数据结构与算法——哈希表与字符串
文章目录
-
- 1.预备知识
-
- 1.1 最简单的哈希——统计字符个数
- 1.2 哈希表排序整数
- 1.3 哈希映射的问题
- 2.最长回文串
-
- 2.1 题目描述
- 2.2 C++代码实现
- 3.单词规律
-
- 3.1 题目描述
- 3.2 算法思路
- 3.3 C++代码实现
- 4.字母异位词分组
-
- 4.1 题目描述
- 4.2 算法思路
- 4.3 C++代码实现
- 5.无重复字符的最长子串
-
- 5.1 题目描述
- 5.2 算法思路
- 5.3 C++代码实现
- 6.重复的DNA序列
-
- 6.1 题目描述
- 6.2 算法思路
- 6.3 C++代码实现
- 7.最小覆盖子串
-
- 7.1 题目描述
- 7.2 算法思路
- 7.3 C++代码实现
1.预备知识
1.1 最简单的哈希——统计字符个数
1.题目描述
输入一个字符串,输出字符串中每个字符的个数
例如:simple_hash(“abcdefgaaxxy”)
输出:
[a][97]:3
[b][98]:1
[c][99]:1
[d][100]:1
[e][101]:1
[f][102]:1
[g][103]:1
[x][120]:2
[y][121]:1
2.C++代码实现
class solution {
public:
//1.最简单的哈希,输入字符串,输出字符串中重复字符的个数
void simple_hash(string str){
int char_map[128] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char_map[str[i]]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 128; i++) {
if (char_map[i] > 0) {
printf("[%c][%d]:%d\n", i, i, char_map[i]);
}
}
}
};
1.2 哈希表排序整数
1.题目描述
输入:{999,1,444,7,20,9,1,3,7,7}
输出:1,1,3,7,7,7,9,444,999
2.C++代码实现
class solution {
public:
vector<int> sort_hash(vector<int>& array){
vector<int> result;
int hash_map[1000] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < array.size(); i++) {
hash_map[array[i]]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < hash_map[i]; j++) {
result.push_back(i);
}
}
return result;
}
};
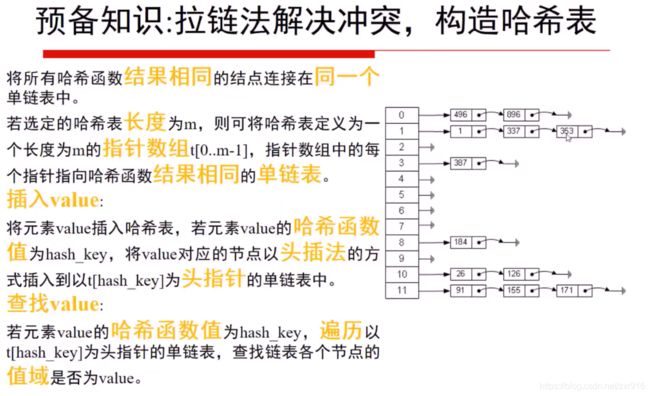
1.3 哈希映射的问题
1.任意元素的哈希映射
int solution::hash_func(int key, int table_len) {
return key % table_len;
}
void solution::insert(ListNode* hash_table[], ListNode* node, int table_len) {
int hash_key = hash_func(node->val, table_len);
node->next = hash_table[hash_key];
hash_table[hash_key] = node;
}
bool solution::search(ListNode* hash_table[], int value, int table_len) {
int hash_key = hash_func(value, table_len);
ListNode* head = hash_table[hash_key];
while (head) {
if (value == head->val) {
return true;
}
head = head->next;
}
return false;
}
2.最长回文串
2.1 题目描述
给定一个包含大写字母和小写字母的字符串,找到通过这些字母构造成的最长的回文串。
在构造过程中,请注意区分大小写。比如 “Aa” 不能当做一个回文字符串。
示例 1:
输入:
“abccccdd”
输出:
7
解释:
我们可以构造的最长的回文串是"dccaccd", 它的长度是 7。
2.2 C++代码实现
class Solution {
public:
int longestPalindrome(string s) {
int array[123]={0};
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){
array[s[i]]++;
if(array[s[i]]%2==0){
count+=2;
}
}
if(count<s.size()){
count++;
}
return count;
}
};
3.单词规律
3.1 题目描述
