【图像分割】图像检测(分割、特征提取)、各种特征(面积等)的测量和过滤(Matlab代码实现)
欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️
博主优势:博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
本文目录如下:
目录
1 概述
2 运行结果
3 参考文献
4 Matlab代码实现
1 概述
【图像分割】图像检测(分割、特征提取)、各种特征(面积等)的测量和过滤
本文提供了一个适合初学者的教程,旨在演示图像检测(分割、特征提取)以及各种特征(如面积)的测量和过滤(只提取某些对象)。
首先,该教程介绍了如何找到图像中的所有对象(硬币),然后根据指定的直径过滤结果,筛选出特定直径的对象。通过一个简单的示例,展示了阈值处理、标记和区域属性的基本概念。
对于那些刚开始接触 MATLAB 图像处理功能的同学来说,这个教程是一个很好的起点。在他们深入学习更复杂的算法之前,可以通过这个教程加深对基本概念和技术的理解。
为了完成这个教程,需要安装图像处理工具箱,因为它演示了该工具箱提供的某些功能。同时,教程使用了工具箱自带的一个名为“硬币”的示例图像作为演示对象。
该教程的优点在于,它提供了一种直观和实用的方法,帮助初学者理解如何使用 MATLAB 对图像进行处理和分析。通过学习如何进行图像分割、特征提取和过滤,读者将受益于这些基本概念,并能够应用它们解决更为复杂的图像处理问题。这个教程对于那些有兴趣进一步探索图像处理领域的学生、研究人员和工程师来说,都是一个很好的起点。
2 运行结果
部分代码:
% Read in a standard MATLAB demo image of coins (US nickles and dimes, which are 5 cent and 10 cent coins). This image ships with MATLAB.
baseFileName = 'coins.png';
folder = fileparts(which(baseFileName)); % Determine where demo folder is (works with all versions).
fullFileName = fullfile(folder, baseFileName);
fprintf('Full File Name = "%s".\n', fullFileName);
if ~exist(fullFileName, 'file')
% It doesn't exist in the current folder.
% Look on the search path.
if ~exist(baseFileName, 'file')
% It doesn't exist on the search path either.
% Alert user that we can't find the image.
warningMessage = sprintf('Error: the input image file\n%s\nwas not found.\nClick OK to exit the demo.', fullFileName);
uiwait(warndlg(warningMessage));
fprintf(1, 'Finished running BlobsDemo.m.\n');
return;
end
% Found it on the search path. Construct the file name.
fullFileName = baseFileName; % Note: don't prepend the folder.
end
% If we get here, we should have found the image file.
originalImage = imread(fullFileName);
% Check to make sure that it is grayscale, just in case the user substituted their own image.
[rows, columns, numberOfColorChannels] = size(originalImage);
if numberOfColorChannels > 1
promptMessage = sprintf('Your image file has %d color channels.\nThis demo was designed for grayscale images.\nDo you want me to convert it to grayscale for you so you can continue?', numberOfColorChannels);
button = questdlg(promptMessage, 'Continue', 'Convert and Continue', 'Cancel', 'Convert and Continue');
if strcmp(button, 'Cancel')
fprintf(1, 'Finished running BlobsDemo.m.\n');
return;
end
% Do the conversion using standard book formula
originalImage = rgb2gray(originalImage);
end
% Display the grayscale image.
subplot(3, 3, 1);
imshow(originalImage);
% Maximize the figure window.
hFig1 = gcf;
hFig1.Units = 'normalized';
hFig1.WindowState = 'maximized'; % Go to full screen.
hFig1.NumberTitle = 'off'; % Get rid of "Figure 1"
hFig1.Name = 'Demo by Image Analyst'; % Put this into title bar.
