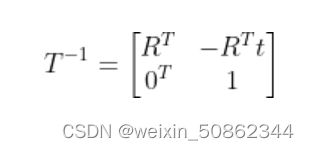orb-slam2 从单目开始的简单学习(3):Tracking
1. tracking逻辑和运行顺序
1.1 初始化
第一次出现Tracking是在System SLAM(argv[1],argv[2],ORB_SLAM2::System::MONOCULAR,true);初始化slam系统时
System.cc中的使用如下
mpTracker = new Tracking(this, mpVocabulary, mpFrameDrawer, mpMapDrawer,
mpMap, mpKeyFrameDatabase, strSettingsFile, mSensor);
1.1.1 tracking构造函数
Tracking::Tracking(System *pSys, ORBVocabulary* pVoc, FrameDrawer *pFrameDrawer, MapDrawer *pMapDrawer, Map *pMap, KeyFrameDatabase* pKFDB, const string &strSettingPath, const int sensor):
mState(NO_IMAGES_YET), mSensor(sensor), mbOnlyTracking(false), mbVO(false), mpORBVocabulary(pVoc),
mpKeyFrameDB(pKFDB), mpInitializer(static_cast<Initializer*>(NULL)), mpSystem(pSys), mpViewer(NULL),
mpFrameDrawer(pFrameDrawer), mpMapDrawer(pMapDrawer), mpMap(pMap), mnLastRelocFrameId(0)
{
// Load camera parameters from settings file
cv::FileStorage fSettings(strSettingPath, cv::FileStorage::READ);//相机环境配置的yaml文件
float fx = fSettings["Camera.fx"];
float fy = fSettings["Camera.fy"];
float cx = fSettings["Camera.cx"];
float cy = fSettings["Camera.cy"];
cv::Mat K = cv::Mat::eye(3,3,CV_32F);//内参矩阵
K.at<float>(0,0) = fx;
K.at<float>(1,1) = fy;
K.at<float>(0,2) = cx;
K.at<float>(1,2) = cy;
K.copyTo(mK);
cv::Mat DistCoef(4,1,CV_32F);//畸变矩阵
DistCoef.at<float>(0) = fSettings["Camera.k1"];
DistCoef.at<float>(1) = fSettings["Camera.k2"];
DistCoef.at<float>(2) = fSettings["Camera.p1"];
DistCoef.at<float>(3) = fSettings["Camera.p2"];
const float k3 = fSettings["Camera.k3"];
if(k3!=0)
{
DistCoef.resize(5);
DistCoef.at<float>(4) = k3;
}
DistCoef.copyTo(mDistCoef);
//双目摄像头baseline*fx 此处为50
mbf = fSettings["Camera.bf"];//双目baseline=mbf/fx
float fps = fSettings["Camera.fps"];
if(fps==0)
fps=30;
// Max/Min Frames to insert keyframes and to check relocalisation
mMinFrames = 0;
mMaxFrames = fps;
cout << endl << "Camera Parameters: " << endl;
cout << "- fx: " << fx << endl;
cout << "- fy: " << fy << endl;
cout << "- cx: " << cx << endl;
cout << "- cy: " << cy << endl;
cout << "- k1: " << DistCoef.at<float>(0) << endl;
cout << "- k2: " << DistCoef.at<float>(1) << endl;
if(DistCoef.rows==5)
cout << "- k3: " << DistCoef.at<float>(4) << endl;
cout << "- p1: " << DistCoef.at<float>(2) << endl;
cout << "- p2: " << DistCoef.at<float>(3) << endl;
cout << "- fps: " << fps << endl;
int nRGB = fSettings["Camera.RGB"];
mbRGB = nRGB;//读入图片是RGB还是BGR(0: BGR, 1: RGB)
if(mbRGB)
cout << "- color order: RGB (ignored if grayscale)" << endl;
else
cout << "- color order: BGR (ignored if grayscale)" << endl;