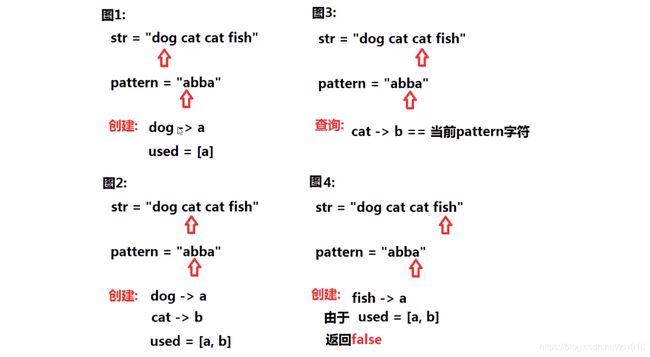
给定一种规律 pattern 和一个字符串 str ,判断 str 是否遵循相同的规律。
这里的 遵循 指完全匹配,例如, pattern 里的每个字母和字符串 str 中的每个非空单词之间存在着双向连接的对应规律。
示例1:
输入: pattern = "abba", str = "dog cat cat dog"
输出: true
示例 2:
输入:pattern = "abba", str = "dog cat cat fish"
输出: false
示例 3:
输入: pattern = "aaaa", str = "dog cat cat dog"
输出: false
示例 4:
输入: pattern = "abba", str = "dog dog dog dog"
输出: false
3.2 算法思路
3.3 C++代码实现
class Solution {
public:
bool wordPattern(string pattern, string s) {
map<string,char> word_map;
int used[128]={0};
string word;
int pos=0;
s.push_back(' ');
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(s[i]==' '){
if(pos==pattern.length()){
return false;
}
if(word_map.find(word)==word_map.end()){
if(used[pattern[pos]]==1){
return false;
}
word_map[word]=pattern[pos];
used[pattern[pos]]=1;
}
else{
if(word_map[word]!=pattern[pos]){
return false;
}
}
pos++;
word="";
}
else{
word+=s[i];
}
}
if(pos!=pattern.length()){
return false;
}
return true;
}
};
4.字母异位词分组
4.1 题目描述
给定一个字符串数组,将字母异位词组合在一起。字母异位词指字母相同,但排列不同的字符串。
示例:
输入: ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"]
输出:
[
["ate","eat","tea"],
["nat","tan"],
["bat"]
]
4.2 算法思路
4.3 C++代码实现
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> groupAnagrams(vector<string>& strs) {
map<string,vector<string>> anagram;
vector<vector<string>> result;
for(int i=0;i<strs.size();i++){
string str=strs[i];
sort(str.begin(),str.end());
if(anagram.find(str)==anagram.end()){
vector<string> item;
anagram[str]=item;
}
anagram[str].push_back(strs[i]);
}
map<string,vector<string>>::iterator it;
for(it=anagram.begin();it!=anagram.end();it++){
result.push_back((*it).second);
}
return result;
}
};
5.无重复字符的最长子串
5.1 题目描述
给定一个字符串,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
示例 1:
输入: s = "abcabcbb"
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "abc",所以其长度为 3。
示例 2:
输入: s = "bbbbb"
输出: 1
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "b",所以其长度为 1。
示例 3:
输入: s = "pwwkew"
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "wke",所以其长度为 3。
请注意,你的答案必须是 子串 的长度,"pwke" 是一个子序列,不是子串。
示例 4:
输入: s = ""
输出: 0
5.2 算法思路
5.3 C++代码实现
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int begin=0;
int result=0;
string word="";
int char_map[128]={0};
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
char_map[s[i]]++;