% Force it to display RIGHT NOW (otherwise it might not display until it's all done, unless you've stopped at a breakpoint.)
drawnow;
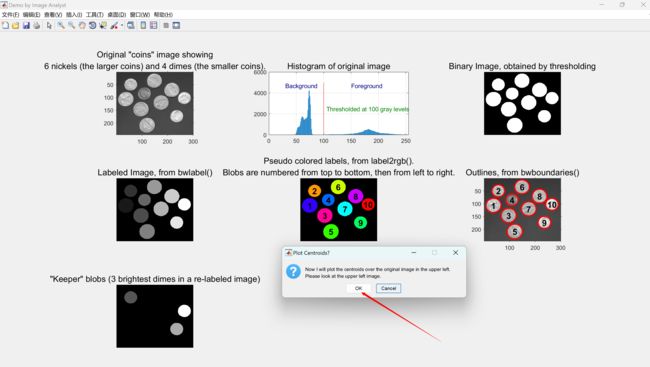
caption = sprintf('Original "coins" image showing\n6 nickels (the larger coins) and 4 dimes (the smaller coins).');
title(caption, 'FontSize', captionFontSize);
axis('on', 'image'); % Make sure image is not artificially stretched because of screen's aspect ratio.
% Just for fun, let's get its histogram and display it.
[pixelCount, grayLevels] = imhist(originalImage);
subplot(3, 3, 2);
bar(pixelCount);
title('Histogram of original image', 'FontSize', captionFontSize);
xlim([0 grayLevels(end)]); % Scale x axis manually.
grid on;
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Threshold the image to get a binary image (only 0's and 1's) of class "logical."
% Method #1: using im2bw()
% normalizedThresholdValue = 0.4; % In range 0 to 1.
% thresholdValue = normalizedThresholdValue * max(max(originalImage)); % Gray Levels.
% binaryImage = im2bw(originalImage, normalizedThresholdValue); % One way to threshold to binary
% Method #2: using a logical operation.
thresholdValue = 100;
binaryImage = originalImage > thresholdValue; % Bright objects will be chosen if you use >.
% ========== IMPORTANT OPTION ============================================================
% Use < if you want to find dark objects instead of bright objects.
% binaryImage = originalImage < thresholdValue; % Dark objects will be chosen if you use <.
% Do a "hole fill" to get rid of any background pixels or "holes" inside the blobs.
binaryImage = imfill(binaryImage, 'holes');
% Show the threshold as a vertical red bar on the histogram.
hold on;
maxYValue = ylim;
line([thresholdValue, thresholdValue], maxYValue, 'Color', 'r');
% Place a text label on the bar chart showing the threshold.
annotationText = sprintf('Thresholded at %d gray levels', thresholdValue);
% For text(), the x and y need to be of the data class "double" so let's cast both to double.
text(double(thresholdValue + 5), double(0.5 * maxYValue(2)), annotationText, 'FontSize', 10, 'Color', [0 .5 0]);
text(double(thresholdValue - 70), double(0.94 * maxYValue(2)), 'Background', 'FontSize', 10, 'Color', [0 0 .5]);
text(double(thresholdValue + 50), double(0.94 * maxYValue(2)), 'Foreground', 'FontSize', 10, 'Color', [0 0 .5]);
% Display the binary image.
subplot(3, 3, 3);
imshow(binaryImage);
title('Binary Image, obtained by thresholding', 'FontSize', captionFontSize);
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Identify individual blobs by seeing which pixels are connected to each other. This is called "Connected Components Labeling".
% Each group of connected pixels will be given a label, a number, to identify it and distinguish it from the other blobs.
% Do connected components labeling with either bwlabel() or bwconncomp().
[labeledImage, numberOfBlobs] = bwlabel(binaryImage, 8); % Label each blob so we can make measurements of it
% labeledImage is an integer-valued image where all pixels in the blobs have values of 1, or 2, or 3, or ... etc.
subplot(3, 3, 4);
imshow(labeledImage, []); % Show the gray scale image.
title('Labeled Image, from bwlabel()', 'FontSize', captionFontSize);
drawnow;
% Let's assign each blob a different color to visually show the user the distinct blobs.
coloredLabels = label2rgb (labeledImage, 'hsv', 'k', 'shuffle'); % pseudo random color labels
% coloredLabels is an RGB image. We could have applied a colormap instead (but only with R2014b and later)
subplot(3, 3, 5);
imshow(coloredLabels);
axis image; % Make sure image is not artificially stretched because of screen's aspect ratio.
caption = sprintf('Pseudo colored labels, from label2rgb().\nBlobs are numbered from top to bottom, then from left to right.');
title(caption, 'FontSize', captionFontSize);
%======================================================================================================================================================
% MAIN PART IS RIGHT HERE!!!
