resnet50网络结构复现——pytorch
一、resnet基本介绍
(一)问题的出现
- 从经验来看,网络的深度对模型的性能至关重要,当增加网络层数后,网络可以进行更加复杂的特征模式的提取,但是更深的网络其性能一定会更好吗?实验发现深度网络出现了退化问题(Degradation problem):网络深度增加时,网络准确度出现饱和,甚至出现下降。
- 这个现象从下图可以看出来:56层的网络比20层网络效果还要差。这不会是过拟合问题,因为56层网络的训练误差同样高。我们知道深层网络存在着梯度消失或者爆炸的问题,这使得深度学习模型很难训练。但是现在已经存在一些技术手段如BatchNorm来缓解这个问题。

(二)网络退化问题的解决——残差学习
- 对于一个堆积层结构(几层堆积而成),当输入为 x 时其学习到的特征记为 H(x) ,现在我们希望其可以学习到残差 F(x)=H(x)-x ,这样其实原始的学习特征是 F(x)+x 。之所以这样是因为残差学习相比原始特征直接学习更容易。当残差为0时,此时堆积层仅仅做了恒等映射,至少网络性能不会下降,实际上残差不会为0,这也会使得堆积层在输入特征基础上学习到新的特征,从而拥有更好的性能。
- 残差学习 ——y = F(x,{Wi}) + x
残差学习的block一共包含两个分支或者两种映射(mapping):
1. identity mapping:是上图右边那条弯的曲线。是指本身的映射,也就是x自身;
2. residual mapping,指的是另一条分支,即F(x)部分,这部分称为残差映射,也就是y-x
- 残差单元
 ResNet使用两种残差单元,如上图所示。左图对应的是浅层网络,而右图对应的是深层网络。
ResNet使用两种残差单元,如上图所示。左图对应的是浅层网络,而右图对应的是深层网络。
这里1x1的卷积起到了降维的作用,并且引入了更多的非线性变换,明显的增加了残差块的深度,能提高残差网络的表示能力
对于短路连接,当输入和输出维度一致时,可以直接将输入加到输出上。
但是当维度不一致时(对应的是维度增加一倍),就不能直接相加。有两种方法:
(1)采用zero-padding增加维度,此时一般要先做一个downsamp,可以采用stride = 2的pooling,这样不会增加参数
(2)采用新的映射(projection shortcut),一般用1x1的卷积,这样会增加参数,也会增加计算量。
短路连接除了直接使用恒等映射,还可以采用projection shortcut。
最优的残差结构
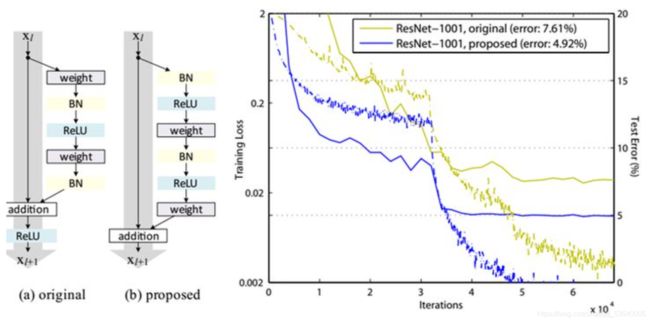 如上图所示,改进前后一个明显的变化是采用pre-activation,BN和ReLU都提前了。作者推荐短路连接采用恒等变换,这样保证短路连接不会有阻碍
如上图所示,改进前后一个明显的变化是采用pre-activation,BN和ReLU都提前了。作者推荐短路连接采用恒等变换,这样保证短路连接不会有阻碍
(三)resnet的网络结构
- ResNet网络是参考了VGG19网络,在其基础上进行了修改,并通过短路机制加入了残差单元
- 变化主要体现在ResNet直接使用stride=2的卷积做下采样,并且用global average pool层(全局平均池化)替换了全连接层,可以减少大量参数
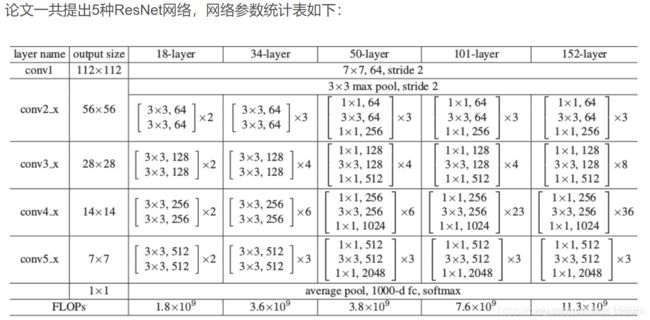
从表中可以看到,对于18-layer和34-layer的ResNet,其进行的两层间的残差学习,当网络更深时,其进行的是三层间的残差学习,三层卷积核分别是1x1,3x3和1x1,一个值得注意的是隐含层的feature map数量是比较小的,并且是输出feature map数量的1/4。
首先都通过一个7x7的卷积层,接着是一个最大池化,
之后就是堆叠残差块,其中50,101,152层的残差网络使用的残差块是瓶颈结构,各网络中残差块的个数从左到右依次是8,16,16,33,50。
最后在网络的结尾通常连接一个全局平均池化。全局平均池化的好处是没有参数需要最优化防止过拟合,对输入输出的空间变换更具有
鲁棒性,加强了特征映射与类别的一致性。
鲁棒性:对于前向无反馈神经网络而言,神经网络的鲁棒性是指当输入信息或神经网络发生有限摄动时,神经网络仍能保持正常的输入—输出关系的特性;对于反馈神经网络而言,神经网络的鲁棒性是指当输入信息或神经网络发生有限摄动时,神经网络仍能保持稳定的输入—输出关系的特性。
-
ResNet的一个重要设计原则是:当feature map大小降低一半时,feature map的数量增加一倍,这保持了网络层的复杂度。
-
从下图可以看到,ResNet相比普通网络每两层间增加了短路机制,这就形成了残差学习,其中虚线表示feature map数量发生了改变

-
ResNet50有两个基本的块,分别名为Conv Block和Identity Block,其中Conv Block输入和输出的维度是不一样的,所以不能连续串联,它的作用是改变网络的维度;Identity Block输入维度和输出维度相同,可以串联,用于加深网络
二、resnet的特点
1. 学习结果对网络权重的波动变化更加敏感
设 input :x , output :y , 待学习的 layer 参数为 w, 在 w 的改变增量一致时, H(x) 和 F(x) 分别改变 9% 和 100 %,在引入残差结构后,网络权重的轻微变化就引起了教大的输出变化,所以,如果想要得到好的输出结构,必须小心的调整权重。
2.残差结果对数据的波动更加敏感。
3.残差学习相对更容易
从直观上看残差学习需要学习的内容少,因为残差一般会比较小,学习难度会减小
残差网络与普通网络不同的地方就是引入了跳跃连接,这可以使上一个残差块的信息没有阻碍的流入到下一个残差块,提高了信息流通,并且也避免了由于网络过深所引起的消失梯度问题和退化问题。
- 总结:
ResNet通过残差学习解决了深度网络的退化问题,让我们可以训练出更深的网络 - 残差网络的本质
残差网络事实上是由多个浅的网络融合而成,它没有在根本上解决消失的梯度问题,只是避免了消失的梯度问题,因为它是由多个浅的网络融合而成,浅的网络在训练时不会出现消失的梯度问题,所以它能够加速网络的收敛
三、resnet18网络代码复现
import torch.nn as nn
# 定义堆叠残差块
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input, output, stride=1,padding=1):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=input, out_channels=output, kernel_size=3,