if(char_map[s[i]]==1){
word+=s[i];
if(result<word.length()){
result=word.length();
}
}
else{
while(begin<i&&char_map[s[i]]>1){
char_map[s[begin]]--;
begin++;
}
word="";
for(int j=begin;j<=i;j++){
word+=s[j];
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
6.重复的DNA序列
6.1 题目描述
所有 DNA 都由一系列缩写为 ‘A’,‘C’,‘G’ 和 ‘T’ 的核苷酸组成,例如:“ACGAATTCCG”。在研究 DNA 时,识别 DNA 中的重复序列有时会对研究非常有帮助。
编写一个函数来找出所有目标子串,目标子串的长度为 10,且在 DNA 字符串 s 中出现次数超过一次。
示例 1:
输入:s = "AAAAACCCCCAAAAACCCCCCAAAAAGGGTTT"
输出:["AAAAACCCCC","CCCCCAAAAA"]
示例 2:
输入:s = "AAAAAAAAAAAAA"
输出:["AAAAAAAAAA"]
6.2 算法思路
6.3 C++代码实现
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> findRepeatedDnaSequences(string s) {
map<string,int> word_map;
vector<string> result;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
string word=s.substr(i,10);
if(word_map.find(word)==word_map.end()){
word_map[word]=1;
}
else{
word_map[word]++;
}
}
map<string,int>::iterator it;
for(it=word_map.begin();it!=word_map.end();it++){
if(it->second>1){
result.push_back(it->first);
}
}
return result;
}
};
7.最小覆盖子串
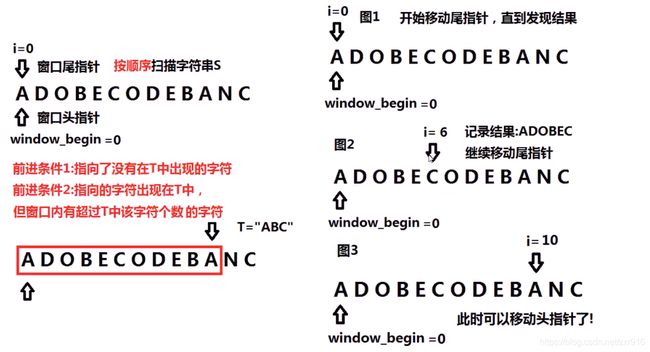
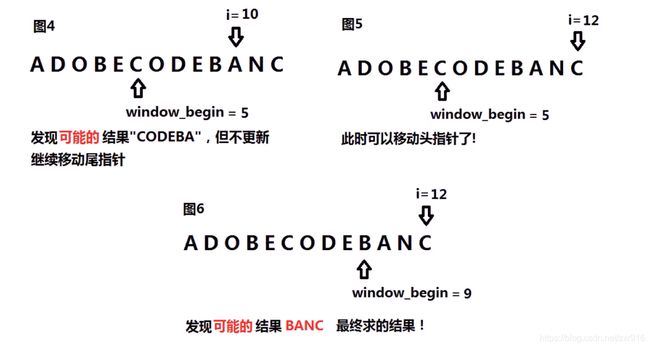
7.1 题目描述
给你一个字符串 s 、一个字符串 t 。返回 s 中涵盖 t 所有字符的最小子串。如果 s 中不存在涵盖 t 所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串 “” 。
注意:如果 s 中存在这样的子串,我们保证它是唯一的答案。
示例 1:
输入:s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC"
输出:"BANC"
示例 2:
输入:s = "a", t = "a"
输出:"a"
7.2 算法思路
7.3 C++代码实现
class Solution {
public:
bool is_window_ok(int map_s[],int map_t[],vector<int>& vec_t){
for(int i=0;i<vec_t.size();i++){
if(map_s[vec_t[i]]<map_t[vec_t[i]]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
string minWindow(string s, string t) {
int map_s[128]={0};
int map_t[128]={0};
vector<int> vec_t;
for(int i=0;i<t.length();i++){
map_t[t[i]]++;
}
for(int i=0;i<128;i++){
if(map_t[i]>0){
vec_t.push_back(i);
}
}
int window_begin=0;
string result;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
map_s[s[i]]++;
while(window_begin<i){
char begin_ch=s[window_begin];
if(map_t[begin_ch]==0){
window_begin++;
}
else if(map_s[begin_ch]>map_t[begin_ch]){
map_s[begin_ch]--;
window_begin++;
}
else{
break;
}
}
if(is_window_ok(map_s,map_t,vec_t)){
int new_window_len=i-window_begin+1;
if(result==""||result.length()>new_window_len){
result=s.substr(window_begin,new_window_len);
}
}
}
return result;
}
};