【业务功能篇59】Springboot + Spring Security 权限管理 【下篇】
UserDetails接口定义了以下方法:
- getAuthorities(): 返回用户被授予的权限集合。这个方法返回的是一个集合类型,其中每个元素都是一个GrantedAuthority对象,表示用户被授予的权限。
- getPassword(): 返回用户的密码。这个方法返回的是一个字符串类型,表示用户的密码。
- getUsername(): 返回用户的用户名。这个方法返回的是一个字符串类型,表示用户的用户名。
- isAccountNonExpired(): 返回一个布尔值,表示用户的账户是否未过期。
- isAccountNonLocked(): 返回一个布尔值,表示用户的账户是否未锁定。
- isCredentialsNonExpired(): 返回一个布尔值,表示用户的凭证(如密码)是否未过期。
- isEnabled(): 返回一个布尔值,表示用户是否已激活。
第三步 测试
访问登录地址 http://localhost:8080/login ,输入用户名密码
登录失败,后台报错
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: There is no PasswordEncoder mapped for the id "null"
报错原因
- Spring Security中密码的存储格式是“{id}…………”.前面的id是加密方式,id可以是bcrypt、sha256等,后面跟着的是加密后的密码.也就是说,程序拿到传过来的密码的时候,会首先查找被“{”和“}”包括起来的id,来确定后面的密码是被怎么样加密的,如果找不到就认为id是null.
如果要测试,需要往用户表中写入用户数据,并且如果你想让用户的密码是明文存储,需要在密码前加{noop}。就可以正常登录了, 例如
(3) BCryptPasswordEncoder 密码加密存储
1. BCryptPasswordEncoder 介绍
在实际的项目中,为了保护密码的安全,我们通常不会将密码以明文的形式存储在数据库中。通常,我们使用SpringSecurity提供的BCryptPasswordEncoder来进行加密。
BCryptPasswordEncoder是Spring Security提供的一个PasswordEncoder实现类,它使用了bcrypt算法对密码进行加密和解密。
2. 常用方法测试
BCryptPasswordEncoder主要有以下方法:
encode(CharSequence rawPassword):对原始密码进行加密处理,并返回加密后的密码字符串。matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String encodedPassword):对比原始密码和加密后的密码是否匹配。rawPassword为原始密码,encodedPassword为从数据库或其他地方获取的已经加密的密码字符串,如果匹配则返回true,否则返回false。
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Test
public void testBcryp(){
String e1 = passwordEncoder.encode("123456");
String e2 = passwordEncoder.encode("123456");
System.out.println(e1);
System.out.println(e2);
System.out.println(e1.equals(e2));
//$2a$10$0CS95XYw7GyDQNXq6FO7FuWDHR4yLTVyFXgQICjgTddWIG9OJ6isy
boolean b = passwordEncoder.matches("123456",
"$2a$10$0CS95XYw7GyDQNXq6FO7FuWDHR4yLTVyFXgQICjgTddWIG9OJ6isy");
System.out.println("=============== " + b);
}
BCryptPasswordEncoder使用随机盐值对密码进行加密,每次加密的结果都不同,即使相同的原始密码,加密后得到的字符串也是不同的。这种随机性增加了密码的安全性,防止了攻击者通过破解一个用户密码的方式,来破解其他用户的密码。
3.引入 BCryptPasswordEncoder
我们只需要将BCryptPasswordEncoder对象注入到Spring容器中,SpringSecurity就会使用该PasswordEncoder来验证密码。
为了配置SpringSecurity,我们可以定义一个继承自WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的配置类。
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
修改数据库的明文密码为加密后的密码, 测试一下
(4) 自定义登录接口
我们需要自定义一个登陆接口,并让SpringSecurity不要对该接口进行登录验证,以允许未登录用户访问。
在该接口中,我们使用AuthenticationManager的authenticate方法进行用户认证,需要在SecurityConfig中配置将AuthenticationManager注入到容器中。
如果认证成功,则需要生成一个jwt并将其放入响应中返回。为了让用户在下次请求时能够通过jwt识别出具体的用户,我们需要将用户信息存储在redis中,可以将用户id作为key。
当需要自定义登录接口时,可以按照以下步骤进行:
- 创建一个新的登录接口,例如LoginController , 用于接收用户的登录信息。
@RestController
public class LoginController {
@Autowired
private LoginService loginService;
@PostMapping("/user/login")
