Flink源码剖析:flink-streaming-java 之 JobGraph
文章目录
-
- 1. 调用链路
- 2. 源码剖析
-
- 2.1 JobVertex
- 2.2 JobEdge
- 2.3 IntermediateDataSet
- 2.4 StreamConfig
- 2.5 StreamGraph 到 JobGraph 的核心转换
- 3. 自带 WordCount 示例详解
本文主要围绕 Flink 源码中 flink-streaming-java 模块。介绍下 StreamGraph 转成 JobGraph 的过程等。
StreamGraph 和 JobGraph 都是在 Client 端生成的,也就是说我们可以在 IDE 中通过断点调试观察 StreamGraph 和 JobGraph 的生成过程。
StreamGraph 实际上只对应 Flink 作业在逻辑上的执行计划图,Flink 会进一步对 StreamGraph 进行转换,得到另一个执行计划图,即 JobGraph。
1. 调用链路
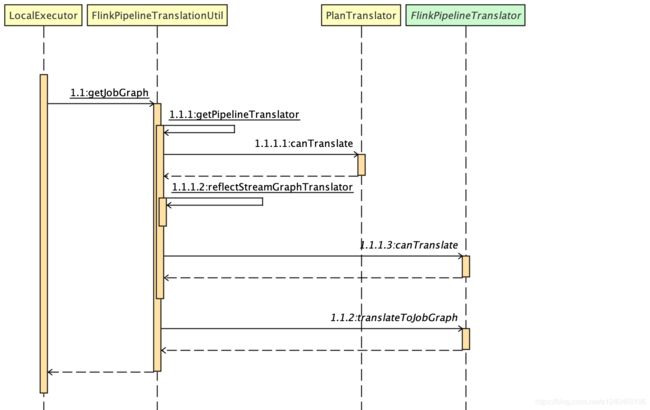
使用 DataStream API 编写好程序之后,就会调用到 StreamExecutionEnvironment.execute() 方法了,首先会调用 getStreamGraph 生成 StreamGraph,接着就会将 StreamGraph 转成 JobGraph,调用链路如下:
- 首先,调用 StreamExecutionEnvironment 的 executeAsync() 方法,根据 Configuration 获取 PipelineExecutorFactory 和 PipelineExecutor 。
@Public
public class StreamExecutionEnvironment {
/**
* 根据 execution.target 配置反射得到 PipelineExecutorFactory,拿出工厂类对应的 PipelineExecutor,执行其 execute() 方法
* execute的主要工作是将 StreamGraph 转成了 JobGraph,并创建相应的 ClusterClient 完成提交任务的操作。
*/
@Internal
public JobClient executeAsync(StreamGraph streamGraph) throws Exception {
checkNotNull(streamGraph, "StreamGraph cannot be null.");
checkNotNull(configuration.get(DeploymentOptions.TARGET), "No execution.target specified in your configuration file.");
// SPI机制
// 根据flink Configuration中的"execution.target"加载 PipelineExecutorFactory
// PipelineExecutorFactory 的实现类在flink-clients包或者flink-yarn包里,因此需要在pom.xml中添加对应的依赖
final PipelineExecutorFactory executorFactory =
executorServiceLoader.getExecutorFactory(configuration);
// 反射出的 PipelineExecutorFactory 类不能为空
checkNotNull(
executorFactory,
"Cannot find compatible factory for specified execution.target (=%s)",
configuration.get(DeploymentOptions.TARGET));
// 根据加载到的 PipelineExecutorFactory 工厂类,获取其对应的 PipelineExecutor,
// 并执行 PipelineExecutor 的 execute() 方法,将 StreamGraph 转成 JobGraph
CompletableFuture<JobClient> jobClientFuture = executorFactory
.getExecutor(configuration)
.execute(streamGraph, configuration);
// 异步调用的返回结果
// ...
