kitti之ros可视化_学习笔记--第10课:添加id到3d侦测盒上方
环境:ubuntu16.04,ros-kinetic,python2,vscode,opencv,rviz
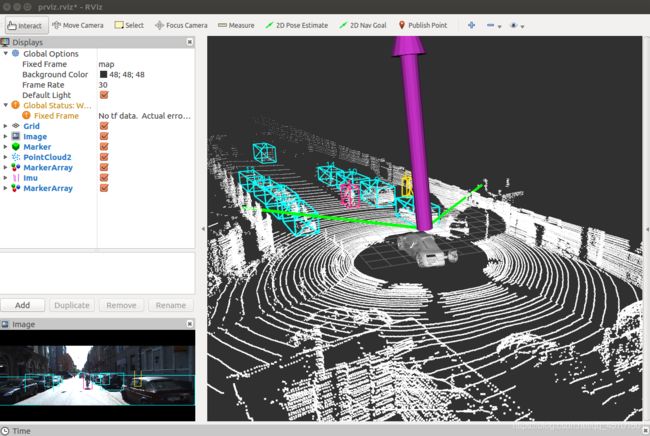
概要:这节课笔记,新增展示的是,在物体3d侦测盒上方显示id。
资料准备及预处理可参考博客,https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45701501/article/details/116447770
tracking资料准备:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45701501/article/details/116586427
1、思路
包存储位置、创建、编译、运行这些参考本人这系列前面的博客。
主要思路:添加id给3d侦测盒,也就是从tracking数据集中,读取track_id,并转为np数组格式;给发布3d侦测盒函数添加一个用于传入id的形参,在函数体中添加用于显示id的marker。
2、源码
包含四个文件:读取资料文件data_utils.py,发布函数文件publish_utils.py,将3d侦测框从相机坐标系转为雷达坐标系显示文件kitti_utils.py,主函数文件p15_kitti.py.
data_utils.py:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
import pandas as pd #用于读取imu资料
IMU_COLUMN_NAMES = ['lat','lon','alt','roll','pitch','yaw','vn','ve','vf','vl','vu',
'ax','ay','az','af','al','au','wx','wy','wz','wf','wl','wu',
'posacc','velacc','navstat','numsats','posmode','velmode','orimode'
]#根据kitti数据集中的名称进行定义的,个人理解是对照c里面的宏定义
TRACKING_COLUMN_NAMES=['frame', 'track_id', 'type', 'truncated', 'occluded', 'alpha',
'bbox_left', 'bbox_top','bbox_right', 'bbox_bottom', 'height',
'width', 'length', 'pos_x', 'pos_y', 'pos_z', 'rot_y']#tracking数据单位
#读取图片路径函数
def read_camera(path):
return cv2.imread(path)
#读取点云路径函数
def read_point_cloud(path):
return np.fromfile(path,dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1,4)
#读取imu资料
def read_imu(path):
df=pd.read_csv(path,header=None,sep=' ')#读取数据
df.columns=IMU_COLUMN_NAMES#给数据赋予单位
return df
#读取trackiing资料
def read_tracking(path):
df=pd.read_csv(path,header=None,sep=' ')#读取tracking资料
df.columns=TRACKING_COLUMN_NAMES#给资料数据添加单位
df.loc[df.type.isin(['Truck','Van','Tram']),'type']='Car'#将这三种车子,统一定义为Car
df=df[df.type.isin(['Car','Pedestrian','Cyclist'])]#只是获取数据集中类型为指定的数据,注意car为重定义类型
return df#返回读取的资料
publish_utils.py:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf8 -*-
import rospy
from std_msgs.msg import Header
from visualization_msgs.msg import Marker,MarkerArray#Marker绘制相机视野指示线模块,MarkerArray解决Marker带来发布的不同步问题
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image,PointCloud2,Imu,NavSatFix
from geometry_msgs.msg import Point#Point来自ros包定义,所以需要定义;若不清楚,则需要到ros官网上面查看具体那个包
import sensor_msgs.point_cloud2 as pcl2
from cv_bridge import CvBridge
import numpy as np
import tf
import cv2
FRAME_ID='map'
DETECTION_COLOR_DICT = {'Car':(255,255,0),'Pedestrian':(0,226,255),'Cyclist':(141,40,255)}#颜色字典
#车头朝前,左上点为0,顺时针,0,1,2,3四个点,顶部同样顺时针,依次为(0顶部)4,5,6,7
#侦测盒资料,连线顺序
LINES = [[0, 1], [1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 0]] # lower face
LINES+= [[4, 5], [5, 6], [6, 7], [7, 4]] #upper face
LINES+= [[4, 0], [5, 1], [6, 2], [7, 3]] #connect lower face and upper face
LINES+= [[4, 1], [5, 0]] #front face 对角线表示叉叉以表示正前方
#侦测盒存在的时长
LIFETIME = 0.1
#发布图片函数
def publish_camera(cam_pub,bridge,image,boxes,types):#增加参数boxes、types