// Load ORB parameters
//每张图片的特征点数量
int nFeatures = fSettings["ORBextractor.nFeatures"];
//比例金字塔中级别之间的比例因子
float fScaleFactor = fSettings["ORBextractor.scaleFactor"];
//比例金字塔的层级数量
int nLevels = fSettings["ORBextractor.nLevels"];
//图像在网格中分割。在每个单元提取FAST,施加最小响应。首先,我们实施iniThFAST。如果未检测到拐角,我们将施加较低的值minThFAST
int fIniThFAST = fSettings["ORBextractor.iniThFAST"];
int fMinThFAST = fSettings["ORBextractor.minThFAST"];
//左目
mpORBextractorLeft = new ORBextractor(nFeatures,fScaleFactor,nLevels,fIniThFAST,fMinThFAST);
//实际上只是计算基本属性
//右目(双目条件下)
if(sensor==System::STEREO)
mpORBextractorRight = new ORBextractor(nFeatures,fScaleFactor,nLevels,fIniThFAST,fMinThFAST);
//用于单目初始化
if(sensor==System::MONOCULAR)
mpIniORBextractor = new ORBextractor(2*nFeatures,fScaleFactor,nLevels,fIniThFAST,fMinThFAST);
cout << endl << "ORB Extractor Parameters: " << endl;
cout << "- Number of Features: " << nFeatures << endl;
cout << "- Scale Levels: " << nLevels << endl;
cout << "- Scale Factor: " << fScaleFactor << endl;
cout << "- Initial Fast Threshold: " << fIniThFAST << endl;
cout << "- Minimum Fast Threshold: " << fMinThFAST << endl;
//用于双目相机
if(sensor==System::STEREO || sensor==System::RGBD)
{
mThDepth = mbf*(float)fSettings["ThDepth"]/fx;//mbf=baseline*fx(在双目配置文件中给出,单目不会给)
cout << endl << "Depth Threshold (Close/Far Points): " << mThDepth << endl;
}
if(sensor==System::RGBD)
{
mDepthMapFactor = fSettings["DepthMapFactor"];
if(fabs(mDepthMapFactor)<1e-5)
mDepthMapFactor=1;
else
mDepthMapFactor = 1.0f/mDepthMapFactor;
}
}
1.2 真正进入到tracking线程(程序入口)
在mono_tum.cc
SLAM.TrackMonocular(im,tframe);
才算是进入正式进入tracking
cv::Mat System::TrackMonocular(const cv::Mat &im, const double ×tamp)
{
if(mSensor!=MONOCULAR)
{
cerr << "ERROR: you called TrackMonocular but input sensor was not set to Monocular." << endl;
exit(-1);
}
//检查模式改变(系统初始化时均置为False,即不会进入) Check mode change
//主要有两种模式:(1)mbActivateLocalizationMode:激活定位模式 和 (2)mbDeactivateLocalizationMode清空局部地图
{
unique_lock<mutex> lock(mMutexMode);
if(mbActivateLocalizationMode)// mbActivateLocalizationMode:激活定位模式
{
mpLocalMapper->RequestStop();
//RequestStop进行的操作:
//mbStopRequested = true;
//mbAbortBA = true;
// Wait until Local Mapping has effectively stopped
while(!mpLocalMapper->isStopped())//return mbStopped
{
usleep(1000);
}//while
mpTracker->InformOnlyTracking(true);
//mbOnlyTracking = flag;----->true
//只进行追踪的线程
// 只计算相机的位姿,没有对局部地图进行更新
mbActivateLocalizationMode = false;
//使读入系统的每一帧图像都进行定位模式,可以将将该语句注释掉from《ORB_SLAM2 定位模式》
}
if(mbDeactivateLocalizationMode)// mbDeactivateLocalizationMode是否清空局部地图.