}
}
PipelineExecutorFactory 是通过 SPI ServiceLoader 加载的,我们看下 flink-clients 模块的 META-INF.services 文件:

PipelineExecutorFactory 的实现子类,分别对应着 Flink 的不同部署模式,如 local、standalone、yarn、kubernets 等:

这里我们只看下 LocalExecutorFactory 的实现:
@Internal
public class LocalExecutorFactory implements PipelineExecutorFactory {
/**
* execution.target 配置项对应的值为 "local"
*/
@Override
public boolean isCompatibleWith(final Configuration configuration) {
return LocalExecutor.NAME.equalsIgnoreCase(configuration.get(DeploymentOptions.TARGET));
}
/**
* 直接 new 一个 LocalExecutor 返回
*/
@Override
public PipelineExecutor getExecutor(final Configuration configuration) {
return new LocalExecutor();
}
}
PipelineExecutor 的实现子类与 PipelineExecutorFactory 与工厂类一一对应,负责将 StreamGraph 转成 JobGraph,并生成 ClusterClient 执行任务的提交:

- 接着,调用到 LocalExecutor 中的 getJobGraph() 方法,会反射出 StreamGraphTranslator 类,并调用它的 translateToJobGraph() 方法。
@Internal
public class LocalExecutor implements PipelineExecutor {
// ...
private JobGraph getJobGraph(Pipeline pipeline, Configuration configuration) {
// ...
// 这里调用 FlinkPipelineTranslationUtil 的 getJobGraph() 方法
return FlinkPipelineTranslationUtil.getJobGraph(pipeline, configuration, 1);
}
}
FlinkPipelineTranslationUtil 中通过反射得到一个 FlinkPipelineTranslator ,即 StreamGraphTranslator:
public class FlinkPipelineTranslationUtil{
public static JobGraph getJobGraph(
Pipeline pipeline,
Configuration optimizerConfiguration,
int defaultParallelism) {
// 通过反射得到 FlinkPipelineTranslator
FlinkPipelineTranslator pipelineTranslator = getPipelineTranslator(pipeline);
return pipelineTranslator.translateToJobGraph(pipeline,
optimizerConfiguration,
defaultParallelism);
}
private static FlinkPipelineTranslator getPipelineTranslator(Pipeline pipeline) {
PlanTranslator planToJobGraphTransmogrifier = new PlanTranslator();
if (planToJobGraphTransmogrifier.canTranslate(pipeline)) {
return planToJobGraphTransmogrifier;
}
FlinkPipelineTranslator streamGraphTranslator = reflectStreamGraphTranslator();
// 其实就是判断当前的 Pipeline 实例是不是 StreamGraph
if (!streamGraphTranslator.canTranslate(pipeline)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Translator " + streamGraphTranslator + " cannot translate "
+ "the given pipeline " + pipeline + ".");
}
return streamGraphTranslator;
}
private static FlinkPipelineTranslator reflectStreamGraphTranslator() {
Class<?> streamGraphTranslatorClass;
try {
streamGraphTranslatorClass = Class.forName(
// 因为这个类在 flink-streaming-java 模块中,FlinkPipelineTranslationUtil 在 flink-clients 模块中,
// flink-clients 模块没有引入 flink-streaming-java 模块,所以只能通过反射拿到
"org.apache.flink.streaming.api.graph.StreamGraphTranslator",
true,
FlinkPipelineTranslationUtil.class.getClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Could not load StreamGraphTranslator.", e);
}
FlinkPipelineTranslator streamGraphTranslator;
try {
streamGraphTranslator =
(FlinkPipelineTranslator) streamGraphTranslatorClass.newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Could not instantiate StreamGraphTranslator.", e);
}
return streamGraphTranslator;
}
}
public class StreamGraphTranslator implements FlinkPipelineTranslator {
/**
* 其实就是调用 StreamGraph 自己的 getJobGraph() 方法生成 JobGraph
*/
@Override
public JobGraph translateToJobGraph(
Pipeline pipeline,
Configuration optimizerConfiguration,
int defaultParallelism) {
checkArgument(pipeline instanceof StreamGraph,
"Given pipeline is not a DataStream StreamGraph.");
StreamGraph streamGraph = (StreamGraph) pipeline;
return streamGraph.getJobGraph(null);
}
@Override
public boolean canTranslate(Pipeline pipeline) {
return pipeline instanceof StreamGraph;
}
}
到此,我们知道 StreamGraph 到 JobGraph 转换的核心转换方法是 StreamingJobGraphGenerator 的 createJobGraph() 方法。
接下来我们先看下 JobGraph 涉及到的几个类:
2. 源码剖析
2.1 JobVertex
在 StreamGraph 中,每一个算子(Operator)对应了图中的一个节点(StreamNode)。StreamGraph 会被进一步优化,将多个符合条件的节点 Chain 在一起形成一个节点,从而减少数据在不同节点之间流动产生的序列化、反序列化、网络传输的开销。多个算子被 chain 在一起的形成的节点在 JobGraph 中对应的就是 JobVertex。
每个 JobVertex 中包含一个或多个 Operators。
public class JobVertex {
/**
* The ID of the vertex.