#绘制框框到图片中
for typ,box in zip(types,boxes):#给对应类型每个box绘制对应颜色图线
top_left=int(box[0]),int(box[1])#box的左上角点,像素为整数,所以需要转换int类型
bottom_right=int(box[2]),int(box[3])#box的右下角点
#绘制框框,依次指定图片、左上角点、右下角点、根据类型不同给的颜色(bgr)、线粗细
cv2.rectangle(image,top_left,bottom_right,DETECTION_COLOR_DICT[typ],2)
cam_pub.publish(bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(image,"bgr8"))
#发布点云函数
def publish_point_cloud(pcl_pub,point_clond):
header=Header()
header.stamp=rospy.Time.now()
header.frame_id=FRAME_ID
pcl_pub.publish(pcl2.create_cloud_xyz32(header,point_clond[:,:3]))
#发布相机视野以及车子模型marker函数
def publish_ego_car(ego_car_pub):
#publish left and right 45 degree FOV lines and ego car model mesh
marker_array=MarkerArray()#解决marker发布不同步问题
marker=Marker()
marker.header.frame_id=FRAME_ID
marker.header.stamp=rospy.Time.now()
marker.id=0#每个marker只能有一个id,有重复的id,只会显示一个
marker.action=Marker.ADD#表示添加marker
marker.lifetime=rospy.Duration()#lifetime表示marker在画面中显示的时长;Duration()函数,不给任何参数时,表示一直存在
marker.type=Marker.LINE_STRIP#所发布marker的类型
#设定指示线颜色
marker.color.r=0.0
marker.color.g=1.0
marker.color.b=0.0
marker.color.a=1.0#透明度,1表示完全不透明
marker.scale.x=0.2#大小,这里表示线的粗细
#根据激光点云的坐标系来定义2号相机的视野范围
marker.points=[]
marker.points.append(Point(10,-10,0))#Point,属于ros的资料包里面的定义,所以需要导入
marker.points.append(Point(0,0,0))
marker.points.append(Point(10,10,0))
marker_array.markers.append(marker)#将指示线marker放到MarkerArray中
#发布车子外形函数
mesh_marker=Marker()
mesh_marker.header.frame_id=FRAME_ID
mesh_marker.header.stamp=rospy.Time.now()
mesh_marker.id=-1#id只能设置整数,不能设置带有小数的
mesh_marker.lifetime=rospy.Duration()
mesh_marker.type=Marker.MESH_RESOURCE#这里的MESH_RESOURCE表示导入的是3d模型
mesh_marker.mesh_resource="package://kitti_tutorial/Audi R8/Models/Audi R8.dae"#下载的dae模型存在问题,只是显示部分
#设定模型位置
mesh_marker.pose.position.x=0.0
mesh_marker.pose.position.y=0.0
mesh_marker.pose.position.z=-1.73#这里负数,是因为以激光雷达坐标系而定义的,1.73是根据官方发布的位置定义所取的
#设计车子模型的旋转量
q=tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(0,0,np.pi/2)#(np.pi/2,0,np.pi)这里根据下载的车子模型进行调整
mesh_marker.pose.orientation.x=q[0]
mesh_marker.pose.orientation.y=q[1]
mesh_marker.pose.orientation.z=q[2]
mesh_marker.pose.orientation.w=q[3]
#设置车子模型的颜色
mesh_marker.color.r=1.0
mesh_marker.color.g=1.0
mesh_marker.color.b=1.0
mesh_marker.color.a=1.0
#设置车子模型的大小
mesh_marker.scale.x=0.6
mesh_marker.scale.y=0.6
mesh_marker.scale.z=0.6
marker_array.markers.append(mesh_marker)#将车子marker放到MarkerArray中
ego_car_pub.publish(marker_array)
#发布imu资料函数
def publish_imu(imu_pub,imu_data):
imu=Imu()#ros,imu 进行google可以查看文档说明
imu.header.frame_id=FRAME_ID
imu.header.stamp=rospy.Time.now()
#旋转角度、加速度,角速度
q=tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(float(imu_data.roll),float(imu_data.pitch),float(imu_data.yaw))#(np.pi/2,0,np.pi)这里根据下载的车子模型进行调整
imu.orientation.x=q[0]#以下四个表示旋转角,将读取的数据转为四元数表示
imu.orientation.y=q[1]
