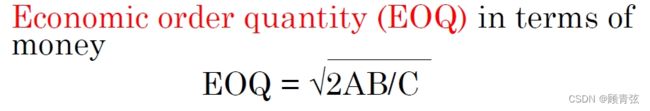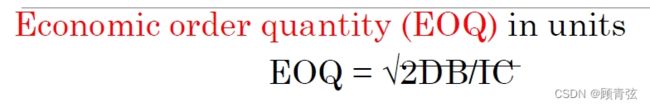【北邮国院大三下】Logistics and Supply Chain Management 物流与供应链管理 Week3
北邮国院大三电商在读,随课程进行整理知识点。仅整理PPT中相对重要的知识点,内容驳杂并不做期末突击复习用。个人认为相对不重要的细小的知识点不列在其中。如有错误请指出。转载请注明出处,祝您学习愉快。
如需要pdf格式的文件请私信联系或微信联系
Manufacturing Costs vs. Non-manufacturing costs
Manufacturing Costs are those costs that are directly involved in manufacturing of products. E.g. raw materials costs and charges related workers.
制造成本是指与产品制造直接相关的成本。例如原材料成本和相关工人费用。
- Direct materials cost 直接原料成本
- Direct labour cost 直接人工成本
- Manufacturing overhead cost 制造费用成本
Non-manufacturing Costs are those costs that are not directly incurred to manufacture a product, such as: salary of sales personnel and advertising expenses.
非制造成本是指不直接产生于制造产品的成本,如:销售人员的工资和广告费用。
- Selling and distribution costs 营销费用
- Administrative costs 行政成本
Cost Reduction vs. Sales Increase
省流:cost reduction对于提高利润来说更effective
Profit Leverage Effect 利润杠杆效应
Measurable cost savings that don’t hurt sales have a tremendous impact on the bottom line.
不影响销售的可衡量的成本节约对底线有巨大的影响。
Profit impact of cost reduction is much greater than the impact of increased sales.
成本降低对利润的影响远大于销售增加的影响。
The lower the average profit margin, the greater the impact.
平均利润率越低,影响越大。
Strategic Cost Management: Principles 战略成本管理:原则
Strategic cost management uses cost management techniques to reduce the organisations costs and improve profit while supporting its value proposition.
战略成本管理使用成本管理技术来降低组织的成本,提高利润,同时支持其价值主张。
Three elements of strategic cost management:
战略成本管理的三个要素:
- Supply Chain Analysis 基于供应链的分析
- Value Proposition Analysis 价值主张分析
- Cost Driver Analysis 成本动因分析
Supply Chain Analysis
Supply chain analysis is the examination of the management of the flow of information, inventory, processes, and cash flows from the earliest supplier to the ultimate consumer, including the final disposal process.
供应链分析是对从最早的供应商到最终消费者的信息流、库存、流程和现金流的管理的检查,包括最终的处置过程。
Value Proposition Analysis
Value proposition analysis is the essence of a corporation strategy, determining how an organisation chooses to compete in its markets.Generic value propositions include:
价值主张分析是公司战略的本质,决定了一个组织如何选择在其市场上竞争。一般价值主张包括:
- Cost leadership 成本领导:一种竞争优势策略,企业通过降低生产成本、提高生产效率等方式,使其产品或服务的成本低于竞争对手,从而在市场上取得优势。
- Technology leadership 技术领导
- Differentiation strategies 差异化战略:一种企业竞争策略,通过提供独特的产品或服务来吸引客户,从而在市场上脱颖而出。
New approaches for achieving competitive advantage include:
获得竞争优势的新方法包括:
- First to market provider: This was a very popular strategy in the late 1990s and continues to be an important approach to doing business today. 率先进入市场的供应商:这在20世纪90年代后期是一种非常流行的策略,并且仍然是今天开展业务的重要方法。
- Service/solution provider: This has become one of the key ways for organisations to compete in this decade. Being a full-service solution provider requires a high level of understanding of customer needs and flexibility and willingness to meet those customer needs. 服务/解决方案提供商:这已成为组织在这十年中竞争的关键方式之一。作为一个提供全方位服务的解决方案提供商,需要对客户需求有高度的了解,并具备满足这些客户需求的灵活性和意愿。
- Technology Leader: This is a focused innovation approach, whereby the organisation competes by providing the latest and greatest technology to its customers. 技术领导者:这是一种专注的创新方法,组织通过向客户提供最新最好的技术来竞争。
Companies may choose a combination of value propositions.
公司可能会选择价值主张的组合。
Different strategic business units within the same company may choose different value propositions.
同一公司内不同的战略业务单位可能选择不同的价值主张。
Value propositions may change over the product life cycle.
价值主张可能在产品生命周期中发生变化。
Cost Driver Analysis
Cost driver analysis identifies processes, activities, and decisions that actually create cost for the supply chain.
成本驱动分析确定了实际为供应链创造成本的过程、活动和决策。
Cost drivers vary over time and among different products and services.
成本驱动因素随着时间和不同的产品和服务而变化。
Generic Cost Drivers 一般成本驱动因素
Level of outsourcing within a company. Companies that outsource may experience higher costs for additional services than if it had internal operations.
**公司内部的外包水平。**外包的公司可能会比内部运营的公司在额外服务上付出更高的成本。
Use of nonstandard materials, components and parts. Custom items are more costly because of low economies of scale. Custom parts may have better performance or lower operating costs.
**使用非标准材料、零部件。**由于规模经济低,定制物品的成本更高。定制部件可能具有更好的性能或更低的操作成本。
Scale of operations. Very large manufacturing operations must have high stable volume.
**经营规模。**非常大的制造业务必须有高稳定的产量。
High level of finished goods product mix. The more options the organisation offers its customers, the more inventory it may have to carry, and the more flexible its production operations must be.
**高水平的成品产品组合。**组织为客户提供的选择越多,它可能需要携带的库存就越多,其生产操作就必须更加灵活。
Cost Driver Analysis - Considerations
Cost drivers are not inherently good or bad.
成本驱动因素本身没有好坏之分。
Cost reduction strategies must analyse cost drivers in relation to their impact on the value proposition.
成本降低策略必须分析成本驱动因素对价值主张的影响。
Cost-Reduction Considerations
For each product or service, how do you become aware of the value proposition in your organisation at any point in time?
对于每一种产品或服务,你如何在任何时候意识到你的组织的价值主张?
What is the value proposition for your organisation, product, service?
你的组织、产品、服务的价值主张是什么?
Does the value proposition vary among business units and products or services?
不同业务单位、不同产品或服务的价值主张是否不同?
If so, are you certain you have identified the right value proposition?
如果是这样,你确定你已经确定了正确的价值主张吗?
Does the value proposition vary over time?
价值主张是否随时间变化?
- If so, are you certain you have identified the current or future value proposition? 如果是,你确定你已经确定了当前或未来的价值主张吗?
Will current/proposed activities be transparent to the customer?
当前/提议的活动对客户是否透明?
- If not, what in what way will they be visible? 如果没有,他们将以何种方式被看到?
- Are these areas that the customer values? 这些领域是客户所看重的吗?
- Will the impact be positive, negative or neutral? 影响是正面的、负面的还是中性的?
Responsibility for Strategic Cost Management
Historically accounting and finance had responsibility for reporting and managing costs.
历史上,会计和财务部门负责报告和管理成本。
SCM requires a broader cost perspective.
供应链管理需要更广阔的成本视角。
Strategic Cost Management Tools
Cost analysis: including “should-cost” analysis or zero-based pricing, as well as analysis of service provider cost elements.
成本分析:包括“应该成本”分析或零基定价,以及服务提供商成本要素分析。
Price analysis: understanding the prices available in the competitive marketplace.