stride=stride, padding=padding, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(input,eps = 1e-5,momentum=0.1,affine=True,track_running_stats=True)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace = True)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=input, out_channels=output, kernel_size=3,
stride=stride, padding=padding, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(input,eps = 1e-5,momentum=0.1,affine=True,track_running_stats=True)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.conv2(out)
return out
BasicBlock = BasicBlock(64,64,1,1)
print(BasicBlock)
# 构建网络
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__( self, block, num_block, numclasses):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.input = 3
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3,64,kernel_size = 7,stride = 2,padding = 3) # 7x7卷积
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64,eps = 1e-5,momentum = 0.1)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace = True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1) # 最大池化
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
self._make_layer(block, 64, num_block[0], stride=1,padding=1),
self._make_layer(block, 64, num_block[1], stride=1,padding=1))
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
self._make_layer(block, 128, num_block[0], stride=1,padding=1),
self.downsample(nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=1, stride=2),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-5, momentum=0.1)),
self._make_layer(block, 128, num_block[1], stride=1,padding=1))
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
self._make_layer(block, 256, num_block[0], stride=1,padding=1),
self.downsample(nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=2),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-5, momentum=0.1)),
self._make_layer(block, 256, num_block[1], stride=1,padding=1))
self.layer4 = nn.Sequential(
self._make_layer(block, 512, num_block[0], stride=1,padding=1),
self.downsample(nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=1, stride=2),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-5, momentum=0.1)),
self._make_layer(block, 512, num_block[1], stride=1,padding=1))
self.avgpool=nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1) # 全局平均池化
self.fc = nn.Linear(512,1000)
def _make_layer(self,block, output, num_block, stride,padding):
layers = []
for i in range(num_block):
if i == 0:
layers.append(block(self.input, output, stride,padding))
else:
layers.append(block(output, output, 1, 1))
self.input = output
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.maxpool(self.conv1(x))
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = x.view(-1, 512 * 3 * 3)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = self.fc1(x)
return x
model = ResNet(BasicBlock,[1,1,1,1],5)
print(model)
四、用resnet网络对mnist数据集进行分类
import torch
import torchvision
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.utils.data as Data
Batch_size = 128
Lr = 0.01
Epoch = 1000
train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root='./data',
train=True,