imu.orientation.z=q[2]
imu.orientation.w=q[3]
imu.linear_acceleration.x=imu_data.af#根据雷达坐标系,确定x方向线性加速度
imu.linear_acceleration.y=imu_data.al#根据雷达坐标系,确定y方向线性加速度
imu.linear_acceleration.z=imu_data.au#根据雷达坐标系,确定z方向线性加速度
imu.angular_velocity.x=imu_data.wf#这三个表示不同方向的角速度
imu.angular_velocity.y=imu_data.wl
imu.angular_velocity.z=imu_data.wu
imu_pub.publish(imu)
#发布gps资料函数
def publish_gps(gps_pub,imu_data):
gps=NavSatFix()#ros里面对于gps资料识别包
gps.header.frame_id=FRAME_ID
gps.header.stamp=rospy.Time.now()
gps.latitude=imu_data.lat#纬度
gps.longitude=imu_data.lon#经度
gps.altitude=imu_data.alt#海拔
gps_pub.publish(gps)
#发布侦测盒函数
#def publish_3dbox(box3d_pub,corners_3d_velos):#侦测盒颜色一致写法
#def publish_3dbox(box3d_pub,corners_3d_velos,types):#types指定物体种类以表示不同颜色
def publish_3dbox(box3d_pub,corners_3d_velos,types,track_ids):#再增加track_id参数
marker_array=MarkerArray()#把所有marker放在一起发布
for i,corners_3d_velo in enumerate(corners_3d_velos):#对每个顶点建立marker
marker = Marker()
marker.header.frame_id = FRAME_ID
marker.header.stamp =rospy.Time.now()
marker.id =i
marker.action = Marker.ADD
#由于车子一直在运动,0.1秒会更新一次,所以侦测盒更新时间为LIFETIME=0.1秒,防止侦测盒一直存在
marker.lifetime =rospy.Duration(LIFETIME)
marker.type = Marker.LINE_LIST
# marker.color.r = 0.0#这几行表示发布的侦查盒颜色都一样的
# marker.color.g = 1.0
# marker.color.b = 1.0
b, g, r = DETECTION_COLOR_DICT[types[i]]#根据不同类型,侦测盒颜色给不一样
marker.color.r = r/255.0 #由于是python2,所以需要加.0才会做小数点除法
marker.color.g = g/255.0
marker.color.b = b/255.0
marker.color.a = 1.0
marker.scale.x = 0.1
marker.points = []
for l in LINES:#给8个顶点指定连线顺序,上面有定义
p1 = corners_3d_velo[l[0]]
marker.points.append(Point(p1[0],p1[1],p1[2]))
p2 = corners_3d_velo[l[1]]
marker.points.append(Point(p2[0],p2[1],p2[2]))
marker_array.markers.append(marker)
#track_id的marker
text_marker = Marker()
text_marker.header.frame_id = FRAME_ID
text_marker.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
text_marker.id = i +1000 #i和上面定义一致,保证发布正常显示
text_marker.action = Marker.ADD
text_marker.lifetime = rospy.Duration(LIFETIME)
text_marker.type = Marker.TEXT_VIEW_FACING #TEXT表示文字,VIEW_FACING表示一直朝向你观看方向
#p4 = corners_3d_velo[4]#upper front left corner定义设置的marker位置,这里表示上左角
p4 = np.mean(corners_3d_velo,axis=0)#axis=0表示取的是垂直方向的轴的平均,是的显示在侦测盒中心上方
text_marker.pose.position.x = p4[0]
text_marker.pose.position.y = p4[1]
text_marker.pose.position.z = p4[2] + 1 #让track_id显示在侦测盒上方
text_marker.text = str(track_ids[i]) #指定marker显示文字内容,str将track_id内容转换为string类型才行显示
#指定marker大小
text_marker.scale.x = 1
text_marker.scale.y = 1
text_marker.scale.z = 1
b, g, r = DETECTION_COLOR_DICT[types[i]] #track_id文字显示颜色根据物体种类显示
text_marker.color.r = r/255.0
text_marker.color.g = g/255.0
text_marker.color.b = b/255.0
text_marker.color.a = 1.0
marker_array.markers.append(text_marker)
box3d_pub.publish(marker_array)#发布
kitti_utils.py:
""" Helper methods for loading and parsing KITTI data.