public ResponseResult login(@RequestBody SysUser user){
//登录
return loginService.login(user);
}
}
- 创建LoginService和其实现类 LoginServiceImpl, 登录操作主要的实现逻辑都在实现类中
public interface LoginService {
ResponseResult login(SysUser sysUser);
}
@Service
public class LoginServiceImpl implements LoginService {
@Override
public ResponseResult login(SysUser sysUser) {
//1.调用AuthenticationManager的 authenticate方法,进行用户认证。
//2.如果认证没有通过,给出错误提示
//3.如果认证通过,使用userId生成一个JWT,并将其保存到 ResponseResult对象中返回
//4.将用户信息存储在Redis中,在下一次请求时能够识别出用户,userid作为key
return null;
}
}
- 配置SecurityConfig 在SecurityConfig中添加一个配置,将自定义登录接口添加到Spring Security中,并设置为放行。
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
/**
* 注入 AuthenticationManager,供外部类使用
*/
@Bean
@Override
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
//该方法用于配置 HTTP 请求的安全处理
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
//关闭csrf
.csrf().disable()
//不会创建会话,每个请求都将被视为独立的请求。
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
//定义请求授权规则
.authorizeRequests()
// 对于登录接口 允许匿名访问
.antMatchers("/user/login").anonymous()
// 除上面外的所有请求全部需要鉴权认证
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
}
后面我们再去详细说明一下configure方法中的细节.
- 回到loginService的login方法,补全剩余步骤
@Service
public class LoginServiceImpl implements LoginService {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@Autowired
private RedisCache redisCache;
@Override
public ResponseResult login(SysUser sysUser) {
//1.调用AuthenticationManager的 authenticate方法,进行用户认证。
//1.1 需要传入一个Authentication对象的实现,该对象包含用户信息
Authentication usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken =
new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(sysUser.getUserName(),sysUser.getPassword());
Authentication authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken);
//2.如果认证没有通过,给出错误提示
if(Objects.isNull(authentication)){
throw new RuntimeException("登录失败");
}
//3.如果认证通过,使用userId生成一个JWT,并将其保存到 ResponseResult对象中返回
//3.1 获取经过身份验证的用户的主体信息
LoginUser loginUser = (LoginUser) authentication.getPrincipal();
//3.2 获取到userID 生成JWT
String userId = loginUser.getSysUser().getUserId().toString();
String jwt = JwtUtil.createJWT(userId);
//4.将用户信息存储在Redis中,在下一次请求时能够识别出用户,userid作为key
redisCache.setCacheObject("login:"+userId,loginUser);
//5.封装ResponseResult,并返回
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("token",jwt);
return new ResponseResult(200,"登录成功",map);
}
}
(5) 使用postman测试
(6) 实现认证过滤器
当用户再次发送请求的时候,要进行校验,用户会携带登录时生成的JWT,所以我们需要自定义一个Jwt认证过滤器
- 获取token
- 解析token获取其中的userid login:+userId
- 从redis中获取用户信息
- 存入SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContextHolder 记录如下信息:当前操作的用户是谁,该用户是否已经被认证,他拥有哪些角色或权限等等。
经过自定义认证过滤器过滤后的用户信息会被保存到SecurityContextHolder中,后面的过滤器会从SecurityContextHolder中获取用户信息.
