前言
Hadoop二次排序简单说就是先根据字段A分组排序,然后在对组内根据字段B排序。Hadoop二次排序在面试的时候出现频率也是比较高的。今天花了点时间通过源码深入学习了一下。(后面内容以Hadoop自带实例——SecondarySort讲解,见本文附录)
Hadoop默认是根据reduce key排序,通过Hadoop二次排序可以实现根据value值(需要将其放入复合key中)进行排序,排序后做可以取TOP值。比如可以做,每个网站访问量最大前10个URL等分析。
关键点
1、Partitioner
它的作用是决定数据分区,说白了就是决定map输出key-value由哪个reduce处理,每个map task输出的key-value都会执行Partitioner的getPartition()方法,用于返回当前key-value由哪个reduce处理。
本例中Partitioner基于map函数输出IntPair(first, second)第一个元素,即first,进行求余运算,所以得到的结果是first相同的key-value会发送到同一reduce。
2、IntPair的compareTo()方法
IntPair是map输出的key,它的compareTo()方法决定map输出排序规则。IntPair的实现规则是:先按照first排序,相同first按照second排序(所谓的二次排序其实在这里就实现了)。结果如下:
-------------
1982 6
1984 3
1984 4
1984 5
1984 5
1988 10
-------------
运行时机:
- map函数,从缓冲区spill key-value到本地磁盘
- reduce函数。获取逻辑:如果有GroupingComparator就返回,否则返回map输出比较函数。
3、GroupingComparator
实现逻辑
根据IntPair的first字段进行排序
运行时机:
ReduceTask.run() ->
// copy、sort完成之后
RawComparator comparator = job.getOutputValueGroupingComparator(); // 这里获取comparator
runNewReducer(job, umbilical, reporter, rIter, comparator, keyClass, valueClass);
runNewReducer() ->
....
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer.Context
reducerContext = createReduceContext(reducer, job, getTaskID(),
rIter, reduceInputKeyCounter,
reduceInputValueCounter,
trackedRW, committer,
reporter, comparator, keyClass,
valueClass);
reducer.run(reducerContext); // reducerContext拥有comparator
reducer.run() ->
while (context.nextKey()) { <-
...
}
context.nextKey() ->
while (hasMore && nextKeyIsSame) {
nextKeyValue(); <- ①
}
if (hasMore) {
if (inputKeyCounter != null) {
inputKeyCounter.increment(1);
}
return nextKeyValue(); <- ②
} else {
return false;
}
nextKeyValue() ->
....
if (hasMore) {
next = input.getKey();
nextKeyIsSame = comparator.compare(currentRawKey.getBytes(), 0,
currentRawKey.getLength(),
next.getData(),
next.getPosition(),
next.getLength() - next.getPosition()
) == 0;
} else {
nextKeyIsSame = false;
}
....
可以看到GroupingComparator在reduce函数内被调用,用于迭代读取reduce输入文件过程中,判断key是否发生变化。那它有什么作用呢?要会回答这个问题,不如先问问,如果没有GroupingComparator结果会如何?
如果在Job提交时不设置GroupingComparator,那comparator将使用conf中"mapred.output.key.comparator.class"对应的类,如果没有设置"mapred.output.key.comparator.class",则根据map输出key从WritableComparator获取注册的comparator(IntPair通过" WritableComparator.define(IntPair.class, new Comparator());"注册)。本例中,如果不设置GroupingComparator,就会使用IntPair的内嵌类Comparator的compareTo()方法判断,即先比较first,再比较second。这样在迭代读取reduce输入数据的时候,会发生这样的情况:first相同,second不同,comparator会认为两条记录不一致,从而变更key值,继续迭代,这样就无法将相同first的数据聚合到一个迭代中进行处理的,即相同first通过second进行排序。
其它
- pig可以通过内嵌foreach方式实现二次排序功能
- SQL中需要使用子查询实现该功能,见:http://heipark.iteye.com/blog/1776101
附录
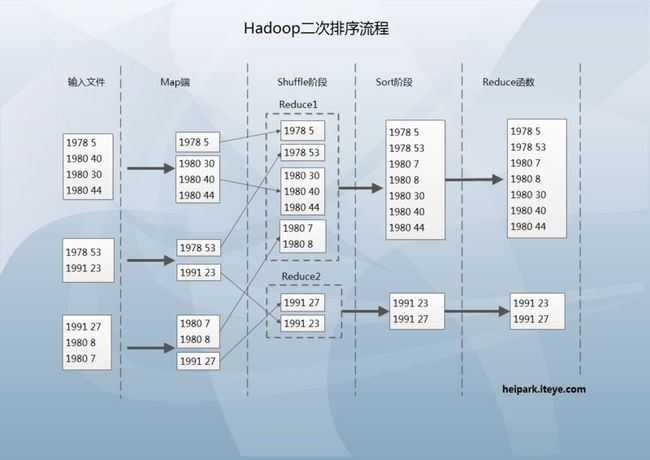
下图是我整理的流程,更易于理解^_^
public class SecondarySort {
/**
* Define a pair of integers that are writable.