Author: Charles R. Qi
Date: September 2017
"""
from __future__ import print_function
import numpy as np
import cv2
import os
class Object3d(object):
''' 3d object label '''
def __init__(self, label_file_line):
data = label_file_line.split(' ')
data[1:] = [float(x) for x in data[1:]]
# extract label, truncation, occlusion
self.type = data[0] # 'Car', 'Pedestrian', ...
self.truncation = data[1] # truncated pixel ratio [0..1]
self.occlusion = int(data[2]) # 0=visible, 1=partly occluded, 2=fully occluded, 3=unknown
self.alpha = data[3] # object observation angle [-pi..pi]
# extract 2d bounding box in 0-based coordinates
self.xmin = data[4] # left
self.ymin = data[5] # top
self.xmax = data[6] # right
self.ymax = data[7] # bottom
self.box2d = np.array([self.xmin,self.ymin,self.xmax,self.ymax])
# extract 3d bounding box information
self.h = data[8] # box height
self.w = data[9] # box width
self.l = data[10] # box length (in meters)
self.t = (data[11],data[12],data[13]) # location (x,y,z) in camera coord.
self.ry = data[14] # yaw angle (around Y-axis in camera coordinates) [-pi..pi]
def print_object(self):
print('Type, truncation, occlusion, alpha: %s, %d, %d, %f' % \
(self.type, self.truncation, self.occlusion, self.alpha))
print('2d bbox (x0,y0,x1,y1): %f, %f, %f, %f' % \
(self.xmin, self.ymin, self.xmax, self.ymax))
print('3d bbox h,w,l: %f, %f, %f' % \
(self.h, self.w, self.l))
print('3d bbox location, ry: (%f, %f, %f), %f' % \
(self.t[0],self.t[1],self.t[2],self.ry))
class Calibration(object):
''' Calibration matrices and utils
3d XYZ in
def __init__(self, calib_filepath, from_video=False):
if from_video:
calibs = self.read_calib_from_video(calib_filepath)
else:
calibs = self.read_calib_file(calib_filepath)
# Projection matrix from rect camera coord to image2 coord
self.P = calibs['P2']
self.P = np.reshape(self.P, [3,4])
# Rigid transform from Velodyne coord to reference camera coord
self.V2C = calibs['Tr_velo_to_cam']
self.V2C = np.reshape(self.V2C, [3,4])
self.C2V = inverse_rigid_trans(self.V2C)
# Rotation from reference camera coord to rect camera coord
self.R0 = calibs['R0_rect']
self.R0 = np.reshape(self.R0,[3,3])
# Camera intrinsics and extrinsics
self.c_u = self.P[0,2]
self.c_v = self.P[1,2]
self.f_u = self.P[0,0]
self.f_v = self.P[1,1]
self.b_x = self.P[0,3]/(-self.f_u) # relative
self.b_y = self.P[1,3]/(-self.f_v)
def read_calib_file(self, filepath):
''' Read in a calibration file and parse into a dictionary.