操作步骤如下
- 自定义一个过滤器,这个过滤器会去获取请求头中的token,对token进行解析取出其中的userid
自定义过滤器要去继承OncePerRequestFilter,OncePerRequestFilter 旨在简化过滤器的编写,并确保每个请求只被过滤一次,避免多次过滤的问题。
/**
* 自定义认证过滤器,用来校验用户请求中携带的Token
* @date 2023/4/25
**/
@Component
public class JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Autowired
private RedisCache redisCache;
/**
* 封装过滤器的执行逻辑
* @param request
* @param response
* @param filterChain
*/
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.从请求头中获取token
String token = request.getHeader("token");
//2.判断token是否为空,为空直接放行
if(!StringUtils.hasText(token)){
//放行
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
//return的作用是返回响应的时候,避免走下面的逻辑
return;
}
//3.解析Token
String userId;
try {
Claims claims = JwtUtil.parseJWT(token);
userId = claims.getSubject();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException("非法token");
}
//4.从redis中获取用户信息
String redisKey = "login:" + userId;
LoginUser loginUser = redisCache.getCacheObject(redisKey);
if(Objects.isNull(loginUser)){
throw new RuntimeException("用户未登录");
}
//5.将用户新保存到SecurityContextHolder,以便后续的访问控制和授权操作使用。
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(loginUser, null, null);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authenticationToken);
//6.放行
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
}
}
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 三个参数的构造方法:
- principal:表示认证请求的主体,通常是一个用户名或者其他识别主体的信息。
- credentials:表示认证请求的凭据,通常是密码或者其他证明主体身份的信息。
- authorities: 权限信息
将Token检验过滤器 添加到过滤器链中
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Autowired
private JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter jwtAuthenticationTokenFilter;
/**
* 注入 AuthenticationManager,供外部类使用
*/
@Bean
@Override
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
//该方法用于配置 HTTP 请求的安全处理
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
//关闭csrf
.csrf().disable()
//不会创建会话,每个请求都将被视为独立的请求。
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
//定义请求授权规则
.authorizeRequests()
// 对于登录接口 允许匿名访问
.antMatchers("/user/login").anonymous()
// 除上面外的所有请求全部需要鉴权认证
.anyRequest().authenticated();
//将自定义认证过滤器,添加到过滤器链中
http.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthenticationTokenFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
}
使用postman进行测试
(7) 实现退出功能
定义一个登出接口,删除redis中对应的用户数据即可。
为什么不需要清除SecurityContextHolder中的数据
在退出登录时,如果使用 JWT 进行认证,并将 JWT 保存在 Redis 中,需要清除 Redis 中的 JWT 数据。由于 JWT 是无状态的,它本身不会与 Spring Security 的认证信息产生关联,因此在退出登录时,不需要清除
SecurityContextHolder中的认证信息。
@RestController
public class LoginController {
@GetMapping("/user/logout")
public ResponseResult logout(){
//登录
return loginService.logout();
}
}
public interface LoginService {
ResponseResult login(SysUser sysUser);
ResponseResult logout();
}
@Service
public class LoginServiceImpl implements LoginService {
@Autowired
private RedisCache redisCache;
@Override
public ResponseResult logout() {
//获取当前用户的认证信息
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken =
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if(Objects.isNull(authenticationToken)){
throw new RuntimeException("获取用户认证信息失败,请重新登录!");
}
LoginUser loginUser = (LoginUser) authenticationToken.getPrincipal();
Long userId = loginUser.getSysUser().getUserId();
//删除redis中的用户信息
redisCache.deleteObject("login:" + userId);
return new ResponseResult(200,"注销成功");