价格分析:了解竞争市场中可用的价格。
Total cost of ownership: analysing the true cost of acquisition, use, maintenance and disposal of a good, service, capital equipment, or process.
总拥有成本:分析商品、服务、资本设备或过程的获取、使用、维护和处置的真实成本。
Target costing: determining what the market will bear and working backwards to see how much you can afford to produce the product or service for, and still make a profit
目标成本:确定市场将承受什么,并向后工作,看看你能负担多少生产产品或服务,仍然有利润
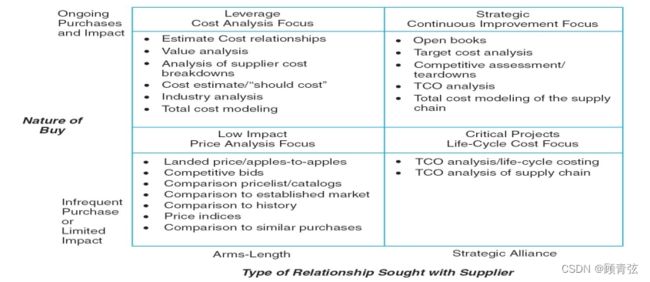
Decision Classification 决策分类
Once the process has been mapped and a good understanding of the system has been achieved, a decision matrix can be used to determine the appropriate cost management tool.
一旦对流程进行了映射,并且对系统有了很好的理解,就可以使用决策矩阵来确定适当的成本管理工具。
The decision matrix classifies decisions according to:
决策矩阵对决策进行分类:
- Nature of the Buy 购买的性质
- Relationship with Supplier 与供应商的关系
Nature of the Buy
Is the cost of the item or service important, perhaps due to high volume?
产品或服务的成本是否重要,也许是由于量大?
Is the technology used by the supplier critical to the product’s image, performance or quality?
供应商使用的技术对产品的形象、性能或质量是否至关重要?
Does the supplier have a critical brand name or image that you can use to generate sales?
供应商是否有一个关键的品牌名称或形象,你可以用它来产生销售?
Is the technology used by the supplier critical to future products, line extensions, or the next generations of products?
供应商使用的技术对未来的产品、生产线扩展或下一代产品是否至关重要?
Is the item critical to getting leverage with supplier for other buys?
该项目是否对其他采购的供应商至关重要?
Could the item create environmental or safety concerns?
该项目是否会造成环境或安全问题?
Are there limited good sources available?
可用的优质资源有限吗?
Is the item purchase ongoing?
物品是否正在购买?
Other issues that complicate the buying situation for your organisation at this time?
还有其他问题使您的组织目前的采购情况复杂化吗?
Relationship with Supplier
Supplier Relationships Sought
How long would we like to continue to do business with this supplier?
我们想和这家供应商继续做多久的生意?
If we desire an on-going relationship, would we like this supplier to be aware of our intentions?
如果我们想要一个持续的关系,我们希望这个供应商知道我们的意图吗?
Would we like to share information related to the buy with the supplier?
我们是否愿意与供应商分享与采购相关的信息?
Would we like the supplier to become involved in our product or service development?
我们是否希望供应商参与我们的产品或服务开发?
Would we like the supplier to locate one or more of its employees at our facility?
我们是否希望供应商在我们的工厂安排一名或多名员工?
Other issues that affect the nature of the desired relationship with this supplier at this time?
目前是否有其他问题影响到与该供应商的预期关系?
根据decision matrix的分类,可以把Suppliers/Purchases分成四类
- Low Impact – low-cost commodity items; focus is on price analysis/comparison 低影响-低成本商品项目;重点是价格分析/比较(买的少,不需要和供应商建立长期合作关系)
- Leverage – large purchases of items in competitive markets; focus is on cost analysis 杠杆——在竞争激烈的市场上大量购买物品;重点是成本分析(买的多,不需要和供应商建立长期合作关系)
- Strategic Item – large purchases from important suppliers; focus is on continuous improvement 策略性项目-从重要供应商大量采购;专注于持续改进(买的多,需要和供应商建立合作关系)
- Critical Projects – large dollar volume infrequent purchase; focus is on life cycle cost 关键项目-大量不频繁的采购;重点是生命周期成本(买的多 但不频繁 ,需要和供应商建立合作关系,或者说这个东西极其重要)
Tool Selection
感觉意思是对这四种分类各自的分析方法
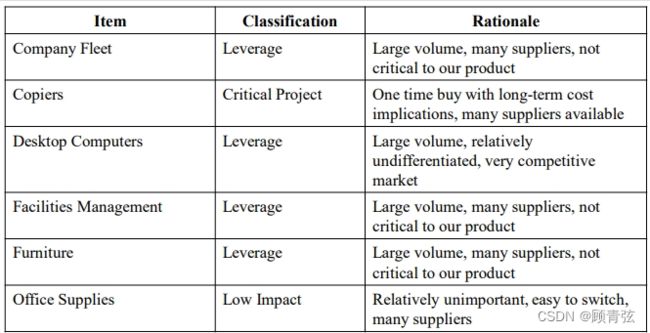
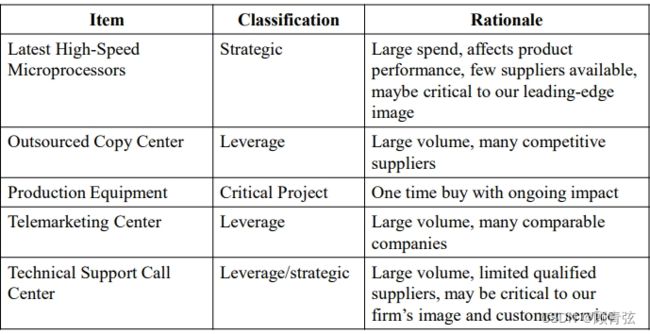
Commodity Classifications
根据上面的定义,分析每个为什么这么分类的原因
Activity-Based Cost (ABC) Management 作业成本管理
Traditional cost accounting systems are used for internal reporting costs.
传统的成本会计系统用于内部报告成本。
Ideally, cost accounting would like to use direct costing which determines cost based on actual expenditures.
理想情况下,成本会计会采用直接成本法,根据实际支出来确定成本。
Overhead, a pool of indirect costs, complicates direct costing.
间接费用池使直接成本计算复杂化。
Traditional Cost Accounting
Traditional cost accounting aggregates all indirect expenses into a classification called “overhead”.
传统的成本会计把所有间接费用归为“间接费用”一类。
Overhead is then allocated to production based on some benchmark activity.
然后根据一些基准测试活动将开销分配给生产。
Changes to the benchmark activity may distort true cost performance.
对基准活动的更改可能会扭曲真实的成本性能。
Activity-Based Cost Management
Activity-based accounting provides a more accurate alternative to traditional cost accounting.
作业会计为传统成本会计提供了一种更准确的替代方案。
Activity-based accounting attempts to match indirect costs with the products or services that generate them.
基于作业的会计试图将间接成本与产生间接成本的产品或服务相匹配。
Activity-based accounting allocates indirect costs based on the cost drivers that actually create them.
作业会计根据实际产生间接成本的成本驱动因素来分配间接成本。
反正就是更精确的确定了成本
Implementation of an ABC accounting system is a nontrivial event. Organisations may have to rethink:
实施ABC会计制度是一件非常重要的事情。组织可能不得不重新考虑:
- Pricing strategy 定价策略:企业制定的一种用于确定产品或服务价格的方法,以实现特定的市场目标,如提高市场份额、提高利润或吸引新客户。
- Marketing strategy 营销策略:一种为产品或服务制定的计划,旨在实现市场目标和提高销售业绩。
- Manufacturing strategy 制造策略
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
…includes all relevant costs, such as administration, follow-up, expediting, inbound transportation, inspection, and testing, rework, storage, warranty, service, downtime, customer returns, and lost sales.
