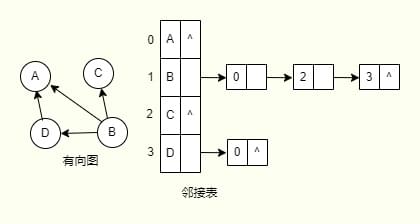
拓扑排序:求取拓扑序列
拓扑排序简单讲就是在可求拓扑序列的有向无回路图(有向无环图)中求取拓扑序列的排序算法。
相关概念
拓扑序列
通俗讲就是按活动的先后次序进行排序的序列,并且每一个顶点只出现一次,它可以表述出完成某一项活动所需要的前置活动都有哪一些!当然,一个图的拓扑排序不唯一。
例子:
-
修学课程都有其先修课程,利用拓扑序列就能快速的获得所有的先修课程
-
游戏任务都有前置任务,利用拓扑序列,就能清楚所有的任务链条
-
依赖包的加载顺序也是利用拓扑序列来处理的
求取拓扑序列的图:有向无环图
- 有向:对于一个顶点到另一个顶点的方向是确定的,也就是连接线出现箭头的图
- 无环:也可称为无回路,从一个顶点出发,经历所有的路径,也不能回到该顶点
所有顶点都满足以上两种情况的图就叫做有向无环图,基本可以认为只有有向无环图才能求取拓扑序列
入度与出度
在有向图中,一个顶点的入度为其所有指向该顶点的箭头个数,出度为其所指向其他顶点的箭头个数。
算法思路
基本思想
- 找到无入度的顶点,输出该顶点,并将其指向的顶点入度数减一
- 重复第一步,直至所有顶点被输出,拓扑序列完成,如果输出的顶点数小于图中顶点的个数,无拓扑序列
代码实现思路
-
定义一个队列、输出数组以及 HashMap
- 队列存储拓扑序列,并最后输出
- 输出数组存放最后队列输出的拓扑序列
- HashMap 存储结点及其入度值
-
遍历所有结点,将所有结点(除入度为零的结点)的入度及其值存放到 HashMap 中,将入度为 0 的结点放置到队列之中
遍历结点可用深度优先遍历,也可广度优先遍历
-
当队列不为空时
- 输出队列一个结点到输出数组中,设为 a
- 将结点 a 所有指向的顶点入度减一
- 若出现入度为 0 的结点,则存入队列之中
-
队列为空,输出的顶点个数小于图顶点数,无拓扑序列,输出 null,否则,拓扑序列输出结束,并返回输出数组
邻接矩阵的拓扑序列
public static char[] foundTopology(GraphM g){
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
HashMap<String,Integer> hashMap= new HashMap<>();
char[] res = new char[g.VertexNum];
//计算每个结点入度值
for (int i = 0;i < g.VertexNum;i++){
String key = String.valueOf(g.Vertex[i]);
int value = 0;
for (int j = 0;j < g.VertexNum;j++){
if (g.EdgeWeight[j][i]!=0){
value++;
}
}
if (value==0){
queue.add(i);
}
hashMap.put(key,value);
}
int j = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int getKey = queue.remove();
res[j++] = g.Vertex[getKey];
for (int k = 0;k < g.VertexNum;k++){
String getPointKey = String.valueOf(g.Vertex[k]);
int getPointValue = hashMap.get(getPointKey);
if (g.EdgeWeight[getKey][k] != 0 && getPointValue != 0){
hashMap.put(getPointKey,getPointValue-1);
if (getPointValue-1==0){
queue.add(k);
}
}
}
}
if (j == g.VertexNum){
return res;
}
return null;
}
邻接表的拓扑序列
由于拓扑序列的求取只需对两点之间的关联关系做出判断,采取邻接矩阵存储结构的图会是更好的选择。如果需要采取邻接表的存储结构来实现的话,更为推荐反向邻接表的形式来进行求取,即以终点指向起点的方式,求取对应的入度值会更为方便,在这里就不对其在多加讨论,可以自行扩展。
当然,实现本代码的前提是能够定义一个有向图,并且遍历图,也为方便以上拓扑排序代码的阅读,故此补充相关的知识。
定义图及其遍历
图的定义一般如下两种方法:
- 邻接矩阵法
- 邻接表法
邻接:两个顶点间存在边或弧
图的遍历可以分为如下两种方法:
- 深度优先遍历 DFS
- 广度优先遍历 BFS
同一遍历方法的遍历顺序可能唯一,原因如下:
- 存储结构不同:邻接表、邻接矩阵
- 出发结点不同
- 连通与否
邻接矩阵法
定义一个二维数组,其中行代表起点,列代表终点,如果两者之间存在连接关系,值为 1 ,否则为 0 。它关于主对角线对称。
算法步骤:
- 确定图的类型(有向图、无向图)、顶点个数、边个数、权值
- 输入所有顶点,存进顶点数组中
- 将边数组定义为 EdgeWeight[顶点数] [顶点数],
- 输入所有边的起点、终点以及权值,在顶点数组中找到对应起点、终点的下标
- 输入对应权值,赋值给 EdgeWeight[起点下标] [终点下标],若为无向图,对应权值再赋值给 EdgeWeight[终点下标] [起点下标],保证双向
- 输出邻接矩阵
邻接矩阵代码
//图邻接矩阵结构
class GraphM {
static final int MaxNum = 20; //图的最大顶点数
static final int MaxValue = 65535; //最大值
int GType; //图的类型(0:无向图 1:有向图)
int VertexNum;//顶点数量
int EdgeNum; //边的数量
char[] Vertex = new char[MaxNum]; //保存顶点信息
int[][] EdgeWeight = new int[MaxNum][MaxNum];//保存权
public GraphM(int GType,int VertexNum,int EdgeNum){
this.GType = GType;
this.EdgeNum = EdgeNum;
this.VertexNum = VertexNum;
}
}
