for person re-identification, Pattern Recognition 76 (2018) 739–751.