{
mpTracker->InformOnlyTracking(false);
mpLocalMapper->Release();
//mbStopped = false;
//mbStopRequested = false;
//清理关键帧
mbDeactivateLocalizationMode = false;
}
}
//检查是否重启系统 Check reset
{
unique_lock<mutex> lock(mMutexReset);
if(mbReset)
{
mpTracker->Reset();//重置tracking线程,清空之前的东西
mbReset = false;
}
}
//图像预处理并开始追踪
cv::Mat Tcw = mpTracker->GrabImageMonocular(im,timestamp);
unique_lock<mutex> lock2(mMutexState);
mTrackingState = mpTracker->mState;
mTrackedMapPoints = mpTracker->mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints;
mTrackedKeyPointsUn = mpTracker->mCurrentFrame.mvKeysUn;
return Tcw;
}
进入track有两个模式:mbActivateLocalizationMode(激活定位模式) 和DeactivateLocalizationMode(停止定位模式),但是不一定会进入
1.2.1 mbActivateLocalizationMode模式
- mbStopRequested = true;
- mbAbortBA = true;
- mbOnlyTracking= true;
- mbActivateLocalizationMode = false;
1.2.2 DeactivateLocalizationMode模式
- mbOnlyTracking= false;
- mbStopped = false;
- mbStopRequested = false;
1.2.3 reset
if(mbReset)
{
mpTracker->Reset();
mbReset = false;
}
mpTracker->Reset()操作
mpLocalMapper 重置局部建图
mpLoopClosing 重置回环检测
mpKeyFrameDB 重置BoW Database
清理关键帧,地图点和地图
1.2.4 进入GrabImageMonocular
cv::Mat Tcw = mpTracker->GrabImageMonocular(im,timestamp);
GrabImageMonocular操作也很简单:
(1)对图像进行预处理,即转灰度图像
(2)mCurrentFrame = Frame(...)初始化当前帧
(3)进入track()(后面讲)进入跟踪
2. 进入Tracking.cc
2.1
2.2 track()
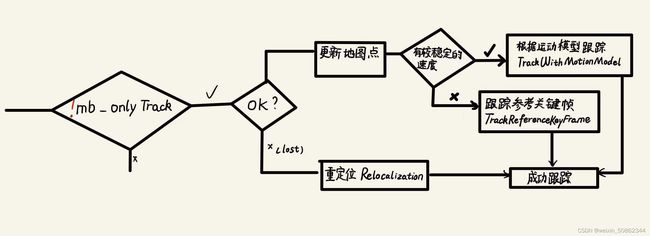
2.1.1 整体架构
State为tracking的状态:
SYSTME_NOT_READY, NO_IMAGE_YET, NOT_INITIALIZED, OK, LOST
2.1.2 非单追踪
//------------------1 !mbOnlyTracking 非单追踪---------------------------------------------------------------
if(!mbOnlyTracking)
{
// Local Mapping is activated. This is the normal behaviour, unless
// you explicitly activate the "only tracking" mode.
//------------------1.1 mState==OK 系统状态---------------------------------------------------------------
if(mState==OK)
{
// Local Mapping might have changed some MapPoints tracked in last frame
//局部建图可能已更改上一帧中跟踪的某些映地图点
CheckReplacedInLastFrame();//mLastFrame中的点两个来源:原先的mvpMapPoints[i]/被替换的--->更新
//Motion Model
//-------------1.2判断当前关键帧是否有较稳定的速度---------------------------
if(mVelocity.empty() || mCurrentFrame.mnId<mnLastRelocFrameId+2)
{
bOK = TrackReferenceKeyFrame();
}//if(mVelocity.empty() || mCurrentFrame.mnId<mnLastRelocFrameId+2)
else
{
bOK = TrackWithMotionModel();
if(!bOK)
bOK = TrackReferenceKeyFrame();
}//else
}//if
//------------------mState==OK---------------------------------------------------------------
//------------------1.2 mState==LOST:上一帧跟踪丢失----------------------------
else
{
bOK = Relocalization();
}//if(mState==OK)---else
//------------------mState==LOST--------------
}//if(!mbOnlyTracking)
2.1.3 系统状态更新
//------------------3 系统状态更新----------------------------------
mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF = mpReferenceKF;
// If we have an initial estimation of the camera pose and matching. Track the local map.