包括所有相关成本,如管理、跟踪、加急、入库运输、检验和测试、返工、储存、保修、服务、停机、客户退货和销售损失。
Attempts to look at the big picture, considering cost beyond that of the purchase price.
试图从大局出发,考虑购买价格之外的成本。
a philosophy for understanding all relevant supply chain related costs of doing business with a particular supplier for a particular goods/service, or the cost of the process, e.g. supply chain design.
一种理解与特定供应商就特定商品/服务开展业务的所有相关供应链相关成本的理念,或流程成本,例如供应链设计。
我的理解是,TCO像冰山(icgberg)一样,比表面上看着多很多
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
Step 1: Identification of Benefits Sought 确定所寻求的利益
Step 2: Form a TCO Team 组建TCO团队
Step 3: Identify Cost Drivers 识别成本驱动因素
Step 4: Fine Tune 微调
Step 5: Present 呈现
Step 1: Identification of Benefits Sought 确定所寻求的利益
The first step in TCO analysis is to determine the benefits sought from the analysis. Reasons to conduct TCO analysis include:
TCO分析的第一步是确定从分析中寻求的利益。进行TCO分析的原因包括:
- Performance measurement 绩效评估:一种对个人、团队或组织的工作表现进行定量和定性评价的方法,以便了解其是否达到预期目标和标准。
- Framework for cost analysis 成本分析框架
- Benchmarking performance 对标绩效
- More informed decision making 更明智的决策
- Communication of cost issues internally and with suppliers 与公司内部及供应商沟通成本问题
- Encourages cross-functional interaction 鼓励跨职能互动
- Support external teams with suppliers 为外部团队提供供应商支持
- Better insight/understanding of cost drivers 更好的洞察/理解成本驱动因素
- Build a business case 建立一个商业案例
- Support an outsourcing analysis 支持外包分析
- Support continuous improvement 持续的质量改进
- Helps identify cost savings opportunities 帮助确定节省成本的机会
- Prioritise/focus your time on high potential opportunities 把你的时间放在高潜力的机会上
Good Candidates for TCO Analysis TCO分析的良好候选人
Products and services that match the following criteria are good candidates for TCO Analysis:
符合以下标准的产品和服务是TCO分析的良好候选者:
- The firm spends a relatively large amount of money on the item 公司在这个项目上花了相当大的一笔钱
- The firm purchases the item with some degree of regularity, in order to provide some historical data, but more importantly, to allow opportunities to gather current cost information. 公司以某种程度的规律性购买物品,以便提供一些历史数据,但更重要的是,允许有机会收集当前成本信息。
- Purchasing believes the item has significant transaction costs associated with it that are not currently recognised. 采购部门认为,该项目有重大的交易成本,目前尚未确认。
- Purchasing believes that one or more of the currently unrecognised transaction costs is individually significant. 采购部认为,一项或多项当前未确认的交易成本单独具有重大意义。
- Purchasing has the opportunity to have an impact on transactions costs, via negotiation, changing suppliers, or improving internal operations. 采购有机会对交易成本产生影响,通过谈判,更换供应商,或改善内部运作。
- Those purchasing/using the item will cooperate in data gathering to learn more about the item’s cost structure. 购买/使用该物品的人将合作收集数据,以更多地了解该物品的成本结构。
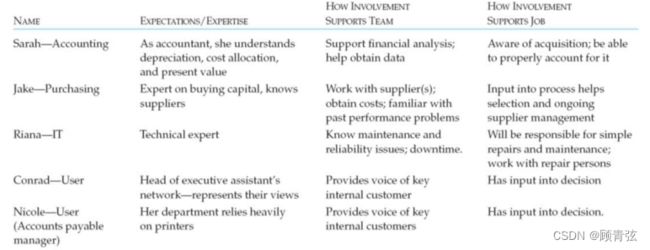
Step 2: Form a TCO Team 组建TCO团队
Once a project has been identified, a TCO team should be formed. Members should include purchasing, users, and any functional/technical experts.
一旦确定了项目,就应该组建TCO团队。成员应包括采购、用户和任何功能/技术专家。
Step 3: Identify Cost Drivers 识别成本驱动因素
Begin the analysis by expressly identifying potential costs by mapping the process flow for all aspects of the project.
通过映射项目的所有方面的过程流,明确地识别潜在的成本,从而开始分析。
From the flowcharts, brainstorm key cost drivers.
根据流程图,对主要的成本驱动因素进行头脑风暴。
Gather cost data for all identified cost driver for each alternative.
收集成本数据,为所有确定的成本驱动方案。
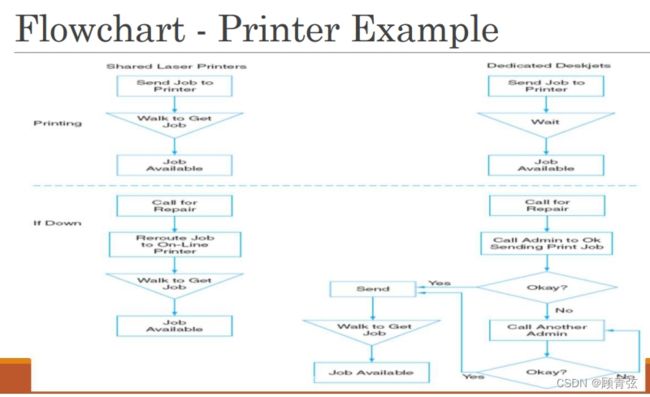
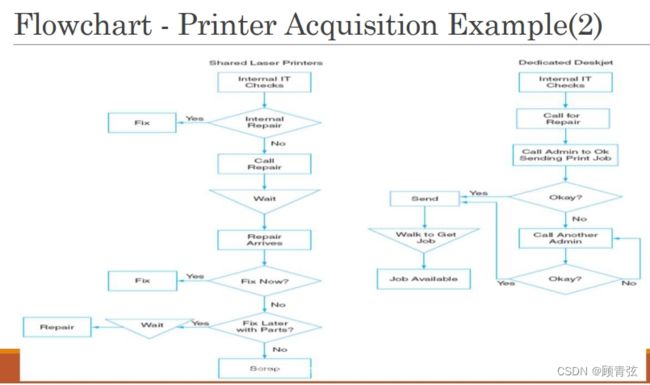
举个例子 - printer
根据流程图分析出key cost drivers
确定了这些yes,下一步就是gather cost data
Step 4: Fine Tune 微调
Step 4 allows for fine tuning of the TCO analysis including the use of sensitivity analysis.
步骤4允许对TCO分析进行微调,包括使用灵敏度分析。
- Sensitivity analysis allows for testing of “what-if” scenarios. 敏感性分析允许测试“假设”场景。
- Decisions that do not change based on changes to assumptions of data are said to be robust. 不因数据假设的变化而改变的决策被称为稳健决策。
- Managers can have more confidence in robust decisions 管理者可以对强有力的决策更有信心
Step 5: Present 呈现
Step 5 requires that the TCO analysis findings be presented to the appropriate management level.
第5步要求将TCO分析结果呈现给适当的管理层。
- Format for presentation should include: 展示的格式应包括:
- Summary of TCO analysis results TCO分析结果总结
- Sensitivities 灵敏度
- Non-Cost Issues 非成本问题
- Recommendation 正式建议
- Presentation should also include “soft” costs 报告还应包括“软”成本
Inventory 库存
Inventories are stocks of goods and materials that are maintained to satisfy normal demand patterns
存货是为了满足正常需求模式而储存的货物和材料
Reason (of having inventory) #1: to meet anticipated demand and protect against stock-outs 以满足预期的需求和防止缺货
Why Study Inventory Management?