}
}
测试
4.2.4 授权
4.2.4.1 什么是授权
授权是指在认证通过之后,根据用户的身份和角色,确定用户是否有权执行某项操作或访问某个资源的过程。
在应用程序中,授权通常是通过访问控制机制来实现的,例如基于角色的访问控制(Role-Based Access Control,RBAC)
4.2.4.2 Spring Security 授权基本流程
Spring Security 的授权基本流程如下:
- 进行认证操作,会生成一个
Authentication对象 - 确定了用户的身份和角色之后,可以通过 Spring Security 提供的注解进行授权操作。
- 如果授权通过,则可以执行相关操作。
其中第一步操作 将权限信息保存到Authentication,有两个地方与保存权限有关
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//TODO 查询用户权限信息
//方法的返回值是UserDetails类型,需要返回自定义的实现类,并且将user信息通过构造方法传入
return new LoginUser(sysUser);
}
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
//TODO 获取权限信息封装到 Authentication
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken =
new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(loginUser,null,null);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authenticationToken);
//6.放行
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
}
4.2.4.2 SpringSecurity授权实现
(1) 设置资源访问所需要的权限
在security中添加注解 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)是 Spring Security 提供的一个注解,用于启用全局方法级别的安全控制,在使用 Spring Security 进行方法级别的授权控制时,需要使用该注解来启用相关功能。其中,
prePostEnabled = true表示开启 Spring Security 的方法级别安全控制。pre表示在方法执行前进行授权校验,post表示在方法执行后进行授权校验。
在HelloController中添加 @PreAuthorize(“hasAuthority(‘test’)”) 注解
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('test')")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
}
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('test')")是 Spring Security 提供的一个注解,用于在方法执行前进行权限校验。它的作用是检查当前登录用户是否具有指定的权限,如果有,则允许执行该方法,否则抛出AccessDeniedException异常,阻止方法执行。
hasAuthority()方法用于检查用户是否具有指定的权限
hasAuthority('test')表示检查当前用户是否具有名为test的权限
@PreAuthorize 注解是在方法执行前进行权限校验的,因此如果当前用户不具有指定的权限,该方法将不会被执行。如果需要在方法执行后进行权限校验,可以使用 @PostAuthorize 注解。
(2) 封装权限信息
第一步 在UserDetailsServiceImpl中 ,根据用户查询权限信息,添加到LoginUser中
@Service
public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//根据用户名查询用户信息
LambdaQueryWrapper wrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq(SysUser::getUserName,username);
SysUser user = userMapper.selectOne(wrapper);
//如果查询不到数据,抛出异常 给出提示
if(Objects.isNull(user)){
throw new RuntimeException("用户名或密码错误");
}
//TODO 根据用户查询权限信息,添加到LoginUser中,这里的权限信息我们写死,封装到list集合
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("test"));
//方法的返回值是 UserDetails接口类型,需要返回自定义的实现类
return new LoginUser(user,list);
}
}
第二步 由于LoginUser中还有这个构造函数,所以我们要修改一下LoginUser
/* LoginUser */
//存储权限信息集合
private List permissions;
public LoginUser(SysUser user, ArrayList permissions) {
this.sysUser = user;
this.permissions = permissions;
}
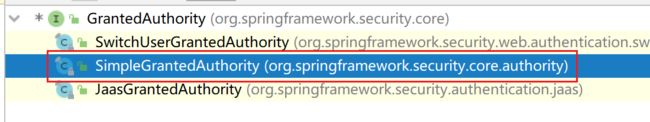
第三步 如果SpringSecurity想要获取用户权限信息,其实最终要调用 getAuthorities()方法,所以要在这个方法中将查询到的权限信息进行转换,转换另一个List集合,其中保存的数据类型是 GrantedAuthority 类型.这是一个接口,我们用它下面的这个实现
package com.mashibing.springsecurity_example.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* @date 2023/4/24
**/
@Data
public class LoginUser implements UserDetails {
private SysUser sysUser;
//存储权限信息集合
private List permissions;
public LoginUser(SysUser user, ArrayList permissions) {
this.sysUser = user;
this.permissions = permissions;
}
/**
* 用于获取用户被授予的权限,可以用于实现访问控制。
*/
@Override
public Collection getAuthorities() {
//将permissions集合中的String类型权限信息,转换为SimpleGrantedAuthority类型
// List authorities = new ArrayList<>();
// for (String permission : permissions) {
// SimpleGrantedAuthority simpleGrantedAuthority = new SimpleGrantedAuthority(permission);