* 顶点的id
*/
private final JobVertexID id;
/**
* The alternative IDs of the vertex.
* 顶点的可选id
*/
private final ArrayList<JobVertexID> idAlternatives = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* The IDs of all operators contained in this vertex.
* 此顶点中包含的所有运算符的ID
*/
private final ArrayList<OperatorID> operatorIDs = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* The alternative IDs of all operators contained in this vertex.
* 此顶点中包含的所有运算符的可选ID
*/
private final ArrayList<OperatorID> operatorIdsAlternatives = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* List of produced data sets, one per writer.
* 生成的数据集列表,每个 writer 一个
*/
private final ArrayList<IntermediateDataSet> results = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* List of edges with incoming data. One per Reader.
* 包含传入数据的边的列表,每个 reader 一个
*/
private final ArrayList<JobEdge> inputs = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* Number of subtasks to split this task into at runtime.
* 运行时要将此任务拆分为的子任务数
*/
private int parallelism = ExecutionConfig.PARALLELISM_DEFAULT;
}
2.2 JobEdge
在 StreamGraph 中,StreamNode 之间是通过 StreamEdge 建立连接的。在 JobGraph 中对应的是 JobEdge 。
和 StreamEdge 中同时保留了源节点和目标节点(sourceId 和 targetId) 不同,在 JobEdge 中只有源节点的信息,JobEdge 是和节点的输出结果相关联的。
public class JobEdge {
/**
* The vertex connected to this edge.
* 连接到该边的顶点
*/
private final JobVertex target;
/**
* The distribution pattern that should be used for this job edge.
* 应用于此作业边的分发模式
*/
private final DistributionPattern distributionPattern;
/**
* The data set at the source of the edge, may be null if the edge is not yet connected
* 如果边尚未连接,则边的 source 源处的数据集可能为空
*/
private IntermediateDataSet source;
/**
* The id of the source intermediate data set
* 源中间数据集的id
*/
private IntermediateDataSetID sourceId;
/** Optional name for the data shipping strategy (forward, partition hash, rebalance, ...),
* to be displayed in the JSON plan
* JSON计划中显示的数据传送策略(转发、分区哈希、重新平衡…)的可选名称
*/
private String shipStrategyName;
/** Optional name for the pre-processing operation (sort, combining sort, ...),
* to be displayed in the JSON plan
* JSON计划中显示的预处理操作的可选名称(排序、组合排序...)的可选名称
*/
private String preProcessingOperationName;
/**
* Optional description of the caching inside an operator, to be displayed in the JSON plan
* JSON计划中显示的操作内部缓存的可选描述
*/
private String operatorLevelCachingDescription;
}
2.3 IntermediateDataSet
JobVertex 产生的数据被抽象为 IntermediateDataSet ,字面意思为中间数据集。
JobVertex 是 IntermediateDataSet 的生产者,JobEdge 是 IntermediateDataSet 的消费者。
public class IntermediateDataSet {
/**
* the identifier
* IntermediateDataSet ID
*/
private final IntermediateDataSetID id;
/**
* the operation that produced this data set
* JobVertex 是 IntermediateDataSet 的生产者
*/
private final JobVertex producer;
/**
* JobEdge 是和节点的输出结果相关联的,其实就是指可以把 JobEdge 看作是 IntermediateDataSet 的消费者
*/
private final List<JobEdge> consumers = new ArrayList<JobEdge>();
/**
* The type of partition to use at runtime
* 运行时要使用的分区类型,表示中间结果类型
*/
private final ResultPartitionType resultType;
}
ResultPartitionType 表示中间结果枚举类型,有以下几个属性:
要结合 Flink 任务运行时的内存管理机制来看,后续再作分析。
public enum ResultPartitionType {
BLOCKING(false, false, false, false),
BLOCKING_PERSISTENT(false, false, false, true),
PIPELINED(true, true, false, false),
/**
* 在 Stream 模式下使用的类型
*/
PIPELINED_BOUNDED(true, true, true, false);
/**
* Can the partition be consumed while being produced?