Inventory is the largest factor in manufacturing costs, and efficient Inventory Management has the greatest potential for increasing profitability
库存是制造成本中最大的因素,有效的库存管理具有提高盈利能力的最大潜力
E.g. For a typical US manufacturer 60% of corporate income goes towards the purchase of materials
对于一个典型的美国制造商来说,60%的公司收入用于购买材料
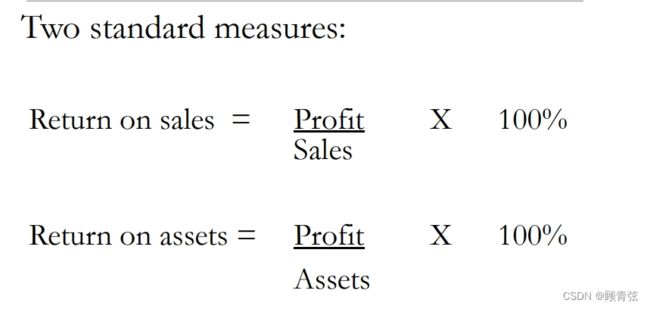
Stockholding & Profitability 库存量&利润率
(ROS & ROA)
Inventory reduces the return on sales, but the effect on asset return is even greater.
库存降低了销售回报率,但对资产回报率的影响更大。
- 这里PPT里有个计算的例子,自己去看一下算一下会更明白
Inventory Management
Inventory costs are important to consider
库存成本是需要考虑的重要因素
- Inventory turnover: cost of goods sold divided by average inventory at cost 存货周转率:售出商品的成本除以按成本计算的平均存货

Compare with competitors or benchmarked companies
与竞争对手或基准公司进行比较
Inventory holding always carries COST. This COST should be set against the BENEFITS provided.
存货持有总是包含成本。该费用应与所提供的效益相对照。
Role of Inventory in the Supply Chain
Inventory Management - considerations
Why is there a need to hold stock?
为什么需要持有库存?
Evens out fluctuations in demand
平衡需求的波动
Categorisation of different types of stock
对不同类型的库存进行分类
Costs associated with stockholding
与持有库存有关的成本
Planning stock levels
规划库存水平
Replenishment systems
补货系统
Trade-off areas
平衡地区
Why carry Inventory?
- Provide product availability 提供产品可用性
- Buffer production or acquisition costs 缓冲生产或购置成本
- Buffer distribution costs 缓冲配送成本
- Hedge against inflation 抵御通涨
- Protect against uncertainty 防范不确定性
- Protect against unexpected events 防范突发事件
Inventory Management
Low inventory turnover = high inventory carrying costs, little (or no) stockout costs
低库存周转率=高库存持有成本,很少(或没有)缺货成本
High inventory turnover = low inventory carrying costs, high stockout costs
高库存周转率=低库存持有成本,高缺货成本
Managing the trade-off (product availability/responsiveness vs. cost/efficiency) is important to maintain service levels
管理权衡(产品可用性/响应性vs.成本/效率)对于维持服务水平非常重要
Demand planning 需求规划
一共有三种type:Trend, Seasonality, Random
Trend
- Description: Underlying growth or decline 描述:潜在的增长或下降
- Planning: Monitor and forecast 计划:监控和预测
Seasonality
- Description: Predictable peaks and troughs 描述:可预测的高峰和低谷
- Planning: make seasonal allowances 计划:做季节性补贴
Random
- Description: Day-to-day variation 描述:日常变化
- Planning: Appropriate safety stock level 计划:适当的安全库存水平
Inventory Classifications
- Psychic stock (stimulates demand) 心理储备(刺激需求)
- Cycle or base stock 循环或基础原料
- Safety or buffer stock 安全或缓冲库存
- Pipeline or in-transit stock 管道或在途库存
- Speculative stock 投机性库存
Inventory-related costs(四种)
Holding costs: 持有成本
- Opportunity (interest) 机会利率
- Storage and warehousing 仓库及货仓
- Insurance 保险
- Obsolescence, shrinkage, deterioration, depreciation 陈旧、萎缩、变质、折旧
Capital costs: 基本建设成本
- Set up and skills 设置和技能
- Waste 浪费
- Quality control 质量控制:一种对产品或服务的质量进行监督和管理的过程,以确保其满足既定的质量标准和客户需求。
- Administration 管理
Stock-out costs
缺货成本
Production and transportation costs
生产和运输成本
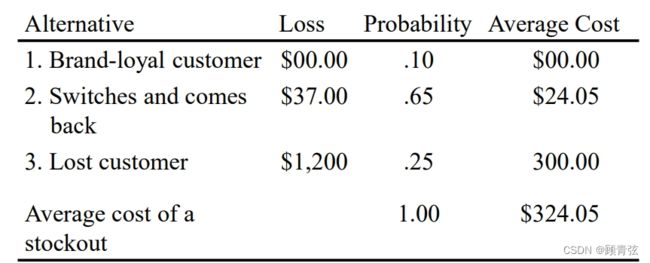
Determination of the Average Cost of a Stockout
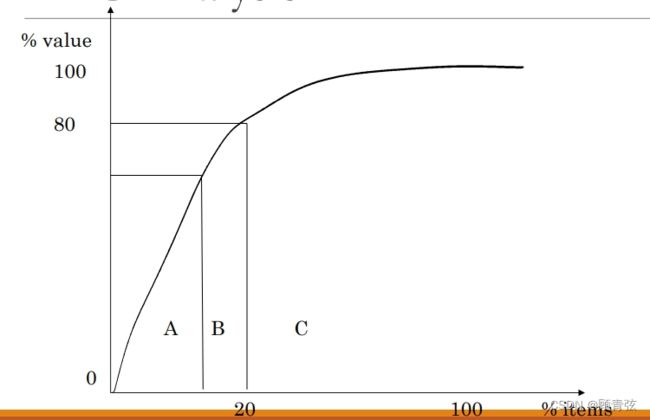
Pareto Curve & ABC Analysis
The Pareto Curve is a mathematical illustration of a common real life event. In a distribution of items and frequencies, nearly always it will be found that 80% of items account for 20% of frequencies. Thus with stocks:
帕累托曲线是对现实生活中常见事件的数学说明。在项目和频率的分布中,几乎总是会发现80%的项目占20%的频率。库存也是如此:
Typically:
- Class A 5% items covering 55% value
- Class B 15% items covering 25% value
- Class C 80% items covering 20% value
Advantages of the techniques:
- Assess criticality of some parts 评估某些部件的临界性
- Assess relative importance of different parts 评估不同部分的相对重要性
- Identify potential obsolete stock line 识别潜在的废弃库存线
- Control frequency size of replenishment orders 控制补货订单的频率大小
- Balance service levels against stockholdings 平衡服务水平和库存
CLASS A
- Can be controlled statistically. Good forecasting essential. Major stock control effort in this group. Safety stock usually employed, recalculated on frequent basis. Expert market knowledge desirable. 可以被统计控制。良好的预测是必不可少的。本组主要的库存控制工作。通常使用的安全库存,经常重新计算。精通市场知识尤佳。
CLASS B
- Often controlled by computerised methods (materials requirements planning). Good forecasting desirable. Lean stock buffers. Manage by exception where possible 通常由计算机化方法控制(物料需求计划)。良好的预测是可取的。精益库存缓冲。在可能的情况下通过异常进行管理
CLASS C
- Simple methods (two bin … ) may be used. Larger safety stocks allowed. Orders can be less frequent. Simple, often visual controls. 简单的方法(两个罐子…)可以使用。允许更大的安全库存。订单可以不那么频繁。简单,通常是视觉控制。
Note: annual stock usage must be used, not current consumption
注:必须使用年度库存用量,而不是当前用量
Inventory Management (图片分析)
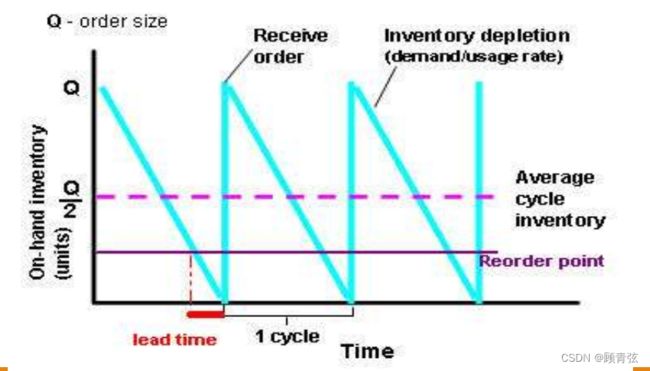
When to Order (Reorder point)
Reorder point (ROP)
- ROP = DD x RC under certainty
- ROP = (DD x RC) + SS under uncertainty
Where
DD = daily demand 每日需求量
RC = length of replenishment cycle 补给周期的长度
SS = safety stock 安全库存
How Much to Reorder (Reorder Quantity)
Economic order quantity (EOQ) 经济定货量
Where
EOQ = the most economic order size, in dollars EOQ =最经济的订单规模,以美元为单位
A = annual usage, in dollars 年使用量,以美元计
B = administrative costs per order of placing the order 每笔订单的行政费用
C = carrying costs of the inventory (%) 存货的持有成本(%)
Where
EOQ = the most economic order size, in units