// authorities.add(simpleGrantedAuthority);
// }
//1.8 语法
List authorities = permissions.stream()
.map(SimpleGrantedAuthority::new)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return authorities;
}
}
第四步 对上面的代码进行优化, 将权限的集合提取到方法外,除第一次调用需要正在查询以外,后面判断只要authorities集合不为空,就直接返回
@Data
public class LoginUser implements UserDetails {
private SysUser sysUser;
public LoginUser() {
}
public LoginUser(SysUser sysUser) {
this.sysUser = sysUser;
}
//存储权限信息集合
private List permissions;
public LoginUser(SysUser user, ArrayList permissions) {
this.sysUser = user;
this.permissions = permissions;
}
//authorities集合不需要序列化,只需要序列化permissions集合即可
@JSONField(serialize = false)
private List authorities;
/**
* 用于获取用户被授予的权限,可以用于实现访问控制。
*/
@Override
public Collection getAuthorities() {
//将permissions集合中的String类型权限信息,转换为SimpleGrantedAuthority类型
// List authorities = new ArrayList<>();
// for (String permission : permissions) {
// SimpleGrantedAuthority simpleGrantedAuthority = new SimpleGrantedAuthority(permission);
// authorities.add(simpleGrantedAuthority);
// }
if(authorities != null){
return authorities;
}
//1.8 语法
authorities = permissions.stream()
.map(SimpleGrantedAuthority::new)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return authorities;
}
}
第五部分 在 JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter认证过滤器中, 将权限信息保存到 SecurityContextHolder
//TODO 5.将用户保存到SecurityContextHolder,以便后续的访问控制和授权操作使用。
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken =
new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(loginUser, null, loginUser.getAuthorities());
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authenticationToken);
第六步 debug 测试一下
(3) 根据RBAC权限模型创建表
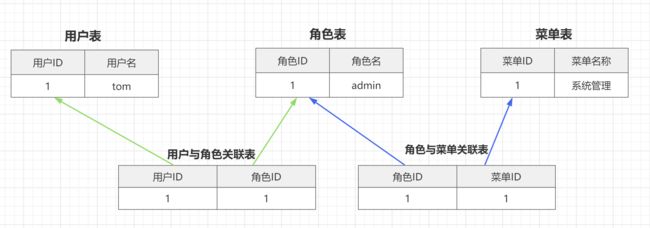
1. RBAC权限模型
- RBAC权限模型(Role-Based Access Control)即:基于角色的权限控制。这是目前最常被开发者使用也是相对易用、通用权限模型。
2. 创建RBAC模型所需的表
CREATE TABLE `sys_menu` (
`menu_id` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '菜单ID',
`menu_name` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL COMMENT '菜单名称',
`path` VARCHAR(200) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '路由地址',
`component` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '组件路径',
`visible` CHAR(1) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '菜单状态(0显示 1隐藏)',
`status` CHAR(1) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '菜单状态(0正常 1停用)',
`perms` VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '权限标识',
`icon` VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT '#' COMMENT '菜单图标',
`create_by` VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '创建者',
`create_time` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_by` VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '更新者',
`update_time` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '更新时间',
`remark` VARCHAR(500) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '备注',
PRIMARY KEY (`menu_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=2068 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC COMMENT='菜单权限表'
CREATE TABLE `sys_role` (
`role_id` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '角色ID',
`role_name` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT '角色名称',
`role_key` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '角色权限字符串',