% Get all the blob properties.
props = regionprops(labeledImage, originalImage, 'all');
% Or, if you want, you can ask for only a few specific measurements. This will be faster since we don't have to compute everything.
% props = regionprops(labeledImage, originalImage, 'MeanIntensity', 'Area', 'Perimeter', 'Centroid', 'EquivDiameter');
numberOfBlobs = numel(props); % Will be the same as we got earlier from bwlabel().
%======================================================================================================================================================
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% PLOT BOUNDARIES.
% Plot the borders of all the coins on the original grayscale image using the coordinates returned by bwboundaries().
% bwboundaries() returns a cell array, where each cell contains the row/column coordinates for an object in the image.
subplot(3, 3, 6);
imshow(originalImage);
title('Outlines, from bwboundaries()', 'FontSize', captionFontSize);
axis('on', 'image'); % Make sure image is not artificially stretched because of screen's aspect ratio.
% Here is where we actually get the boundaries for each blob.
boundaries = bwboundaries(binaryImage); % Note: this is a cell array with several boundaries -- one boundary per cell.
% boundaries is a cell array - one cell for each blob.
% In each cell is an N-by-2 list of coordinates in a (row, column) format. Note: NOT (x,y).
% Column 1 is rows, or y. Column 2 is columns, or x.
numberOfBoundaries = size(boundaries, 1); % Count the boundaries so we can use it in our for loop
% Here is where we actually plot the boundaries of each blob in the overlay.
hold on; % Don't let boundaries blow away the displayed image.
for k = 1 : numberOfBoundaries
thisBoundary = boundaries{k}; % Get boundary for this specific blob.
x = thisBoundary(:,2); % Column 2 is the columns, which is x.
y = thisBoundary(:,1); % Column 1 is the rows, which is x.
plot(x, y, 'r-', 'LineWidth', 2); % Plot boundary in red.
end
hold off;
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Print out the measurements to the command window, and display blob numbers on the image.
textFontSize = 14; % Used to control size of "blob number" labels put atop the image.
% Print header line in the command window.
fprintf(1,'Blob # Mean Intensity Area Perimeter Centroid Diameter\n');
% Extract all the mean diameters into an array.
% The "diameter" is the "Equivalent Circular Diameter", which is the diameter of a circle with the same number of pixels as the blob.
% Enclosing in brackets is a nice trick to concatenate all the values from all the structure fields (every structure in the props structure array).
blobECD = [props.EquivDiameter];
% Loop over all blobs printing their measurements to the command window.
for k = 1 : numberOfBlobs % Loop through all blobs.
% Find the individual measurements of each blob. They are field of each structure in the props strucutre array.
% You could use the bracket trick (like with blobECD above) OR you can get the value from the field of this particular structure.
% I'm showing you both ways and you can use the way you like best.
meanGL = props(k).MeanIntensity; % Get average intensity.
blobArea = props(k).Area; % Get area.
blobPerimeter = props(k).Perimeter; % Get perimeter.
blobCentroid = props(k).Centroid; % Get centroid one at a time
% Now do the printing of this blob's measurements to the command window.
fprintf(1,'#%2d %17.1f %11.1f %8.1f %8.1f %8.1f % 8.1f\n', k, meanGL, blobArea, blobPerimeter, blobCentroid, blobECD(k));
% Put the "blob number" labels on the grayscale image that is showing the red boundaries on it.
text(blobCentroid(1), blobCentroid(2), num2str(k), 'FontSize', textFontSize, 'FontWeight', 'Bold', 'HorizontalAlignment', 'center', 'VerticalAlignment', 'middle');
end
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Now, I'll show you a way to get centroids into an N -by-2 array directly from props,
% rather than accessing them as a field of the props strcuture array.
