基因功能分析——哈佛大学
文章目录
- 描述
- 学习目标
- 一、安装
-
- 数据集
- 读取数据文件
- 加载R包
- 二、基因组注释
-
- 数据库
-
- 通用数据库
- 注释用数据库
- 基因组构建
- 访问数据库的工具
- AnnotationHub
- AnnotationDbi
-
- org.Hs.eg.db
-
- 为什么有如此多重复?
- 为什么会出现基因有gene symbol但没有与之相关的ID?
- EnsDb.Hsapiens.v75
- 三、功能分析
-
- Over-representation analysis
-
- 超几何检验
- Gene Ontology project
-
- GO Ontologies
- GO术语层级
- clusterProfiler
-
- 下载注释文件
- 创建基因列表
- 使用ClusterProfiler
- 可视化clusterProfiler结果
- 其他功能分析方法
- Functional class scoring 工具
-
- 使用clusterProfiler和Pathview进行GSEA
- Pathway topology 工具
- 其他工具
-
- 共表达聚类
- 功能分析资源
- 推荐阅读
描述
功能分析方法能帮助我们一窥所得基因背后所蕴含的生物学意义。这些基因列表 (gene list) 可能来自差异表达分析、GWAS分析、蛋白组学分析。不论是何种来源,功能分析可以探索特定的通路或生物学过程是否富集在一列基因中。
本次学习中,将使用过表征分析 (over-representation analysis, ORA) 和功能分类评分 (functional class scoring, FCS) 法来鉴定出与基因列表相关的潜在通路。我们将会使用clusterProfiler R包确定基因列表中是否存在任何 基因本体(gene ontology, GO) 过程的富集,并根据结果生成图。我们还将简要介绍使用 clusterProfiler 通过 基因集富集分析 (gene set enrichment analysis, GSEA) 执行 FCS,然后使用 Pathview R 包进行可视化。
学习目标
- 使用GO术语来探索富集的过程
- 解释富集检验的结果
- 描述不同类别的功能分析工具 (over-representation analysis, functional class scoring, and pathway topology methods)
- 利用功能分析工具产生关于富集过程/途径的假设
一、安装
首先下载该课程提供的R project
下好后可看到文件名为Functional_analysis.zip,解压然后移动文件夹到合适的位置,打开文件夹后可见以下:

双击.Rproj file,将在RStudio中打开“Functional_analysis” project,如下:

数据集
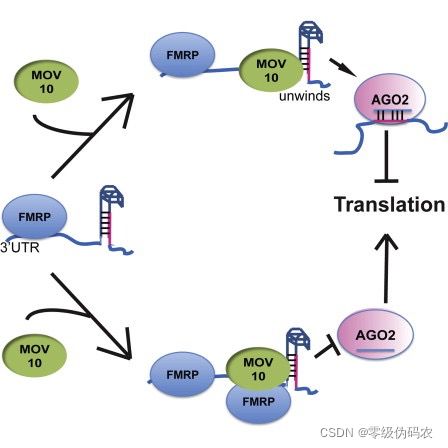
来自文章 Kenny PJ et al, Cell Rep 2014
研究目的:研究脆性X综合征中多种基因之间的相互作用。脆性X综合征患者FMRP蛋白异常产生,导致认知受损和自闭症样特点。
FMRP“最常见于大脑中,对正常的认知发育和女性生殖功能至关重要。该基因的突变可导致脆性 X 综合征、智力低下、卵巢早衰、自闭症、帕金森病、发育迟缓和其他认知缺陷。” - 来自wikipedia
MOV10 是一种假定的 RNA 解旋酶,在 microRNA 通路的背景下也与 FMRP 相关。
本篇文章的科学假设:FMRP和MOV10具有关联性,可调节部分RNA的翻译。
对本课程,使用从DESeq2 R包分析得到的差异表达数据(过表达Mov10蛋白后相比对照组的差异表达基因)。数据在下载好的Mov10oe_DE_results.csv文件里。
读取数据文件
打开已有的空R script文件Functional_analysis.R,读取差异表达结果文件,将对象命名为res_tableOE (OE为过表达之意)。
## Load libraries
library(tidyverse)
## Read in differential expression results
res_tableOE <- read.csv("data/Mov10oe_DE_results.csv", row.names = 1)
## Create a tibble
res_tableOE_tb <- res_tableOE %>%
rownames_to_column(var="gene") %>%
as_tibble()
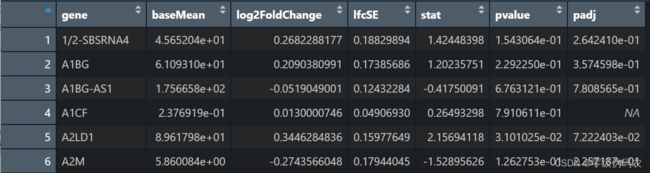
第一步read.csv()读取后View()一下,row.names = 1参数即将第一列视为行名(观测);列变量包括"baseMean", “log2FoldChange”, “lfcSE”, “stat”, “pvalue”, “padj”