//如果我们有摄像机姿态和匹配的初始估计。系统状态更新
//-----------step1.跟踪局部地图点进行系统状态更新---------------------------------------
if(!mbOnlyTracking)
{
if(bOK)
bOK = TrackLocalMap();
//对摄像机姿态进行了估计,并在帧中跟踪了一些地图点,检索本地地图并尝试查找与本地地图中的点的匹配
}
else//mbOnlyTracking
{
// mbVO true means that there are few matches to MapPoints in the map. We cannot retrieve
// a local map and therefore we do not perform TrackLocalMap(). Once the system relocalizes
// the camera we will use the local map again.
//mbVO true意味着地图中的地图点很少匹配。我们无法检索本地映射,因此不执行TrackLocalMap()。
//一旦系统重新定位相机,我们将再次使用本地地图
if(bOK && !mbVO)
bOK = TrackLocalMap();
}
if(bOK)
mState = OK;
else
mState=LOST;
// Update drawer
mpFrameDrawer->Update(this);
//-----------step1.跟踪局部地图点进行系统状态更新(结束)---------------------------------------
//-----------step2.插入关键帧---------------------------------------
// If tracking were good, check if we insert a keyframe
if(bOK)
{
// -----------step2.1 更新运动模型Update motion model-----------
if(!mLastFrame.mTcw.empty())
{
cv::Mat LastTwc = cv::Mat::eye(4,4,CV_32F);
mLastFrame.GetRotationInverse().copyTo(LastTwc.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3));
//return mRwc.clone()返回相机坐标系下的旋转
mLastFrame.GetCameraCenter().copyTo(LastTwc.rowRange(0,3).col(3));
//return mOw.clone();返回相机光心
mVelocity = mCurrentFrame.mTcw*LastTwc;//表示上一帧到当前帧的变换
}
else
mVelocity = cv::Mat();
mpMapDrawer->SetCurrentCameraPose(mCurrentFrame.mTcw);
// -----------step2.2清除没有共视关系的关键帧----------Clean VO matches
for(int i=0; i<mCurrentFrame.N; i++)
{
MapPoint* pMP = mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i];
if(pMP)//物理存在
if(pMP->Observations()<1)//不存在共视清理
{
mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i] = false;
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=static_cast<MapPoint*>(NULL);
}
}
// -----------step2.3删除临时地图点---------- Delete temporal MapPoints
for(list<MapPoint*>::iterator lit = mlpTemporalPoints.begin(), lend = mlpTemporalPoints.end(); lit!=lend; lit++)
{
MapPoint* pMP = *lit;
delete pMP;
}
mlpTemporalPoints.clear();
// -----------step2.4 检查是否需要插入关键帧---------Check if we need to insert a new keyframe
if(NeedNewKeyFrame())
CreateNewKeyFrame();
// We allow points with high innovation (considererd outliers by the Huber Function)
// pass to the new keyframe, so that bundle adjustment will finally decide
// if they are outliers or not. We don't want next frame to estimate its position
// with those points so we discard them in the frame.
//我们允许具有高变化的点(由Huber函数考虑异常值)传递到新的关键帧,以bundle adjustment最终决定它们是否为异常值。
//我们不希望下一帧使用这些点来估计其位置,因此我们在帧中丢弃它们。
for(int i=0; i<mCurrentFrame.N;i++)
{
if(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i] && mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i])
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=static_cast<MapPoint*>(NULL);
}
}
//初始化化很快就lost了就重置系统 Reset if the camera get lost soon after initialization
if(mState==LOST)
{
if(mpMap->KeyFramesInMap()<=5)
{
cout << "Track lost soon after initialisation, reseting..." << endl;
mpSystem->Reset();
return;
}
}
if(!mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF)
mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF = mpReferenceKF;
mLastFrame = Frame(mCurrentFrame);
}
// 存储帧姿态信息,以随后检索完整的相机轨迹。Store frame pose information to retrieve the complete camera trajectory afterwards.