Ref: https://github.com/utiasSTARS/pykitti/blob/master/pykitti/utils.py
'''
data = {}
with open(filepath, 'r') as f:
for line in f.readlines():
line = line.rstrip()
if len(line)==0: continue
key, value = line.split(':', 1)
# The only non-float values in these files are dates, which
# we don't care about anyway
try:
data[key] = np.array([float(x) for x in value.split()])
except ValueError:
pass
return data
def read_calib_from_video(self, calib_root_dir):
''' Read calibration for camera 2 from video calib files.
there are calib_cam_to_cam and calib_velo_to_cam under the calib_root_dir
'''
data = {}
cam2cam = self.read_calib_file(os.path.join(calib_root_dir, 'calib_cam_to_cam.txt'))
velo2cam = self.read_calib_file(os.path.join(calib_root_dir, 'calib_velo_to_cam.txt'))
Tr_velo_to_cam = np.zeros((3,4))
Tr_velo_to_cam[0:3,0:3] = np.reshape(velo2cam['R'], [3,3])
Tr_velo_to_cam[:,3] = velo2cam['T']
data['Tr_velo_to_cam'] = np.reshape(Tr_velo_to_cam, [12])
data['R0_rect'] = cam2cam['R_rect_00']
data['P2'] = cam2cam['P_rect_02']
return data
def cart2hom(self, pts_3d):
''' Input: nx3 points in Cartesian
Oupput: nx4 points in Homogeneous by pending 1
'''
n = pts_3d.shape[0]
pts_3d_hom = np.hstack((pts_3d, np.ones((n,1))))
return pts_3d_hom
# ===========================
# ------- 3d to 3d ----------
# ===========================
def project_velo_to_ref(self, pts_3d_velo):
pts_3d_velo = self.cart2hom(pts_3d_velo) # nx4
return np.dot(pts_3d_velo, np.transpose(self.V2C))
def project_ref_to_velo(self, pts_3d_ref):
pts_3d_ref = self.cart2hom(pts_3d_ref) # nx4
return np.dot(pts_3d_ref, np.transpose(self.C2V))
def project_rect_to_ref(self, pts_3d_rect):
''' Input and Output are nx3 points '''
return np.transpose(np.dot(np.linalg.inv(self.R0), np.transpose(pts_3d_rect)))
def project_ref_to_rect(self, pts_3d_ref):
''' Input and Output are nx3 points '''
return np.transpose(np.dot(self.R0, np.transpose(pts_3d_ref)))
def project_rect_to_velo(self, pts_3d_rect):
''' Input: nx3 points in rect camera coord.
Output: nx3 points in velodyne coord.
'''
pts_3d_ref = self.project_rect_to_ref(pts_3d_rect)
return self.project_ref_to_velo(pts_3d_ref)
def project_velo_to_rect(self, pts_3d_velo):
pts_3d_ref = self.project_velo_to_ref(pts_3d_velo)
return self.project_ref_to_rect(pts_3d_ref)
# ===========================
# ------- 3d to 2d ----------
# ===========================
def project_rect_to_image(self, pts_3d_rect):
''' Input: nx3 points in rect camera coord.
Output: nx2 points in image2 coord.
'''
pts_3d_rect = self.cart2hom(pts_3d_rect)
pts_2d = np.dot(pts_3d_rect, np.transpose(self.P)) # nx3
pts_2d[:,0] /= pts_2d[:,2]
pts_2d[:,1] /= pts_2d[:,2]
return pts_2d[:,0:2]
def project_velo_to_image(self, pts_3d_velo):
''' Input: nx3 points in velodyne coord.
Output: nx2 points in image2 coord.
'''
pts_3d_rect = self.project_velo_to_rect(pts_3d_velo)
return self.project_rect_to_image(pts_3d_rect)
# ===========================
# ------- 2d to 3d ----------
# ===========================
def project_image_to_rect(self, uv_depth):
''' Input: nx3 first two channels are uv, 3rd channel
is depth in rect camera coord.
Output: nx3 points in rect camera coord.