% We can get the centroids of ALL the blobs into 2 arrays,
% one for the centroid x values and one for the centroid y values.
allBlobCentroids = vertcat(props.Centroid); % A 10 row by 2 column array of (x,y) centroid coordinates.
centroidsX = allBlobCentroids(:, 1); % Extract out the centroid x values into their own vector.
centroidsY = allBlobCentroids(:, 2); % Extract out the centroid y values into their own vector.
% Put the labels on the rgb labeled image also.
subplot(3, 3, 5);
for k = 1 : numberOfBlobs % Loop through all blobs.
% Place the blob label number at the centroid of the blob.
text(centroidsX(k), centroidsY(k), num2str(k), 'FontSize', textFontSize, 'FontWeight', 'Bold', 'HorizontalAlignment', 'center', 'VerticalAlignment', 'middle');
end
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Now I'll demonstrate how to select certain blobs based using the ismember() function and extract them into new subimages.
% Let's say that we wanted to find only those blobs
% with an intensity between 150 and 220 and an area less than 2000 pixels.
% This would give us the three brightest dimes (the smaller coin type).
allBlobIntensities = [props.MeanIntensity];
allBlobAreas = [props.Area];
subplot(3, 3, 7);
histogram(allBlobAreas);
% Get a list of the blobs that meet our criteria and we need to keep.
% These will be logical indices - lists of true or false depending on whether the feature meets the criteria or not.
% for example [1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, .....]. Elements 1, 4, 5, 7, ... are true, others are false.
allowableIntensityIndexes = (allBlobIntensities > 150) & (allBlobIntensities < 220);
allowableAreaIndexes = allBlobAreas < 2000; % Take the small objects.
% Now let's get actual indexes, rather than logical indexes, of the features that meet the criteria.
% for example [1, 4, 5, 7, .....] to continue using the example from above.
keeperIndexes = find(allowableIntensityIndexes & allowableAreaIndexes);
% Extract only those blobs that meet our criteria, and
% eliminate those blobs that don't meet our criteria.
% Note how we use ismember() to do this. Result will be an image - the same as labeledImage but with only the blobs listed in keeperIndexes in it.
keeperBlobsImage = ismember(labeledImage, keeperIndexes);
% Re-label with only the keeper blobs kept.
labeledDimeImage = bwlabel(keeperBlobsImage, 8); % Label each blob so we can make measurements of it
% Now we're done. We have a labeled image of blobs that meet our specified criteria.
subplot(3, 3, 7);
imshow(labeledDimeImage, []);
axis image;
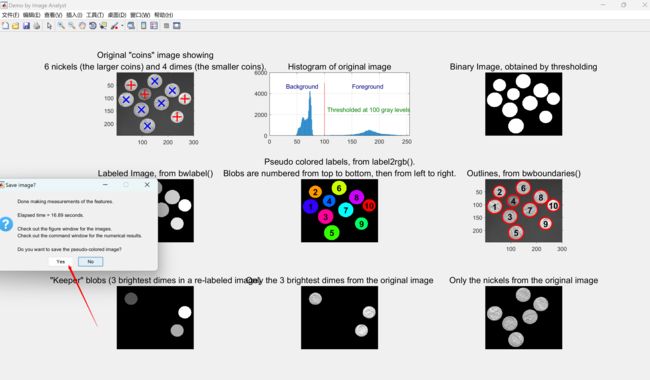
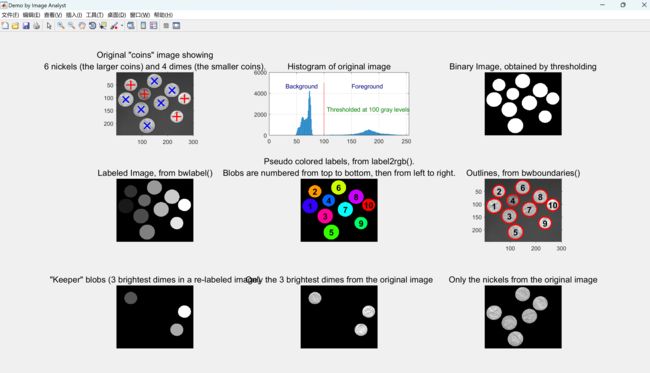
title('"Keeper" blobs (3 brightest dimes in a re-labeled image)', 'FontSize', captionFontSize);
elapsedTime = toc;
fprintf('Blob detection and measurement took %.3f seconds.\n', elapsedTime)
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Plot the centroids in the overlay above the original image in the upper left axes.