* 分区正在生产时是否能被消费?
*/
private final boolean isPipelined;
/**
* Does the partition produce back pressure when not consumed?
* 当分区不消费时是否产生背压?
*/
private final boolean hasBackPressure;
/**
* Does this partition use a limited number of (network) buffers?
* 分区是否使用有限制的网络 buffer 数?
*/
private final boolean isBounded;
/**
* This partition will not be released after consuming if 'isPersistent' is true.
* 如果 isPersistent 为 true,则在使用后不会释放此分区
*/
private final boolean isPersistent;
}
2.4 StreamConfig
对于每一个 StreamOperator ,也就是 StreamGraph 中的每一个 StreamNode ,在生成 JobGraph 的过程中 StreamingJobGraphGenerator 都会创建一个对应的 StreamConfig 。 StreamConfig 中保存了这个算子 (operator) 在运行时需要的所有配置信息,这些信息都是 k/v 存储在 Configuration 中的。
public class StreamConfig {
/**
* 保存 StreamOperator 信息
*/
@VisibleForTesting
public void setStreamOperator(StreamOperator<?> operator) {
setStreamOperatorFactory(SimpleOperatorFactory.of(operator));
}
/**
* 设置数据集的消费出边集合
*/
public void setChainedOutputs(List<StreamEdge> chainedOutputs) {
try {
InstantiationUtil.writeObjectToConfig(chainedOutputs, this.config, CHAINED_OUTPUTS);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new StreamTaskException("Cannot serialize chained outputs.", e);
}
}
// ...
}
2.5 StreamGraph 到 JobGraph 的核心转换
- 下面我们就来看看 StreamGraph 中的 getJobGraph() 这个核心方法:
public class StreamGraph {
public JobGraph getJobGraph(@Nullable JobID jobID) {
return StreamingJobGraphGenerator.createJobGraph(this, jobID);
}
}
public class StreamingJobGraphGenerator {
/**
* 传入 StreamGraph,生成 JobGraph
*/
public static JobGraph createJobGraph(StreamGraph streamGraph) {
return createJobGraph(streamGraph, null);
}
public static JobGraph createJobGraph(StreamGraph streamGraph, @Nullable JobID jobID) {
return new StreamingJobGraphGenerator(streamGraph, jobID).createJobGraph();
}
private final StreamGraph streamGraph;
/**
* id -> JobVertex 的对应关系
*/
private final Map<Integer, JobVertex> jobVertices;
private final JobGraph jobGraph;
/**
* 已经构建的JobVertex的id集合
*/
private final Collection<Integer> builtVertices;
/**
* 物理边集合(排除了chain内部的边), 按创建顺序排序
*/
private final List<StreamEdge> physicalEdgesInOrder;
/**
* 保存chain信息,部署时用来构建 OperatorChain,startNodeId -> (currentNodeId -> StreamConfig)
*/
private final Map<Integer, Map<Integer, StreamConfig>> chainedConfigs;
/**
* 所有节点的配置信息,id -> StreamConfig
*/
private final Map<Integer, StreamConfig> vertexConfigs;
/**
* 保存每个节点的名字,id -> chainedName
*/
private final Map<Integer, String> chainedNames;
private final Map<Integer, ResourceSpec> chainedMinResources;
private final Map<Integer, ResourceSpec> chainedPreferredResources;
private final Map<Integer, InputOutputFormatContainer> chainedInputOutputFormats;
/**
* 用于计算 hash 值的算法
*/
private final StreamGraphHasher defaultStreamGraphHasher;
private final List<StreamGraphHasher> legacyStreamGraphHashers;