'''
n = uv_depth.shape[0]
x = ((uv_depth[:,0]-self.c_u)*uv_depth[:,2])/self.f_u + self.b_x
y = ((uv_depth[:,1]-self.c_v)*uv_depth[:,2])/self.f_v + self.b_y
pts_3d_rect = np.zeros((n,3))
pts_3d_rect[:,0] = x
pts_3d_rect[:,1] = y
pts_3d_rect[:,2] = uv_depth[:,2]
return pts_3d_rect
def project_image_to_velo(self, uv_depth):
pts_3d_rect = self.project_image_to_rect(uv_depth)
return self.project_rect_to_velo(pts_3d_rect)
def rotx(t):
''' 3D Rotation about the x-axis. '''
c = np.cos(t)
s = np.sin(t)
return np.array([[1, 0, 0],
[0, c, -s],
[0, s, c]])
def roty(t):
''' Rotation about the y-axis. '''
c = np.cos(t)
s = np.sin(t)
return np.array([[c, 0, s],
[0, 1, 0],
[-s, 0, c]])
def rotz(t):
''' Rotation about the z-axis. '''
c = np.cos(t)
s = np.sin(t)
return np.array([[c, -s, 0],
[s, c, 0],
[0, 0, 1]])
def transform_from_rot_trans(R, t):
''' Transforation matrix from rotation matrix and translation vector. '''
R = R.reshape(3, 3)
t = t.reshape(3, 1)
return np.vstack((np.hstack([R, t]), [0, 0, 0, 1]))
def inverse_rigid_trans(Tr):
''' Inverse a rigid body transform matrix (3x4 as [R|t])
[R'|-R't; 0|1]
'''
inv_Tr = np.zeros_like(Tr) # 3x4
inv_Tr[0:3,0:3] = np.transpose(Tr[0:3,0:3])
inv_Tr[0:3,3] = np.dot(-np.transpose(Tr[0:3,0:3]), Tr[0:3,3])
return inv_Tr
def read_label(label_filename):
lines = [line.rstrip() for line in open(label_filename)]
objects = [Object3d(line) for line in lines]
return objects
def load_image(img_filename):
return cv2.imread(img_filename)
def load_velo_scan(velo_filename):
scan = np.fromfile(velo_filename, dtype=np.float32)
scan = scan.reshape((-1, 4))
return scan
def project_to_image(pts_3d, P):
''' Project 3d points to image plane.
Usage: pts_2d = projectToImage(pts_3d, P)
input: pts_3d: nx3 matrix
P: 3x4 projection matrix
output: pts_2d: nx2 matrix
P(3x4) dot pts_3d_extended(4xn) = projected_pts_2d(3xn)
=> normalize projected_pts_2d(2xn)
<=> pts_3d_extended(nx4) dot P'(4x3) = projected_pts_2d(nx3)
=> normalize projected_pts_2d(nx2)
'''
n = pts_3d.shape[0]
pts_3d_extend = np.hstack((pts_3d, np.ones((n,1))))
print(('pts_3d_extend shape: ', pts_3d_extend.shape))
pts_2d = np.dot(pts_3d_extend, np.transpose(P)) # nx3
pts_2d[:,0] /= pts_2d[:,2]
pts_2d[:,1] /= pts_2d[:,2]
return pts_2d[:,0:2]
def compute_box_3d(obj, P):
''' Takes an object and a projection matrix (P) and projects the 3d
bounding box into the image plane.
Returns:
corners_2d: (8,2) array in left image coord.
corners_3d: (8,3) array in in rect camera coord.
'''
# compute rotational matrix around yaw axis
R = roty(obj.ry)
# 3d bounding box dimensions
l = obj.l;
w = obj.w;
h = obj.h;
# 3d bounding box corners
x_corners = [l/2,l/2,-l/2,-l/2,l/2,l/2,-l/2,-l/2];
y_corners = [0,0,0,0,-h,-h,-h,-h];
z_corners = [w/2,-w/2,-w/2,w/2,w/2,-w/2,-w/2,w/2];
# rotate and translate 3d bounding box
corners_3d = np.dot(R, np.vstack([x_corners,y_corners,z_corners]))
#print corners_3d.shape
corners_3d[0,:] = corners_3d[0,:] + obj.t[0];
corners_3d[1,:] = corners_3d[1,:] + obj.t[1];
corners_3d[2,:] = corners_3d[2,:] + obj.t[2];
#print 'cornsers_3d: ', corners_3d
# only draw 3d bounding box for objs in front of the camera
if np.any(corners_3d[2,:]<0.1):
corners_2d = None
return corners_2d, np.transpose(corners_3d)
# project the 3d bounding box into the image plane
corners_2d = project_to_image(np.transpose(corners_3d), P);
#print 'corners_2d: ', corners_2d
return corners_2d, np.transpose(corners_3d)
def compute_orientation_3d(obj, P):
''' Takes an object and a projection matrix (P) and projects the 3d
object orientation vector into the image plane.
Returns:
orientation_2d: (2,2) array in left image coord.
orientation_3d: (2,3) array in in rect camera coord.