public class graphMaterix {
//创建图邻接矩阵
public static void creatGraph(GraphM gm) {
int i, j, k;
int weight; //权
char startV, endV; //起始,终止顶点
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输入图中各顶点信息:");
for (i = 0; i < gm.VertexNum; i++) {
System.out.println("第" + (i + 1) + "个顶点");
gm.Vertex[i] = (input.next().toCharArray())[0];//保存到顶点数组中
}
System.out.println("输入各边的顶点及权值:");
for (k = 0; k < gm.EdgeNum; k++) {
System.out.println("第" + (k + 1) + "条边");
System.out.println("边的起点为:");
startV = input.next().charAt(0);
System.out.println("边的终点为:");
endV = input.next().charAt(0);
System.out.println("边的权值为:");
weight = input.nextInt();
for (i = 0; gm.Vertex[i] != startV; i++) ; //在顶点数组中查找起点位置
for (j = 0; gm.Vertex[j] != endV; j++) ; //在顶点数组中查找终点位置
gm.EdgeWeight[i][j] = weight;
if (gm.GType == 0) {
gm.EdgeWeight[j][i] = weight;
}
}
input.close();
}
//显示图邻接矩阵
public static void outGraph(GraphM gm){
for(int i=0;i<gm.VertexNum;i++){
System.out.printf(String.valueOf(gm.Vertex[i])+" "); //第一行输出顶点信息
}
System.out.println();
for(int i=0;i<gm.VertexNum;i++){
System.out.printf(String.valueOf(gm.Vertex[i])+" ");
for(int j=0;j<gm.VertexNum;j++){
if(gm.EdgeWeight[i][j]==gm.MaxValue){
System.out.printf(" ");
}else{
System.out.printf(String.valueOf(gm.EdgeWeight[i][j])+" ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Gtype;//图的类型(0:无向图 1:有向图)
int VertexNum;//顶点数量
int EdgeNum; //边的数量
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入图类型(0:无向图 1:有向图)");
Gtype = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入顶点数目!");
VertexNum = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入边数目!");
EdgeNum = in.nextInt();
GraphM gm = new GraphM(Gtype,VertexNum,EdgeNum);
creatGraph(gm);
outGraph(gm);
in.close();
}
}
邻接表法
邻接表是以单链表的进行存储的,每个单链存储某个点可到达的所有点,当然,也可使用数组来实现,这里暂时不提及
算法步骤
-
确定图的类型(有向图、无向图)、顶点个数、边个数、权值
-
定义三个结点类,
- 包含结点编号、下一结点指针以及权值的边结点类 A,
- 包含结点编号以及下一边结点指针的表头结点类 B
- 包含起点字符、终点字符、权值的边结点类 C
-
输入所有顶点,并构造为一个结点类 A 类型 ,下一个边结点设置为空,存进顶点结点数组中,作为链表表头,其下标为其编号
-
输入所有边的起点、终点以及权值,构造出一个结点类型 C 类型,并存进边数组中
-
插入边(前插法:在表头指针与下一边结点指针之间插入)
- 在顶点数组中找到对应起点、终点的下标
- 构造一个边结点 A 类型,使其值为终点值,下一指针值为表头结点的原下一个结点指针,并赋值权值
- 使其起点对应的表头结点的下一指针值为新边结点
- 若为无向图,起点终点转换,再插入边,保证双向边
-
直至遍历完所有边数组即可输出邻接表
- 表头结点下一结点指针为空
- 输入表头元素->NULL
- 若表头结点下一结点指针不为空
- 遍历其单链表,输出所有元素
邻接表代码
import java.util.Scanner;
//边结点类
class edgeNode{
int index; //边终点对应的下标
edgeNode next; //下一个结点
int edgeWeight; //权值
public edgeNode(int index,edgeNode next,int edgeWeight){
this.index = index;
this.next = next;
this.edgeWeight = edgeWeight;
}
}
//顶点结点类
class vertexNode{
char date; //顶点元素
edgeNode firstNode; //第一个边结点
public vertexNode(char date,edgeNode firstNode){
this.date = date;
this.firstNode = firstNode;
}
}
//图邻接表
class graph{
int GType; //图的类型(0:无向图 1:有向图)
int verNum; //顶点数
int edgeNum; //边数
vertexNode[] vertex; //所有的顶点
