【线程管理】之篇一
【线程管理】之篇一
摘要: 原创出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/Alandre/ 泥沙砖瓦浆木匠 希望转载,保留摘要,谢谢!
亲爱我,孝何难;亲恶我,孝方贤。
一、简介
二、简单介绍线程创建和运行
三、线程信息的获取和设置
四、线程中断:interrupt() 或者 使用java异常控制
五、线程的休眠和恢复
六、等待线程的终止
一、简介
并发(Concurrency)指的是一系列任务的同时运行。如果一台电脑多个处理器或者多核处理器,这个同时性是真正意义上的并发;但一电脑只有一个单核处理器,这个同时性并不是真正的并发。
线程(thread)是操作系统能够进行运算调度的最小单位。它被包含在进程之中,是进程中的实际运作单位。一条线程指的是进程中一个单一顺序的控制流,一个进程中可以并发多个线程,每条线程并行执行不同的任务。
举个例子:在唱歌的时候,你可以同时阅读电子邮件,又可以浏览网页。这种存在着 进程级(Process-Level)并发。在浏览网页中,可以看书,视频,写日志,写博…有着多个同时进行的任务,这种进程并发任务为 线程(Thread)。
二、简单介绍线程创建和运行
java程序创建线程有两种方法:
继承Thread类,覆盖run方法。
创建一个Runnable接口的类。使用带参数的Thread构造器创建Thread对象。这个参数就是实现Runnable接口的类的一个对象。
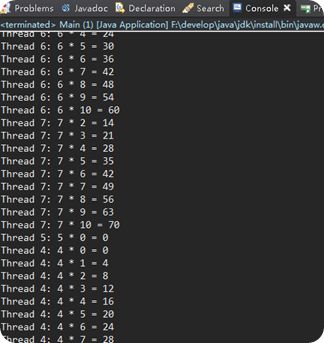
用第二种方式,举个很简单的例子:Calculator.java
![]()
public class Calculator implements Runnable
{ private int number; public Calculator(int number)
{ this.number = number;
}
@Override public void run()
{ for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
{
System.out.printf("%s: %d * %d = %d \n", Thread.currentThread()
.getName(), number, i, i * number);
}
} public static void main(String[] args)
{ new Thread(new Calculator(1)).start();;
}
}
![]()
你可以看到以下输出:
![]()
Thread-0: 1 * 0 = 0 Thread-0: 1 * 1 = 1 Thread-0: 1 * 2 = 2 Thread-0: 1 * 3 = 3 Thread-0: 1 * 4 = 4 ...
![]()
Java 虚拟机会继续执行线程,直到下列任一情况出现时为止:
调用了
Runtime类的exit方法,并且安全管理器允许退出操作发生。非守护线程的所有线程都已停止运行,无论是通过从对 run 方法的调用中返回,还是通过抛出一个传播到
run方法之外的异常。
注意:其实 java.lang.Thread 实现的接口:Runnable 。只有当调用Thread对象的start方法,新的线程才会被创建。
相关资料:
java.lang.Thread
Thread(Runnable target)
分配新的 Thread 对象。
void start()
使该线程开始执行;Java 虚拟机调用该线程的 run 方法。
static Thread currentThread()
返回对当前正在执行的线程对象的引用。
String getName()
返回该线程的名称。
三、线程信息的获取和设置
Thread类有了一些保存信息的属性,这些属性用来标识线程,显示线程状态或控制线程优先级。
ID: 保存了线程唯一标识符
Name: 线程名称
Priority: 线程的优先级。 1-10 最低优先级为1 最高优先级为10.