if(!mCurrentFrame.mTcw.empty())
{
cv::Mat Tcr = mCurrentFrame.mTcw*mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF->GetPoseInverse();//计算当前帧相对于参考帧的变换矩阵
mlRelativeFramePoses.push_back(Tcr); //返回Twc
mlpReferences.push_back(mpReferenceKF);
mlFrameTimes.push_back(mCurrentFrame.mTimeStamp);
mlbLost.push_back(mState==LOST);
}
else
{
// 正常和丢失都是进入这个This can happen if tracking is lost
mlRelativeFramePoses.push_back(mlRelativeFramePoses.back());
mlpReferences.push_back(mlpReferences.back());
mlFrameTimes.push_back(mlFrameTimes.back());
mlbLost.push_back(mState==LOST);
}
mVelocity = mCurrentFrame.mTcw*LastTwc;
表示这是前一帧的Twc 和后一帧的Tcw相乘,从而得到两帧位姿的转化关系,定义为速度。
//TODO 三维landmark
2.2 初始化
2.2.1 双目初始化 StereoInitialization()
双目和RGB-D都要使用StereoInitialization()双目初始化
双目初始化说白了,其实就是如果当前帧的关键点大于500,使当前帧成为关键帧,然后在地图等操作中添加该关键帧并增加相关属性
2.2.2 单目初始化MonocularInitialization()
//todo:绘制流程图
void Tracking::MonocularInitialization()
{
//如果没有初始化器,设置参数(当前帧为参考帧&上一帧,...),新建单目初始化器
if(!mpInitializer)//没有初始化器
{
// 设置参考帧 Set Reference Frame
if(mCurrentFrame.mvKeys.size()>100)
{
mInitialFrame = Frame(mCurrentFrame);//将当前帧设置为初始帧
mLastFrame = Frame(mCurrentFrame);//将当前帧设置为上一帧
mvbPrevMatched.resize(mCurrentFrame.mvKeysUn.size());//mvbPrevMatched预留空间
for(size_t i=0; i<mCurrentFrame.mvKeysUn.size(); i++)
mvbPrevMatched[i]=mCurrentFrame.mvKeysUn[i].pt;//填充入mvbPrevMatched
if(mpInitializer)//删除已有的初始化器(虽然好像没啥意义)
delete mpInitializer;
mpInitializer = new Initializer(mCurrentFrame,1.0,200);//创建新的初始化器
fill(mvIniMatches.begin(),mvIniMatches.end(),-1);//用-1填充
return;
}
}
//如果有初始化器
else
{
//尝试初始化 Try to initialize
//---------考量1:关键点数量>100--------
if((int)mCurrentFrame.mvKeys.size()<=100)
{
delete mpInitializer;
mpInitializer = static_cast<Initializer*>(NULL);
fill(mvIniMatches.begin(),mvIniMatches.end(),-1);
return;
}
//---------考量2:匹配点数量>100-----------
// Find correspondences
ORBmatcher matcher(0.9,true);
int nmatches = matcher.SearchForInitialization(mInitialFrame,mCurrentFrame,mvbPrevMatched,mvIniMatches,100);
// Check if there are enough correspondences
if(nmatches<100)
{
delete mpInitializer;
mpInitializer = static_cast<Initializer*>(NULL);
return;
}
cv::Mat Rcw; // 当前帧相机的旋转矩阵 Current Camera Rotation
cv::Mat tcw; // 当前帧相机的平移向量 Current Camera Translation
vector<bool> vbTriangulated; // 三角化的对应数量 Triangulated Correspondences (mvIniMatches)
//----------初始化----------------
if(mpInitializer->Initialize(mCurrentFrame, mvIniMatches, Rcw, tcw, mvIniP3D, vbTriangulated))
{
for(size_t i=0, iend=mvIniMatches.size(); i<iend;i++)
{
if(mvIniMatches[i]>=0 && !vbTriangulated[i])
{
mvIniMatches[i]=-1;
nmatches--;
}
}
// 设置当前帧位姿 Set Frame Poses
mInitialFrame.SetPose(cv::Mat::eye(4,4,CV_32F));
cv::Mat Tcw = cv::Mat::eye(4,4,CV_32F);
Rcw.copyTo(Tcw.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3));
tcw.copyTo(Tcw.rowRange(0,3).col(3));