A = annual demand, in units
B = administrative costs per order of placing the order
C = carrying costs of the inventory (%)
I = dollar value of the inventory, per unit 每单位存货的美元价值
Inventory Flows
Safety stock can prevent against two problem areas
安全库存可以防止两个问题区域
- Increased rate of demand 需求增加率
- Longer-than-normal replenishment 比往常更久的补货时间
When fixed order quantity system like EOQ is used, time between orders may vary
当使用EOQ等固定订单数量系统时,订单之间的时间可能会有所不同
When reorder point is reached, fixed order quantity is ordered
当到达再订货点时,订购固定数量的订货
Contemporary Approaches of IM
- ABC Analysis
- Just-in Time (JIT)
- Approach Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI) 供应商管理库存方法(VMI)
- VMI employs the same principles as those of JIT inventory, however, the responsibilities of managing inventory is placed with the vendor VMI采用与JIT库存相同的原则,但是,管理库存的责任由供应商承担
- Inventory Tracking 库存跟踪
Just-in-time
Just in time (JIT) is a production strategy that strives to improve a business return on investment (ROI) by reducing in-process inventory and associated carrying costs. To meet JIT objectives, the process relies on signals or Kanban between different points in the process, which tell production when to make the next part.
准时制(JIT)是一种生产策略,致力于通过减少过程中库存和相关的携带成本来提高业务投资回报(ROI)。为了达到JIT的目标,过程依赖于过程中不同点之间的信号或看板,这些信号或看板告诉生产部门什么时候制造下一个部件。
Kanban
Kanban are usually ‘tickets’ but can be simple visual signals, such as the presence or absence of a part on a shelf. Implemented correctly, JIT focuses on continuous improvement and can improve a manufacturing organization’s return on investment, quality, and efficiency.
看板通常是“票”,但也可以是简单的视觉信号,比如货架上的某个部件是否存在。如果实施得当,JIT关注于持续改进,可以提高制造企业的投资回报、质量和效率。
Benefits of JIT
-
Reduced setup time. Cutting setup time allows the company to reduce or eliminate inventory for “changeover” time. 减少设置时间。缩短安装时间使公司能够减少或消除“转换”时间的库存。
-
The flow of goods from warehouse to shelves improves. Small or individual piece lot sizes reduce lot delay inventories, which simplifies inventory flow and its management. 货物从仓库到货架的流动得到改善。小批量或单件批量减少了延迟库存,简化了库存流程和管理。
-
Employees with multiple skills are used more efficiently. Having employees trained to work on different parts of the process allows companies to move workers where they are needed. 拥有多种技能的员工会得到更有效的利用。对员工进行培训,让他们在生产过程的不同环节工作,这样公司就可以把工人派到需要他们的地方。
-
Production scheduling and work hour consistency synchronized with demand. If there is no demand for a product at the time, it is not made. 生产调度和工时与需求同步。如果一种产品在当时没有需求,它就不会被生产出来。
-
Increased emphasis on supplier relationships. 加强对供应商关系的重视。
-
Supplies come in at regular intervals throughout the production day. 在整个生产过程中,每隔一段时间就会有供应。
-
Minimises storage space needed. 最大限度地减少所需的存储空间。
-
Smaller chance of inventory breaking/expiring. 更小的库存破损/过期的机会。
Problems of JIT philosoph
JIT relies on other elements in the inventory chain as well. For instance, its effective application cannot be independent of other key components of a lean manufacturing system or it can "end up with the opposite of the desired result.“
JIT也依赖于库存链中的其他元素。例如,它的有效应用不能独立于精益制造系统的其他关键组成部分,或者它可能“以与预期结果相反的结果结束”。”
Manufacturers have continued to try to hone forecasting methods such as applying a trailing 13-week average as a better predictor for JIT planning; however, some research demonstrates that basing JIT on the presumption of stability is inherently flawed.
制造商们一直在努力改进预测方法,比如采用过去13周的平均值作为JIT计划的更好预测指标;然而,一些研究表明,将JIT建立在稳定性假设的基础上是有缺陷的。
Vendor-Managed Replenishment (VMR/VMI)
Suppliers actively manage inventory for customers.
供应商积极为客户管理库存。
Vendor monitors the buyer’s inventory levels (physically or via electronic messaging), makes periodic resupply decisions regarding order quantities, shipping, and timing.
供应商监控买方的库存水平(物理上或通过电子消息传递),根据订单数量、运输和时间做出定期的再供应决策。
Transactions customarily initiated by the buyer (such as purchase orders) are initiated by the supplier.
通常由买方发起的交易(如采购订单)由供应商发起。
Benefits for suppliers
- Improved demand information 改善需求信息
- Improved ability to allocate productive resources 提高分配生产资源的能力
Benefits for customers
- Lower labour and inventory costs 降低劳动力和库存成本
- Improved item availability 改进物品可用性
- Improved responsiveness 改善响应时间
Examples of VMI
PET granules for bottle blowing
吹瓶用PET颗粒
Car seats to trackside at NISSAN
尼桑汽车座椅改为轨道边座椅
Soap to TESCO
给TESCO的肥皂
Beer/drinks to managed pubs
到有管理的酒吧喝啤酒/饮料
Chemicals to process company
化学品加工公司
Role of Safety Inventory
Forecasts are rarely completely accurate
预测很少是完全准确的
If average demand is 1000 units per week, then half the time actual demand will be greater than 1000, and half the time actual demand will be less than 1000; what happens when actual demand is greater than 1000?
如果平均需求是每周1000台,那么一半的时间实际需求将大于1000台,一半的时间实际需求将小于1000台;实际需求大于1000会怎样?
If you kept only enough inventory in stock to satisfy average demand, half the time you would run out
如果你只保留足够的库存来满足平均需求,一半的时间你会用完
Safety inventory: Inventory carried for the purpose of satisfying demand that exceeds the amount forecasted in a given period
安全库存:为满足超过某一时期预测数量的需求而进行的库存
Safety inventory is carried because product demand and lead time are uncertain and a product shortage may result if actual demand during lead time exceeds the forecast amount.