`status` CHAR(1) NOT NULL COMMENT '角色状态(0正常 1停用)',
`del_flag` CHAR(1) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '删除标志(0代表存在 2代表删除)',
`create_by` VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '创建者',
`create_time` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_by` VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '更新者',
`update_time` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '更新时间',
`remark` VARCHAR(500) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '备注',
PRIMARY KEY (`role_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC COMMENT='角色信息表'
CREATE TABLE `sys_role_menu` (
`role_id` bigint(200) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '角色ID',
`menu_id` bigint(200) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '菜单id',
PRIMARY KEY (`role_id`,`menu_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
CREATE TABLE `sys_user` (
`user_id` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '用户ID',
`user_name` VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'NULL' COMMENT '用户名',
`nick_name` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户昵称',
`password` VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '密码',
`phonenumber` VARCHAR(11) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '手机号码',
`sex` CHAR(1) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '用户性别(0男 1女 2未知)',
`status` CHAR(1) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '帐号状态(0正常 1停用)',
PRIMARY KEY (`user_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC COMMENT='用户信息表'
CREATE TABLE `sys_user_role` (
`user_id` bigint(200) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '用户id',
`role_id` bigint(200) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '角色id',
PRIMARY KEY (`user_id`,`role_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
3. 查询当前有用户所拥有的菜单权限
SELECT
sm.perms
FROM sys_user su
LEFT JOIN sys_user_role sur ON su.user_id = sur.user_id
LEFT JOIN sys_role sr ON sur.role_id = sr.role_id
LEFT JOIN sys_role_menu srm ON sr.role_id = srm.role_id
LEFT JOIN sys_menu sm ON srm.menu_id = sm.menu_id
WHERE su.user_id = 2
4. 创建菜单实体
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL)
@TableName(value = "sys_menu")
public class Menu implements Serializable {
@TableId
private Long id;
//菜单名
private String menuName;
//路由地址
private String path;
//组件路径
private String component;
//菜单状态 (0 显示, 1隐藏)
private String visible;
//菜单状态 (0 正常, 1 停用)
private String status;
//权限标识
private String perms;
//菜单图标
private String icon;
private String createBy;
private String updateBy;
private Date updateTime;
private Date createTime;
private String remark;
}
(4) 从数据库获取权限信息
我们要做的就是根据用户id去查询到其所对应的菜单权限信息即可
1.mapper编写
/**
* @date 2023/4/26
**/
public interface MenuMapper extends BaseMapper SELECT
DISTINCT sm.perms
FROM sys_user_role sur
LEFT JOIN sys_role sr ON sur.role_id = sr.role_id
LEFT JOIN sys_role_menu srm ON sr.role_id = srm.role_id
LEFT JOIN sys_menu sm ON srm.menu_id = sm.menu_id
WHERE
user_id = #{userid}
AND sr.status = 0
AND sm.status = 0
在application.yml中配置mapperXML文件的位置
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test_security?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: classpath*:/mapper/**/*.xml
2.service编写
UserDetailsServiceImpl中去调用mapper的方法查询权限信息, 然后封装到LoginUser对象中.
@Service