% Dimes will have a red cross, nickels will have a blue X.
message = sprintf('Now I will plot the centroids over the original image in the upper left.\nPlease look at the upper left image.');
reply = questdlg(message, 'Plot Centroids?', 'OK', 'Cancel', 'Cancel');
% Note: reply will = '' for Upper right X, 'OK' for OK, and 'Cancel' for Cancel.
if strcmpi(reply, 'Cancel')
return;
end
subplot(3, 3, 1);
hold on; % Don't blow away image.
for k = 1 : numberOfBlobs % Loop through all keeper blobs.
% Identify if blob #k is a dime or nickel.
itsADime = allBlobAreas(k) < 2200; % Dimes are small.
if itsADime
% Plot dimes with a red +.
plot(centroidsX(k), centroidsY(k), 'r+', 'MarkerSize', 15, 'LineWidth', 2);
else
% Plot nickels with a blue x.
plot(centroidsX(k), centroidsY(k), 'bx', 'MarkerSize', 15, 'LineWidth', 2);
end
end
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Now use the keeper blobs as a mask on the original image so we will get a masked gray level image.
% This will keep the regions in the mask as original but erase (blacken) everything else (outside of the mask regions).
% This will let us display the original image in the regions of the keeper blobs.
maskedImageDime = originalImage; % Simply a copy at first.
maskedImageDime(~keeperBlobsImage) = 0; % Set all non-keeper pixels to zero.
subplot(3, 3, 8);
imshow(maskedImageDime);
axis image;
title('Only the 3 brightest dimes from the original image', 'FontSize', captionFontSize);
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Now let's get the nickels (the larger coin type).
keeperIndexes = find(allBlobAreas > 2000); % Take the larger objects.
% Note how we use ismember to select the blobs that meet our criteria. Get a binary image with only nickel regions present.
nickelBinaryImage = ismember(labeledImage, keeperIndexes);
% Let's get the nickels from the original grayscale image, with the other non-nickel pixels blackened.
% In other words, we will create a "masked" image.
maskedImageNickel = originalImage; % Simply a copy at first.
maskedImageNickel(~nickelBinaryImage) = 0; % Set all non-nickel pixels to zero.
subplot(3, 3, 9);
imshow(maskedImageNickel, []);
axis image;
title('Only the nickels from the original image', 'FontSize', captionFontSize);
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% WE'RE BASICALLY DONE WITH THE DEMO NOW.
elapsedTime = toc;
% Alert user that the demo is done and give them the option to save an image.
message = sprintf('Done making measurements of the features.\n\nElapsed time = %.2f seconds.', elapsedTime);
message = sprintf('%s\n\nCheck out the figure window for the images.\nCheck out the command window for the numerical results.', message);
message = sprintf('%s\n\nDo you want to save the pseudo-colored image?', message);
reply = questdlg(message, 'Save image?', 'Yes', 'No', 'No');
% Note: reply will = '' for Upper right X, 'Yes' for Yes, and 'No' for No.
if strcmpi(reply, 'Yes')
% Ask user for a filename.
FilterSpec = {'*.PNG', 'PNG Images (*.png)'; '*.tif', 'TIFF images (*.tif)'; '*.*', 'All Files (*.*)'};
DialogTitle = 'Save image file name';
% Get the default filename. Make sure it's in the folder where this m-file lives.