mCurrentFrame.SetPose(Tcw);
CreateInitialMapMonocular();
}
}
}
初始化器Initializer和初始化mpInitializer->Initialize(...) 参考
orb匹配matcher.SearchForInitialization参考
2.2.2.1 构建初始化器
单目的话是需要使用单目初始化器的Initializer
建议是移步去单目初始化器
2.3 追踪方法
在我的理解中,对于视觉追踪来说,区别与RM比赛中的装甲板追踪,它不倾向于锁定单一目标,而是在运行过程中标记路标点,从而获得对整体区域的了解。路标点是一个相对宏观的概念,放到微观角度上就是MapPoint,因此我们是 准确的 有纪念意义的 KeyPoint 成为了MapPoint。
为了保证 有纪念意义的,一般不会使一个KeyPoint对应多个MapPoint(MapPoint具有唯一性),取最大值的同时也会考虑方向等:通过ORBmatcher实现
为了保证准确性,在考虑keypoint故有限制(orb方向,最小距离)的同时也要考虑自身相机位姿给keypoint带来的影响:位姿优化等操作实现
2.3.1 TrackReferenceKeyFrame()
- step1:计算并匹配词袋
- step2:计算位姿并优化
- step3:剔除离群点
bool Tracking::TrackReferenceKeyFrame()
{
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
//step1:计算并匹配词袋
// Compute Bag of Words vector
mCurrentFrame.ComputeBoW();//计算词包mBowVec和mFeatVec
ORBmatcher matcher(0.7,true);
vector<MapPoint*> vpMapPointMatches;
int nmatches = matcher.SearchByBoW(mpReferenceKF,mCurrentFrame,vpMapPointMatches);
if(nmatches<15)
return false;
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
//step2:计算位姿并优化
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints = vpMapPointMatches;
mCurrentFrame.SetPose(mLastFrame.mTcw);
//位姿优化
Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
//step3:剔除离群点
// Discard outliers
int nmatchesMap = 0;
for(int i =0; i<mCurrentFrame.N; i++)
{
if(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i])//有一部分是从SearchByBoW中来的
{
if(mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i])// Flag to identify outlier associations.
{
MapPoint* pMP = mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i];
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=static_cast<MapPoint*>(NULL);
mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i]=false;
pMP->mbTrackInView = false;
pMP->mnLastFrameSeen = mCurrentFrame.mnId;
nmatches--;
}
else if(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]->Observations()>0)
nmatchesMap++;
}
}
return nmatchesMap>=10;
}
1.SearchByBoW是为了找到当前帧和参考帧匹配子的对应关系
2.SetPose是为了获得相机坐标系到世界坐标系的旋转矩阵和平移向量以及当前相机光心在世界坐标系下坐标
3.PoseOptimization位姿优化,会将异常值mvbOutlier[i]为True
4.最后将异常值丢弃
(2)TrackWithMotionModel()
会发现其实也主要也只是做了两方面:ORBmatcher 位姿优化
区别 无非是
- (a)使用SearchByProjection(比较严格,因此要考虑匹配点少的问题)
- (b)使用UpdateLastFrame() 描述连续的上一帧
bool Tracking::TrackWithMotionModel()
{
ORBmatcher matcher(0.9,true);
UpdateLastFrame();
mCurrentFrame.SetPose(mVelocity*mLastFrame.mTcw);
// Project points seen in previous frame
int th;
if(mSensor!=System::STEREO)
th=15;
else
th=7;
int nmatches = matcher.SearchByProjection(mCurrentFrame,mLastFrame,th,mSensor==System::MONOCULAR);
// 匹配到的点数少,限制放松一些
if(nmatches<20)
{
fill(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.begin(),mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.end(),static_cast<MapPoint*>(NULL));
nmatches = matcher.SearchByProjection(mCurrentFrame,mLastFrame,2*th,mSensor==System::MONOCULAR);