/**
* 核心方法
* StreamGraph 转 JobGraph 的整体流程
*/
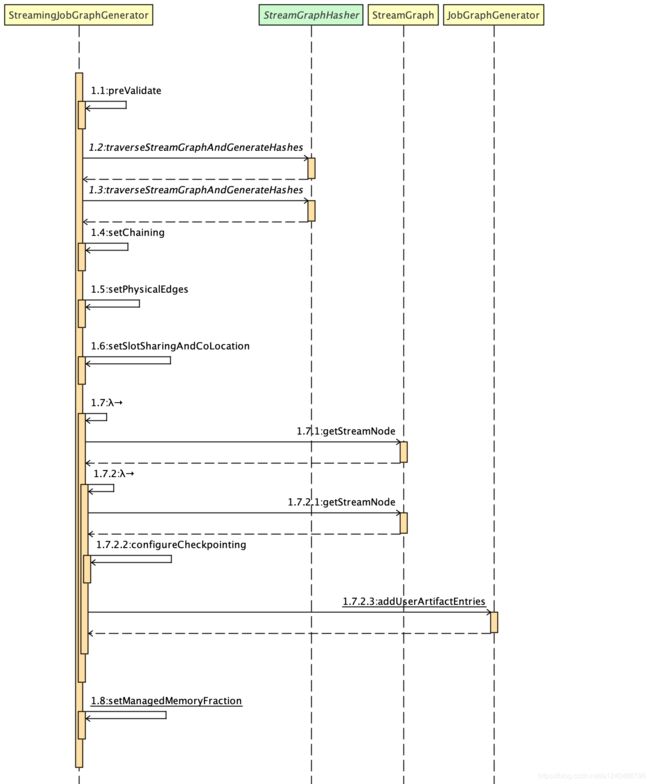
private JobGraph createJobGraph() {
preValidate();
// make sure that all vertices start immediately
// 设置调度模式,streaming 模式下,默认是 ScheduleMode.EAGER ,调度模式是所有节点一起启动
jobGraph.setScheduleMode(streamGraph.getScheduleMode());
// 1. 广度优先遍历 StreamGraph 并且为每个 SteamNode 生成一个唯一确定的 hash id
// Generate deterministic hashes for the nodes in order to identify them across
// submission iff they didn't change.
// 保证如果提交的拓扑没有改变,则每次生成的 hash id 都是一样的,这里只要保证 source 的顺序是确定的,就可以保证最后生产的 hash id 不变
// 它是利用 input 节点的 hash 值及该节点在 map 中位置(实际上是 map.size 算的)来计算确定的
Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes = defaultStreamGraphHasher.traverseStreamGraphAndGenerateHashes(streamGraph);
// Generate legacy version hashes for backwards compatibility
// 这个设置主要是为了防止 hash 机制变化时出现不兼容的情况
List<Map<Integer, byte[]>> legacyHashes = new ArrayList<>(legacyStreamGraphHashers.size());
for (StreamGraphHasher hasher : legacyStreamGraphHashers) {
legacyHashes.add(hasher.traverseStreamGraphAndGenerateHashes(streamGraph));
}
Map<Integer, List<Tuple2<byte[], byte[]>>> chainedOperatorHashes = new HashMap<>();
// 2. 最重要的函数,生成 JobVertex/JobEdge/IntermediateDataSet 等,并尽可能地将多个 StreamNode 节点 chain 在一起
setChaining(hashes, legacyHashes, chainedOperatorHashes);
// 3. 将每个 JobVertex 的入边集合也序列化到该 JobVertex 的 StreamConfig 中 (出边集合已经在 setChaining 的时候写入了)
setPhysicalEdges();
// 4. 根据 group name,为每个 JobVertex 指定所属的 SlotSharingGroup 以及设置 CoLocationGroup
setSlotSharingAndCoLocation();
// 5. 其他设置
// 设置 ManagedMemory 因子
setManagedMemoryFraction(
Collections.unmodifiableMap(jobVertices),
Collections.unmodifiableMap(vertexConfigs),
Collections.unmodifiableMap(chainedConfigs),
id -> streamGraph.getStreamNode(id).getMinResources(),
id -> streamGraph.getStreamNode(id).getManagedMemoryWeight());
// checkpoint相关的配置
configureCheckpointing();
// savepoint相关的配置
jobGraph.setSavepointRestoreSettings(streamGraph.getSavepointRestoreSettings());
// 用户的第三方依赖包就是在这里(cacheFile)传给 JobGraph
JobGraphGenerator.addUserArtifactEntries(streamGraph.getUserArtifacts(), jobGraph);
// set the ExecutionConfig last when it has been finalized
try {
// 将 StreamGraph 的 ExecutionConfig 序列化到 JobGraph 的配置中
jobGraph.setExecutionConfig(streamGraph.getExecutionConfig());
}
catch (IOException e) {
throw new IllegalConfigurationException("Could not serialize the ExecutionConfig." +
"This indicates that non-serializable types (like custom serializers) were registered");
}
return jobGraph;
}
}
这个方法首先为所有节点生成一个唯一的 hash id,如果节点在多次提交中没有改变(包括并发度、上下游等),那么这个 id 就不会改变,这主要用于故障恢复。这里之所以不能用 StreamNode.id 代替,是因为 StreamNode.id 是一个从 1 开始的静态计数变量,同样的 job 在不同的提交中会得到不同的 id 。
如下所示两个 job 是完全一样的,但是 source A 和 B 的 id 却不一样了。
// 范例1: A.id=1 B.id=2
DataStream A = ...