% (If they run this file but the cd is another folder then pwd will show that folder, not this one.
thisFile = mfilename('fullpath');
[thisFolder, baseFileName, ext] = fileparts(thisFile);
DefaultName = sprintf('%s/%s.tif', thisFolder, baseFileName);
[fileName, specifiedFolder] = uiputfile(FilterSpec, DialogTitle, DefaultName);
if fileName ~= 0
% Parse what they actually specified.
[folder, baseFileName, ext] = fileparts(fileName);
% Create the full filename, making sure it has a tif filename.
fullImageFileName = fullfile(specifiedFolder, [baseFileName '.tif']);
% Save the labeled image as a tif image.
imwrite(uint8(coloredLabels), fullImageFileName);
% Just for fun, read image back into the imtool utility to demonstrate that tool.
tifimage = imread(fullImageFileName);
imtool(tifimage, []);
end
end
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
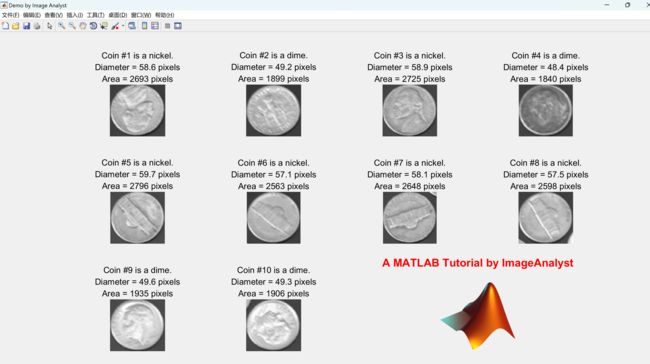
% OPTIONAL : CROP EACH COIN OUT TO A SEPARATE SUB-IMAGE ON A NEW FIGURE.
message = sprintf('Would you like to crop out each coin to individual images?');
reply = questdlg(message, 'Extract Individual Images?', 'Yes', 'No', 'Yes');
% Note: reply will = '' for Upper right X, 'Yes' for Yes, and 'No' for No.
if strcmpi(reply, 'Yes')
% Maximize the figure window.
hFig2 = figure; % Create a new figure window.
hFig2.Units = 'normalized';
hFig2.WindowState = 'maximized'; % Go to full screen.
hFig2.NumberTitle = 'off'; % Get rid of "Figure 1"
hFig2.Name = 'Demo by Image Analyst'; % Put this into title bar.
for k = 1 : numberOfBlobs % Loop through all blobs.
% Find the bounding box of each blob.
thisBlobsBoundingBox = props(k).BoundingBox; % Get list of pixels in current blob.
% Extract out this coin into it's own image.
subImage = imcrop(originalImage, thisBlobsBoundingBox);
% Determine if it's a dime (small) or a nickel (large coin).
if props(k).Area > 2200
coinType = 'nickel';
else
coinType = 'dime';
end
% Display the image with informative caption.
subplot(3, 4, k);
imshow(subImage);
caption = sprintf('Coin #%d is a %s.\nDiameter = %.1f pixels\nArea = %d pixels', ...
k, coinType, blobECD(k), props(k).Area);
title(caption, 'FontSize', textFontSize);
end
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Display the MATLAB "peaks" logo.
logoSubplot = subplot(3, 4, 11:12);
caption = sprintf('A MATLAB Tutorial by ImageAnalyst');
text(0.5,1.15, caption, 'Color','r', 'FontSize', 18, 'FontWeight','b', 'HorizontalAlignment', 'center', 'VerticalAlignment', 'middle') ;
positionOfLowerRightPlot = get(logoSubplot, 'position');
L = 40*membrane(1,25);
logoax = axes('CameraPosition', [-193.4013, -265.1546, 220.4819],...
'Box', 'off', ...
'CameraTarget',[26, 26, 10], ...
'CameraUpVector',[0, 0, 1], ...
'CameraViewAngle',9.5, ...
'DataAspectRatio', [1, 1, .9],...
'Position', positionOfLowerRightPlot, ...