}
if(nmatches<20)
return false;
//————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
// Optimize frame pose with all matches
Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);
剔去离群点
//基本相同
if(mbOnlyTracking)
{
mbVO = nmatchesMap<10;
return nmatches>20;
}
return nmatchesMap>=10;
}
UpdateLastFrame()
void Tracking::UpdateLastFrame()
{
// Update pose according to reference keyframe
//对于每一个帧只使用关键帧和位姿变化来描述
KeyFrame* pRef = mLastFrame.mpReferenceKF;
cv::Mat Tlr = mlRelativeFramePoses.back();//变化矩阵
mLastFrame.SetPose(Tlr * pRef->GetPose());
//pRef->GetPose()获得关键帧在世界坐标系上的位置
if(mnLastKeyFrameId==mLastFrame.mnId || mSensor==System::MONOCULAR || !mbOnlyTracking)
return;
//------------------单目相机到这里就结束了--------------------------------
双目/RGB-D部分
1.打包深度信息和KeyPoint
2.排序
3.判断是否创建新地图点,UnprojectStereo:根据深度信息反投影出(x,y,z)进而成为MapPoint
}
mlRelativeFramePoses:上一关联帧的变化矩阵。
基本上ORB-SLAM2存储每个帧的参考关键帧及其相对变换。在一个范围内通过一个关键帧和多个相对变化可以映射多个帧。
工业单目相机其实有接触过的都知道,处理照片的速度很快,绝对不只是示意图中稀疏的三帧,我感觉,存放参考关键帧及其相对变换内存小速度快
mlRelativeFramePoses变量变化图
(3)Relocalization()
还是那句话,无非又是 ORBmatcher 和位姿优化那一套
Relocalization仅在目标丢失后使用。
闭环候选帧和重定位候选帧之间的区别是闭环候选帧是从关键帧中选取
重定位候选帧是从普通帧中选取
其他的流程和闭环候选帧选取方式相同
vector<KeyFrame*> vpCandidateKFs = mpKeyFrameDB->DetectRelocalizationCandidates(&mCurrentFrame);
bool Tracking::Relocalization()
{
// Compute Bag of Words Vector
mCurrentFrame.ComputeBoW();
// Relocalization is performed when tracking is lost
// Track Lost: Query KeyFrame Database for keyframe candidates for relocalisation
vector<KeyFrame*> vpCandidateKFs = mpKeyFrameDB->DetectRelocalizationCandidates(&mCurrentFrame);
if(vpCandidateKFs.empty())
return false;
const int nKFs = vpCandidateKFs.size();
// We perform first an ORB matching with each candidate
// If enough matches are found we setup a PnP solver
ORBmatcher matcher(0.75,true);
vector<PnPsolver*> vpPnPsolvers;
vpPnPsolvers.resize(nKFs);
vector<vector<MapPoint*> > vvpMapPointMatches;
vvpMapPointMatches.resize(nKFs);
vector<bool> vbDiscarded;
vbDiscarded.resize(nKFs);
int nCandidates=0;
for(int i=0; i<nKFs; i++)
{
KeyFrame* pKF = vpCandidateKFs[i];
if(pKF->isBad())
vbDiscarded[i] = true;
else
{
int nmatches = matcher.SearchByBoW(pKF,mCurrentFrame,vvpMapPointMatches[i]);
if(nmatches<15)
{
vbDiscarded[i] = true;
continue;
}
else
{
PnPsolver* pSolver = new PnPsolver(mCurrentFrame,vvpMapPointMatches[i]);
pSolver->SetRansacParameters(0.99,10,300,4,0.5,5.991);
vpPnPsolvers[i] = pSolver;
nCandidates++;
}
}
}
// Alternatively perform some iterations of P4P RANSAC
// Until we found a camera pose supported by enough inliers
bool bMatch = false;
ORBmatcher matcher2(0.9,true);
while(nCandidates>0 && !bMatch)
{
for(int i=0; i<nKFs; i++)
{
if(vbDiscarded[i])
continue;
// Perform 5 Ransac Iterations
vector<bool> vbInliers;
int nInliers;
bool bNoMore;
PnPsolver* pSolver = vpPnPsolvers[i];