download=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()
)
test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root='./data',
train=False,
download=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()
)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(
dataset=train_dataset,
shuffle=True,
batch_size=Batch_size
)
test_x = torch.unsqueeze(test_dataset.data, dim=1).type(torch.Tensor)
test_y = test_dataset.targets
print(test_y.shape, test_x.shape)
class Basicblock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, planes, stride=1):
super(Basicblock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_planes, out_channels=planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=planes, out_channels=planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes),
)
if stride != 1 or in_planes != planes:
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_planes, out_channels=planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
)
else:
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
def forward(self, x):
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.conv2(out)
out += self.shortcut(x)
out = F.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block, num_block, num_classes):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.in_planes = 16
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(16),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.block1 = self._make_layer(block, 16, num_block[0], stride=1)
self.block2 = self._make_layer(block, 32, num_block[1], stride=2)
self.block3 = self._make_layer(block, 64, num_block[2], stride=2)
self.fc = nn.Linear(64, num_classes)
def _make_layer(self, block, planes, num_block, stride):
layers = []
for i in range(num_block):
if i == 0:
layers.append(block(self.in_planes, planes, stride))
else:
layers.append(block(planes, planes, 1))
self.in_planes = planes
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.maxpool(self.conv1(x))
x = self.block1(x) # [200, 64, 28, 28]
x = self.block2(x) # [200, 128, 14, 14]
x = self.block3(x) # [200, 256, 7, 7]
x = F.avg_pool2d(x, 7) # [200, 256, 1, 1]
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # [200,256]
x = fc(x)
return x
ResNet18 = ResNet(Basicblock, [1, 1, 1, 1], 10)
# print(ResNet18)
opt = torch.optim.SGD(ResNet18.parameters(), lr=Lr)
loss_fun = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
a = []
ac_list = []
for epoch in range(Epoch):
for i, (input, label) in enumerate(train_loader):
output = ResNet18(input)
loss = loss_fun(output, label)
opt.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
opt.step()
if i % 100 == 0:
a.append(i)
test_output = torch.max(ResNet18(test_x), dim=1)[1]
loss = loss_fun(ResNet18(test_x), test_y).item()
acc = torch.sum(torch.eq(test_y, test_output)).item() / test_y.numpy().size
ac_list.append(acc)
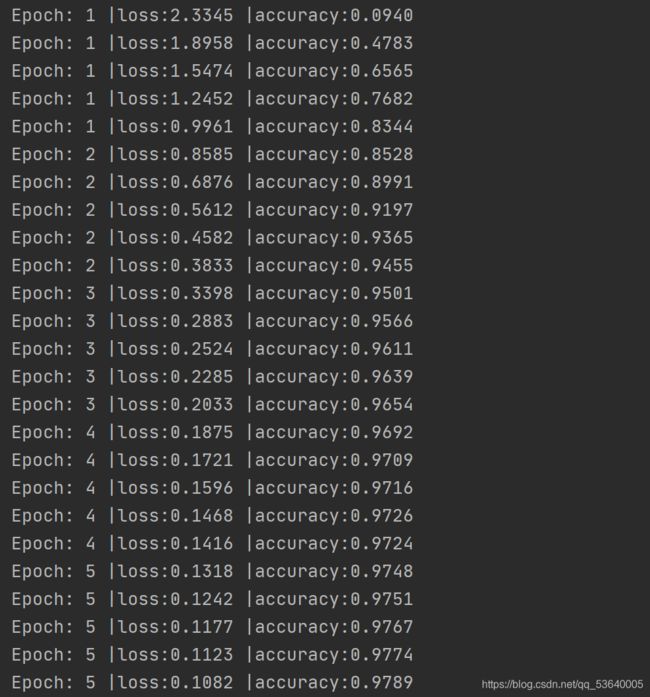
print('Epoch:', epoch+1, '|loss:%.4f' % loss, '|accuracy:%.4f' % acc)
print('real value', test_y[: 10].numpy())
print('train value', torch.max(ResNet18(test_x)[: 10], dim=1)[1].numpy()