进行安全库存是因为产品需求和提前期是不确定的,如果提前期的实际需求超过预测量,可能会导致产品短缺。
Safety Inventory
Average inventory is therefore cycle inventory plus safety inventory
因此平均库存是周期库存加上安全库存
- it tends to have a negative impact on supply chain cost but a positive impact on supply chain responsiveness/availability 它倾向于对供应链成本产生负面影响,但对供应链响应/可用性产生积极影响
There is a fundamental trade-off:
这是一个基本的权衡:
- Raising the level of safety inventory provides higher levels of product availability and customer service 提高安全库存水平可以提供更高水平的产品可用性和客户服务
- Raising the level of safety inventory also raises the level of average inventory and therefore increases holding costs 提高安全库存水平也会提高平均库存水平,从而增加持有成本
Safety Inventory - obsolescence 废弃
Very important in high-tech or other industries where obsolescence is a significant risk (where the value of inventory, such as PCs, can drop in value very quickly)
在高科技或其他行业中非常重要,因为过时是一个重大的风险(在这些行业中,库存的价值,如个人电脑的价值可能会迅速下降)。
- Compaq and Dell in PCs
Two Questions to Answer in Planning Safety Inventory:
What is the appropriate level of safety inventory to carry? .
什么是合适的安全库存级别?
What actions can be taken to improve product availability while reducing safety inventory?
在减少安全库存的同时,可以采取什么措施来提高产品的可用性?
Level of Safety Inventory
- Measuring demand uncertainty 衡量需求不确定性
- Measuring product availability 测量产品可用性
- Replenishment policies 补货政策
- Evaluating cycle service level and fill rate 评估循环服务水平和填充率
- Evaluating safety level given desired cycle service level or fill rate 在给定所需周期服务水平或填充率的情况下评估安全水平
- Impact of required product availability and uncertainty on safety inventory 所需产品的可得性和不确定性对安全库存的影响
Level of Demand Uncertainty
Appropriate level of safety inventory determined by:
安全库存的适当水平由以下因素确定:
- supply or demand uncertainty 供给或需求不确定性
- desired level of product availability 期望的产品可用性水平
Higher levels of uncertainty require higher levels of safety inventory given a particular desired level of product availability
更高水平的不确定性要求更高水平的安全库存,给定特定的期望水平的产品可用性
Higher levels of desired product availability require higher levels of safety inventory given a particular level of uncertainty
更高水平的期望产品可用性需要更高水平的安全库存,给定特定水平的不确定性
Measuring Demand Uncertainty
Demand has a systematic component and a random component
需求有系统成分和随机成分
The estimate of the random component is the measure of demand uncertainty
随机分量的估计是需求不确定性的度量
Random component is usually estimated by the standard deviation of demand
随机分量通常用需求的标准差来估计
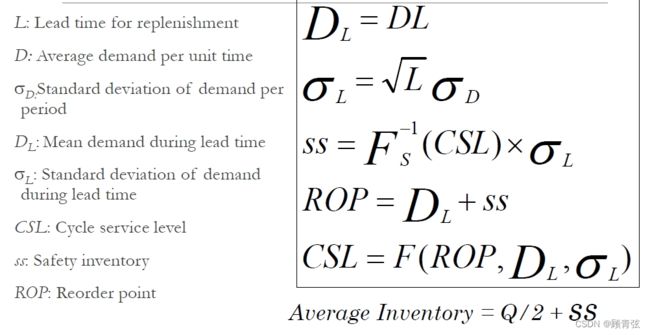
数学计算
Notation:
D = Average demand per period 每期平均需求量
σD = standard deviation of demand per period 每一时期需求的标准差
L = lead time = time between when an order is placed and when it is received 从下订单到收到订单之间的时间
Uncertainty of demand during lead time is what is important
交货期需求的不确定性是重要的
- Demand during L periods = LD
- σL = std dev of demand during L periods = σLSqrt(L)
- Coefficient of variation = cv = σ/μ = stddev/mean = size of uncertainty relative to demand 不确定性相对于需求的大小
(Ω is commonly notated as σL We will use the designation of σL)
Measuring Product Availability
Product availability: a firm’s ability to fill a customer’s order out of available inventory
产品可用性:公司用现有库存来满足客户订单的能力
Stockout/backlog: a customer order arrives when product is not available
缺货/积压:产品缺货时收到客户订单
- Product fill rate (fr): fraction of demand that is satisfied from product in inventory 产品填充率(fr):从库存产品中满足需求的比例
- Order fill rate: fraction of orders that are filled from available inventory 订单填充率:从可用库存中填充的订单的百分比
- Cycle service level: fraction of replenishment cycles that end with all customer demand met 周期服务水平:在满足所有客户需求的补货周期中所占的比例
Replenishment Policies
Replenishment policy: decisions regarding when to reorder and how much to reorder
补货政策:关于何时补货以及补货数量的决定
- Continuous review: inventory is continuously monitored and an order of size Q is placed when the inventory level reaches the reorder point ROP 连续评审:对库存进行持续监控,当库存水平达到再订货点ROP时,下一个尺寸为Q的订单
- Periodic review: inventory is checked at regular (periodic) intervals and an order is placed to raise the inventory to a specified threshold (the “order-up-to” level) 定期审查:定期(周期性的)检查库存,并下订单将库存提高到指定的阈值(“订单至”级别)
Continuous Review Policy: Safety Inventory and Cycle Service Level 持续审查政策:安全库存和循环服务水平
举个例子
Factors Affecting Fill Rate 影响填充率的因素
Safety inventory: Fill rate increases if safety inventory is increased. This also increases the cycle service level.
安全库存:如果安全库存增加,填充率也会增加。这也提高了循环服务水平。
Lot size: Fill rate increases on increasing the lot size even though cycle service level does not change.
批量大小:即使循环服务水平不变,填充率也会随着批量大小的增加而增加。
Impact of Product Availability 产品可用性的影响
Impact of Required Product Availability and Uncertainty on Safety Inventory:
所需产品可得性和不确定性对安全库存的影响
- Desired product availability (cycle service level or fill rate) increases, required safety inventory increases 期望的产品可用性(周期服务水平或填充率)增加,所需的安全库存增加
- Demand uncertainty (σL) increases, required safety inventory increases 需求不确定性(σL)增加,所需的安全库存增加
Managerial levers to reduce safety inventory without reducing product availability
在不降低产品可用性的情况下减少安全库存的管理杠杆
- reduce supplier lead time, L (better relationships with suppliers) 缩短供应商交货期,L(与供应商建立更好的关系)
- reduce uncertainty in demand, σL (better forecasts, better information collection and use) 减少需求的不确定性,σL(更好的预测,更好的信息收集和使用)
【从上面的公式来分析】
Information Centralisation 信息集中化
Virtual aggregation 虚拟聚合
Information system that allows access to current inventory records in all warehouses from each warehouse
信息系统允许从每个仓库访问所有仓库的当前库存记录
Most orders are filled from closest warehouse
大多数订单都是从最近的仓库发货的
In case of a stockout, another warehouse can fill the order
在缺货的情况下,另一个仓库可以填补订单
Better responsiveness, lower transportation cost, higher product availability, but reduced safety inventory
更好的响应,更低的运输成本,更高的产品可用性,但减少了安全库存
Examples: McMaster-Carr, Gap, Wal-Mart
Specialisation 专业化
Stock all items in each location or stock different items at different locations?
在每个地点储存所有物品还是在不同地点储存不同物品?