Status线程状态。线程可以处于下列状态之一:
NEW
至今尚未启动的线程处于这种状态。
RUNNABLE
正在 Java 虚拟机中执行的线程处于这种状态。
BLOCKED
受阻塞并等待某个监视器锁的线程处于这种状态。
WAITING
无限期地等待另一个线程来执行某一特定操作的线程处于这种状态。
TIMED_WAITING
等待另一个线程来执行取决于指定等待时间的操作的线程处于这种状态。
TERMINATED
已退出的线程处于这种状态。
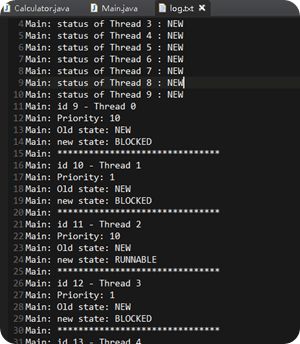
下面演示一个 10个线程 名称和优先级 输出他们的状态信息直到线程结束:
Calculator.java
![]()
public class Calculator implements Runnable
{ private int number; public Calculator(int number)
{ this.number = number;
}
@Override public void run()
{ for (int i = 0; i <= 10 ; i++)
{
System.out.printf("%s: %d * %d = %d \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(),number,i,i*number);
}
}
}
![]()
测试代码:Main.java
![]()
public class Main
{ public static void main(String[] args)
{
Thread threads[] = new Thread[10];
Thread.State status[] = new Thread.State[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
threads[i] = new Thread(new Calculator(i));
if ((i%2) == 0)
threads[i].setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); else
threads[i].setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
threads[i].setName("Thread "+i);
}
try(FileWriter file = new FileWriter(".\\log.txt");
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(file);)
{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
pw.println("Main: status of Thread "+i+" : "+threads[i].getState());
status[i] = threads[i].getState();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
threads[i].start();
}
boolean finish = false; while (!finish)
{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{ if (threads[i].getState() != status[i])
{
writeThreadInfo(pw , threads[i],status[i]);
status[i] = threads[i].getState();
}
}
finish = true; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
finish = finish && (threads[i].getState() == State.TERMINATED);
}
}
} catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
} private static void writeThreadInfo(PrintWriter pw, Thread thread,
State state)
{
pw.printf("Main: id %d - %s \n", thread.getId(),thread.getName());
pw.printf("Main: Priority: %d\n", thread.getPriority());
pw.printf("Main: Old state: %s \n", state);
pw.printf("Main: new state: %s \n", thread.getState());
pw.printf("Main: *******************************\n");
}
}
![]()
你可以看到控制台 和 生成的log.txt记录者每个线程的状态演变。最高的比最低优先级的线程结束的早。
注意:如果没有给线程置顶名字,JVM给分配默认格式名字:Thread-XX(XX为一组数字).同样线程ID和状态是不许改变的。线程类没提供setId() 和 setStatus()。
相关资料:
java.lang.Thread
void setPriority(int newPriority)
更改线程的优先级。
void setName(String name)
改变线程名称,使之与参数 name 相同。
Thread.State getState()
返回该线程的状态。
四、线程中断:interrupt() 或者 使用java异常控制
线程中,java提供了中断机制。但是如果是复杂的算法 和 分布在几个方法中,java提供了InterruptedException一次控制线程中断。
下面各自举个例子:
第一个创建一个线程,运行5秒钟后再通过中断机制强制使其终止。
PrimeGenerator .java
![]()
public class PrimeGenerator extends Thread
{
@Override public void run()
{ long number = 1L; while (true)
{ if(isPrime(number))
System.out.println("Number "+number+" is Prime");
if (isInterrupted())
{
System.out.println("The Prime Generator has been Interrupted"); return ;
}
number++;
}
} private boolean isPrime(long number)
{ if (number < 2) return true; for (long i = 2; i < number; i++)
{ if ((number % i) == 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
![]()
测试代码:Main.java
![]()
public class Main
{ public static void main(String[] args)
{
Thread task = new PrimeGenerator();
task.start(); try
{
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
task.interrupt();
}
}
![]()
你可以观察到,5秒钟内任务在跳动,但是
相关资料:
java.lang.Thread
boolean isInterrupted()
测试线程是否已经中断。
static void sleep(long millis)
在指定的毫秒数内让当前正在执行的线程休眠(暂停执行),此操作受到系统计时器和调度程序精度和准确性的影响。
void interrupt()
中断线程。
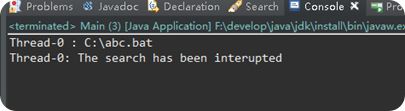
第二个我们用InterruptedException异常来控制线程中断。
FileSearch.java
![]()
public class FileSearch implements Runnable
{ private String initPath; private String fileName;
public FileSearch(String initPath, String fileName)
{ this.initPath = initPath; this.fileName = fileName;
}
@Override public void run()
{
File file = new File(initPath); if (file.isDirectory())
{ try
{
directoryProcess(file);
} catch (InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.printf("%s: The search has been interupted",Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
