链表习题详解
习题主要用于自我复习,若绝对质量不错,也可以自行提取
移除链表元素
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
if(head==NULL)
return NULL;
//这边一定要在前面加一个head 不然就会出现NULL->val这个东西会报错
//同时第一个循环是为了防止出现一开始就出现和val相等的数字
while(head&&head->val==val)
{
head = head->next;
}
struct ListNode*cur = head;//让其等于头指针的位置 方便循环 但是不改变头指针的值
struct ListNode*prev = NULL;
while(cur)//循环的终止条件是当cur为空指针的时候
{
if(cur->val!=val)
{
prev = cur;//prev的地址始终在head之前
cur = cur->next;
}
else
{
prev->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = prev->next;
}
}
return head;
}
链表的逆置
注意刚开始的时候newnode是NULL 因为链表的终点就是NULL,因此这样写
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode*newnode = NULL;
struct ListNode*ret = NULL;
if(head==NULL)
return NULL;
while(cur)
{
//链表逆置关键:下一个指向前一个
ret = cur->next;
cur->next = newnode;//刚开始的newnode是NULL符合题意
newnode = cur;//
cur = ret;
}
head = NULL;
return newnode;
}
配图一张
链表的中间结点
先写我自己的代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode*cur = head;
int sum = 0;
while(cur)
{
sum++;
cur = cur->next;
}//算出结点的总个数
sum = sum/2+1;//此时的sum就是中间结点
struct ListNode*newnode = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
newnode->next = head;
while(sum--)
{
newnode = newnode->next;
}
return newnode;//这样就可以直接得到中间结点
}
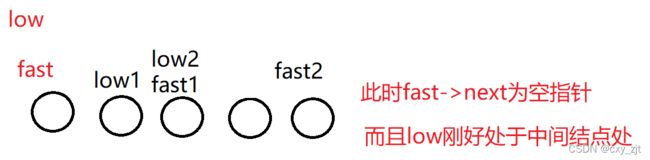
另外一个思路:快慢指针
两个指针的初始位置都一样 但是快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步
这样走的话当快指针为NULL的时候,慢指针的位置就是中间结点的位置
证明如下:
如果是偶数个结点

struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode*fast = head;
struct ListNode*low = head;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
low = low->next;
}
return low;
}
倒数第k个结点
这个也属于快慢指针问题
思路:让快指针先走k步 然后两个指针再同时走,当快指针到NULL时候 慢指针就是倒数第k个结点了
图示如下
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*
* C语言声明定义全局变量请加上static,防止重复定义
*/
/**
*
* @param pListHead ListNode类
* @param k int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k )
{
struct ListNode* fast = pListHead;
struct ListNode*low = pListHead;
if(pListHead==NULL)
return NULL;
while(k--)
{
if(fast ==NULL)
return NULL;//这个一定要加上去 防止k大于结点数 这个时候一定是返回空指针的
fast = fast->next;
}
while(fast)
{
fast = fast->next;
low = low->next;
}
return low;
}
链表分割
题意解释:
假设数字是 3 5 6 7 8 9 7 分割数字取的是8
那么最终的链表是3 5 6 7 7 8 9
假设数字是7 8 9 6 77 2 1 6 分割数字取的是8
那么最终的链表是 7 6 2 1 6 8 9 77
就是把比分割数字小的数字排在前面 比分割数字大的值排在后面 但是顺序不能改变。
思路:我们可以先设置两个链表 less greater
less表示比分割数字小的数字 但是greater表示比分割数字大的数字
然后将less尾结点与greater头结点链接在一起
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {
if(pHead==NULL)
return NULL;
struct ListNode*less = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode*greater = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode*cur = pHead;
struct ListNode*ret = greater;
struct ListNode*start = less;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val<x)
{
less->next = cur;
less = cur;
}
else
{
greater->next = cur;
greater = cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
greater->next = NULL;//这个条件一定得加上,不然有可能会变成循环链表
less->next = ret->next;
return start->next;//这边一定要写start 因为less的值已经改变了
}
};
**注意:**这道题的代码一定得加上这个 greater->next = NULL;
图示理解一下
回文序列
思路一:
暴力求解,直接将链表val上的值转化到数组中去,然后根据双指针解决,土方法,但只适用于结点数较小的问题也是我一开始想到的方法
代码如下:
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {
public:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
int arr[910] = {0};
int k = 0;
while(A->next)
{
arr[k++] = A->val;
A = A->next;
}
arr[k++] = A->val;
int l = 0,r = k-1;
while(l<r)
{
if(arr[l]!=arr[r])
return false;
else
{
l++;
r--;
}
}
return true;
}
};
思路二:
先找到中间结点,然后将中间结点后半部分逆置,接着与前面的结点比较
利用快慢指针找到中间结点,然后链表的逆置即可
代码如下:
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {
public:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A)
{
if(A==NULL)
return NULL;
//先得出中间结点
struct ListNode*fast = A;
struct ListNode*low = A;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
low = low->next;
}
struct ListNode*pp = NULL;
struct ListNode*cur = low;
struct ListNode*newnode = NULL;
while(cur)
{
pp = cur->next;
cur->next = newnode;
newnode = cur;//newnode这一步一定不能忘记h
cur = pp;
}
//再拿原来的链表与从中间结点逆置后的链表比较
struct ListNode* ret = A;
while(ret&&newnode)
{
if(ret->val!=newnode->val)
return false;
else
{
ret = ret->next;
newnode = newnode->next;
}
}
return true;
}
};
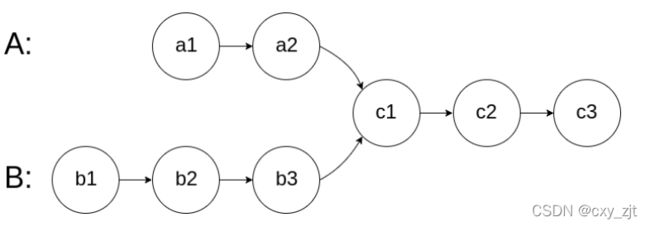
相交链表
思路:
先算出两个链表的长度,命名为lenA 与lenB 假设两个长度的差值是K
让较长的链表走k步,然后两个链表同时走,每走一步就比较二者的地址
一定是地址,数字可能是一样的 若地址相同,则直接返回地址即可
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
int lenA = 0;
int lenB = 0;
struct ListNode * listA = headA;
struct ListNode *listB = headB;
while(listA)
{
lenA++;
listA = listA->next;
}//测出链表的长度
while(listB)
{
lenB++;
listB = listB->next;
}
int k = 0;
struct ListNode *newheadA = NULL;
struct ListNode *newheadB = NULL;
if(lenA>lenB)//这部分可以使得newheadA一定是较长的那个链表
//避免了代码的重复
{
newheadA = headA;
newheadB =headB;
k = lenA-lenB;
}
else
{
newheadA = headB;
newheadB = headA;
k = lenB-lenA;
}
while(k--)
{
newheadA = newheadA->next;
}
while(newheadA&&newheadB)
{
if(newheadA==newheadB)
return newheadA;
else
{
newheadA = newheadA->next;
newheadB = newheadB->next;
}
}
return NULL;
}