Different products may have different demands in different locations (e.g., snow shovels)
不同的产品在不同的位置可能有不同的需求(如雪铲)
There can be benefits from aggregation
聚合可以带来好处
Benefits of aggregation can be affected by:
聚合的好处可能受到以下因素的影响:
- coefficient of variation of demand (higher cv yields greater reduction in safety inventory from centralisation) 需求变化系数(CV越高,安全库存集中减少越多)
- value of item (high value items provide more benefits from centralisation) 物品的价值(高价值的物品可以从集中中获得更多好处)
Product Substitution 产品替代
Substitution: use of one product to satisfy the demand for another product
替代:用一种产品来满足对另一种产品的需求
Manufacturer-driven one-way substitution
制造商驱动的单向替代
Customer-driven two-way substitution
顾客驱动的双向替代
Component Commonality 通用件
Using common components in a variety of different products
在各种不同的产品中使用通用组件
Can be an effective approach to exploit aggregation and reduce component inventories
是一个有效的方法来利用聚合并减少组件库存
Postponement
The ability of a supply chain to delay product differentiation or customisation until closer to the time the product is sold
供应链将产品差异化或定制化推迟到接近产品销售时的能力
Goal is to have common components in the supply chain for most of the push phase and move product differentiation as close to the pull phase as possible
目标是在推动阶段的大部分时间里,在供应链中拥有共同的组件,并尽可能地将产品差异化推向拉动阶段
Examples: Dell, Benetton
Estimating and Managing Safety Inventory in Practice 安全库存的评估与管理
Account for the fact that supply chain demand is lumpy
考虑到供应链需求是不稳定的
Adjust inventory policies if demand is seasonal
如果需求是季节性的,调整库存政策
Use simulation to test inventory policies
使用模拟来测试库存策略
Start with a pilot
从尝试开始
Monitor service levels
监控服务水平
Focus on reducing safety inventories
专注于减少安全库存
Dynamics of Promotional Activity 促销活动的动态
Projected sales uplift of 10% has resulted in a one-off demand increase of 40% on supplier
预计销售额增长10%导致供应商一次性需求增长40%
Complexity 复杂性
Complexity characterises the behaviour of a system or model whose components interact in multiple ways and follow local rules, meaning there is no reasonable higher instruction to define the various possible interactions.
复杂性是系统或模型的行为特征,其组件以多种方式交互并遵循局部规则,这意味着没有合理的高级指令来定义各种可能的交互。
Characteristics of complexity
- Numerousness 多数
- Complexity often involves a large number of elements or components within a system. The sheer quantity of entities or parts can contribute to the complexity, as it increases the potential interactions and relationships among them. Managing and understanding such a multitude of elements can be challenging. 复杂性通常涉及系统中大量的元素或组件。实体或部件的绝对数量会增加复杂性,因为它增加了它们之间潜在的交互和关系。管理和理解如此多的元素是具有挑战性的。
- Variability 可变性
- Complexity is marked by the presence of variations or differences in the attributes, behaviors, or states of the components within a system. These variations can arise from inherent differences, external influences, or dynamic interactions. The existence of variability adds to the intricacy of understanding and predicting system behavior. 复杂性是由系统中组件的属性、行为或状态的变化或差异的存在来标记的。这些变化可能源于内在差异、外部影响或动态相互作用。可变性的存在增加了理解和预测系统行为的复杂性。
- Diversity 多样性
- Complex systems typically exhibit diversity, where the elements or entities differ in terms of their characteristics, functions, or roles. This diversity can encompass variations in size, shape, behavior, preferences, capabilities, or any other relevant attribute. The diverse nature of the system contributes to its complexity by introducing different requirements and interactions. 复杂系统通常表现出多样性,其中的元素或实体在其特征、功能或角色方面是不同的。这种多样性可以包括大小、形状、行为、偏好、能力或任何其他相关属性的变化。系统的多样性通过引入不同的需求和交互而增加了它的复杂性。
- Variety 多样性
- Complexity involves a broad range of possibilities or options within a system. It encompasses different choices, alternatives, or states that the system or its components can exhibit. The presence of variety amplifies the complexity, as it expands the potential configurations and outcomes that the system can manifest. 复杂性涉及系统中广泛的可能性或选项。它包含系统或其组件可以展示的不同选择、替代方案或状态。多样性的存在放大了复杂性,因为它扩展了系统可以显示的潜在配置和结果。
- Interdependency 相关性
- Complex systems are characterized by interdependencies, where the elements or components rely on and influence one another. Changes or actions in one part of the system can propagate and affect other interconnected parts. The interdependencies create intricate webs of relationships, feedback loops, and dependencies that make the system behavior difficult to predict or control. 复杂系统的特点是相互依赖,其中的元素或组件依赖并相互影响。系统中某一部分的更改或操作可以传播并影响其他相互连接的部分。相互依赖关系创造了错综复杂的关系网、反馈循环和依赖关系,使系统行为难以预测或控制。
- Uncertainty 不确定性
- Complexity is often associated with uncertainty due to the inherent difficulty in predicting outcomes or behavior. The interplay of numerousness, variability, diversity, variety, and interdependency makes it challenging to determine the precise course of events or consequences. The system may exhibit sensitivity to initial conditions, non-linear behavior, or unexpected emergent properties, further increasing the level of uncertainty. 由于预测结果或行为的固有困难,复杂性常常与不确定性联系在一起。数量、可变性、多样性、多样性和相互依赖性的相互作用使得确定事件或结果的精确过程具有挑战性。系统可能会对初始条件、非线性行为或意外的紧急特性表现出敏感性,从而进一步增加不确定性水平。
【以上解释来源ChatGPT,不需要背,仅供加深理解】
Challenge of Complexity in Supply Chains
Complexity increases:
复杂度提高了
- Confusion 困惑
- Cost 费用
- The probability of counterproductive decision making and diminished competitiveness. 反生产决策和竞争力下降的可能性。
Complexity may be necessary to drive the value proposition.
复杂性可能是驱动价值主张的必要条件。
Cost of complexity can not outweigh the value.
复杂性的成本不能超过其价值
Sources of Complexity
- Organisational Structure 组织结构:一个公司或机构内部各部门和职位之间的关系和层次安排。
- Value-Added Processes 增值的过程
- The Operating Network 运营网络
- Stock Keeping Units (SKUs) 库存单位(sku)
- The Supply Base 供应基础
- The Customer Base 客户基础
- The Logistics System 物流系统
Organisational Structure
Issue: decision-making authority
议题:决策权
Centralised – leverages scale to reduce cost
集中式-利用规模来降低成本
Decentralised – leverages local knowledge to build relationships and promote rapid response
分散-利用当地知识建立关系并促进快速反应
Centralised vs. Decentralised Structure
Organisational Structure - solutions
Team-based structures
基于团队的结构
Policies to promote centre-led, decentralised organisation
促进中央领导、分权组织的政策
Measurement systems that promote cooperation, support local autonomy and accountability
促进合作、支持地方自治和问责制的衡量体系
Modern communication and database technologies
现代通信和数据库技术
Value-Added Process
Processes add complexity because they:
流程增加了复杂性,因为它们:
- involve a number of people from different functions; 让来自不同职能部门的人参与进来;
- consist of a large number of distinct activities; 复杂的:由大量不同的活动组成的;
- employ a variety of capital equipment; 使用各种资本设备;
- design, produce, or deliver a wide range of products. 设计、生产或交付各种产品。
Value-Added Process - solution
- Standardisation 标准化
- Error Proofing 防错:一种预防错误发生的方法,通过设计和制程改进来减少或消除错误的可能性。
- Synchronisation of Material Flows 物料流的同步
Operating Network
Operating networks add complexity because of the number of distinct facilities that must be coordinated.