'Visible','off', ...
'XLim',[1, 51], ...
'YLim',[1, 51], ...
'ZLim',[-13, 40], ...
'parent', gcf);
axis(logoSubplot, 'off');
s = surface(L, ...
'EdgeColor','none', ...
'FaceColor',[0.9, 0.2, 0.2], ...
'FaceLighting','phong', ...
'AmbientStrength',0.3, ...
'DiffuseStrength',0.6, ...
'Clipping','off',...
'BackFaceLighting','lit', ...
'SpecularStrength',1, ...
'SpecularColorReflectance',1, ...
'SpecularExponent',7, ...
'Tag','TheMathWorksLogo', ...
'parent',logoax);
l1 = light('Position',[40, 100, 20], ...
% OPTIONAL : CROP EACH COIN OUT TO A SEPARATE SUB-IMAGE ON A NEW FIGURE.
message = sprintf('Would you like to crop out each coin to individual images?');
reply = questdlg(message, 'Extract Individual Images?', 'Yes', 'No', 'Yes');
% Note: reply will = '' for Upper right X, 'Yes' for Yes, and 'No' for No.
if strcmpi(reply, 'Yes')
% Maximize the figure window.
hFig2 = figure; % Create a new figure window.
hFig2.Units = 'normalized';
hFig2.WindowState = 'maximized'; % Go to full screen.
hFig2.NumberTitle = 'off'; % Get rid of "Figure 1"
hFig2.Name = 'Demo by Image Analyst'; % Put this into title bar.
for k = 1 : numberOfBlobs % Loop through all blobs.
% Find the bounding box of each blob.
thisBlobsBoundingBox = props(k).BoundingBox; % Get list of pixels in current blob.
% Extract out this coin into it's own image.
subImage = imcrop(originalImage, thisBlobsBoundingBox);
% Determine if it's a dime (small) or a nickel (large coin).
if props(k).Area > 2200
coinType = 'nickel';
else
coinType = 'dime';
end
% Display the image with informative caption.
subplot(3, 4, k);
imshow(subImage);
caption = sprintf('Coin #%d is a %s.\nDiameter = %.1f pixels\nArea = %d pixels', ...
k, coinType, blobECD(k), props(k).Area);
title(caption, 'FontSize', textFontSize);
end
%------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Display the MATLAB "peaks" logo.
logoSubplot = subplot(3, 4, 11:12);
caption = sprintf('A MATLAB Tutorial by ImageAnalyst');
text(0.5,1.15, caption, 'Color','r', 'FontSize', 18, 'FontWeight','b', 'HorizontalAlignment', 'center', 'VerticalAlignment', 'middle') ;
positionOfLowerRightPlot = get(logoSubplot, 'position');
L = 40*membrane(1,25);
logoax = axes('CameraPosition', [-193.4013, -265.1546, 220.4819],...
'Box', 'off', ...
'CameraTarget',[26, 26, 10], ...
'CameraUpVector',[0, 0, 1], ...
'CameraViewAngle',9.5, ...
'DataAspectRatio', [1, 1, .9],...
'Position', positionOfLowerRightPlot, ...
3 参考文献
文章中一些内容引自网络,会注明出处或引用为参考文献,难免有未尽之处,如有不妥,请随时联系删除。
[1]马寅.基于CCD的图像特征提取与识别[D].东北大学,2012.DOI:10.7666/d.J0120301.
[2]王妞,康辉英.基于图像检测的船舶特征分割与提取优化算法[J].舰船科学技术, 2018(4X):3.DOI:CNKI:SUN:JCKX.0.2018-08-049.
[3]尹聪.彩色图像人脸检测与特征提取认证[J].信息技术与信息化, 2009.DOI:JournalArticle/5af35bd8c095d718d80b8d86.
[4]罗文辉,王三武.基于面积和结构特征的水表图像二步分割方法[J].武汉理工大学学报:信息与管理工程版, 2006, 28(5):4.DOI:10.3963/j.issn.1007-144X.2006.05.014.