public graph(int GType, int verNum, int edgeNum) {
this.GType = GType;
this.verNum = verNum;
this.edgeNum = edgeNum;
this.vertex = new vertexNode[verNum];
}
}
//边信息
class edge{
char began; //起点
char end; //终点
int weight; //权值
public edge(char began, char end, int weight) {
this.began = began;
this.end = end;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
public class graphTable {
//查找对应下标
public static int getIndex(graph g,char target){
for (int i = 0;i < g.verNum;i++){
if (g.vertex[i].date == target){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//插入一条边
public static int insertEdge(graph g, edge edge){
int began = getIndex(g,edge.began);
int end = getIndex(g,edge.end);
if (began == -1 || end == -1){//无效边
return -1;
}
//前插法、后插法,这里使用前插法,无需遍历
g.vertex[began].firstNode = new edgeNode(end,g.vertex[began].firstNode, edge.weight);
if (g.vertex[began].firstNode==null){
return -2;
}
if(g.GType == 0){
g.vertex[end].firstNode = new edgeNode(began,g.vertex[end].firstNode,edge.weight);
}
++g.edgeNum;
return 0;
}
//创建图
public static void createGraph(graph g,char[] vertex,
int verNum, edge[] edges,
int edgeNum,int gType){
g.verNum = 0;
g.edgeNum = 0;
g.GType = gType;
for(int i = 0;i<verNum;i++){
g.vertex[i] = new vertexNode(vertex[i],null);
++ g.verNum;
}
for (int i = edgeNum-1;i >= 0;--i){
int value = insertEdge(g,edges[i]);
if (value != 0){
//插入一条边失败
System.out.println("插入边失败");
}
}
}
//展示图
public static void graphShow(graph g){
System.out.println("邻接表如下:");
for(int i = 0;i < g.verNum;i++){
edgeNode firstNode = g.vertex[i].firstNode;
if (firstNode == null){
System.out.println(g.vertex[i].date+"->NULL");
continue;
}
System.out.print(g.vertex[i].date+"->"+firstNode.index);
while (firstNode.next!=null){
System.out.print("->"+firstNode.next.index);
firstNode = firstNode.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入图的类型!(0:无向图;1:有向图)");
int gType = input.nextInt();//图的类型
System.out.println("请输入顶底数");
int vertNum = input.nextInt();//顶点数
System.out.println("请输入边数");
int edgeNum = input.nextInt();//边数
char[] vertex = new char[vertNum];//顶点字符
edge[] edge = new edge[edgeNum];//创建边结点数组
graph g = new graph(gType,vertNum,edgeNum);
//输入顶点
for (int i = 0;i<vertNum;i++){
System.out.println("请输入"+i+"个结点");
vertex[i] = input.next().charAt(0);
}
for (int i = 0;i<edgeNum;i++){
System.out.println("请输入起点");
char began = input.next().charAt(0);
System.out.println("请输入终点");
char end = input.next().charAt(0);
System.out.println("请输入权值");
int weight = input.next().charAt(0);
edge[i] = new edge(began,end,weight);
}
createGraph(g,vertex,vertNum,edge,edgeNum,1);
graphShow(g);
}
}
当然,图的表示不止有以上两者方法,多种多样,可根据需要进行选择。选择方法可参考如下:
- 稀疏图:当边的数量远小于顶点数的平方时
- 稠密图:当边的数量接近或大于顶点数的平方时
通常情况下,使用邻接表表示稀疏图,使用邻接矩阵表示稠密图。不过,如要验证两顶点是否相连,使用邻接矩阵会是个更好选择,因为邻接矩阵为一个二维数组,查询时间复杂度为 O(1),效率更高。