} private void directoryProcess(File file) throws InterruptedException
{
File list[] = file.listFiles(); if (list != null)
{ for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++)
{ if (list[i].isDirectory())
{
directoryProcess(list[i]);
} else {
fileProcess(list[i]);
}
}
} if (Thread.interrupted())
{ throw new InterruptedException();
}
}
private void fileProcess(File file) throws InterruptedException
{ if (file.getName().equals(fileName))
{
System.out.println( Thread.currentThread().getName()+" : "+file.getAbsolutePath());
} if (Thread.interrupted())
{ throw new InterruptedException();
}
}
}
![]()
测试代码:Main.java
![]()
package sedion.jeffli.concurrency4;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class Main
{ public static void main(String[] args)
{
FileSearch fileSearch = new FileSearch("C:\\", "abc.bat");
Thread thread = new Thread(fileSearch);
thread.start();
try
{
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
thread.interrupt();
}
}
![]()
不管地用了多少次,只要线程检测到它已经中断了,立即抛出InterruptedException,继续赤星run方法。你可以看到,当输出:
五、线程的休眠和恢复
有时候你需要在某一个预期时间中中断线程的执行。例如像每隔一分钟检查…我们可以调用线程的sleep()方法,也可以用TimeUtil美剧累元素进行调用。
下面使用sleep()方法,每隔一秒钟就输出实际时间。
FileClock.java
![]()
package sedion.jeffli.concurrency5;import java.util.Date;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class FileClock implements Runnable
{
@Override public void run()
{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
System.out.println(new Date()); try
{
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println("The File Clock has been interrupted");
}
}
}
}
![]()
测试代码:FileMain.java
![]()
package sedion.jeffli.concurrency5;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class FileMain
{ public static void main(String[] args)
{
FileClock fileClock = new FileClock();
Thread thread = new Thread(fileClock);
thread.start();
try
{
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
thread.interrupt();
}
}
![]()
最佳实践:当线程被中断时,释放或者关闭线程正在使用的资源。
六、等待线程的终止
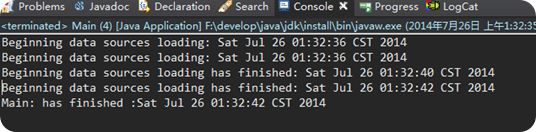
使用线程来完成这些初始化任务,等待线程终止,执行程序的其他任务。为了达到这个目的,我们可以用Thread类的join()方法。当一个线程对象的join方法被调用时,调用它的线程被挂起,知道这个线程对象完成他的任务。
例如 一种初始化资源 join()方法
DataSourcesLoader.java NetworkConnectionsLoader.java
![]()
public class DataSourcesLoader implements Runnable
{
@Override public void run()
{
System.out.println("Beginning data sources loading: "+new Date()); try
{
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
} catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Beginning data sources loading has finished: "+new Date());
}
}public class NetworkConnectionsLoader implements Runnable
{
@Override public void run()
{
System.out.println("Beginning data sources loading: "+new Date()); try
{
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(6);
} catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Beginning data sources loading has finished: "+new Date());
}
}
![]()
测试代码:
![]()
public class Main
{ public static void main(String[] args)
{
DataSourcesLoader dataSourcesLoader = new DataSourcesLoader();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(dataSourcesLoader,"DataSourcesLoader");
NetworkConnectionsLoader connectionsLoader = new NetworkConnectionsLoader();
Thread thread2 = new Thread(connectionsLoader,"NetworkConnectionsLoader");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
try
{
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Main: has finished :"+new Date());
}
}
![]()
这个代码你可以看到两个线程对象是如何运行的。DataSourcesLoader运行结束,直到NetworkConnectionsLoader也结束的时候,主程序的对象继续运行并打出最终的信息。
相关资料:
java.lang.Thread java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit
public final void join() throws InterruptedException
等待该线程终止。
抛出:
InterruptedException- 如果任何线程中断了当前线程。当抛出该异常时,当前线程的中断状态 被清除。
void sleep(long timeout)
使用此单元执行 Thread.sleep.这是将时间参数转换为 Thread.sleep 方法所需格式的便捷方法。
七、感谢知识来源和小结
一、简介
二、简单介绍线程创建和运行
三、线程信息的获取和设置
四、线程中断:interrupt() 或者 使用java异常控制
五、线程的休眠和恢复
六、等待线程的终止
来自:《并发编程》《Think in java》
如以上文章或链接对你有帮助的话,别忘了在文章按钮或到页面右下角点击 “赞一个” 按钮哦。你也可以点击页面右边“分享”悬浮按钮哦,让更多的人阅读这篇文章。