* They are serialized in a byte comparable format.
*/
public static class IntPair
implements WritableComparable<IntPair> {
private int first = 0;
private int second = 0;
/**
* Set the left and right values.
*/
public void set(int left, int right) {
first = left;
second = right;
}
public int getFirst() {
return first;
}
public int getSecond() {
return second;
}
/**
* Read the two integers.
* Encoded as: MIN_VALUE -> 0, 0 -> -MIN_VALUE, MAX_VALUE-> -1
*/
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
first = in.readInt() + Integer.MIN_VALUE;
second = in.readInt() + Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeInt(first - Integer.MIN_VALUE);
out.writeInt(second - Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return first * 157 + second;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object right) {
if (right instanceof IntPair) {
IntPair r = (IntPair) right;
return r.first == first && r.second == second;
} else {
return false;
}
}
/** A Comparator that compares serialized IntPair. */
public static class Comparator extends WritableComparator {
public Comparator() {
super(IntPair.class);
}
public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1,
byte[] b2, int s2, int l2) {
return compareBytes(b1, s1, l1, b2, s2, l2);
}
}
static { // register this comparator
WritableComparator.define(IntPair.class, new Comparator());
}
@Override
public int compareTo(IntPair o) {
if (first != o.first) {
return first < o.first ? -1 : 1;
} else if (second != o.second) {
return second < o.second ? -1 : 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
/**
* Partition based on the first part of the pair.
*/
public static class FirstPartitioner extends Partitioner<IntPair,IntWritable>{
@Override
public int getPartition(IntPair key, IntWritable value,
int numPartitions) {
return Math.abs(key.getFirst() * 127) % numPartitions;
}
}
/**
* Compare only the first part of the pair, so that reduce is called once
* for each value of the first part.
*/
public static class FirstGroupingComparator
implements RawComparator<IntPair> {
@Override
public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, byte[] b2, int s2, int l2) {
return WritableComparator.compareBytes(b1, s1, Integer.SIZE/8,
b2, s2, Integer.SIZE/8);
}
@Override
public int compare(IntPair o1, IntPair o2) {
int l = o1.getFirst();
int r = o2.getFirst();
return l == r ? 0 : (l < r ? -1 : 1);
}
}
/**
* Read two integers from each line and generate a key, value pair
* as ((left, right), right).
*/
public static class MapClass
extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntPair, IntWritable> {
private final IntPair key = new IntPair();
private final IntWritable value = new IntWritable();
@Override
public void map(LongWritable inKey, Text inValue,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(inValue.toString());
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
if (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
left = Integer.parseInt(itr.nextToken());
if (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
right = Integer.parseInt(itr.nextToken());
}
key.set(left, right);
value.set(right);
context.write(key, value);
}
}
}
/**
* A reducer class that just emits the sum of the input values.
*/
public static class Reduce
extends Reducer<IntPair, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
private static final Text SEPARATOR =
new Text("------------------------------------------------");
private final Text first = new Text();
@Override
public void reduce(IntPair key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(SEPARATOR, null);
first.set(Integer.toString(key.getFirst()));
for(IntWritable value: values) {
context.write(first, value);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: secondarysort <in> <out>");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = new Job(conf, "secondary sort");
job.setJarByClass(SecondarySort.class);
job.setMapperClass(MapClass.class);
job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
// group and partition by the first int in the pair
job.setPartitionerClass(FirstPartitioner.class);
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(FirstGroupingComparator.class);
// the map output is IntPair, IntWritable
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(IntPair.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// the reduce output is Text, IntWritable
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
--end