第二步,将行名单独作为一列,变量命名为"gene"
加载R包
需先下载,再进行加载
# Install CRAN packages
install.packages(c("BiocManager", "devtools", "tidyverse"))
# Install Bioconductor packages
BiocManager::install(c("clusterProfiler", "DOSE", "org.Hs.eg.db", "pathview", "AnnotationDbi", "EnsDb.Hsapiens.v75"))
# Optional for the lesson:
BiocManager::install(c("gProfileR", "treemap", "SPIA", "stephenturner/annotables"))
## Load libraries one at a time
library(clusterProfiler)
library(DOSE)
library(org.Hs.eg.db)
library(pathview)
library(tidyverse)
library(AnnotationDbi)
library(EnsDb.Hsapiens.v75)
# Optional for the lesson
library(gProfileR)
library(treemap)
library(SPIA)
library(annotables)
二、基因组注释
本节目标:
- 使用基因组注释数据完成对基因列表的功能分析
- 理解在不同数据库中储存的信息类型
- 探索检索基因组注释信息不同R包的优缺点
二代测序结果需要关联基因、转录本、蛋白等与功能或调控信息。为了对基因列表进行功能分析,我们经常需要获得与我们希望使用的工具兼容的基因标识符,这是很关键的。在这里,我们将讨论获取基因注释信息的方法以及每种方法的一些优缺点。
数据库
我们从存储信息的必要数据库中检索有关过程、通路等(涉及基因)的信息。选择的数据库将取决于尝试获取的信息类型。经常查询的数据库包括:
通用数据库
提供有关基因组特征、特征坐标、同源性、变异信息、表型、蛋白质结构域/家族信息、相关生物过程/途径、相关 microRNA 等的综合信息:
- Ensembl (use Ensembl gene IDs)
- NCBI (use Entrez gene IDs)
- UCSC
- EMBL-EBI
注释用数据库
- Gene Ontology (GO): database of gene ontology biological processes, cellular components and molecular functions - based on Ensembl or Entrez gene IDs or official gene symbols
- KEGG: database of biological pathways - based on Entrez gene IDs
- MSigDB: database of gene sets
- Reactome: database of biological pathways
- Human Phenotype Ontology: database of genes associated with human disease
- CORUM: database of protein complexes for human, mouse, rat
…
除此之外,还有其他很多未列出的数据库。
基因组构建
在开始搜索这些数据库之前,应该知道使用哪个基因组构建 (genome build) 来生成基因列表,并确保在功能分析期间使用相同的build进行注释。当获得新的基因组build时,基因组特征(基因、转录本、外显子等)的名称和/或坐标位置可能会发生变化。因此,关于基因组特征(基因、转录本、外显子等)的注释是特定于基因组duild的,我们需要确保我们的注释是从适当的资源中获得的。
例如,如果我们使用人类基因组的 GRCh38 构建来量化用于差异表达分析的基因表达,那么我们应该使用相同的genome build GRCh38 构建来在基因 ID 之间进行转换并识别每个基因的注释。
访问数据库的工具
在 R 中,有许多流行的包用于基因/转录水平的注释。这些软件包提供的工具可以利用提供的基因列表,并使用上面列出的一个或多个数据库检索每个基因的信息。
注释工具:用于访问/查询来自特定数据库的注释
| Tool | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| org.Xx.eg.db | Query gene feature information for the organism of interest | gene ID conversion, biotype and coordinate information | only latest genome build available |
| EnsDb.Xx.vxx | Transcript and gene-level information directly fetched from Ensembl API (similar to TxDb, but with filtering ability and versioned by Ensembl release) | easy functions to extract features, direct filtering | Not the most up-to-date annotations, more difficult to use than some packages |
| TxDb.Xx.UCSC.hgxx.knownGene | UCSC database for transcript and gene-level information or can create own TxDb from an SQLite database file using the GenomicFeatures package | feature information, easy functions to extract features | only available current and recent genome builds - can create your own, less up-to-date with annotations than Ensembl |
| annotables | Gene-level feature information immediately available for the human and model organisms | super quick and easy gene ID conversion, biotype and coordinate infor |