public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private MenuMapper menuMapper;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//根据用户名查询用户信息
LambdaQueryWrapper wrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq(SysUser::getUserName,username);
SysUser user = userMapper.selectOne(wrapper);
//如果查询不到数据,抛出异常 给出提示
if(Objects.isNull(user)){
throw new RuntimeException("用户名或密码错误");
}
//TODO 根据用户查询权限信息,添加到LoginUser中,这里的权限信息我们写死,封装到list集合
// ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("test"));
List list = menuMapper.selectPermsByUserId(user.getUserId());
//方法的返回值是 UserDetails接口类型,需要返回自定义的实现类
return new LoginUser(user,list);
}
}
测试,用普通用户去测试一下
@RestController
public class HelloController {
//拥有system:user:list权限才能访问
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('system:user:list')")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
//拥有system:role:list 才能访问
@RequestMapping("/ok")
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('system:role:list')")
public String ok(){
return "ok";
}
}
4.4.5 SpringSecurity异常处理
除了保护应用程序中受保护资源的访问,我们还希望在认证失败或授权失败时,能够返回与应用程序其他接口相同的 JSON 格式响应,以便前端能够统一处理。
4.4.5.1 ExceptionTranslationFilter介绍
ExceptionTranslationFilter 是 Spring Security 框架中的一个关键过滤器,用于处理请求过程中抛出的异常,并将其转化为合适的响应。它的主要作用是保护应用程序中受保护资源的访问,并根据用户的身份进行适当的响应。
当 Spring Security 抛出异常时,ExceptionTranslationFilter 将会捕获该异常并根据异常类型去判断是认证失败还是授权失败出现的异常。然后根据 Spring Security 的配置进行处理。
- 如果是认证过程中出现的异常会被封装成
AuthenticationException, 然后调用AuthenticationEntryPoint对象的方法去进行异常处理。 - 如果是授权过程中出现的异常会被封装成
AccessDeniedException, 然后调用AccessDeniedHandler对象的方法去进行异常处理。
4.4.5.2 认证过程中的异常处理
AuthenticationEntryPoint 是 Spring Security 中用于处理未经身份验证的用户访问受保护资源时的异常的接口。
**通过实现 **AuthenticationEntryPoint 接口,我们可以自定义未经身份验证的用户访问需要认证的资源时应该返回的响应。
/**
* 自定义认证过程异常处理
* @date 2023/4/26
**/
@Component
public class AuthenticationEntryPointImpl implements AuthenticationEntryPoint {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
ResponseResult result = new ResponseResult(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value(), "认证失败请重新登录");
String json = JSON.toJSONString(result);
WebUtils.renderString(response,json);
}
}
4.4.5.3 授权过程中的异常处理
**在 Spring Security 中,当用户请求某个受保护的资源,但是由于权限不足或其他原因被拒绝访问时,Spring Security 会调用 **AccessDeniedHandler 来处理这种情况。
**通过自定义实现 **AccessDeniedHandler 接口,并覆盖 handle 方法,我们可以自定义处理用户被拒绝访问时应该返回的响应。
/**
* 自定义处理授权过程中的异常
* @date 2023/4/26
**/
@Component
public class AccessDeniedHandlerImpl implements AccessDeniedHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) throws IOException, ServletException {
ResponseResult result = new ResponseResult(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value(),"权限不足,禁止访问");
String json = JSON.toJSONString(result);
WebUtils.renderString(response,json);
}
}
4.4.5.4 配置SpringSecurity
- 先注入对应的处理器
@Autowired
private AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint;
@Autowired
private AccessDeniedHandler accessDeniedHandler;
- 然后使用HttpSecurity对象的方法去进行配置
//配置异常处理器
http.exceptionHandling()
//配置认证失败处理器
.authenticationEntryPoint(authenticationEntryPoint)
//配置授权失败处理器
.accessDeniedHandler(accessDeniedHandler);
测试一下
4.4.6 跨域解决方案CORS
4.4.6.1 什么是跨域 ?
首先一个url是由:协议、域名、端口 三部分组成。(一般端口默认80)
如:https://mashibing.com:80
跨域是指通过JS在不同的域之间进行数据传输或通信,比如用ajax向一个不同的域请求数据,只要****协议、域名、端口有任何一个不同,都被当作是不同的域,浏览器就不允许跨域请求。
- 跨域的几种常见情
如果跨域调用,会出现如下错误:
has been blocked by CORS policy: No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource.
翻译过来就是:已被CORS策略阻止:对请求的响应未通过访问控制检查 , 这就是没有配置相关的跨域参数,是不能访问这个接口的
由于我们采用的是前后端分离的编程方式,前端和后端必定存在跨域问题。解决跨域问 题可以采用CORS
4.4.6.2 跨域产生原因?
(1) 出于浏览器的同源策略限制
所谓同源(即在同一个域)就是两个页面具有相同的协议(protocol)、主机(host)和端口号(port)。才可以互相访问
否则只要有一个不同,是不能访问的。
同源策略(Same Orgin Policy)是一种约定,它是浏览器核心也最基本的安全功能,它会阻止一个域的js脚本和另外一个域的内容进行交互,如果缺少了同源策略,浏览器很容易受到XSS、CSFR等攻击。
(2) 跨站脚本攻击(XSS)
(3) 跨站请求伪造 (CSRF)
CSRF(Cross-site request forgery)跨站请求伪造:攻击者诱导受害者进入第三方网站,在第三方网站中,向被攻击网站发送跨站请求。利用受害者在被攻击网站已经获取的注册凭证,绕过后台的用户验证,达到冒充用户对被攻击的网站执行某项操作的目的。
总结: XSS 利用的是用户对指定网站的信任,CSRF 利用的是网站对用户网页浏览器的信任。
非同源会出现的限制
- 无法读取非同源网页的cookie、localstorage等
- 无法接触非同源网页的DOM和js对象
- 无法向非同源地址发送Ajax请求
4.4.6.3 如何解决跨域问题
为了安全起见,浏览器在使用XMLHttpRequest对象发起HTTP请求时必须遵守同源策略。否则,这将被视为跨域请求,并且默认情况下将被禁止。同源策略要求协议、域名和端口号必须完全相同,以便进行正常通信。
在前后端分离的项目中,前端项目和后端项目通常不属于同一源,因此必然存在跨域请求的问题。因此,我们需要对其进行处理,以便前端能够进行跨域请求。
(1) CORS介绍
CORS(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing)即跨域资源共享,是一种用于处理跨域请求的机制。它允许浏览器向跨域服务器发送XMLHttpRequest请求,以便在不违反同源策略的情况下获取服务器上的资源。
CORS的实现方式主要是通过HTTP头部来实现的,浏览器会在请求中添加一些自定义的HTTP头部,告诉服务器请求的来源、目标地址等信息。服务器在接收到请求后,会根据请求头中的信息来判断是否允许跨域请求,并在响应头中添加一些自定义的HTTP头部,告诉浏览器是否允许请求、允许哪些HTTP方法、允许哪些HTTP头部等信息。
在响应头中添加以下字段,可以解决跨域问题:
access-control-allow-origin: 该字段是必须的。它的值要么是请求时Origin字段的值,要么是一个*,表示接受任意域名的请求。access-control-allow-credentials: 该字段可选。它的值是一个布尔值,表示是否允许发送Cookie。默认情况下,Cookie不包括在CORS请求之中。设为true,即表示服务器明确许可,Cookie可以包含在请求中,一起发给服务器。这个值也只能设为true,如果服务器不要浏览器发送Cookie,删除该字段即可Access-Control-Allow-Methods: 该字段必需,它的值是逗号分隔的一个字符串,表明服务器支持的所有跨域请求的方法。注意,返回的是所有支持的方法,而不单是浏览器请求的那个方法。这是为了避免多次"预检"请求。
其实最重要的就是 access-control-allow-origin 字段,添加一个 * ,允许所有的域都能访问
(2) 配置SpringBoot的允许跨域
在SpringBoot项目中只需要编写一个配置类使其实现WebMvcConfigurer接口并重写其addCorsMappings方法即可。
@Configuration
public class CorsConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
// 设置允许跨域的路径
registry.addMapping("/**")
// 设置允许跨域请求的域名
.allowedOriginPatterns("*")
// 是否允许cookie
.allowCredentials(true)
// 设置允许的请求方式
.allowedMethods("GET", "POST", "DELETE", "PUT")
// 设置允许的header属性
.allowedHeaders("*")
// 跨域允许时间
.maxAge(3600);
}
}
**你也可以通过使用 **@CrossOrigin 注解来解决跨域问题。例如:
@RestController
public class MyController {
@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:8080")
@GetMapping("/my-endpoint")
public String myEndpoint() {
// ...
}
}
**这里 **@CrossOrigin 注解的 origins 参数指定了允许访问该接口的域名。在上面的例子中,只有来自 http://localhost:8080 域名的请求才能访问 myEndpoint 接口。
(3) 配置SpringSecurity允许跨域
由于我们的资源都会受到SpringSecurity的保护,所以想要跨域访问还要让SpringSecurity运行跨域访问。
//该方法用于配置 HTTP 请求的安全处理
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
//关闭csrf
.csrf().disable()
//不会创建会话,每个请求都将被视为独立的请求。
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
//定义请求授权规则
.authorizeRequests()
// 对于登录接口 允许匿名访问
.antMatchers("/user/login").anonymous()
// 除上面外的所有请求全部需要鉴权认证
.anyRequest().authenticated();
//将自定义认证过滤器,添加到过滤器链中
http.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthenticationTokenFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
//配置异常处理器
http.exceptionHandling()
//配置认证失败处理器
.authenticationEntryPoint(authenticationEntryPoint)
//配置授权失败处理器
.accessDeniedHandler(accessDeniedHandler);
//允许跨域
http.cors();
}
(4) 前后端联调测试
**首先运行我在资料中给大家提供的前端项目, **注意前端环境要提前配置完成
然后运行后端的项目,进行访问测试即可. 在SpringSecurity中这两行代码注释掉,才能复现跨域请求问题
http.csrf().disable();
http.cors();