DataStream B = ...
A.union(B).print();
// 范例2: A.id=2 B.id=1
DataStream B = ...
DataStream A = ...
A.union(B).print();
接着,就是最关键的 chaining 处理,生成 JobVertex、JobEdge 等。
先来看一下,Flink 是如何确定两个 Operator 是否能够被 chain 到同一个节点的,只要 StreamEdge 两端的节点满足以下条件,那么这两个节点就可以被串联在同一个 JobVertex 中:
public class StreamingJobGraphGenerator {
/**
* StreamEdge 两端的节点是否能够被 chain 到同一个 JobVertex 中。
* 只要一条边两端的节点满足下面的条件,那么这两个节点就可以被串联在同一个 JobVertex 中
*/
public static boolean isChainable(StreamEdge edge, StreamGraph streamGraph) {
// 获取到上游和下游节点
StreamNode upStreamVertex = streamGraph.getSourceVertex(edge);
StreamNode downStreamVertex = streamGraph.getTargetVertex(edge);
// 获取到上游和下游节点具体的算子对应的 StreamOperator
StreamOperatorFactory<?> headOperator = upStreamVertex.getOperatorFactory();
StreamOperatorFactory<?> outOperator = downStreamVertex.getOperatorFactory();
// 要求下游节点只有一个输入
return downStreamVertex.getInEdges().size() == 1
&& outOperator != null
&& headOperator != null
// 且在同一个 slot 共享组中
&& upStreamVertex.isSameSlotSharingGroup(downStreamVertex)
// 上下游算子的 chaining 策略,要允许 chaining ,默认是 ALWAYS
// 在添加算子时,也可以强制使用 disableChain 设置为 NEVER
&& outOperator.getChainingStrategy() == ChainingStrategy.ALWAYS
&& (headOperator.getChainingStrategy() == ChainingStrategy.HEAD ||
headOperator.getChainingStrategy() == ChainingStrategy.ALWAYS)
// 上下游节点之间的数据传输方式必须是 FORWARD ,而不能是 REBALANCE 等其他模式
&& (edge.getPartitioner() instanceof ForwardPartitioner)
&& edge.getShuffleMode() != ShuffleMode.BATCH
// 上下游节点的并行度要一致
&& upStreamVertex.getParallelism() == downStreamVertex.getParallelism()
// chain enabled 配置项为 true
&& streamGraph.isChainingEnabled();
}
}
下面来看下 setChaining() 这个关键方法:
public class StreamingJobGraphGenerator {
private void setChaining(Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes, List<Map<Integer, byte[]>> legacyHashes, Map<Integer, List<Tuple2<byte[], byte[]>>> chainedOperatorHashes) {
for (Integer sourceNodeId : streamGraph.getSourceIDs()) {
createChain(sourceNodeId, sourceNodeId, hashes, legacyHashes, 0, chainedOperatorHashes);
}
}
/**
* 构建 operator chain(可能包含一个或多个 StreamNode),返回值是当前的这个 operator chain 实际的输出边(不包含内部的边)
* 如果 currentNodeId != startNodeId ,说明当前节点在 operator chain 的内部。
*
* 通过 DFS 遍历所有的 StreamNode,并按照 chainable 的条件不停的将可以串联的 operator 放在同一个 operator chain 中。
* 每一个 StreamNode 的配置信息都会被序列化到对应的 StreamConfig 中。只有 operator chain 的头部节点会生成对应的 JobVertex ,
* 一个 operator chain 的所有内部节点都会以序列化的形式写入头部节点的 CHAINED_TASK_CONFIG 配置项中。
*/
private List<StreamEdge> createChain(
Integer startNodeId,
Integer currentNodeId,
Map<Integer, byte[]> hashes,
List<Map<Integer, byte[]>> legacyHashes,
int chainIndex,
Map<Integer, List<Tuple2<byte[], byte[]>>> chainedOperatorHashes) {
if (!builtVertices.contains(startNodeId)) {
// 当前 operator chain 最终的输出边,不包括内部的边
List<StreamEdge> transitiveOutEdges = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>();
List<StreamEdge> chainableOutputs = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>();
List<StreamEdge> nonChainableOutputs = new ArrayList<StreamEdge>();
StreamNode currentNode = streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId);