'''
# compute rotational matrix around yaw axis
R = roty(obj.ry)
# orientation in object coordinate system
orientation_3d = np.array([[0.0, obj.l],[0,0],[0,0]])
# rotate and translate in camera coordinate system, project in image
orientation_3d = np.dot(R, orientation_3d)
orientation_3d[0,:] = orientation_3d[0,:] + obj.t[0]
orientation_3d[1,:] = orientation_3d[1,:] + obj.t[1]
orientation_3d[2,:] = orientation_3d[2,:] + obj.t[2]
# vector behind image plane?
if np.any(orientation_3d[2,:]<0.1):
orientation_2d = None
return orientation_2d, np.transpose(orientation_3d)
# project orientation into the image plane
orientation_2d = project_to_image(np.transpose(orientation_3d), P);
return orientation_2d, np.transpose(orientation_3d)
def draw_projected_box3d(image, qs, color=(255,255,255), thickness=2):
''' Draw 3d bounding box in image
qs: (8,3) array of vertices for the 3d box in following order:
1 -------- 0
/| /|
2 -------- 3 .
| | | |
. 5 -------- 4
|/ |/
6 -------- 7
'''
qs = qs.astype(np.int32)
for k in range(0,4):
# Ref: http://docs.enthought.com/mayavi/mayavi/auto/mlab_helper_functions.html
i,j=k,(k+1)%4
# use LINE_AA for opencv3
cv2.line(image, (qs[i,0],qs[i,1]), (qs[j,0],qs[j,1]), color, thickness, cv2.CV_AA)
i,j=k+4,(k+1)%4 + 4
cv2.line(image, (qs[i,0],qs[i,1]), (qs[j,0],qs[j,1]), color, thickness, cv2.CV_AA)
i,j=k,k+4
cv2.line(image, (qs[i,0],qs[i,1]), (qs[j,0],qs[j,1]), color, thickness, cv2.CV_AA)
return image
p15_kitti.py:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf8 -*-
from data_utils import *
from publish_utils import *
from kitti_utils import * #kitti_utils.py文件有报错,但是不影响运行
DATA_PATH='/home/ylh/data/kitti/RawData/2011_09_26/2011_09_26_drive_0005_sync'
#3d侦测盒生成函数
#以特殊情况为例,当rot_y=0时,(pos_x,pos_y,pos_z)就是位于侦测盒的下方平面的中心点
#根据资料中的长宽,可以获取下方平面的四角坐标,然后根据高数据,从而获取侦测盒的八个点的坐标
#对于rot_y!=0情况,需要每个点乘以一个旋转矩阵(对相机坐标系中的y轴进行旋转),那么就可以得到
#带有rot_y!=0也就是yaw非0情况,8个顶点坐标(yaw=0情况时)乘以旋转矩阵,可得到新的8个顶点坐标
def compute_3d_box_cam2(h,w,l,x,y,z,yaw):
#return:3xn in can2 coordinate
#rot_y!=0时的旋转矩阵
R = np.array([[np.cos(yaw),0,np.sin(yaw)],[0,1,0],[-np.sin(yaw),0,np.cos(yaw)]])
#8个顶点所对应的xyz坐标(rot_y=0时)
x_corners = [l/2,l/2,-l/2,-l/2,l/2,l/2,-l/2,-l/2]
y_corners = [0,0,0,0,-h,-h,-h,-h]
z_corners = [w/2,-w/2,-w/2,w/2,w/2,-w/2,-w/2,w/2]
#做旋转,rot_y=0可视为旋转特例,只不过角度为0而已,然后,让8个顶点坐标与旋转矩阵相乘
corners_3d_cam2 = np.dot(R,np.vstack([x_corners,y_corners,z_corners]))
#由于以下方中心点做旋转的,所以,需要加上该旋转中心点坐标(x,y,z)
corners_3d_cam2 += np.vstack([x,y,z])
return corners_3d_cam2#返回侦测盒8个顶点在相机坐标系中的坐标
if __name__=='__main__':
frame = 0
rospy.init_node('kitti_node',anonymous=True)
cam_pub=rospy.Publisher('kitti_cam',Image,queue_size=10)#建立发布图片topic
pcl_pub=rospy.Publisher('kitti_point_cloud',PointCloud2,queue_size=10)#建立发布点云topic