不同结点出发的遍历顺序一定不唯一,同一结点出发的遍历顺序可能不唯一。
深度优先遍历 DFS
每次遍历都先到结点深度最深处,再回溯到上一可切换路径的结点进行又一重复遍历
步骤:
- 从图中某个顶点 v 出发
- 记录此节点,并从 v 未被访问的顶点出发
- 直至与顶点 v 有路径连通的顶点都被访问
- 若图中仍有没被访问的结点,则从其中未被访问的结点出发,重复以上过程
- 直至所有结点都被访问
邻接矩阵深度优先遍历
//深度优先遍历算法
public static void DFSserver(GraphM g, boolean[] visited, int i) {
for (int j = 0;j < g.VertexNum;j++){
if (g.EdgeWeight[i][j] != 0 && !visited[j]){
DFSserver(g,visited,j);
}
}
}
//深度优先遍历操作
public static char[] DFS(GraphM g){
char[] res = new char[g.VertexNum];
boolean[] visited = new boolean[g.VertexNum];
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0;i < g.VertexNum;i++){
if (!visited[i]){
visited[i] = true;
res[k++] = g.Vertex[i];
DFSserver(g,visited,i);
}
}
return res;
}
邻接表深度优先遍历
//深度优先遍历算法 DFS
public static void DFSserver(GraphT g,boolean[] visited,int i) {
edgeNode firstNode = g.vertex[i].firstNode;
while (firstNode!=null){
if (!visited[firstNode.index]){
DFSserver(g,visited,firstNode.index);
}
firstNode = firstNode.next;
}
}
//深度优先遍历操作
public static char[] DFS(GraphT g){
char res[] = new char[g.verNum];
boolean[] visited = new boolean[g.verNum];
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < g.verNum;i++){
if (!visited[i]){
visited[i] = true;
res[j++] = g.vertex[i].date;
DFSserver(g,visited,i);
}
}
return res;
}
广度优先遍历 BFS
遍历一个结点先将其所有指向结点遍历,在进入下一层进行遍历
- 定义一个队列以及一个标记数组
- 取图某一结点 A ,入队,并在标记数组对应值标记为 True
- 将每一个与结点 A 相关联的结点一一判断是否已被标记为 True ,
- 若已标记,跳过
- 若存在未被标记的结点,即结点 A 出队,未被标记的结点入队
- 依次将入队元素一一入队,重复第三步
- 队列为空,广度优先遍历结束
邻接矩阵广度优先遍历
//广度优先遍历 BFS
public static char[] BFS(GraphM g){
boolean[] visited = new boolean[g.VertexNum];
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
char[] res = new char[g.VertexNum];
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < g.VertexNum;i++){
if (!visited[i]){
visited[i] = true;
res[j++] = g.Vertex[i];
queue.add(i);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
queue.remove();
for (int k = 0;k<g.VertexNum;k++){
if (g.EdgeWeight[i][k] != 0 && !visited[k]){
visited[k] = true;
res[j++] = g.Vertex[k];
queue.add(k);
}
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
邻接表广度优先遍历
//邻接表广度优先遍历 BFS
public static char[] BFS(GraphT g){
boolean[] visited = new boolean[g.verNum];
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
char[] res = new char[g.verNum];
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < g.verNum;i++){
if (!visited[i]){
visited[i] = true;
res[j++] = g.vertex[i].date;
queue.add(i);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
queue.remove();
edgeNode firstNode = g.vertex[i].firstNode;
while (firstNode != null){
if (!visited[firstNode.index]){
visited[firstNode.index] = true;
res[j++] = g.vertex[firstNode.index].date;
queue.add(firstNode.index);
}
firstNode = firstNode.next;
}
}
}
}
return res;
}