由于必须协调的不同设施的数量,运营网络增加了复杂性。
Efforts to “optimise the supply chain” using sophisticated mathematical models often fail over the long term because:
使用复杂的数学模型“优化供应链”的努力往往会在长期内失败,因为:
- operating networks evolve over time; 运营网络随着时间的推移而发展;
- acquisitions complicate network design; 收购使网络设计复杂化;
- macroeconomics and political stability influence network design. 宏观经济和政治稳定影响网络设计。
Operating Network - Solutions
Managers should analyse the supply chain in terms of the following questions:
管理者应该从以下几个问题来分析供应链:
- How many facilities do we really need to achieve desired service levels? 我们需要多少设施才能达到预期的服务水平?
- Where should they be located? 他们应该被安置在哪里?
- What activities will be performed at each? 每个会议将进行哪些活动?
- How will the value-added activities be coordinated and controlled? 如何协调和控制增值活动?
Company SKUs
Product proliferation adds to SC complexity.
产品扩散增加了供应链的复杂性。
Breadth complexity
广度复杂性
- Wide range of products 很广泛的产品
- Low profit margin 低利润率:指企业在销售产品或提供服务时所获得的利润与销售额之间的比率较低。
- Relies on inventory turns and efficient operations 依赖于库存周转和高效运作
Depth complexity
深度复杂性
- large number of options for the products carried 大量可供选择的产品携带
- High profit margin 利润率高
- Relies on customer service and distinctive products 依靠客户服务和特色产品
Company SKUs - Solutions
Managers wishing to reduce complexity due to product proliferation should:
希望减少由于产品扩散而导致的复杂性的经理应该:
- Proactively manage the breadth versus depth decision 主动管理广度与深度决策
- Using total cost analysis, eliminate unprofitable SKUs 使用总成本分析,消除无利可图的库存单位
- Institute policies to reduce proliferation 制定减少扩散的政策
- Use postponement strategies 使用延迟策略
- Use database and data mining tools 使用数据库和数据挖掘工具
【反正就是利用这俩方法可以减少options】
The Supply Base
Traditionally, American manufacturers have sourced parts from multiple suppliers to hedge against disruptions and create leverage to drive down costs.
传统上,美国制造商从多家供应商处采购零部件,以对冲中断的风险,并创造降低成本的杠杆。
Multiple redundant suppliers, add complexity to the supply chain.
多个冗余供应商,增加了供应链的复杂性。
The Supply Base - Solutions
To reduce complexity, supply-chain managers may seek to reduce the number of suppliers and aggregate purchasing.
为了降低复杂性,供应链管理者可能会设法减少供应商的数量和总采购量。
- ABC Classification Systems ABC分类系统
- Supplier Certifications 供应商认证
- Long-Term Partnership Style Relationships 长期伙伴型关系
The Customer Base
Customers generally have greater power in supply chain relationships.
在供应链关系中,客户通常拥有更大的权力。
Customers use this power to demand consistently higher levels of service without additional compensation.
客户使用这种能力来要求持续的更高水平的服务,而不需要额外的补偿。
Customer proliferation may result in suboptimal profits.
客户激增可能会导致次优利润。
The Customer Base - Solutions
Managers may seek to address an unwieldy customer base by:
管理人员可以通过以下方式来解决庞大的客户群:
- ABC Classification Systems ABC分类系统
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software to segment customers 客户关系管理(CRM)软件,细分客户
- Sophisticated cost analysis to evaluate customers 对客户进行复杂的成本分析
Logistics System
Logistic systems are complex due to:
物流系统是复杂的,因为:
- The number of transportation modes available 可用的运输方式的数量
- The number of different facilities involved 涉及的不同设施的数量
- Geographic dispersion 地理上的分散
- Product proliferation 产品扩散
- Variation in demand 需求变化
- Variation in customer requirements 客户需求的变化
Logistics System - Solutions
Managers may seek to address logistics system complexity by:
管理人员可以通过以下方式来解决物流系统的复杂性:
- Adopting advanced technology – ERP, DRP, CRM systems; database management; data mining. 采用先进的技术- ERP, DRP, CRM系统;数据库管理;数据挖掘。
- Outsourcing – third-party logistics 外包-第三方物流
- Insourcing – on-site third-party logistics 内包——现场第三方物流
- Innovative practices 创新实践:一种新颖、独特的实践方法,旨在改进现有的工作方式或解决问题
SC Rationalisation
Supply chain rationalisation is the process of systematically evaluating the company’s operating network, suppliers, customers, and product offerings to find and eliminate inefficiencies and redundancies.
供应链合理化是系统地评估公司的运营网络、供应商、客户和产品供应,以发现和消除效率低下和冗余的过程。
The goal is to efficiently allocate scarce resources to a company’s most profitable and strategically important activities and relationships.
目标是有效地将稀缺资源分配给公司最有利可图、最具战略重要性的活动和关系。
例子:Chrysler’s Supply Chain
Rationalisation at Chrysler 合理化
Analysis of the supply chain to eliminate unnecessary or wasteful activities.
分析供应链以消除不必要或浪费的活动。
Step 1 – Identify and eliminate redundant suppliers.
识别并淘汰多余的供应商。
- Result: Fewer SKUs and fewer and higher- performing suppliers 结果:sku减少,供应商数量减少,绩效提高
Step 2 - Classify remaining suppliers on the basis of importance. 根据重要性对剩余供应商进行分类
- Result: Discovery of potential threats and ability to focus resources on collaborative relationships with key suppliers. 结果:发现潜在威胁,并有能力将资源集中在与主要供应商的合作关系上。
Shifting Roles Among Members
Traditionally, roles for individual members of the supply chain were well defined.
传统上,供应链中各个成员的角色都有很好的定义
Today, roles are far less certain.
如今,角色远没有那么确定。
To insure survivability, supply-chain participants must add unique value.
为了确保生存能力,供应链参与者必须增加独特的价值。
Role Shifting
Role shifting enhances supply chain efficiency thereby enhancing the value proposition.
角色转换提高了供应链效率,从而增强了价值主张。
Functional shiftability – allows firms with unique capabilities to undertake additional roles.
功能可转移性-允许具有独特能力的公司承担额外的角色。
Dis-intermediated – a company that is shifted out of the supply chain, replaced by a more capable firm.
去中介化——被转移出供应链的公司,被更有能力的公司所取代。
Role Shifting – Best Practices
Second-Tier Sourcing Contracts
二级采购合同
Supplier Certification
供应商认证
Vendor-Managed Replenishment
供应商管理的补货
Supplier-Integrated Manufacturing
供应商集成制造
Second-Tier Sourcing Contracts
Coordinated purchasing with first-tier suppliers.
与一线供应商协调采购。
Allows for aggregation of purchases.
允许汇总购买。
Leverages purchasing power to reduce cost.
利用购买力降低成本。
Supplier Certification
Supplier certification is the formal process of working with selected suppliers to evaluate and improve supplier quality.
供应商认证是与选定的供应商一起评估和改进供应商质量的正式过程。
“Dock to Stock” – incoming shipments no longer are inspected, they go straight to inventory or the point of use.
“码头到库存”-进货不再检查,它们直接进入库存或使用点。
Vendor-Managed Replenishment
Suppliers actively manage inventory for customers.
供应商积极为客户管理库存。
Suppliers benefit due to improved demand information and improved ability to allocate productive resources.
供应商受益于需求信息的改善和生产资源配置能力的提高。
Customers benefit from lower labour and inventory costs, improved item availability.
客户受益于较低的劳动力和库存成本,提高了产品的可用性。
Supplier-Integrated Manufacturing
Customer firm invites suppliers to establish manufacturing facilities at the customer’s location.
客户公司邀请供应商在客户所在地建立生产设施。
Suppliers provide their own specialised equipment, manage their own inventory, and hire and train their own workers.
供应商提供自己的专业设备,管理自己的库存,雇佣和培训自己的工人。