#ego_pub=rospy.Publisher('kitti_ego_car',Marker,queue_size=10)#建立发布指示线marker的topic
ego_pub=rospy.Publisher('kitti_ego_car',MarkerArray,queue_size=10)#MarkerArray方式发布
#model_pub=rospy.Publisher('kitti_car_model',Marker,queue_size=10)#建立发布车子模型的marker的topic
imu_pub=rospy.Publisher('kitti_imu',Imu,queue_size=10)#建立发布imu资料的topic
gps_pub=rospy.Publisher('kitti_gps',NavSatFix,queue_size=10)#建立发布gps资料的topic,NavSatFix,ros里面固定卫星侦测资料包
box3d_pub=rospy.Publisher('kitti_3d',MarkerArray,queue_size=10)#创建发布侦测盒的topic
bridge=CvBridge()
rate=rospy.Rate(10)
#读取tracking资料
df_tracking=read_tracking('/home/ylh/data/kitti/training/label_02/0000.txt')
#读取坐标转换文件,from_video=True表示会读取路径中三个.txt坐标转换文件
calib = Calibration('/home/ylh/data/kitti/RawData/2011_09_26/',from_video=True)
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
#将tracking资料的绘制框框所需资料筛选并处理
df_tracking_frame = df_tracking[df_tracking.frame==frame]
boxes_2d = np.array(df_tracking_frame[['bbox_left','bbox_top','bbox_right','bbox_bottom']])#获取tracking资料第frame帧图片中的box们对应的四边坐标
types=np.array(df_tracking_frame['type'])#读取tracking资料第frame帧图片中的物体种类类型并保存到tpyes数组中
#读取tracking里面侦测盒参数
boxes_3d = np.array(df_tracking_frame[['height','width','length','pos_x','pos_y','pos_z','rot_y']])
#获取track_id
track_ids = np.array(df_tracking_frame['track_id'])#将读取的track_id保存成一个数组
corners_3d_velos = []#存放侦测盒8个顶点数据
for box_3d in boxes_3d:#根据资料生成所有侦测盒
corners_3d_cam2 = compute_3d_box_cam2(*box_3d)#由于该函数有7个参数,所以使用星号自动展开;计算获取侦测盒8个顶点坐标
corners_3d_velo = calib.project_rect_to_velo(corners_3d_cam2.T)#把8个顶点,从相机坐标系装换到雷达坐标系
corners_3d_velos += [corners_3d_velo]#存放所有侦测盒8顶点数据
#读取图片
image=read_camera(os.path.join(DATA_PATH,'image_02/data/%010d.png'%frame))
#发布图片
#publish_camera(cam_pub,bridge,image)
publish_camera(cam_pub,bridge,image,boxes_2d,types)#增加参数boxes,types,为了给图片指定类型绘制框框
#读取点云
point_clond=read_point_cloud(os.path.join(DATA_PATH,'velodyne_points/data/%010d.bin'%frame))
#发布点云
publish_point_cloud(pcl_pub,point_clond)
#发布指示线marker;由于不需要读取资料,所以直接发布即可
#当采用markerarray发布方式,则车子和指示线都放在这个topic
#进行发布即可。故下面的发布车子模型marker可以删除。这样子,可以解决不同marker发布不同步问题
publish_ego_car(ego_pub)
#发布车子模型marker;由于不需要读取资料,所以直接发布即可
#publish_car_model(model_pub)
#读取imu资料,这里也包含了gps资料了
imu_data=read_imu(os.path.join(DATA_PATH,'oxts/data/%010d.txt'%frame))
#发布imu资料
publish_imu(imu_pub,imu_data)
#发布gps资料
publish_gps(gps_pub,imu_data)
#发布侦测盒
#publish_3dbox(box3d_pub,corners_3d_velos)#侦测盒颜色一致写法
#publish_3dbox(box3d_pub,corners_3d_velos,types) #增加侦测盒类型不同而不一样写法
publish_3dbox(box3d_pub,corners_3d_velos,types,track_ids) #增加传递track_id
#发布
rospy.loginfo("published")
rate.sleep()
frame+=1
frame%=154
3、效果
至此,kitti数据集的3d侦测盒的id显示操作完成~
#####################
学习课程来源up主,AI葵:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TBdcwwr5Wyk
致谢AI葵老师
不积硅步,无以至千里
好记性不如烂笔头
感觉有点收获的话,麻烦大大们点赞收藏哈