// 将当前节点的出边分为两组,即 chainable 和 nonChainable
for (StreamEdge outEdge : currentNode.getOutEdges()) {
// 判断当前 StreamEdge 的上下游是否可以串联在一起
if (isChainable(outEdge, streamGraph)) {
chainableOutputs.add(outEdge);
} else {
nonChainableOutputs.add(outEdge);
}
}
// 对于 chainable 的输出边,递归调用,找到最终的输出边并加入到输出列表中
for (StreamEdge chainable : chainableOutputs) {
transitiveOutEdges.addAll(
createChain(startNodeId, chainable.getTargetId(), hashes, legacyHashes, chainIndex + 1, chainedOperatorHashes));
}
// 对于 nonChainable 的边
for (StreamEdge nonChainable : nonChainableOutputs) {
// 这个边本身就应该加入到当前节点的输出列表中
transitiveOutEdges.add(nonChainable);
// 递归调用,以下游节点为起点创建新的 operator chain
createChain(nonChainable.getTargetId(), nonChainable.getTargetId(), hashes, legacyHashes, 0, chainedOperatorHashes);
}
// 用于保存一个 operator chain 所有 operator 的 hash 信息
List<Tuple2<byte[], byte[]>> operatorHashes =
chainedOperatorHashes.computeIfAbsent(startNodeId, k -> new ArrayList<>());
byte[] primaryHashBytes = hashes.get(currentNodeId);
OperatorID currentOperatorId = new OperatorID(primaryHashBytes);
for (Map<Integer, byte[]> legacyHash : legacyHashes) {
operatorHashes.add(new Tuple2<>(primaryHashBytes, legacyHash.get(currentNodeId)));
}
// 当前节点的名称,资源要求等信息
chainedNames.put(currentNodeId, createChainedName(currentNodeId, chainableOutputs));
chainedMinResources.put(currentNodeId, createChainedMinResources(currentNodeId, chainableOutputs));
chainedPreferredResources.put(currentNodeId, createChainedPreferredResources(currentNodeId, chainableOutputs));
if (currentNode.getInputFormat() != null) {
getOrCreateFormatContainer(startNodeId).addInputFormat(currentOperatorId, currentNode.getInputFormat());
}
if (currentNode.getOutputFormat() != null) {
getOrCreateFormatContainer(startNodeId).addOutputFormat(currentOperatorId, currentNode.getOutputFormat());
}
// 如果当前节点是起始节点,则直接创建 JobVertex 并返回 StreamConfig ,否则先创建一个空的 StreamConfig
// createJobVertex 函数就是根据 StreamNode 创建对应的 JobVertex,并返回了空的 StreamConfig
StreamConfig config = currentNodeId.equals(startNodeId)
? createJobVertex(startNodeId, hashes, legacyHashes, chainedOperatorHashes)
: new StreamConfig(new Configuration());
// 设置 JobVertex 的 StreamConfig ,基本上是序列化 StreamNode 中的配置到 StreamConfig 中
// 其中包括 序列化器,StreamOperator,Checkpoint 等相关配置
setVertexConfig(currentNodeId, config, chainableOutputs, nonChainableOutputs);
if (currentNodeId.equals(startNodeId)) {
// 如果是 chain 的起始节点。(不是chain中的节点,也会被标记成 chain start)
config.setChainStart();
config.setChainIndex(0);
config.setOperatorName(streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId).getOperatorName());
// 把实际的输出边写入配置,部署时会用到
config.setOutEdgesInOrder(transitiveOutEdges);
// operator chain 的头部 operator 的输出边,包括内部的边
config.setOutEdges(streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId).getOutEdges());
// 将当前节点(headOfChain)与所有出边相连
for (StreamEdge edge : transitiveOutEdges) {
// 通过 StreamEdge 构建出 JobEdge,创建 IntermediateDataSet,用来将 JobVertex 和 JobEdge 相连
connect(startNodeId, edge);
}
// 将 operator chain 中所有子节点的 StreamConfig 写入到 headOfChain 节点的 CHAINED_TASK_CONFIG 配置中