cv::Mat Tcw = pSolver->iterate(5,bNoMore,vbInliers,nInliers);
// If Ransac reachs max. iterations discard keyframe
if(bNoMore)
{
vbDiscarded[i]=true;
nCandidates--;
}
// If a Camera Pose is computed, optimize
if(!Tcw.empty())
{
Tcw.copyTo(mCurrentFrame.mTcw);
set<MapPoint*> sFound;
const int np = vbInliers.size();
for(int j=0; j<np; j++)
{
if(vbInliers[j])
{
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[j]=vvpMapPointMatches[i][j];
sFound.insert(vvpMapPointMatches[i][j]);
}
else
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[j]=NULL;
}
int nGood = Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);
if(nGood<10)
continue;
for(int io =0; io<mCurrentFrame.N; io++)
if(mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[io])
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[io]=static_cast<MapPoint*>(NULL);
// If few inliers, search by projection in a coarse window and optimize again
if(nGood<50)
{
int nadditional =matcher2.SearchByProjection(mCurrentFrame,vpCandidateKFs[i],sFound,10,100);
if(nadditional+nGood>=50)
{
nGood = Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);
// If many inliers but still not enough, search by projection again in a narrower window
// the camera has been already optimized with many points
if(nGood>30 && nGood<50)
{
sFound.clear();
for(int ip =0; ip<mCurrentFrame.N; ip++)
if(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[ip])
sFound.insert(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[ip]);
nadditional =matcher2.SearchByProjection(mCurrentFrame,vpCandidateKFs[i],sFound,3,64);
// Final optimization
if(nGood+nadditional>=50)
{
nGood = Optimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);
for(int io =0; io<mCurrentFrame.N; io++)
if(mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[io])
mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[io]=NULL;
}
}
}
}
// If the pose is supported by enough inliers stop ransacs and continue
if(nGood>=50)
{
bMatch = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
if(!bMatch)
{
return false;
}
else
{
mnLastRelocFrameId = mCurrentFrame.mnId;
return true;
}
}
变换矩阵的逆代表一个反向的变化
cv::Mat Tcr = mCurrentFrame.mTcw*mCurrentFrame.mpReferenceKF->GetPoseInverse();
//获得变化矩阵
| 函数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| CheckReplacedInLastFrame | 遍历上一帧所有地图点,检查其是否被替代,更新位替代点 |
| MonocularInitialization | 如果没有初始化器,设置参数(当前帧为参考帧&上一帧,…),新建单目初始化器 |
| TrackReferenceKeyFrame() | 计算并匹配词袋,计算位姿并优化,剔除离群点 |
| TrackLocalMap | UpdateLocalMap()清空局部关键帧并重新赋值(更新),SearchLocalPoints()将局部地图点 投影到 当前帧特征点,位姿优化,更新地图点观测 |
| UpdateLocalMap | 参考地图点设置为局部建图的地图点, UpdateLocalKeyFrames()和UpdateLocalPoints()分别更新局部关键帧和局部点 |
| UpdateLocalKeyFrames | 将关键帧设置为(1)当前地图点的所有共视关键帧(2)1中所有关键帧的父子关键帧(3)1中所有关键帧共视关系前10大共视关键帧 |
| KeyFrame::TrackedMapPoints | 获得地图点中大于最小共视数量的点的数量 |
| Frame::UpdatePoseMatrices | 从相机位姿中计算旋转,平移和相机光心 |