config.setTransitiveChainedTaskConfigs(chainedConfigs.get(startNodeId));
} else {
// 如果是 operator chain 内部的节点
chainedConfigs.computeIfAbsent(startNodeId, k -> new HashMap<Integer, StreamConfig>());
config.setChainIndex(chainIndex);
StreamNode node = streamGraph.getStreamNode(currentNodeId);
config.setOperatorName(node.getOperatorName());
// 将当前节点的 StreamConfig 添加到所在的 operator chain 的 config 集合中
chainedConfigs.get(startNodeId).put(currentNodeId, config);
}
// 设置当前 operator 的 OperatorID
config.setOperatorID(currentOperatorId);
if (chainableOutputs.isEmpty()) {
config.setChainEnd();
}
return transitiveOutEdges;
} else {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
}
}
上面的过程实际上就是通过 DFS 遍历所有的 StreamNode,并按照 chainable 的条件不停的将可以串联的 operator 放在同一个 operator chain 中。每一个 StreamNode 的配置信息都会被序列化到对应的 StreamConfig 中。只有 operator chain 的头部节点会生成对应的 JobVertex ,一个 operator chain 的所有内部节点都会以序列化的形式写入头部节点的 CHAINED_TASK_CONFIG 配置项中。
每一个 operator chain 都会为所有的实际输出边创建对应的 JobEdge,并和 JobVertex 连接,我们看下 createChain() 方法中的 connect() 方法:
public class StreamingJobGraphGenerator {
/**
* 每一个 operator chain 都会为所有的实际输出边创建对应的 JobEdge,并和 JobVertex 连接
*/
private void connect(Integer headOfChain, StreamEdge edge) {
physicalEdgesInOrder.add(edge);
Integer downStreamvertexID = edge.getTargetId();
// 上下游节点
JobVertex headVertex = jobVertices.get(headOfChain);
JobVertex downStreamVertex = jobVertices.get(downStreamvertexID);
StreamConfig downStreamConfig = new StreamConfig(downStreamVertex.getConfiguration());
// 下游节点增加一个输入
downStreamConfig.setNumberOfInputs(downStreamConfig.getNumberOfInputs() + 1);
StreamPartitioner<?> partitioner = edge.getPartitioner();
ResultPartitionType resultPartitionType;
switch (edge.getShuffleMode()) {
case PIPELINED:
resultPartitionType = ResultPartitionType.PIPELINED_BOUNDED;
break;
case BATCH:
resultPartitionType = ResultPartitionType.BLOCKING;
break;
case UNDEFINED:
resultPartitionType = streamGraph.isBlockingConnectionsBetweenChains() ?
ResultPartitionType.BLOCKING : ResultPartitionType.PIPELINED_BOUNDED;
break;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Data exchange mode " +
edge.getShuffleMode() + " is not supported yet.");
}
JobEdge jobEdge;
// 创建 JobEdge 和 IntermediateDataSet
// 根据 StreamPartitioner 类型决定在上游节点(生产者)的子任务和下游节点(消费者)之间的连接模式
if (partitioner instanceof ForwardPartitioner || partitioner instanceof RescalePartitioner) {
jobEdge = downStreamVertex.connectNewDataSetAsInput(
headVertex,
DistributionPattern.POINTWISE,
resultPartitionType);
} else {
jobEdge = downStreamVertex.connectNewDataSetAsInput(
headVertex,
DistributionPattern.ALL_TO_ALL,
resultPartitionType);
}
// set strategy name so that web interface can show it.
jobEdge.setShipStrategyName(partitioner.toString());
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("CONNECTED: {} - {} -> {}", partitioner.getClass().getSimpleName(),
headOfChain, downStreamvertexID);
}
}
}
3. 自带 WordCount 示例详解
后续补充debug详细过程。
参考:
http://wuchong.me/blog/2016/05/10/flink-internals-how-to-build-jobgraph/
https://blog.jrwang.me/2019/flink-source-code-jobgraph/